Abstract
Background
Scabies is a contagious infestation transmitted by skin-to-skin contact and sometimes by contact with contaminated material. The scabies mite burrows into the skin, producing a papular rash and severe itch at typical sites of predilection.
Methods
We systematically reviewed the literature to compare the efficacy of various anti-scabies agents, including a calculation of relative risks and intervals.
Results
A literature search yielded 596 initial hits; after screening in accordance with the defined inclusion and exclusion criteria, 16 studies were selected for this review. Among topical treatments for scabies, permethrin was equally effective or more effective than crotamiton or benzyl benzoate. In a comparison of topical versus systemic treatment, topical permethrin and systemic ivermectin did not differ substantially in efficacy (7 comparative studies revealed no difference; one revealed a difference in favor of permethrin). Comparative trials of topical benzyl benzoate versus systemic ivermectin yielded inconsistent findings. Single and double administrations of ivermectin were similarly effective. In trials involving entire populations with a high prevalence of scabies, systemic ivermectin was found to be superior to topical permethrin.
Conclusion
There are hardly any differences in efficacy between the available treatments for scabies. Single administrations of permethrin 5%, crotamiton 10%, and systemic ivermectin are all comparably effective. There are differences in the frequeny and ease of application as well as when eradicating scabies in populations with a high prevalence.
Scabies is a common skin disease worldwide, particularly in developing countries. It affects up to 130 million people (1). Increasing migration means that scabies has once again become a more common suspected or confirmed diagnosis in Germany too, at physician practices and emergency departments. Scabies patients’ main symptom is excruciating pruritus, which is usually particularly severe at night (2).
Scabies is transmitted by the female scabies mite, which burrows into the top layer of the epidermis to lay eggs, before dying 30 to 60 days later. After approximately 2 to 3 weeks, sexually mature mites hatch from the eggs (3). This period is important for treatment with substances that are not ovicidal and are not sufficiently stored in the skin. Mites can survive for only approximately 2 days outside the body (4).
In common scabies, the scabies mite is transmitted during sufficiently long-lasting skin-to-skin contact—at least 10 minutes (4). In contrast, for crusted scabies, with millions of mites on the skin, short contact with patients and contaminated materials is sufficient.
If infestation occurs, the first papules appear within 2 to 5 weeks. These are tunnel-shaped or comma-shaped and range in length from a few millimeters to 1 cm. They occur in typical locations where the outer layer of skin is thin, such as the interdigital folds, the areola, the navel region, and, in men, particularly the shaft of the penis. An eczematous reaction with disseminated, mite-free erythematous papules or papular vesicles, causing the characteristic severe pruritus, is a sign of a cell-mediated immune response.
Scratching, encrustation, and possible impetiginization lead to a varied morphological picture over a matter of weeks. This can vary a great deal in severity and can lead to bacterial infections. A further sign of scabies is itching in contact persons. Diagnosis is confirmed using microscopic evidence of mites, eggs, or feces from skin scrapings or on the basis of evidence of mites obtained by dermatoscope (5).
There is an increased risk of outbreaks in facilities in which large numbers of people live in close contact with each other. Care homes for the elderly are particularly affected because older people with multiple morbidities develop crusted scabies more easily as a result of drug-induced or age-related immunosuppression and because care for residents entails more frequent, longer contact.
During major migrations such as are currently being seen, the prevalence of scabies in those seeking refuge is somewhat higher than in the general German population. The risk of outbreaks is low, however, as those affected are immunocompetent, and ordinary contact with other members of the population is insufficient for transmission.
As no immunity develops to scabies, reinfestations are common unless all relevant contact persons, e.g. life partners and relatives, also receive appropriate treatment. In contrast, resistance to the antiscabies drugs detailed below has not yet been described in Germany and is rarely described elsewhere (6).
The current common treatment options in Germany are permethrin 5% topical, benzyl benzoate 10%/25% topical, and crotamiton 5%/10% topical with ivermectin systemic (7). The latter was authorized in Germany and launched on the market in spring 2016 (8). It is easier to use and had already been recommended in the German guideline for crusted scabies and other conditions as early as 2006 (9). Unlike topical treatments with permethrin, for example, it is not ovicidal. However, it accumulates in the epidermis.
This review summarizes the available data on the efficacy of common antiscabies drugs.
Methods
A systematic review of the literature was performed to evaluate the available evidence comparing the efficacy and safety of various antiscabies drugs. The review was performed according to the Cochrane Method (10).
Inclusion and exclusion criteria
The review included randomized controlled trials in scabies patients. Trials in which whole populations with a high prevalence of scabies received therapeutic and/or preventive treatment were also included.
Studies comparing topical benzyl benzoate, crotamiton, ivermectin, permethrin, and sulfur as well as systemic ivermectin were included. Placebo-controlled trials and trials that compared different dosage forms were not included (etable 1).
eTable 1. The PICO system.
| PICO | Description |
| Patients |
|
| Intervention |
|
| Comparison |
|
| Outcome |
|
PICO, „patients, intervention, comparison, outcome“
Search strategy
Three electronic databases (MEDLINE, MEDLINE In-Process, EMBASE [OvidSP], and the Cochrane Library [Wiley]) were searched (search strategy) (ebox).
eBOX. Search strategy for MEDLINE database.
1. exp Scabies/
2. scabies.ab,ti.
3. 1 or 2
4. Randomized Controlled Trials as Topic/
5. randomized controlled trial/
6. Random Allocation/
7. Double-Blind Method/
8. Single Blind Method/
9. clinical trial/
10. clinical trial, phase I.pt.
11. clinical trial, phase II.pt.
12. clinical trial, phase III.pt.
13. clinical trial, phase IV.pt.
14. controlled clinical trial.pt.
15. randomized controlled trial.pt.
16. multicenter study.pt.
17. clinical trial.pt.
18. exp Clinical Trials as topic/
19. 4 or 5 or 6 or 7 or 8 or 9 or 10 or 11 or 12 or 13 or 14 or 15 or 16 or 17 or 18
20. (clinical adj trial$).tw.
21. ((singl$ or doubl$ or treb$ or tribl$) adj (blind$3 or mask$3)).tw.
22. Placebos/
23. placebo$.tw.
24. randomly allocated.tw.
25. (allocated adj2 random$).tw.
26. 20 or 21 or 22 or 23 or 24 or 25
27. 19 or 26
28. case report.tw.
29. letter/
30. historical article/
31. 28 or 29 or 30
32. 27 not 31
33. 3 and 32
Trial selection
Two authors (CD, SR) independently screened all identified titles and abstracts for compliance with the inclusions/exclusion criteria. The fulltexts of the selected publications were then evaluated on the basis of the same criteria. Using a standard evaluation sheet (MS Excel 2013), data was extracted by one author (CD) and verified by a second (SR). Differences in opinion were resolved through discussion with the third author (RNW). (figure).
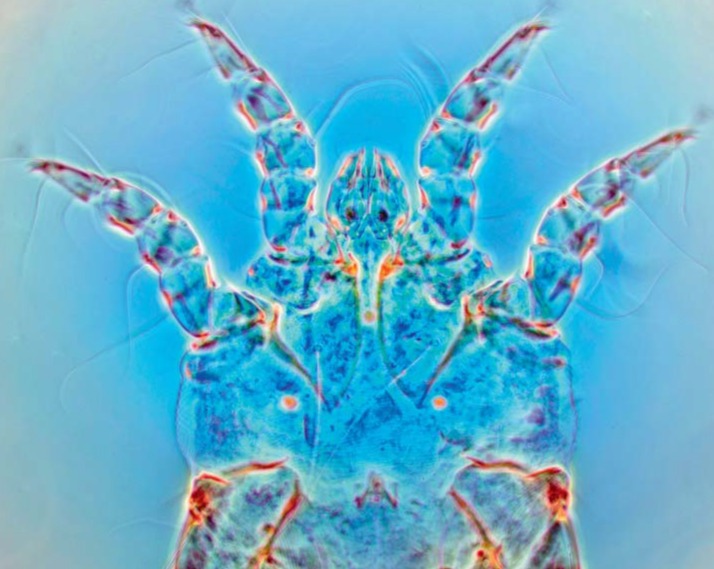
Figure.
Light microscopy images of Sarcoptes scabiei
Statistical analysis
The data extracted was analyzed using Review Manager (11). For binary variables, relative risk (RR) with a selected confidence interval of 95% (95% CI) was calculated as a measure of treatment effect. Calculation in Review Manager is based on the Mantel–Haenszel (M–H) method.
Trials evaluating the same treatment options were examined for clinical comparability and statistical heterogeneity (I2) in order to consider the possibility of pooling them. Where there was statistical heterogeneity, with I2 of 20% or above, sensitivity analyses were planned. Trials were not pooled if I2 was 80% or above (10).
Evaluation of trials’ methodological quality
The risk of bias was evaluated using the Cochrane Risk of Bias (RoB) Assessment Tool (10). The potential risk of overestimating the effect found in each trial was included in the Discussion.
Results
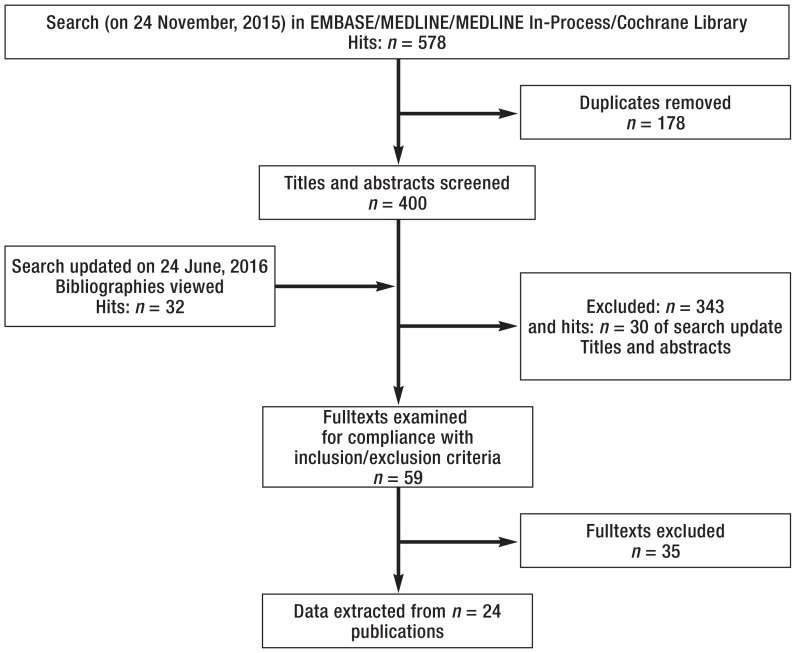
The literature search performed on 24 November, 2015 yielded 578 hits. 178 duplicates were removed, 400 titles/abstracts were viewed, and 57 fulltexts were examined for compliance with the inclusion and exclusion criteria. A list of the 35 excluded trials, including the reasons for exclusion and references, is provided in eTable 2. The search was last updated on 24 June, 2016 (autoalerts), when a further 32 trials were identified.
Sixteen publications were included in the review (etable 3). These reported 6 comparisons of different substances, or different frequencies of administration, or different formulations.
eTable 3. Characteristics of the 16 included RCTs.
|
Author, year, country, |
Intervention |
No. of randomized patients |
Inclusion criteria and diagnosis |
Study
duration |
Severity
(lesions: n) |
Age
(years) |
Sex (female: n;%) |
Definition of cure/effect |
Findings after 2 weeks |
Findings after 4 weeks |
Comments |
| Topical permethrin vs. topical crotamiton | |||||||||||
| Amer (1992) Egypt (13) |
Permethrin 5% topical on 2 consecutive nights | 50 | Clinical diagnosis (microscopic evidence of mites) | 4 weeks | N/S | N/S | N/S | Complete cure of all lesions | N/A | 49/50 | Inpatients; unclear whether contact persons were also treated; whole-body treatment; 3rd trial arm (lindane) not evaluated |
| Crotamiton 10% topical on 2 consecutive nights | 50 | 44/50 | |||||||||
| Taplin (1990) Panama (12) |
Permethrin 5% cream, single application overnight (AC) | 48 | Children aged 2 months to 5 years; diagnosis of scabies, live mites on at least one part of body | 4 weeks + up to 3 weeks permethrin 5% cream if treatment failed | < 50: 29 50 to 100: 17 100: 2 |
2.6 ± 1.8 | 24 (50.0%) | Complete cure of all lesions | 14/47 | 42/47 | Whole-body treatment; only children from a remote island were included; 65/96 children with reinfestation at start of trial; one LTF per trial group; relatives treated with permethrin 5% cream; trial staff removed mites from skin using sterile tweezers in approx. 50% of patients |
| Crotamiton 10% cream, single application overnight (AC) | 48 | < 50: 29 50 to 100: 15 > 100: 4 |
2.5 ± 1.8 | 30 (62.5%) | 6/47 | 28/47 10 children had undergone repeat treatment |
|||||
| Topical permethrin vs. systemic ivermectin | |||||||||||
| Bachewar (2009) India (17) |
Permethrin 5% cream overnight | 34 | Newly diagnosed scabies, age over 12 years, enrolled if at least 3 of the following 5 criteria were met: contact with scabies patient, nocturnal pruritus, positive family history, typical mite burrows on clinical examination, typical scabies lesions such as papules, nodules, or vesicles | 2 weeks | N/S | 12 to 41 (84%) |
12 (35.3%) | No new lesions | 27/28 | N/A | All patients received BB 25% lotion for their relatives and close contact persons; topical whole-body treatment |
| Ivermectin 0.2 mg/kg oral, single dose | 34 | 16 (47.1%) | 27/27 | ||||||||
| BB 25% lotion on 2 consecutive evenings | 35 | 12 (34.3%) | 23/25 | ||||||||
| Chhaiya (2012) India (14) |
Permethrin 5% cream, single application for at least 8 hours (AP) | 105 | Either sex aged 5 to 80 years with 1. clinically-diagnosed scabies, 2. presence of typical scabietic lesions like papules, nodules, or vesicles at classical sites, 3. presence of classical burrows on clinical examination, 4. nocturnal pruritus, 5. history of involvement of family member or similar symptoms in contacts, 6. microscopically-diagnosed scabies (demonstration of egg, larvae, mite, or fecal matter), 7. patients whose microscopic examination was negative, their inclusion in the study was based on clinical criteria, for that patient had to meet at least 3 out of 4 inclusion criteria (inclusion criteria no. 2 to 5), no top. scabicidal therapy for 1 months | 3 weeks + treatment change to permethrin 5% at 4 weeks if treatment failed | Severe: 13.1% Moderate: 36.4% Mild: 46.5% None: 4% | 23.40 ± 13.55 |
47 (44.8%) | Clinical cure | 99% n? |
99/99 | Topical whole-body treatment; concomitant antihistamines: oral hydroxyzine 10 mg or 25 mg b.i.d. for all patients in week 1, subsequently in event of moderate to severe itching |
| Ivermectin 0.2 mg/kg oral, single dose (AP) | 105 | Severe: 19% Moderate: 39% Mild: 38% None: 4% |
21.97 ± 13.26 |
47 (44.8%) | 63% n? |
99/100 | |||||
| Ivermectin 1% lotion, single application to affected areas for at least 8 hours (AP) | 105 | Severe:16.8% Moderate: 40.6% Mild: 38.6% None: 4% |
22.52 ± 12.69 |
46 (43.8%) | 100% n? |
101/101 | |||||
| Usha (2000) India (21) |
Permethrin 5% cream, single application overnight (AP) | 45 | Age >5 years; diagnosis of scabies (demonstration of eggs, larva, mites, or fecal pellets by light microscopy or by the presence of at least 3 of the following clinical criteria confirmed independently by 2 consultants: (1) demonstration of burrow, (2) presence of scabietic lesions at the classical sites, (3) nocturnal pruritus, and (4) family history of similar illness); no antiscabietic treatment in the previous month | 2 months | Severe: 8.9% Moderate: 51.1% Mild: 40.0% |
22.4 ± 12.6 |
12 (26.7%) | Clinical improvement in lesions, no new lesions | 44/45 Repeat treatments: 1 |
45/45 | Family contacts underwent same treatment as trial patients |
| Ivermectin 0.2 mg/kg oral, single dose (AP, supervised) | 40 | Severe: 12.5% Moderate: 60.0% Mild: 27.5% |
21.28 ± 13.44 |
14 (35%) | 28/40 Repeat treatments: 12 |
38/40 | |||||
| Saqib (2012) Pakista n (19) |
Permethrin 5% lotion for 10 to 12 hours (AP) | 60 | Confirmed diagnosis of scabies (evidence of mite burrows using dying and microscopic evidence of Sarcoptes scabiei mites at any stage of development or fecal matter), age 18 to 60 years, no topical or systemic scabicides in last month | 2 weeks | Itching: Severe: 10% Moderate: 70% Mild: 20% |
29.45 ± 9.72 |
N/S | Cure | 40/60 | N/A | Topical whole-body treatment (neck to foot); all patients. were given antihistamines at bed time during 1st week; contact persons of both groups underwent same treatment at same time as trial patients (children under 5 years old, pregnant women, or breastfeeding women received 5 to 10% sulfur ointment) |
| Ivermectin 0.2 mg/kg oral, single dose (AP, supervised) | 60 | Itching: Severe: 16.7% Moderate: 53.3% Mild: 30% |
31.45 ± 12.78 |
40/60 | |||||||
| Sharma (2011) India (20) |
Permethrin 5% cream, single application in evening (day 1) + placebo tablets (days 1 and 15) before breakfast (AP) | 40 | Age over 5 years and/or weight over 15 kg, diagnosis of scabies (eggs, larvae, mites/mite remains, or fecal matter under light microscope in scrapings of multiple representative or suspected skin changes in 10% KOH), and/or at least 3 of the following criteria: (a) mite burrows, (b) scabies lesions in typical locations, (c) nocturnal itching, (d) positive family history of similar complaints; no topical scabicides or topical steroids in last month | 4 weeks | Severe: 65% Moderate: 35% Mild: 0% |
21.38 ± 13.17 |
21 (52.5%) | ≥50% reduction in lesion count |
37/38 |
38/38 | Topical whole-body treatment (neck downwards); all family contacts received permethrin 5% cream for single use overnight |
| Ivermectin 0.2 mg/kg oral, single dose before breakfast, placebo cream in evening (day 1), placebo tablet (day 15) (AP) | 40 | Severe: 72.5% Moderate: 27.5% Mild: 0% |
23.40 ± 11.03 |
11 (27.5%) | 38/40 | 36/40 | |||||
| Ivermectin 0.2 mg/kg oral on days 1 and 15 before breakfast + placebo cream (day 1) in evening (AP) | 40 | Severe: 69.2% Moderate: 30.8% Mild: 0% |
23.53 ± 12.73 |
16 (40.0%) | 36/39 | 36/39 | |||||
| Mushtaq (2010) Pakista n (18) |
Permethrin 5% cream single application overnight for 12 hours | 42 patients completed the trial | Age 2 to 60 years; diagnosis of scabies | 6 months | N/S | N/S | 20 (45.5%) | Cure (no lesions) | 20/42 | 37/42 | Topical whole-body treatment; information on sex shown in table unclear; 14 LTF corresponds to no. of patients not cured after 4 weeks |
| Ivermectin 0.2 mg/kg oral, single dose | 44 patients completed the trial | 24 (54.5%) | 24/44 | 35/44 | |||||||
| Romani (2015) Fiji (26) |
Permethrin for all affected individuals and their contact persons, single application | 803 | 3 previously identified island communities were randomized to 3 treatment options; trial participation was open to all inhabitants; inhabitants were treated according to their treatment group | 12 months | Severe: 5.8% Moderate: 24.8% Mild: 69.4% |
Median (IQR): 22 (8 to 44) |
398 (49.6%) | No. of patients with diagnosis of scabies after 12 months | 140/746 | Topical whole-body treatment (neck to foot); in the ivermectin group children weighing less than 15 kg, pregnant/breastfeeding women, persons with neurological diseases, and persons taking cytochrome P450 inducers or inhibitors received permethrin cream instead of ivermectin | |
| Permethrin for all individuals, single dose (2nd dose in those with scabies at start of trial on days 7 to 14) for 8 to 24 hours (AP with or without supervision) | 532 | Severe: 17.1% Moderate: 32% Mild: 50.9% |
Median (IQR): 25 (8 to 47) |
258 (48.5%) | 71/449 | ||||||
| Ivermectin 0.2 mg/kg oral for all individuals, single dose (2nd dose for those with scabies at start of trial on days 7 to 14), supervised | 716 (93 received permethrin) | Severe: 10.9% Moderate: 29.1% Mild: 60% |
Median (IQR): 24 (8 to 44) |
331 (46.2%) | 11/587 | ||||||
| Systemic ivermectin vs. systemic ivermectin | |||||||||||
| See above: Sharma (2011) (20) | |||||||||||
| Topical ivermectin vs. systemic ivermectin | |||||||||||
| See above: Chhaiya (2012) (14) | |||||||||||
| Topical permethrin vs. topical ivermectin | |||||||||||
| See above: Chhaiya (2012) (14). Sharma (2011) (20) | |||||||||||
| BB vs. systemic ivermectin | |||||||||||
| Ly (2009) Senegal (25) |
BB 12.5%, single application for 24 hours (AP) |
68 | Age 5 to 65 years, weight 15 kg or more, itching in 3 or more significant parts of the body, typical scabies lesions (i.e. vesicles, papules, nodules, or pustules) in 3 or more locations typical for scabies (i.e. interdigital folds of hands, elbows, joints of hands, buttocks, underarms, nipples and areolas in women, external genitalia in men); no scabies treatment during the month before consultation | 4 weeks + 2 weeks (if treatment failed in the ivermectin or BB group with single application, patients received second application; if treatment failed after second application in the BB group, patients received ivermectin) | No. of affected locations (n patients): ≤5 n = 41 ≥6 n = 27 |
16.5 (5 to 63) | 25 (36.8%) | Complete cure of visible lesions | 37/68 | 52/68 | Information on treatment of relatives unclear: same treatment as trial patients/relatives not enrolled in the trial received single-dose BB |
| BB 12.5%, 2 applications at 24-hour intervals (AP) | 48 | No. of affected locations (n patients): ≤5 n = 30 ≥6 n = 18 |
20 (41.7%) | 33/48 | 46/48 | ||||||
| Ivermectin 0.15 to 0.2 mg/kg oral, single dose (AP) |
65 | No. of affected locations (n patients): ≤5 n = 31 ≥6 n = 34 |
20 (30.8%) | 16/65: 8 patients underwent repeat treatment after 1 week | 28/65 | ||||||
| Brooks (2002) Vanuatu (24) |
BB 10%, single application (APP) | 37 (at follow-up) | Children aged 0.5 to 14/15 years; diagnosis of scabies (typical lesions: mite burrow, intact papulovesicular lesions or excoriated, encrusted lesions); no scabies treatment in last 2 months | 3 weeks | No. of lesions: 44.9 ± 31.9 |
Week 3: 4.7 ± 3.8 |
N/S | No lesions after 3 weeks | 19/37 | N/A | Relatives underwent same treatment as trial patients; children under 6 months received BB; 30 LTF |
| Ivermectin 0.2 mg/kg oral, single dose (AC) |
43 (at follow-up) | No. of lesions: 50.7 ± 29.1 |
Week 3: 5.1 ± 3.9 |
24/43 | |||||||
| Glaziou (1993) French Polynesia (23) |
Ivermectin 100 µg/kg, single dose |
23 | Scabies, clinically diagnosed, defined as itching and at least one typical mite burrow; age 5 to 60 years, no scabies treatment in last 2 weeks | 4 weeks | Clinical score [0 to 24] Mean (range): 13.0 (4 to 22) |
17.5 (5 to 56) | 21 (47.7%) | Complete cure of initial lesion | 8/23 | 16/23 | Topical whole-body treatment (excluding head); all household members treated with BB 10% at same time as trial patients; one concomitant antibiotic treatment was allowed if necessary |
| BB 10% to 12 hours, then washed off, application repeated (AP) |
21 | Clinical score [0 to 24] Mean (range): 13.1 (6 to 22) |
3/21 | 10/21 | |||||||
| Nnoruka (2001) Nigeria (22) |
Ivermectin 200 µg/kg, single dose |
29 | Age over 5 years; scabies confirmed clinically and using laboratory tests (itching with at least one typical mite burrow or several pustular eruptions, blisters, or nodules); pre-existing lesions for approx. 2 weeks to 3 months or more on initial presentation | 4 weeks | Clinical score [0 to 24] Mean (range): 16.1 (4 to 28.2) |
27.9 (5 to 63) | Inconsistent data in text: 33 women + 35 men = 68 patients; 33 (48.5%) | Complete cure of initial lesions | 19/29 | 27/29 | Topical whole-body treatment (neck to foot); all household members underwent same treatment at same time as trial patients |
| BB 25% emulsion for 72 hours |
29 | Clinical score [0 to 24] Mean (range): 16.0 (6 to 26) |
10/29 | 14/29 | |||||||
| See above: Bachewar (2009) | |||||||||||
| BB vs. sulfur | |||||||||||
| Gulati (1978) India (15) |
Sulfur ointment in morning, at night, and on following morning (AP) | 69 | Scabies diagnosed on basis of clinical findings | 6 months | N/S | 16.9 ± 16.1 |
35 (50.7%) | Clearance of lesions | 67/69 | N/A | Families also treated; whole-body treatment |
| BB 25% emulsion in morning, at night, and on following morning (AP) | 89 | 16.4 ± 17.0 |
48 (53.9%) | 81/89 | |||||||
| Sulfur vs. sulfur or other | |||||||||||
| Avila-Romay (1991) Mexico (27) |
Sulfur 10% cold cream on 3 consecutive nights and one night 3 days later (AP, supervised) | 26 (+32 contact persons) | Resident of orphanage, age 6 to 17 years | N/S | N/S | 6 to 17 years |
N/S | No cutaneous lesions after 10 days | 26/26 | N/A | Orphanage; all contact persons also randomized and treated; whole-body treatment |
| Sulfur 10% and salicylic acid 1% in pork fat on 3 nights and one night 3 days later (AP, supervised) | 25 (+28 contact persons) | 22/25 | |||||||||
| Sharquie (2012) Iraq (16) |
Sulfur 8% and 10%, single application | 33 | Clinical history and clinical examination, confirmed mainly via mite extraction and viewing under light microscope of mites, ova, or scybala; age over 2 years; new infestations excluded | 4 weeks | 100% of patients had mite burrows. | Male: 26.74 ± 15.98 Female: 24.05 ± 14.53 (similar in both groups) |
15 (45.5%) | Cure of mite burrows | 18/33 | 14/33 | – |
| Sulfur 8% and 10% on 3 consecutive nights | 32 | 11 (34.4%) | 30/32 | 29/32 | |||||||
| Sulfur 8% and 10% on 3 consecutive days | 32 | 13 (40.6%) | 31/32 | 31/32 | |||||||
BB: Benzyl benzoate; b.i.d.: Twice a day; APP: Applied by patients’ parents; AC: Applied by specialized clinical staff; LTF: Lost to follow-up; N/S: Not stated; N/A: Not applicable; AP: Applied by patients; q.d.: Once a day
An additional 8 trials were also identified. These met the inclusion criteria but are reported separately, as their validity is questionable (etable 4).
eTable 4. Trials with limited plausibility*1.
|
Author, year, country |
Interventions |
No. of randomized patients*2 |
Severity at start of trial*2, 3 |
Definition of cure/efficacy*4 | Findings after 2 weeks |
Findings after 4 weeks (patients undergoing repeat treatment) |
Other queries, comments, or discrepancies |
| Alipour (2015) (e59)Iran |
Ivermectin 0.2 mg/kg oral, single dose |
210 | Mild: 30 Moderate: 60 Severe: 120 |
Cure = absence of new lesions and healing of old lesions, regardless of the presence of postscabetic nodules [p. 80]) | 130/210 Repeat treatments: 80 |
35/80 | “None of the 400 patients experienced allergic reactions“ (p. 81);400 patients: information does not match no. of patients. |
| 10% sulfur ointment on 3 consecutive days (AP) | 210 | Mild: 35 Moderate: 55 Severe: 130 |
95/210 Repeat treatments: 115 |
30/115 | |||
| Pourhasan (2013) (e52) Iran |
Permethrin 5% cream | 175 Corrected by author: 200 |
Mild: 25 Moderate: 60 Severe: 90 Total: n = 175 |
Cure = absence of new lesions and healing of all old lesions, regardless of the presence of postscabetic nodules [p. 144]) | 140/175 70% (should be 80%) Repeat treatments: 60 (should be 35) Confirmed by author: 140/200 70% |
30/60 (should be 30/35) Confirmed: 30/60 |
„[…] 450 were initially enrolled. Of those, 50 were not able to return […]. The remaining 350 patients […]“ (p. 144). The reported cure rates are stated with reference to a total of 400 patients. Corrected by author: 400, i.e. 200 per group. “ The total followed up patients were 400 (200 each) and the total analysis in this study is correct and is based on 200 patients in each group not 175. ” “None of the 360 patients experienced allergic reactions” (p. 145) This sentence has been deleted by Dr. Goldust. |
| Crotamiton 10% | 175 Corrected by author: 200 |
Mild: 35 Moderate: 30 Severe: 110 Total: n = 175 |
90/175 45 % (should be 51%) Repeat treatments: 110 (should be 85) Confirmed by author: 90/200 45% |
40/110 Confirmed: 40/110 |
|||
| Goldust (2012) (e53) Iran | Permethrin 5% cream | 139 139 |
Mild: 21 Moderate: 34 Severe: 66 Total: n = 121 |
Cure= absence of new lesions and all old lesions healed (p. 546) | 112/121 Confirmed: 112/121 |
2/9 | Table 1 contains contradictory information: demographic information n = 121 per trial arm, but total no. (male plus female) stated as n = 118 in the permethringroup and n = 124 in the ivermectin group. Corrected by author: “ 49 female patients were in permethrin group and 61 female patients were in ivermectin group). ” This matches Table 1 but still does not match the confirmed no. of trial patients. |
| Ivermectin 0.2 mg/kg oral | 133 133 |
Mild: 24 Moderatee: 27 severe: 70 Total: n = 121 |
104/121 Confirmed: 104/121 | 17/17 | |||
| Ranjkesh (2013) (e54) Iran | Permethrin 5% lotion or cream? Confirmed: cream |
30 30 |
Mild: 4 Moderate: 8 Severe: 18 |
Cure = absence of new lesions and healing of all old lesions, regardless of the presence of postscabetic nodules. (p. 190); paper also states “demonstrated symptomatic improvement”? Author: They mean the same in this study. | 28/30 Repeat treatments: 2 |
2/2 | “… group A were to receive ivermectin, and group B were to receive sulfur 10 % ointment.” (page 190) Information on drugs ivermectin and sulfur 10% ointment incorrect. |
| Ivermectin 0.2 mg/kg oral | 30 30 |
Mild: 6 Moderatee: 7 Severe: 17 |
22/30 Repeat treatments: 8 | 6/8 | |||
| Goldust (2013) (e55) Iran | Permethrin 2.5% cream | 190 190 |
Mild: 30 Moderatee: 50 severe: 110 |
Cure = absence of new lesions and healing of all old lesions, regardless of presence of postscabetic nodules (p. 80) | 125/190 Confirmed: 125/190 |
45/65 Confirmed: 45/65 |
“None of the 400 participants experienced allergic reactions.” 400 patients: information does not match no. of patients. Corrected by author 380 |
| Ivermectin 1% solution, 0.4 mg/kg | 190 190 |
Mild: 40 Moderate: 50 Severe: 100 |
120/190 Confirmed: 120/190 |
40/70 Confirmed: 40/70 |
|||
| Goldust (2014) (e56) Iran |
Crotamiton 10% cream, twice a day on 5 consecutive days | 170 170 |
Mild: 30 Moderate: 40 Severe: 100 |
Cure = absence of new lesions and healing of all old lesions, regardless of presence of postscabetic nodules (p. 905) | 70/170 Confirmed: 70/170 |
40/100 Confirmed: 40/100 |
|
| Ivermectin 1% cream, 0.4 mg/kg once a week for 2 weeks | 170 170 |
Mild: 40 Moderate: 50 Severe: 80 |
110/170 Confirmed: 110/170 |
40/70 Corrected by author: 30/60 |
|||
| Goldust (2014) (e57) Iran | Crotamiton 10% cream | 160 160 |
Mild: 25 Moderatee: 40 Severe: 95 |
Cure = absence of new lesions and healing of all old lesions, regardless of the presence of postscabetic nodules (p. 334) | 75/160 Confirmed: 75/160 |
25/85 Confirmed: 25/85 |
|
| Ivermectin 0.2 mg/kg oral, single dose | 160 160 |
Mild: 30 Moderate: 40 Severe: 90 |
100/160 Confirmed: 100/160 |
40/60 Corrected by author: 24/60 |
|||
| Goldust (2013) (e58) Iran |
8% sulfur ointment on 3 consecutive days (AP) | 190 Confirmed: 190 |
Mild: 30 Moderate: 55 Severe: 105 |
Efficacy/effective treatment (p. 229) |
85/190 Repeat treatments:95 (10 patients missing) Corrected by author: 105 |
20/95 Corrected by author: 20/105 |
|
| Ivermectin 0.2 mg/kg oral, single dose | 190 Confirmed: 190 |
Mild: 40 Moderate: 50 Severe: 100 |
120/190 Repeat treatments: 70 Confirmed: 70 |
35/70 Confirmed: 35/70 |
*1Eight trials (e52– e59) conducted in Iran were identified that had been published by the same corresponding author and whose evaluation poses questions regarding plausibility. The reported patient numbers do not match, and the reporting in the publications is unsatisfactory. This led us to rate the validity of the trial findings as questionable and the risk of bias as very high. These trials were therefore subsequently reported separately.
N.B.: A letter to the editor regarding 4 trials published in the Annals of Parasitology was published in June 2016 (Dressler C, Rosumeck S, Nast A: Reporting in the clinical trials evaluating scabies treatments. Ann Parasitol 2016; 62: 153–5).
The corresponding author of all the above-mentioned trials, Dr. Mohamad Goldust, was contacted and asked to provide a correction or confirmation of inconsistent data (red text indicates inconsistent data extracted from the publications, blue text indicates information corrected by Dr. Goldust, and green text indicates confirmed information). Dressler C, Rosumeck S, Nast A: Reporting in the clinical trials evaluating scabies treatments. Ann Parasitol 2016; 62: 153–5. Goldust, et al.: Treatment of scabies, comparing the different medications. Ann Parasitol 2016; 62: 243.
AP: Applied by patients themselves
Black: Information from publications
Red: Information from publications, but contains contradictions
Blue: Corrections/comments by the main author, Dr. Mohamad Goldust
Green: Information confirmed by the main author, Dr. Mohamad Goldust
Italics: Authors’ comments
*2 “We used simple table randomization and after the exclusion of missing to follow up patients, the patients were randomly assigned to different treatment modalities” (e-mail correspondence dated 19 February, 2015)
*3 With the exception of the Severity column and information from Alipour 2015, this table was sent to the main author
The Table provides a simplified summary of individual comparisons. This includes only the lowest relative risk with a 95% confidence interval and the highest relative risk with a 95% confidence interval for each treatment comparison.
Table. Overview of treatment comparisons; lowest and highest calculated effect estimates (RR) with confidence intervals (95% CIs) (outcome parameters: healing, cure, reduction in lesion count) and number of trials.
| Interventions | Results after 2 weeks: RR [95% CI] | Results after 4 weeks: RR [95% CI], no. of trials |
| Topical treatments | ||
| Topical permethrin vs. topical crotamiton (12, 13) | 2.33 [0.98; 5.55] | 1.11 [1.00; 1.24] and 1.50 [1.16; 1.94] 2 RCTs |
| Topical ivermectin vs. topical permethrin (14) | – | 0.99 [0.96; 1.02] |
| Sulfur vs. benzyl benzoate (15) | 1.07 [0.99; 1.15] | – |
| Sulfur vs. sulfur (8%/10% as single dose, 3 days, and 3 nights) (16) | 1.72 [1.24; 2.38] to 1.78 [1.29; 2.44] 1 RCT, 3 arms | 2.14 [1.41; 3.23] to2.28 [1.53; 3.41] 1 RCT, 3 arms |
| Benzyl benzoate vs. permethrin (17) | 0.95 [0.83; 1.09] | – |
| Topical vs. systemic treatment | ||
| Topical permethrin vs. systemic ivermectin (14, 17– 21) | 0.80 [0.52; 1.21] to 1.40 [1.13; 1.72] 5 RCTs | 1.01 [0.98; 1.04] to 1.11 [0.92;1.33] 4 RCTs |
| Topical ivermectin vs. systemic ivermectin (14) | – | 1.01 [0.98; 1.04] |
| Systemic ivermectin vs. benzyl benzoate (BB) (17, 22– 25) | 0.36 [0.22; 0.57] to 2.43 [0.74; 7.99] 4 RCTs | 0.45 [0.34; 0.60] to 1.93 [1.31; 2.85] 4 RCTs |
| Systemic treatments | ||
| Systemic ivermectin vs. systemic ivermectin (1 vs. 2 doses) (20) | – | 0.97 [0.85; 1.12] |
| Therapy and prophylaxis (treatment of all island inhabitants; orphanage residents; one RCT each) | ||
| Permethrin, single-dose treatment for all affected individuals vs. permethrin, single dose for all island inhabitants and 2 doses for all affected individuals (26) | 1 year: 0.96 [0.92; 1.02] | |
| Permethrin, single-dose treatment for all affected individuals vs. oral ivermectin for all island inhabitants (26) | 1 year: 0.86 [0.82; 0.89] | |
| Permethrin, single dose for all island inhabitants and 2 doses for all affected individuals vs. oral ivermectin, single dose for all island inhabitants (26) | 1 year: 0.83 [0.80; 0.86] | |
| Sulfur 10% cold cream vs. sulfur 10% and salicylic acid 1% treatment for all orphanage residents (27) | 10 days: 1.13 [0.97; 1.33] | |
*Pooled data; 95% CI: 95% confidence interval; RR ###: Relative risk; RCT, randomized controlled trial; –: not applicable
A detailed description of the study results, including findings on safety, as well as selected forest plots can be found in the eMethods section, showing the results of all studies included.
Due to the statistical heterogeneity (I2 greater than 80%) and clinical heterogeneity meant it was only possible to pool the results once. The studies differ from each other in terms of their design, frequency of treatment, and/or in their definition of the outcome parameters (etable 3).
The following conclusions can be drawn from the comparison of different topical treatments: after 2 weeks a single dose of permethrin was found to be of comparable efficacy to crotamiton, but after 4 weeks, it was superior to crotamiton (12). When administered twice, neither drug was superior after 4 weeks (13).
In comparison of topical ivermectin and topical permethrin, neither was found to be superior.
No difference in efficacy was found between sulfur and benzyl benzoate. The only superiority found was in favor of three-time application of sulfur versus a single application of sulfur; however, possible skin irritation, the aroma of sulfur, and the frequency of application limit its use.
Studies describing 3 comparisons of topical and systemic therapies were also included. A total of 6 trials reported findings after 2 and/or 4 weeks on the efficacy of topical permethrin versus systemic ivermectin. Efficacy was comparable, although the trials differed in terms of their outcome parameter and other factors. Frequency of repeat treatment was inadequately reported.
Five trials investigated the efficacy of topical benzyl benzoate versus systemic ivermectin. Comparison revealed heterogeneous findings, hence no firm conclusion can be drawn (eMethods).
Topical ivermectin was also found to be of comparable efficacy to systemic ivermectin, but only one trial investigating this could be included.
Two trials investigating treatment of mixed populations—confirmed scabies cases and preventive treatment of the unaffected population—were included. No difference was found in terms of the efficacy of various sulfur-containing drugs. In contrast, after 12 months population-based treatment with systemic ivermectin was superior to permethrin as both standard and population-based treatment.
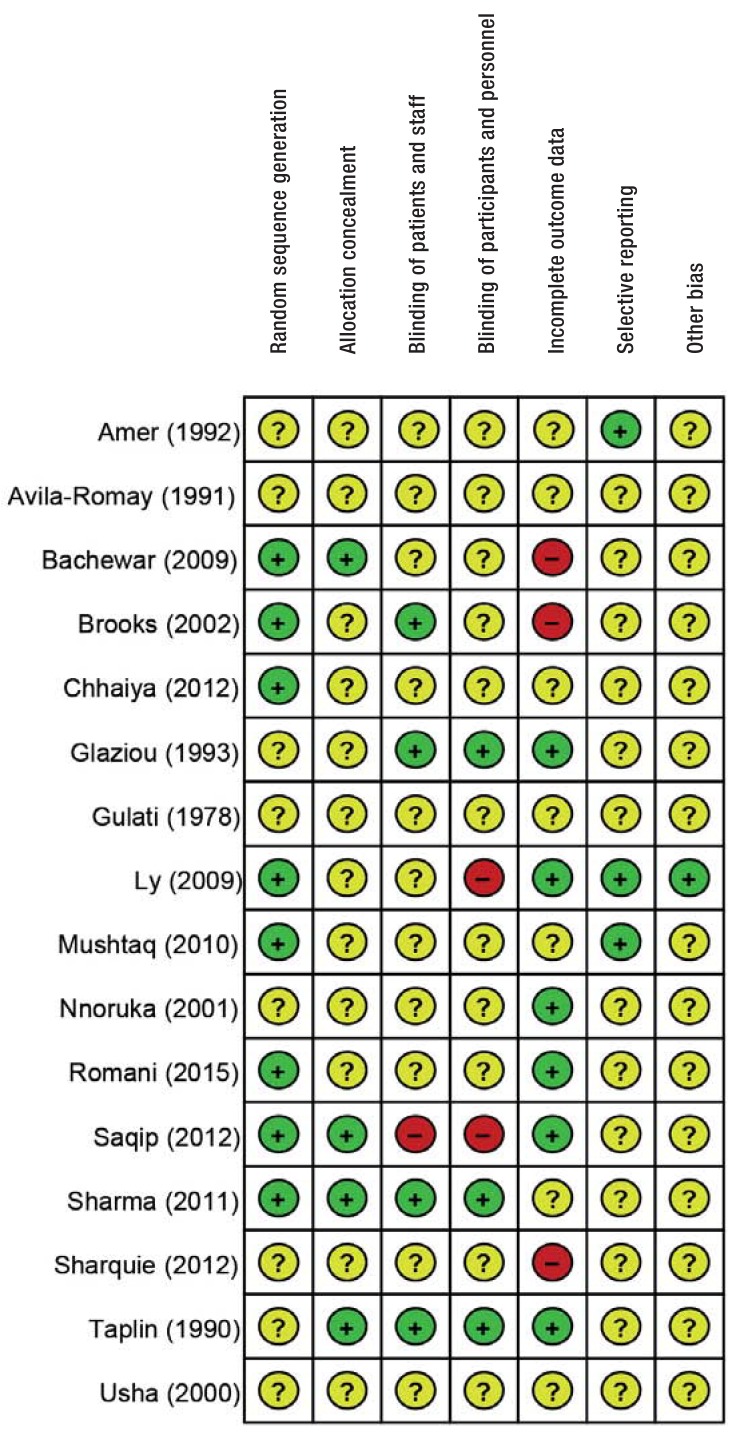
Evaluation of risk of bias
The risk of bias was rated as “unclear” in 14 trials and “low” in 2 trials (12, 20) (efigure). The authors’ confidence in the findings of the selected trials is therefore similar for all comparisons.
eFigure.
Risk of bias for each included trial The risk of systematic bias of trial findings was evaluated using the Cochrane Risk of Bias Assessment Tool.
Publication bias cannot be ruled out, as no search was performed to locate unpublished or unregistered trials. No experts were asked about this.
Discussion
The 16 included trials found little difference in terms of efficacy or tolerability. Crotamiton and permethrin were found to be of similar efficacy, as were topical permethrin and systemic ivermectin. Despite the lack of ovicidal effect of single-dose ivermectin, in most trials efficacy after 2 weeks was comparable to that of single-dose topical ovicidal drugs such as permethrin.
However, there were considerable differences between the included trials in terms of treatment frequency and the definition of the outcome parameters. The comparison of benzyl benzoate and ivermectin, for example, yielded varying findings; this makes it impossible to draw a firm conclusion.
It should be critically noted that one article published in Russian was not included for reasons of cost. This trial and the 8 trials with questionable validity would probably have had no effect, or only a negligible effect, on the overall findings of this review.
The trials included here do not provide an unambiguous answer to the question of whether repeat treatment is needed. There are not enough trials addressing this question; in addition, repeat treatment is often inadequately reported.
In certain conditions repeat treatment should be recommended to ensure that treatment is effective, in order to interrupt a potential chain of infection. Repeat treatment is particularly recommended in cases of crusted scabies, severe scabies with many papules caused by burrows, immunosuppressed patients, doubt as to whether initial treatment was consistently followed, and scabies outbreaks in care homes and situations in which multiple individuals are affected (5).
When large populations with a high prevalence of scabies are treated, systemic ivermectin seems to be superior to topical treatments (26). When large patient groups are treated, the issue of practicability is also significant. Single oral administration of tablets is considerably simpler than professional applications of cream over the whole body. This is also significant in view of the increased risk of reinfestation in residences where space is limited and there is physical contact between individuals.
Treatment of contact persons is important to long-term treatment success (2, 5). The guideline recommends that, as a rule, contact persons such as those in the affected individual’s family or household should also be treated.
The German guideline recommends permethrin for common scabies (5), as it is applied locally and usually only needs to be used once. Based on our findings, no preference can be determined for permethrin or crotamiton in terms of efficacy—crotamiton is a potential alternative, according to our analysis. The guideline recommends it as a pragmatic option for second-line treatment of infants, pregnant women, and breastfeeding women (5). There are no trials in these patient groups. The German guideline recommends that children return to school and adults to work after initial treatment is completed.
Follow-up examinations checking for new-onset efflorescences suggesting scabies should be performed 2 weeks and at least 4 to 6 weeks after treatment (end of mite cycle). Furthermore, treatment should be repeated if there are still signs of active infestation, such as new papules caused by burrows or microscopic or dermatoscopic evidence of live scabies mites, 14 days (or more) after treatment.
Supplementary Material
Findings of all included trials
This section contains an effect estimate—risk ratio, also referred to as relative risk (RR)—and the corresponding confidence interval for each comparison. In the eFigures, the effect estimate is shown as a short, vertical line, and the confidence interval (i.e. the region in which there is a 95% probability that the true effect lies) is shown as a horizontal bar.
Permethrin 5% versus crotamiton 10%
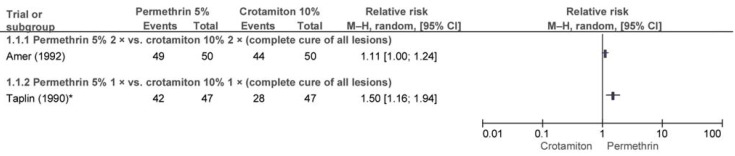
Two trials compared permethrin 5% (PER) and crotamiton 10% (CRO). Inpatients in a trial by Amer and el-Gharib (e36) with clinically suspected scabies were treated with PER or CRO on 2 consecutive nights. No statistically significant difference was found in terms of complete cure of lesions after 4 weeks (efigure 1). Adverse events were not reported.
In the trial by Taplin et al. (e37) children received a single dose of PER or CRO. After 2 weeks no statistically significant difference was found between PER and CRO in terms of complete cure of lesions (RR: 2.33; 95% confidence interval [95% CI]: [0.98; 5.55]). After 4 weeks permethrin was found to be superior to crotamiton (efigure 1). Five and 9 patients with pruritus were reported respectively.
Figure.
Study selection process
Key Messages.
Single-dose permethrin 5%, crotamiton 10%, and ivermectin systemic are of comparable efficacy.
Ivermectin 0.2 mg/kg bodyweight was found to be superior to permethrin 5% for preventive and therapeutic treatment of a whole island population in an area with endemic scabies.
Adverse events were rare with all the investigated drugs.
The investigated therapies varied in terms of frequency of administration.
Where efficacy is comparable, practicability issues, particularly frequency of administration and type of application, determine therapy selection.
eTable 2. Excluded fulltexts.
| Main author, year (source) | Reason for exclusion |
| k. A. 2009 (e1) | No abstracts on scabies included |
| Abedin 2007 (e2) | Not an RCT |
| Alrawashdeh 2013 (e3) | Not an RCT |
| Amerio 2003 (e4) | No relevant comparison |
| Asad 2011 (e5) | Not available via the German inter-library loan service |
| Asad 2014 (e6) | Not available via the German inter-library loan service |
| Ayaz 2011 (e7) | No relevant comparison |
| Azulay 1975 (e8) | No relevant comparison |
| Banez 1999 (e9) | No relevant comparison |
| Biele 2006 (e10) | No relevant comparison |
| Burgess 1986 (e11) | Not an RCT |
| Camasmie 1984 (e12) | No relevant comparison |
| Castillo 2013 (e13) | No relevant comparison |
| Daneshhpajooh 1999 (e14) | No relevant comparison |
| Dourmishev 1998 (e15) | Not an RCT |
| Goldust 2014 (e16) | No relevant comparison |
| Goldust 2013 (e17) | No relevant comparison |
| Gupta 1981 (e18) | Not an RCT |
| Henderson 1992 (e19) | Not an RCT |
| Kenawi 1993 (e20) | Not an RCT |
| Landegren 1979 (e21) | No relevant comparison |
| Mohamed 1993 (e22) | Abstract only: data insufficient |
| Mozgunov 1978 (e23) | Russian |
| Neto 1984 (e24) | Not available via the German inter-library loan service |
| Oladimeji 2005 (e25) | Not available via the German inter-library loan service |
| Oyelami 2009 (e26) | No relevant comparison |
| Panja 1969 (e27) | Not an RCT |
| Rahman 2015 (e28) | No relevant comparison |
| Rohatgi 2013 (e29) | Abstract only: data insufficient |
| Saeedi 2015 (e30) | No relevant comparison |
| Schenone 1986 (e31) | No relevant comparison |
| Srinivas 1996 (e32) | No relevant comparison (dosage form) |
| Sule 2007 (e33) | Not an RCT |
| Tausch 1999 (e34) | Same active ingredient at same concentration |
| Wankhade 2013 (e35) | Abstract only: data insufficient |
“No relevant comparison” refers to comparisons not in line with PICO system (e.g. drugs other than those included).
RCT: Randomized controlled trial
eFigure 1.
Efficacy of permethrin 5% versus crotamiton 10% after 4 weeks *10 children in the CRO group had undergone repeat treatment. 95% CI: 95% confidence interval
Permethrin 5% versus ivermectin (IVER) 0.2 mg/kg
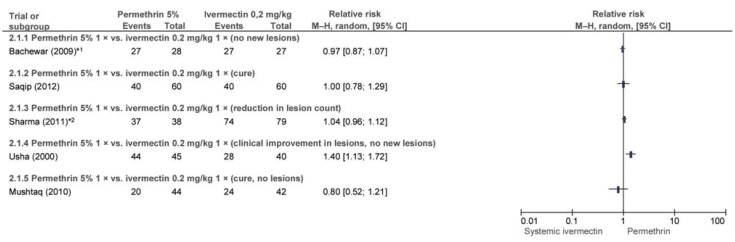
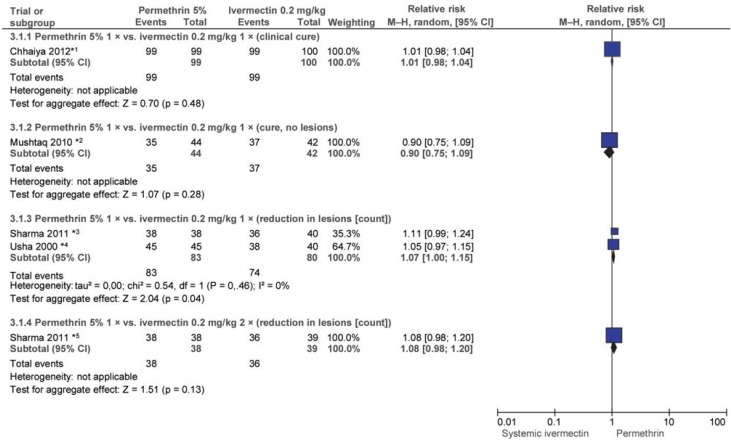
Six trials (e38– e41) conducted in India and Pakistan evaluated single-dose PER 5% with single-dose ivermectin 0.2 mg/kg systemic after 2 and/or 4 weeks. After 2 weeks permethrin had achieved better outcomes than ivermectin in one trial (e40), and the difference was statistically significant (efigure 2). Four other trials found no significant difference. Differences between the trials included differences in the outcome parameter (complete cure/no new lesions/reduction in lesion count/improvement in lesion severity).
eFigure 2.
Efficacy of single-dose permethrin 5% (PER) vs. single-dose ivermectin 0.2 mg/kg (IVER) after 2 weeks
*1 17.8% (PER) and 44.4% (IVER) of patients underwent repeat treatment after 1 week; in the other trials, there were no repeat treatments within 2 weeks.
*2 Ivermectin arms combined.
In addition, patients in the trials by Bachewar et al. (e38) and Chhaiya et al. (e39) who had not attained the outcome parameter after one week received a further dose of the trial drugs (eFigure 2 and 3). Usha and Gopalakrishnan Nair (e40) and Mushtaq (e41) also administered an additional dose to patients who were not cured but not until 2 weeks after initial treatment. After 4 weeks neither drug was found to be statistically superior in either subgroup (efigure 3).
eFigure 3.
eFigure 3: Efficacy of single-dose permethrin 5% (PER) vs. 1 or 2 doses of ivermectin (IVER) 0.2 mg/kg after 4 weeks
*1 Patients not successfully cured underwent repeat treatment (weeks 1 to 4; n/N not reported).
*2 Patients not successfully cured underwent repeat treatment (week 2; n/N not reported).
*3 All patients were treated every 2 weeks.
*4 One patient in the PER group and 12 patients in the IVER group underwent repeat treatment after 2 weeks.
*5 All patients were treated every 2 weeks.
Adverse events (AEs) were reported in 5 of the 6 trials: in 2 trials (e38, e40) there were no AEs; in 2 trials one and 3 patients respectively reported a burning sensation (PER), and one and 4 respectively reported headache and pruritus (one patient) and dizziness (2 patients; systemic IVER) (e39, e42). In one other trial, headache, pruritus, and bacterial infections were reported in 7 patients (IVER), and erythema in one patient (PER) (e41).
Ivermectin 0.2 mg/kg single-dose versus 2 doses
In the 3-arm trial by Sharma and Singal (e43), patients in the third arm received 2 doses of ivermectin 0.2 mg/kg. No statistically significant difference in efficacy was found between this and a single dose after 4 weeks. Efficacy was measured using the outcome parameter “=50% improvement in lesion count” (RR: 0.97; 95% CI: [0.85; 1.12]).
Permethrin 5% versus ivermectin 1% versus IVER 0.2 mg/kg
Chhaiya et al. (e39) investigated ivermectin 1% topical versus permethrin 5% topical and ivermectin systemic (all single dose). After 4 weeks all patients were cured and there was no statistically significant difference in favor of either permethrin or systemic ivermectin (IVER 1% versus PER 5%: RR: 0.99; 95% CI: [0.96; 1.02]); IVER 1% versus IVER 0.2 mg/kg: RR: 1.01; 95% CI: [0.98; 1.04]). Patients whose treatment was unsuccessful underwent repeat treatment in weeks 1, 2, 3, and 4 (number not reported).
Ivermectin 0.15 to 0.2 mg/kg versus benzyl benzoate (BB) 10%/12.5%/25%
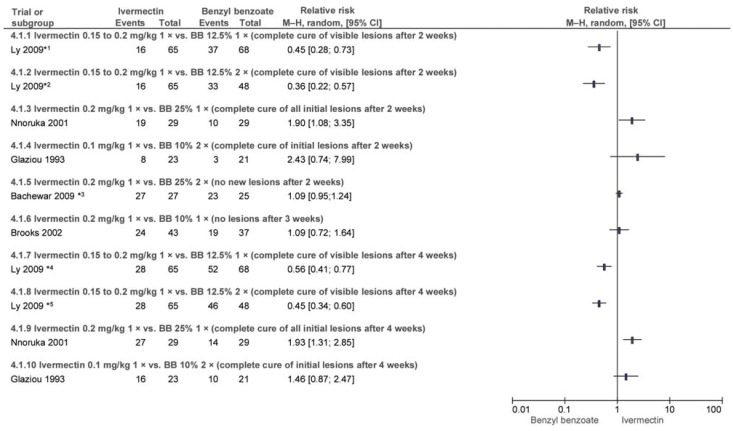
Five trials conducted in Nigeria, Senegal, and Oceania evaluated the efficacy of ivermectin versus BB at various doses and frequencies of administration. Some outcome parameters varied between trials (efigure 4).
Ly et al. (e44) compared one and two doses of BB 12.5% with IVER 0.5 to 0.2 mg/kg. After one week all patients whose condition had worsened substantially underwent one further treatment. After 2 and 4 weeks BB was found to be superior (efigure 4). In the BB groups 18% and 37% of patients respectively reported skin irritation during treatment. Nnoruka and Agu (e45) compared IVER 0.2 mg/kg to BB 25%, both single-dose. After 2 and 4 weeks ivermectin was found to be superior (efigure 4). Seven patients in the BB group reported irritation and pruritus (e45). It was reported that there were no AEs in the IVER group (e45).
Brooks and Grace (e46) also compared single-dose BB 10% to single-dose IVER 0.2 mg/kg; this trial included only children. There was no statistically significant difference after 3 weeks (efigure 4). Considerably more cases of skin irritation were reported in the BB group.
Glaziou et al. (e47) investigated two doses of BB 10% versus IVER 0.1 mg/kg. No statistically significant difference in efficacy was found after 2 or 4 weeks (efigure 4). Five patients in the BB group reported increased pruritus. No adverse events (AEs) were reported in the IVER arm of the trial.
Bachewar et al. (e38) compared IVER 0.2 mg/kg to BB 25% applied on 2 consecutive nights and found no statistically significant difference in efficacy after 2 weeks (efigure 4). However, 44.4% and 24% of patients respectively underwent repeat treatment after one week. No AEs occurred.
Most trials did not report whether any patients underwent repeat treatment (efigure 4).
Sulfur ointment versus benzyl benzoate 25%
Gulati and Singh (e48) conducted a trial on the efficacy of sulfur versus BB 25%. Both ointments were to be applied 3 times, at intervals of 12 hours. After 14 days, no statistically significant difference was found in terms of the outcome parameter “clearance of lesions” (RR: 1.07; 95% CI: [0.99; 1.15]). Patients who still had lesions after day 10 underwent repeat treatment. AEs were not reported.
eFigure 4.
Efficacy of ivermectin (IVER) 0.15 to 0.2 mg/kg (single dose) vs. benzyl benzoate (BB) 10%/12.5%/25% (1 or 2 doses) after 2, 3 [4.1.1 to 4.1.6], and 4 weeks [4.1.7 to 4.1.10]
*1 Treatment repeated on day 7 if condition worsened (IVER: 8 patients).
*2 See above.
*3 44.4% (IVER) and 24% (BB) of patients underwent repeat treatment after 1 week if there were no signs of improvement.
*4 Treatment repeated on day 7 (IVER: 8 patients) and day 14 (n/N not reported) if condition worsened.
*5 Treatment repeated on day 7 (IVER: 8 patients) and day 14 (n/N not reported) if condition worsened.
Sulfur 8%/10% applied as a single dose, on 3 days, and on 3 nights
Sharquie et al. (e49) investigated the efficacy of sulfur 8% and 10% applied as a single dose, on 3 consecutive days nights (dosage unclear). After 2 weeks the use of 3 applications was found to be superior, and the difference was statistically significant (RR: 1.72; 95% CI: [1.24; 2.38], RR: 1.78; 95% CI: [1.29; 2.44]). In week 2, 6 of the 33 patients receiving a single application, 9 of the 32 receiving 3 daytime applications, and 14 of the 32 receiving 3 nighttime applications reported dermatitis.
Mass treatment: therapeutic and preventive
Avila-Romay et al. (e50) investigated the efficacy of sulfur in 10% cold cream versus sulfur 10% and salicylic acid 1% in pork fat. Both preparations were to be administered on 3 consecutive nights and once more 3 nights later. After 10 days neither preparation was found to be statistically superior (RR: 1.13; 95% CI: [0.97; 1.33]; outcome parameter: no cutaneous lesions).
Romani et al. (e51) randomized 3 island communities in Fiji and compared the following:
1. Standard treatment of those affected and their relatives with permethrin
2. Whole-community permethrin treatment
3. Whole-community ivermectin 0.2 mg/kg systemic treatment
After 12 months no statistical superiority was found in terms of efficacy in favor of permethrin as standard treatment versus whole-community treatment (RR: 0.96; 95% CI: [0.92; 1.02]). However, whole-community ivermectin 0.2% mg/kg treatment was found to be superior to permethrin (both standard and whole-community treatment), and the difference was statistically significant (RR: 0.83; 95% CI: [0.80; 0.86] and RR: 0.86; 95% CI: [0.82; 0.89]).
Acknowledgments
Translated from the original German by Caroline Shimakawa-Devitt, M.A.
Footnotes
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that no conflict of interest exists.
References
- 1.World Health Organization. Scabies. www.who.int/lymphatic_filariasis/epidemiology/scabies/en/ (last accessed on 10 March 2016) [Google Scholar]
- 2.Wolff HH. Ivermectin als orale Einmalbehandlung der Skabies: Das Ende der Lokaltherapie? Dtsch Arztebl. 1998;95:2095–2097. [Google Scholar]
- 3.Arlian LG, Runyan RA, Estes SA. Cross infestivity of Sarcoptes scabiei. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1984;10:979–986. doi: 10.1016/s0190-9622(84)80318-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Arlian LG, Runyan RA, Achar S, Estes SA. Survival and infectivity of sarcoptes scabiei var canis and var. hominis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1984;11:210–215. doi: 10.1016/s0190-9622(84)70151-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Sunderkötter C, Feldmeier H, Fölster-Holst R, et al. S1-Leitlinie zur Diagnostik und Therapie der Skabies - Kurzfassung. J Dtsch Dermatol Ges. 2016 doi: 10.1111/ddg.13130_g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Mounsey KE, Holt DC, McCarthy J, Currie BJ, Walton SF. Scabies: molecular perspectives and therapeutic implications in the face of emerging drug resistance. Future Microbiol. 2008;3:57–66. doi: 10.2217/17460913.3.1.57. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Robert-Koch-Institute Skabies (Krätze) RKI-Ratgeber für Ärzte. www.rki.de/DE/Content/Infekt/EpidBull/Merkblaetter/Ratgeber_Skabies.html#doc2374546bodyText10 (last accessed on 3 April 2016) [Google Scholar]
- 8.Tabassam SM, Iqbal Z, Jabbar A, Sindhu ZU, Chattha AI. Efficacy of crude neem seed kernel extracts against natural infestation of sarcoptes scabiei var ovis. J Ethnopharmacol. 2008;115:284–287. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2007.10.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Sunderkötter C, Mayser P, Fölster-Holst R, Maier W, Kampen H, Hamm H. Therapie der Skabies Leitlinie der Deutschen Dermatologischen Gesellschaft. J Dtsch Dermatol Ges. 2006;5:424–430. doi: 10.1111/j.1610-0387.2007.06298.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Higgins JPT, Green S, Cochrane Colloboration. Cochrane handbook for systematic reviews of interventions. www.cochrane-handbook.org/ (last accessed on 9 June 2016) [Google Scholar]
- 11.Review Manager (RevMan) Copenhagen The Nordic Cochrane Centre. The Cochrane Collaboration. 2014 [Google Scholar]
- 12.Taplin D, Meinking TL, Chen JA, Sanchez R. Comparison of crotamiton 10% cream (Eurax) and permethrin 5% cream (Elimite) for the treatment of scabies in children. Pediatr Dermatol. 1990;7:67–73. doi: 10.1111/j.1525-1470.1990.tb01078.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Amer M, el-Gharib I. Permethrin versus crotamiton and lindane in the treatment of scabies. Int J Dermatol. 1992;31:357–358. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-4362.1992.tb03958.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Chhaiya SB, Patel VJ, Dave JN, Mehta DS, Shah HA. Comparative efficacy and safety of topical permethrin, topical ivermectin, and oral ivermectin in patients of uncomplicated scabies. Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol. 2012;78:605–610. doi: 10.4103/0378-6323.100571. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Gulati PV, Singh KP. A family based study on the treatment of scabies with benzyl benzoate and sulphur ointment. Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol. 1978;44:269–273. [Google Scholar]
- 16.Sharquie KE, Al-Rawi JR, Noaimi AA, Al-Hassany HM. Treatment of scabies using 8% and 10% topical sulfur ointment in different regimens of application. J Drugs Dermatol. 2012;11:357–364. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Bachewar NP, Thawani VR, Mali SN, Gharpure KJ, Shingade VP, Dakhale GN. Comparison of safety, efficacy, and cost effectiveness of benzyl benzoate, permethrin, and ivermectin in patients of scabies. Indian J Pharmacol. 2009;41:9–###14. doi: 10.4103/0253-7613.48882. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Mushtaq A, Khurshid K, Suhail Pal S. Comparison of efficacy and safety of oral ivermectin with topical permethrin in treatment of scabies. J Pak Assoc Derma. 2010;20:227–231. [Google Scholar]
- 19.Saqib M, Malik LM, Jahangir M. A comparison of efficacy of single topical permethrin and single oral ivermectin in the treatment of scabies. J Pak Assoc Derma. 2012;22:45–49. [Google Scholar]
- 20.Sharma R, Singal A. Topical permethrin and oral ivermectin in the management of scabies: a prospective, randomized, double blind, controlled study. Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol. 2011;77:581–586. doi: 10.4103/0378-6323.84063. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Usha V, Gopalakrishnan Nair TV. A comparative study of oral ivermectin and topical permethrin cream in the treatment of scabies. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2000;42:236–240. doi: 10.1016/S0190-9622(00)90131-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Nnoruka EN, Agu CE. Successful treatment of scabies with oral ivermectin in Nigeria. Trop Doct. 2001;31:15–18. doi: 10.1177/004947550103100105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Glaziou P, Cartel JL, Alzieu P, Briot C, Moulia-Pelat JP, Martin PM. Comparison of ivermectin and benzyl benzoate for treatment of scabies. Trop Med Parasitol. 1993;44:331–332. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Brooks PA, Grace RF. Ivermectin is better than benzyl benzoate for childhood scabies in developing countries. J Paediatr Child H. 2002;38:401–404. doi: 10.1046/j.1440-1754.2002.00015.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Ly F, Caumes E, Ndaw CA, Ndiaye B, Mahe A. Ivermectin versus benzyl benzoate applied once or twice to treat human scabies in Dakar, Senegal: a randomized controlled trial. Bull World Health Organ. 2009;87:424–430. doi: 10.2471/BLT.08.052308. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Romani L, Whitfeld MJ, Koroivueta J, et al. Mass drug administration for scabies control in a population with endemic disease. New Engl J Med. 2015;373:2305–2313. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1500987. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Avila-Romay A, Alvarez-Franco M, Ruiz-Maldonado R. Therapeutic efficacy, secondary effects, and patient acceptability of 10% sulfur in either pork fat or cold cream for the treatment of scabies. Pediatr Dermatol. 1991;8:64–66. doi: 10.1111/j.1525-1470.1991.tb00844.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- E1.Abstracts—New Zealand dermatological society incorporated annual scientific meeting. Australas. J Dermatol. 2009;50 [Google Scholar]
- E2.Abedin S, Narang M, Gandhi V, Narang S. Efficacy of permethrin cream and oral ivermectin in treatment of scabies. Indian J Pediatr. 2007;74:915–916. doi: 10.1007/s12098-007-0168-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- E3.Alrawashdeh B, Alazab K. Comparison between 25% benzyl benzoate, 5% permethrin and 10% crotamiton in the treatment of scabies in Gaza. RMJ. 2013;38:125–126. [Google Scholar]
- E4.Amerio P, Capizzi R, Milani M. Efficacy and tolerability of natural synergised pyrethrins in a new thermo labile foam formulation in topical treatment of scabies: a prospective, randomised, investigator-blinded, comparative trial vs permethrin cream. Eur J Dermatol. 2003;13:69–71. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- E5.Asad F, Khan M, Samdani A, Alam R, Rizvi F. To study therapeutic effect and benefit on quality of life in scabies patients. Medical Forum Monthly. 2011;22:34–37. [Google Scholar]
- E6.Asad F, Rizvi F, Iqbal J. Beneficial effect and safety of 5% permethrin cream in scabies patients. Medical Forum Monthly. 2014;25:18–21. [Google Scholar]
- E7.Ayaz S, Hannan A, Usmanghani K, et al. ScaNeem: herbo-mineral therapy for scabies. J Med Plant Res. 2011;5:5706–5712. [Google Scholar]
- E8.Azulay RD, Marinho DEA, Lapolli N, Pola LBP. Topical thiabendazole in the treatment of scabies Double blind trial in comparison with benzyl benzoate. [Portuguese] Rev Bras Med. 1975;32:800–802. [Google Scholar]
- E9.Banez JA, Nazareno RC, Medel RB. Clinical trial on the effectiveness of gliricidia sepium (kakawate) in treating patients with scabies in the antipolo CBHP. Phil J Microbiol Infect Dis. 1999;28:115–324. [Google Scholar]
- E10.Biele M, Campori G, Colombo R, et al. Efficacy and tolerability of a new synergized pyrethrins thermofobic foam in comparison with benzyl benzoate in the treatment of scabies in convicts: the ISAC study (Studio Della scabbia in ambiente carcerario) J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2006;20:717–720. doi: 10.1111/j.1468-3083.2006.01623.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- E11.Burgess I, Robinson RJ, Robinson J, Maunder JW, Hassan Z. Aqueous malathion 05% as a scabicide: clinical trial. BMJ. 1986;292 doi: 10.1136/bmj.292.6529.1172. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- E12.Camasmie Curiati WJ. Double-blind study with decamethrin in scabies and head louse [Portuguese] Rev Bras Med. 1984;41:81–83. [Google Scholar]
- E13.Castillo AL, Osi MO, Ramos JDA, De Francia JL, Dujunco MU, Quilala PF. Efficacy and safety of tinospora cordifolia lotion in sarcoptes scabiei var hominis-infected pediatric patients: a single blind, randomized controlled trial. J Pharmacol Pharmacother. 2013;4:39–46. doi: 10.4103/0976-500X.107668. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- E14.Daneshpajooh M. The comparison of oral ivermectin and topical gamma-benzene hexachloride 1% in treatment of scabies (Persian) Iran J Dermatol. 1999;3 [Google Scholar]
- E15.Dourmishev A, Serafimova D, Dourmishev L. Efficacy and tolerance of oral ivermectin in scabies. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 1998;11:247–251. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- E16.Goldust M, Rezaee E, Raghifar R, Hemayat S. Comparing the efficacy of oral ivermectin vs malathion 05% lotion for the treatment of scabies. SKINmed. 2014;12:284–287. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- E17.Goldust M, Rezaee E, Raghifar R, Naghavi-Behzad M. Comparison of permethrin 25 % cream vs. tenutex emulsion for the treatment of scabies. Ann Parasitol. 2013;59:31–35. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- E18.Gupta LC, Gupta SR, Sahu UC. Scabies: Survey and clinical trial. Indian J Dermatol. 1981;26:33–35. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- E19.Henderson CA, Nykia M. Treatment of scabies in rural east Africa? A comparative study of two regimens. Trop Doct. 1992;22:165–167. doi: 10.1177/004947559202200408. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- E20.Kenawi MZ, Morsy TA, Abdalla KF, Hady HM. Treatment of human scabies by sulfur and permethrin. J-Egypt-Soc-Parasitol. 1993;23:691–696. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- E21.Landegren J, Borglund E, Storgards K. Treatment of scabies with disulfiram and benzyl benzoate emulsion: a controlled study. Acta Derm Venereol. 1979;59:274–276. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- E22.Mohamed A, Ibrahim G. Permethrin versus crotamiton and lindane in the treatment of scabies [abstract no:2] Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol. 1993;58 [Google Scholar]
- E23.Mozgunov VN, Klimenko AV. [Effectiveness of preparations used in treating scabies] Voen Med Zh. 1978 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- E24.Neto VS. Comparative study of monosulfiram and benzyl benzoate in the treatment of scabies. Anais Brasileiros de Dermatologia. 1984;59:213–214. [Google Scholar]
- E25.Oladimeji FA, Orafidiya LO, Ogunniyi TAB, Adewunmi TA, Onayemi O. A comparative study of the scabicidal activities of formulations of essential oil of lippia multiflora moldenke and benzyl benzoate emulsion BP. International Journal of Aromatherapy. 2005;15:87–93. [Google Scholar]
- E26.Oyelami OA, Onayemi A, Oyedeji OA, Adeyemi LA. Preliminary study of effectiveness of aloe vera in scabies treatment. Phytother Res. 2009;23:1482–1484. doi: 10.1002/ptr.2614. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- E27.Panja RK, Choudhury S. A clinical trial with gamma benzene hexachloride in scabies. Indian J Dermatol. 1969;14:136–137. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- E28.Rahman J, Farooqi AH, Sultana A, Rahman K, Rahman A. Clinical efficacy of a herbo-mineral unani formulation in scabies: an open-label randomized controlled study. Orient Pharm Exp Med. 2015;15:173–181. [Google Scholar]
- E29.Rohatgi V, Narayana Reddy S, Vagge DS. A prospective, randomized, open labelled, comparative study of efficacy and cost effectiveness of permethrin and ivermectin in 5-15 years age group patients with scabies in a tertiary care hospital. Indian J Pharmacol. 2013;45 [Google Scholar]
- E30.Saeedi M, Hajheydari Z, Akbari J, Morteza-Semnani K, Emadian A. Preparation of malathion 05% lotion and studying its effect on healing scabies compared with permethrin cream 5%. [Persian] Journal of Mazandaran University of Medical Sciences. 2015;25:128–131. [Google Scholar]
- E31.Schenone H, Prieto R, Lobos M, Fabres P, Boresi R. Treatment of scabies with a dermatological lotion of decamethrin at 0.02%. Study of 127 patients using 2 therapeutic regimens. [Tratamiento de la sarna con locion dermatologica de decametrine al 0,02%. Estudio en 127 pacientes mediante la utilizacion de dos esquemas terapeuticos] Bol Chil Parasitol. 1986;41:3–7. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- E32.Srinivas CR, Sathish PB, Sukumar J. Treatment of scabies with 1% gamma benzene hexachloride Efficacy of drug delivery by bath, spray and painbrush. Indian J Dermatol. 1996:51–52. [Google Scholar]
- E33.Sule HM, Thacher TD. Comparison of ivermectin and benzyl benzoate lotion for scabies in Nigerian patients. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2007;76:392–395. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- E34.Tausch I. Crotamiton—An effective and safe drug for the treatment of scabies Results of a controlled clinical trial [German] Z Hautkr. 1999;74:162–166. [Google Scholar]
- E35.Wankhade PA, Tamboli SB, Rathod P, Deshmukh JB, Shirure PA, Ghadlinge MS. Comparison of safety, efficacy, cost effectiveness of permethrin and ivermectin in patients of scabies. Indian J Pharmacol. 2013;45 [Google Scholar]
- E36.Amer M, el-Gharib I. Permethrin versus crotamiton and lindane in the treatment of scabies. Int J Dermatol. 1992;31:357–358. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-4362.1992.tb03958.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- E37.Taplin D, Meinking TL, Chen JA, Sanchez R. Comparison of crotamiton 10% cream (Eurax) and permethrin 5% cream (Elimite) for the treatment of scabies in children. Pediatr Dermatol. 1990;7:67–73. doi: 10.1111/j.1525-1470.1990.tb01078.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- E38.Bachewar NP, Thawani VR, Mali SN, Gharpure KJ, Shingade VP, Dakhale GN. Comparison of safety, efficacy, and cost effectiveness of benzyl benzoate, permethrin, and ivermectin in patients of scabies. Indian J Pharmacol. 2009;41:9–14. doi: 10.4103/0253-7613.48882. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- E39.Chhaiya SB, Patel VJ, Dave JN, Mehta DS, Shah HA. Comparative efficacy and safety of topical permethrin, topical ivermectin, and oral ivermectin in patients of uncomplicated scabies. Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol. 2012;78:605–610. doi: 10.4103/0378-6323.100571. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- E40.Usha V, Gopalakrishnan Nair TV. A comparative study of oral ivermectin and topical permethrin cream in the treatment of scabies. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2000;42:236–40. doi: 10.1016/S0190-9622(00)90131-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- E41.Mushtaq A, Khurshid K, Suhail Pal S. Comparison of efficacy and safety of oral ivermectin with topical permethrin in treatment of scabies. J Pak Assoc Derma. 2010;20:227–231. [Google Scholar]
- E42.Sharma VK, Khandpur S. Evaluation of cyclophosphamide pulse therapy as an adjuvant to oral corticosteroid in the management of pemphigus vulgaris. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2013;38:659–664. doi: 10.1111/ced.12073. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- E43.Sharma R, Singal A. Topical permethrin and oral ivermectin in the management of scabies: a prospective, randomized, double blind, controlled study. Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol. 2011;77:581–586. doi: 10.4103/0378-6323.84063. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- E44.Ly F, Caumes E, Ndaw CA, Ndiaye B, Mahe A. Ivermectin versus benzyl benzoate applied once or twice to treat human scabies in Dakar, Senegal: a randomized controlled trial. Bull World Health Organ. 2009;87:424–430. doi: 10.2471/BLT.08.052308. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- E45.Nnoruka EN, Agu CE. Successful treatment of scabies with oral ivermectin in Nigeria. Trop Doct. 2001;31:15–18. doi: 10.1177/004947550103100105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- E46.Brooks PA, Grace RF. Ivermectin is better than benzyl benzoate for childhood scabies in developing countries. J Paediatr Child H. 2002;38:401–404. doi: 10.1046/j.1440-1754.2002.00015.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- E47.Glaziou P, Cartel JL, Alzieu P, Briot C, Moulia-Pelat JP, Martin PM. Comparison of ivermectin and benzyl benzoate for treatment of scabies. Trop Med Parasitol. 1993;44:331–332. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- E48.Gulati PV, Singh KP. A family based study on the treatment of scabies with benzyl benzoate and sulphur ointment. Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol. 1978;44:269–273. [Google Scholar]
- E49.Sharquie KE, Al-Rawi JR, Noaimi AA, Al-Hassany HM. Treatment of scabies using 8% and 10% topical sulfur ointment in different regimens of application. J Drugs Dermatol. 2012;11:357–364. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- E50.Avila-Romay A, Alvarez-Franco M, Ruiz-Maldonado R. Therapeutic efficacy, secondary effects, and patient acceptability of 10% sulfur in either pork fat or cold cream for the treatment of scabies. Pediatr Dermatol. 1991;8:64–66. doi: 10.1111/j.1525-1470.1991.tb00844.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- E51.Romani L, Whitfeld MJ, Koroivueta J, et al. Mass drug administration for scabies control in a population with endemic disease. N Engl J Med. 2015;373:2305–2313. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1500987. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- E52.Pourhasan A, Goldust M, Rezaee E. Treatment of scabies, permethrin 5% cream vs crotamiton 10% cream. Ann Parasitol. 2013;59:143–147. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- E53.Goldust M, Rezaee E, Hemayat S. Treatment of scabies: Comparison of permethrin 5% versus ivermectin. J Dermatol. 2012;39:545–547. doi: 10.1111/j.1346-8138.2011.01481.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- E54.Ranjkesh MR, Naghili B, Goldust M, Rezaee E. The efficacy of permethrin 5% vs oral ivermectin for the treatment of scabies. Ann Parasitol. 2013;59:189–194. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- E55.Goldust M, Rezaee E, Raghifar R, Hemayat S. Treatment of scabies: the topical ivermectin vs permethrin 2.5% cream. Ann Parasitol. 2013;59:79–84. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- E56.Goldust M, Rezaee E, Raghiafar R. Topical ivermectin versus crotamiton cream 10% for the treatment of scabies. Int J Dermatol. 2014;53:904–908. doi: 10.1111/ijd.12447. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- E57.Goldust M, Rezaee E, Raghifar R. Comparison of oral ivermectin versus crotamiton 10% cream in the treatment of scabies. Cutan Ocul Toxicol. 2014;33:333–336. doi: 10.3109/15569527.2013.768258. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- E58.Goldust M, Rezaee E. Comparative trial of oral ivermectin versus sulfur 8% ointment for the treatment of scabies. J Cutan Med Surg. 2013;17:299–300. doi: 10.2310/7750.2013.12123. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- E59.Alipour H, Goldust M. The efficacy of oral ivermectin vs sulfur 10% ointment for the treatment of scabies. Ann Parasitol. 2015;61:79–84. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Findings of all included trials
This section contains an effect estimate—risk ratio, also referred to as relative risk (RR)—and the corresponding confidence interval for each comparison. In the eFigures, the effect estimate is shown as a short, vertical line, and the confidence interval (i.e. the region in which there is a 95% probability that the true effect lies) is shown as a horizontal bar.
Permethrin 5% versus crotamiton 10%
Two trials compared permethrin 5% (PER) and crotamiton 10% (CRO). Inpatients in a trial by Amer and el-Gharib (e36) with clinically suspected scabies were treated with PER or CRO on 2 consecutive nights. No statistically significant difference was found in terms of complete cure of lesions after 4 weeks (efigure 1). Adverse events were not reported.
In the trial by Taplin et al. (e37) children received a single dose of PER or CRO. After 2 weeks no statistically significant difference was found between PER and CRO in terms of complete cure of lesions (RR: 2.33; 95% confidence interval [95% CI]: [0.98; 5.55]). After 4 weeks permethrin was found to be superior to crotamiton (efigure 1). Five and 9 patients with pruritus were reported respectively.