Erratum
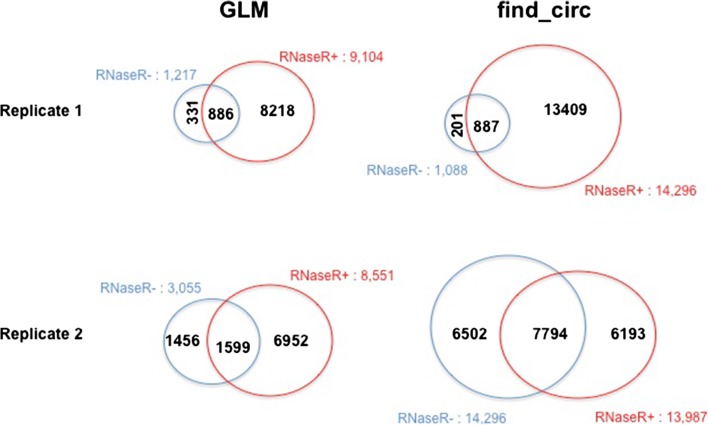
In this version of this article that was originally published [1] the authors had analysed two HeLa samples, SRR1637089 and SRR1637090, in Fig. 3 of the original publication. The authors had respectively analysed the samples as RNaseR+ and Ribominus, due to their incorrect annotations in a public database, but they were both Ribominus samples. The authors have now analysed appropriate positive and negative controls using their method, KNIFE, and find_circ. The results are presented in an amended version of Fig. 3c, please see updated version below. Furthermore, the authors have now provided a list of accession codes for the ENCODE data they analysed, please see the Table 1 below. Please note this was not part of the original article.
Fig. 3.
Statistical algorithm improves the sensitivity of circular RNA detection. a, b Circular RNA detected by both algorithms are divided into false positives (FP; flagged as false positives due to low posterior probability) or true positives (TP; our posterior probability ≥ 0.9). a Number of circular RNAs detected by our GLM or CIRI in ENCODE BJ poly(A)+/− data and HeLa RNase-R+/− data generated by Gao et al. [23]. CIRI results are based on all default parameters except the -E flag set to exclude false positives resulting from identical colinear exons. b Number of circular RNAs detected by our GLM or find_circ in ENCODE BJ poly(A)+/− data and HeLa RNase-R- data generated by Gao et al. [23]. c Circular RNAs detected in HeLa RNase-R+ and Ribo- data generated by Gao et al. [23] and poly(A)+, and poly(A)- data generated by ENCODE. Number of circular RNAs detected by our GLM method (one or more reads, posterior probability ≥ 0.9) compared with CIRI (default parameters except -E). For GLM results, the first number is the total number of circles and the number of those which were detected by the de novo portion of the algorithm are listed in parentheses. d Venn diagram comparing the number of putative circular RNAs identified by our annotation-dependent algorithm in Rnase-R-treated H9 cells and the results published by Zhang et al. [22]. Green circles and red circles show circular RNA identified by our algorithm with high and low confidence, respectively; the blue circle shows those identified by Zhang et al. e Total junctional reads for circles comprised of a single exon (posterior probability ≥ 0.9, read count > 1) shown by size for same data as in panel (d). Median exon length is shown in red. The x-axis is truncated at 2000 excluding 31 long exons, all but one with total read counts < 50]
Table 1.
ENCODE accession codes
| Source | Type | ACCESSION |
|---|---|---|
| A549 | cell line, polyA+ | GSM758564 |
| AGO4450 | cell line, polyA+ | GSM758561 |
| BJ | cell line, polyA+ | GSM758562 |
| GM12878 | cell line, polyA+ | GSM758559 |
| H1 | cell line, polyA+ | GSM758566 |
| HMEC | cell line, polyA+ | GSM758571 |
| HeLa | cell line, polyA+ | GSM765402 |
| HepG2 | cell line, polyA+ | GSM758575 |
| HSSM | cell line, polyA+ | GSM758578 |
| HUVEC | cell line, polyA+ | GSM758563 |
| IMR90 | cell line, polyA+ | GSM981249 |
| K562 | cell line, polyA+ | GSM765405 |
| MCF7 | cell line, polyA+ | GSM765388 |
| NHEK | cell line, polyA+ | GSM765401 |
| NHLF | cell line, polyA+ | GSM765394 |
| SKNSHRA | cell line, polyA+ | GSM765395 |
| A549 | cell line, polyA- | GSM767854 |
| AGO4450 | cell line, polyA- | GSM765396 |
| BJ | cell line, polyA- | GSM767855 |
| GM12878 | cell line, polyA- | GSM758572 |
| H1 | cell line, polyA- | GSM758573 |
| HMEC | cell line, polyA- | GSM765397 |
| HeLa | cell line, polyA- | GSM767847 |
| HepG2 | cell line, polyA- | GSM758567 |
| HSSM | cell line, polyA- | GSM765391 |
| HUVEC | cell line, polyA- | GSM767856 |
| K562 | cell line, polyA- | GSM758577 |
| MCF7 | cell line, polyA- | GSM767851 |
| NHEK | cell line, polyA- | GSM765398 |
| NHLF | cell line, polyA- | GSM765389 |
| SKNSHRA | cell line, polyA- | GSM767845 |
| camera-type eye | tissue | ENCSR000AFO |
| cerebellum | tissue | ENCSR000AEW |
| diencephalon | tissue | ENCSR000AEX |
| frontal cortex | tissue | ENCSR000AEY |
| heart | tissue | ENCSR000AEZ |
| heart | tissue | ENCSR000AHH |
| liver | tissue | ENCSR000AEU |
| liver | tissue | ENCSR000AFB |
| lung | tissue | ENCSR000AFC |
| metanephros | tissue | ENCSR000AFA |
| mononuclear cell | tissue | ENCSR000CUT |
| occipital lobe | tissue | ENCSR000AFD |
| parietal lobe | tissue | ENCSR000AFE |
| skeletal muscle | tissue | ENCSR000AFF |
| skin of body | tissue | ENCSR000AFG |
| spinal cord | tissue | ENCSR000AFH |
| stomach | tissue | ENCSR000AFI |
| temporal lobe | tissue | ENCSR000AFJ |
| thyroid gland | tissue | ENCSR000AFK |
| tongue | tissue | ENCSR000AFL |
| umbilical cord | tissue | ENCSR000AFM |
| urinary bladder | tissue | ENCSR000AEV |
| uterus | tissue | ENCSR000AFN |
Source (cell line name or tissue type), Type of sample (tissue, polyA+ cell line, or polyA- cell line), and Accession code for all ENCODE data analyzed.]
Footnotes
The online version of the original article can be found under doi:10.1186/s13059-015-0690-5.
Contributor Information
Louise C. Laurent, Email: llaurent@ucsd.edu
Julia Salzman, Email: julia.salzman@stanford.edu.
Reference
- 1.Szabo L, Morey R, Palpant NJ, Wang PL, Afari N, Jiang C, et al. Statistically based splicing detection reveals neural enrichment and tissue-specific induction of circular RNA during human fetal development. Genome Biol. 2016;16:126. doi: 10.1186/s13059-015-0690-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]