Abstract
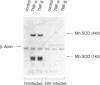
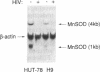
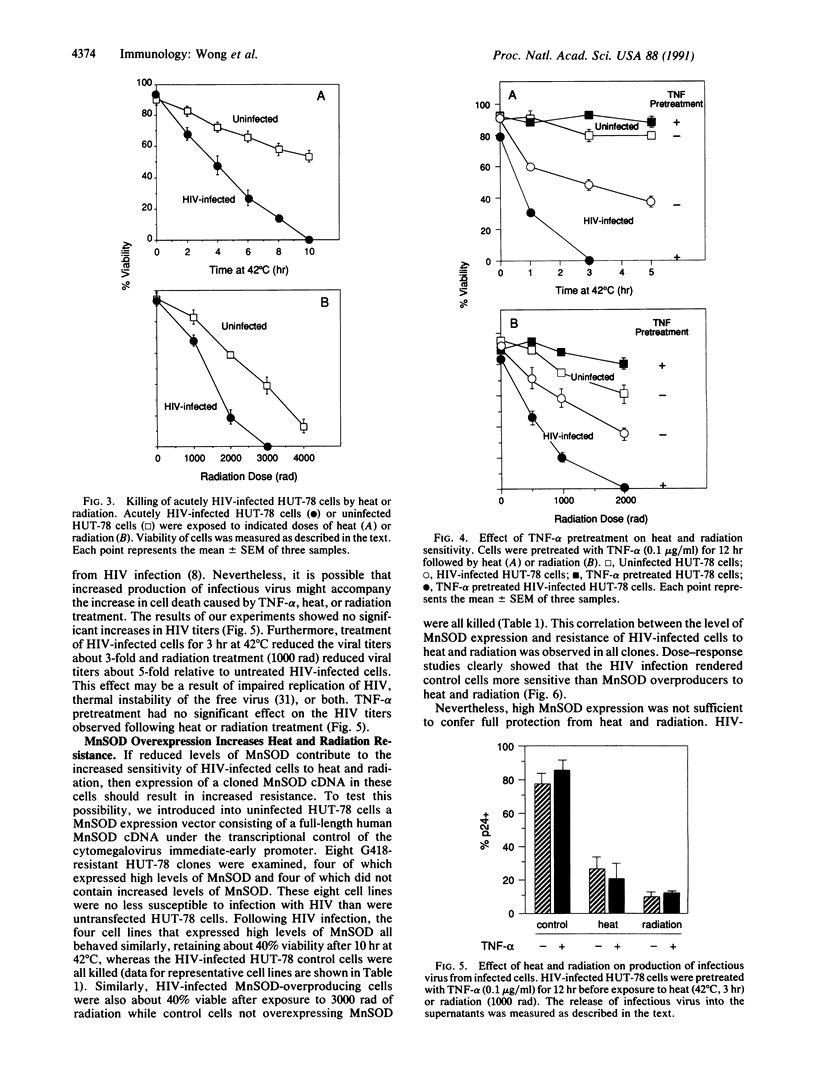
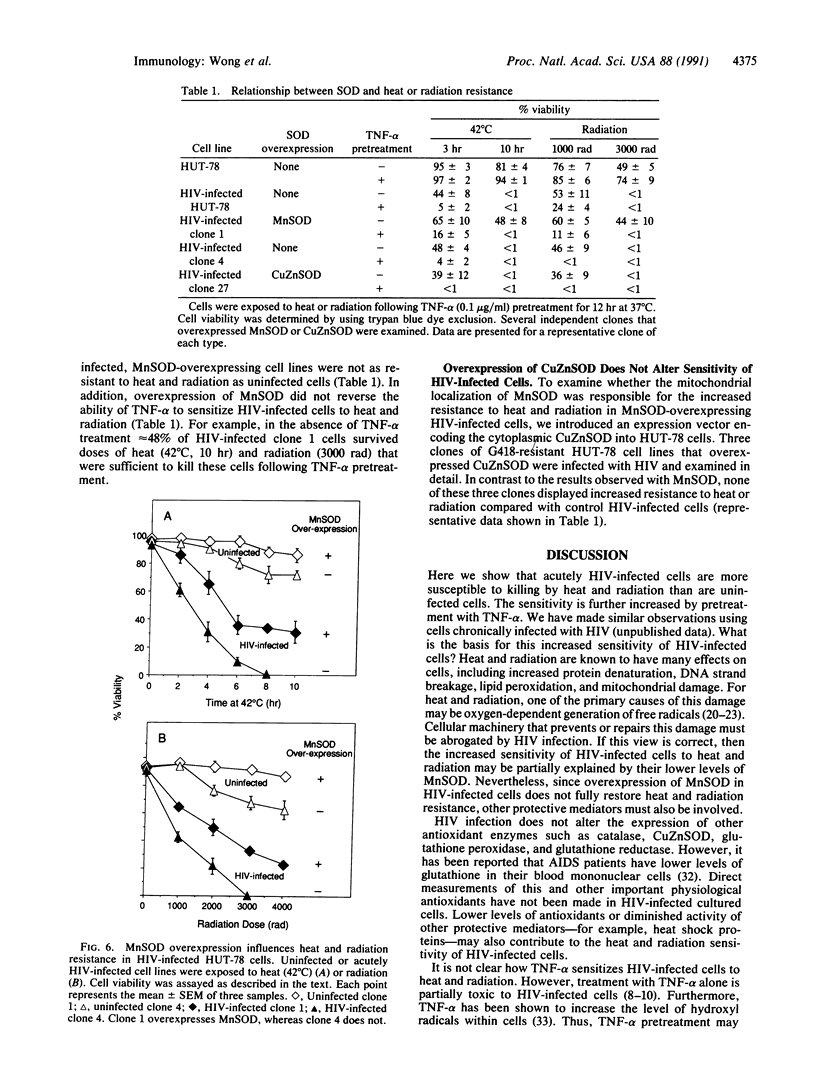
We report here that infection of the human T-cell line HUT-78 with human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) increases its sensitivity to heat and radiation toxicity. A possible explanation for this result may be the reduced expression of manganous superoxide dismutase (MnSOD) in HIV-infected cells compared to uninfected cells. Tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-alpha) further sensitizes HIV-infected cells but not uninfected cells to heat and radiation. This is consistent with the ability of TNF-alpha to induce the expression of MnSOD in uninfected but not in HIV-infected cells. HIV-infected HUT-78 cell lines engineered to overexpress MnSOD are more resistant to heat and radiation than HIV-infected cells that do not overexpress MnSOD. However, treatment with TNF-alpha still sensitizes these cells to heat and radiation.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aderka D., Novick D., Hahn T., Fischer D. G., Wallach D. Increase of vulnerability to lymphotoxin in cells infected by vesicular stomatitis virus and its further augmentation by interferon. Cell Immunol. 1985 May;92(2):218–225. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(85)90003-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carswell E. A., Old L. J., Kassel R. L., Green S., Fiore N., Williamson B. An endotoxin-induced serum factor that causes necrosis of tumors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Sep;72(9):3666–3670. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.9.3666. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cole A., Armour E. P. Ultrastructural study of mitochondrial damage in CHO cells exposed to hyperthermia. Radiat Res. 1988 Sep;115(3):421–435. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins T., Lapierre L. A., Fiers W., Strominger J. L., Pober J. S. Recombinant human tumor necrosis factor increases mRNA levels and surface expression of HLA-A,B antigens in vascular endothelial cells and dermal fibroblasts in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jan;83(2):446–450. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.2.446. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Creagan R., Tischfield J., Ricciuti F., Ruddle F. H. Chromosome assignments of genes in man using mouse-human somatic cell hybrids: mitochondrial superoxide dismutase (indophenol oxidase-B, tetrameric) to chromosome 6. Humangenetik. 1973 Dec 10;20(3):203–209. doi: 10.1007/BF00385731. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cross C. E., Halliwell B., Borish E. T., Pryor W. A., Ames B. N., Saul R. L., McCord J. M., Harman D. Oxygen radicals and human disease. Ann Intern Med. 1987 Oct;107(4):526–545. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-107-4-526. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dinarello C. A., Cannon J. G., Wolff S. M., Bernheim H. A., Beutler B., Cerami A., Figari I. S., Palladino M. A., Jr, O'Connor J. V. Tumor necrosis factor (cachectin) is an endogenous pyrogen and induces production of interleukin 1. J Exp Med. 1986 Jun 1;163(6):1433–1450. doi: 10.1084/jem.163.6.1433. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duerksen-Hughes P., Wold W. S., Gooding L. R. Adenovirus E1A renders infected cells sensitive to cytolysis by tumor necrosis factor. J Immunol. 1989 Dec 15;143(12):4193–4200. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eck H. P., Gmünder H., Hartmann M., Petzoldt D., Daniel V., Dröge W. Low concentrations of acid-soluble thiol (cysteine) in the blood plasma of HIV-1-infected patients. Biol Chem Hoppe Seyler. 1989 Feb;370(2):101–108. doi: 10.1515/bchm3.1989.370.1.101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goeddel D. V., Aggarwal B. B., Gray P. W., Leung D. W., Nedwin G. E., Palladino M. A., Patton J. S., Pennica D., Shepard H. M., Sugarman B. J. Tumor necrosis factors: gene structure and biological activities. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1986;51(Pt 1):597–609. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1986.051.01.072. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman C., Padmanabhan R., Howard B. H. High efficiency DNA-mediated transformation of primate cells. Science. 1983 Aug 5;221(4610):551–553. doi: 10.1126/science.6306768. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gregersen J. P., Hilfenhaus J., Lemp J. F., Jr Heat inactivation of human immunodeficiency virus type 2 (HIV-2). J Biol Stand. 1989 Oct;17(4):377–379. doi: 10.1016/s0092-1157(89)80009-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamamoto Y., Matsuyama T., Yamamoto N., Kobayashi N. Augmentation of cytotoxic effect of tumor necrosis factor on human immunodeficiency virus-infected cells by staurosporine, a potent protein kinase C inhibitor. Cancer Res. 1990 Sep 1;50(17):5287–5290. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jamieson D. Oxygen toxicity and reactive oxygen metabolites in mammals. Free Radic Biol Med. 1989;7(1):87–108. doi: 10.1016/0891-5849(89)90103-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koff W. C., Fann A. V. Human tumor necrosis factor-alpha kills herpesvirus-infected but not normal cells. Lymphokine Res. 1986 Summer;5(3):215–221. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuyama T., Hamamoto Y., Soma G., Mizuno D., Yamamoto N., Kobayashi N. Cytocidal effect of tumor necrosis factor on cells chronically infected with human immunodeficiency virus (HIV): enhancement of HIV replication. J Virol. 1989 Jun;63(6):2504–2509. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.6.2504-2509.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCord J. M., Fridovich I. The biology and pathology of oxygen radicals. Ann Intern Med. 1978 Jul;89(1):122–127. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-89-1-122. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McHugh T. M., Stites D. P., Casavant C. H., Carlson J. R., Yee J., McVay P. A., Busch M. P., Levy J. A. Evaluation of the indirect immunofluorescence assay as a confirmatory test for detecting antibodies to the human immunodeficiency virus. Diagn Immunol. 1986;4(5):233–240. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neta R., Oppenheim J. J., Douches S. D. Interdependence of the radioprotective effects of human recombinant interleukin 1 alpha, tumor necrosis factor alpha, granulocyte colony-stimulating factor, and murine recombinant granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor. J Immunol. 1988 Jan 1;140(1):108–111. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poli G., Kinter A., Justement J. S., Kehrl J. H., Bressler P., Stanley S., Fauci A. S. Tumor necrosis factor alpha functions in an autocrine manner in the induction of human immunodeficiency virus expression. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jan;87(2):782–785. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.2.782. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salet C., Passarella S., Quagliariello E. Effects of selective irradiation on mammalian mitochondria. Photochem Photobiol. 1987 Mar;45(3):433–438. doi: 10.1111/j.1751-1097.1987.tb05399.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherman L., Dafni N., Lieman-Hurwitz J., Groner Y. Nucleotide sequence and expression of human chromosome 21-encoded superoxide dismutase mRNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Sep;80(18):5465–5469. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.18.5465. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slørdal L., Muench M. O., Warren D. J., Moore M. A. Radioprotection by murine and human tumor-necrosis factor: dose-dependent effects on hematopoiesis in the mouse. Eur J Haematol. 1989 Nov;43(5):428–434. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0609.1989.tb00331.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slørdal L., Warren D. J., Moore M. A. Protective effects of tumor necrosis factor on murine hematopoiesis during cycle-specific cytotoxic chemotherapy. Cancer Res. 1990 Jul 15;50(14):4216–4220. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanley S. K., Bressler P. B., Poli G., Fauci A. S. Heat shock induction of HIV production from chronically infected promonocytic and T cell lines. J Immunol. 1990 Aug 15;145(4):1120–1126. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanley S. K., Folks T. M., Fauci A. S. Induction of expression of human immunodeficiency virus in a chronically infected promonocytic cell line by ultraviolet irradiation. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 1989 Aug;5(4):375–384. doi: 10.1089/aid.1989.5.375. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugarman B. J., Aggarwal B. B., Hass P. E., Figari I. S., Palladino M. A., Jr, Shepard H. M. Recombinant human tumor necrosis factor-alpha: effects on proliferation of normal and transformed cells in vitro. Science. 1985 Nov 22;230(4728):943–945. doi: 10.1126/science.3933111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsan M. F., White J. E., Santana T. A., Lee C. Y. Tracheal insufflation of tumor necrosis factor protects rats against oxygen toxicity. J Appl Physiol (1985) 1990 Mar;68(3):1211–1219. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1990.68.3.1211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallach D. Preparations of lymphotoxin induce resistance to their own cytotoxic effect. J Immunol. 1984 May;132(5):2464–2469. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weisiger R. A., Fridovich I. Superoxide dismutase. Organelle specificity. J Biol Chem. 1973 May 25;248(10):3582–3592. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong G. H., Elwell J. H., Oberley L. W., Goeddel D. V. Manganous superoxide dismutase is essential for cellular resistance to cytotoxicity of tumor necrosis factor. Cell. 1989 Sep 8;58(5):923–931. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90944-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong G. H., Goeddel D. V. Induction of manganous superoxide dismutase by tumor necrosis factor: possible protective mechanism. Science. 1988 Nov 11;242(4880):941–944. doi: 10.1126/science.3263703. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong G. H., Goeddel D. V. Tumour necrosis factors alpha and beta inhibit virus replication and synergize with interferons. 1986 Oct 30-Nov 5Nature. 323(6091):819–822. doi: 10.1038/323819a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong G. H., Krowka J. F., Stites D. P., Goeddel D. V. In vitro anti-human immunodeficiency virus activities of tumor necrosis factor-alpha and interferon-gamma. J Immunol. 1988 Jan 1;140(1):120–124. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamauchi N., Kuriyama H., Watanabe N., Neda H., Maeda M., Niitsu Y. Intracellular hydroxyl radical production induced by recombinant human tumor necrosis factor and its implication in the killing of tumor cells in vitro. Cancer Res. 1989 Apr 1;49(7):1671–1675. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]