Abstract
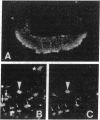
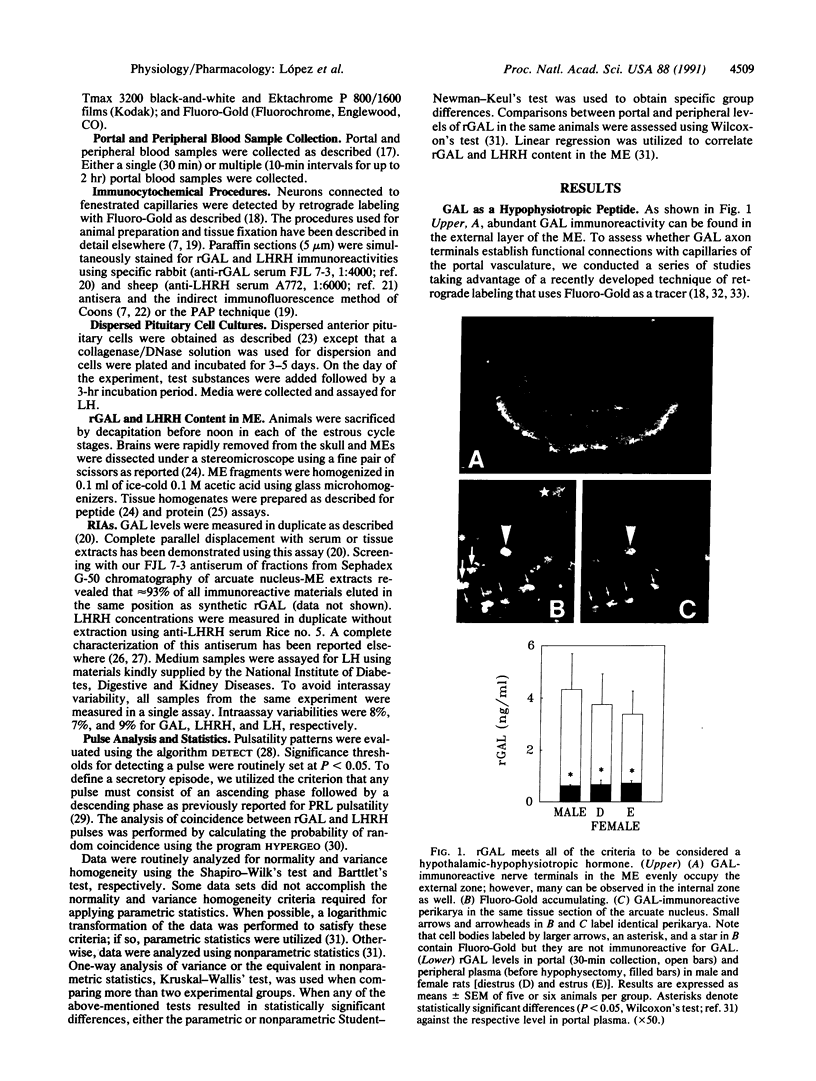
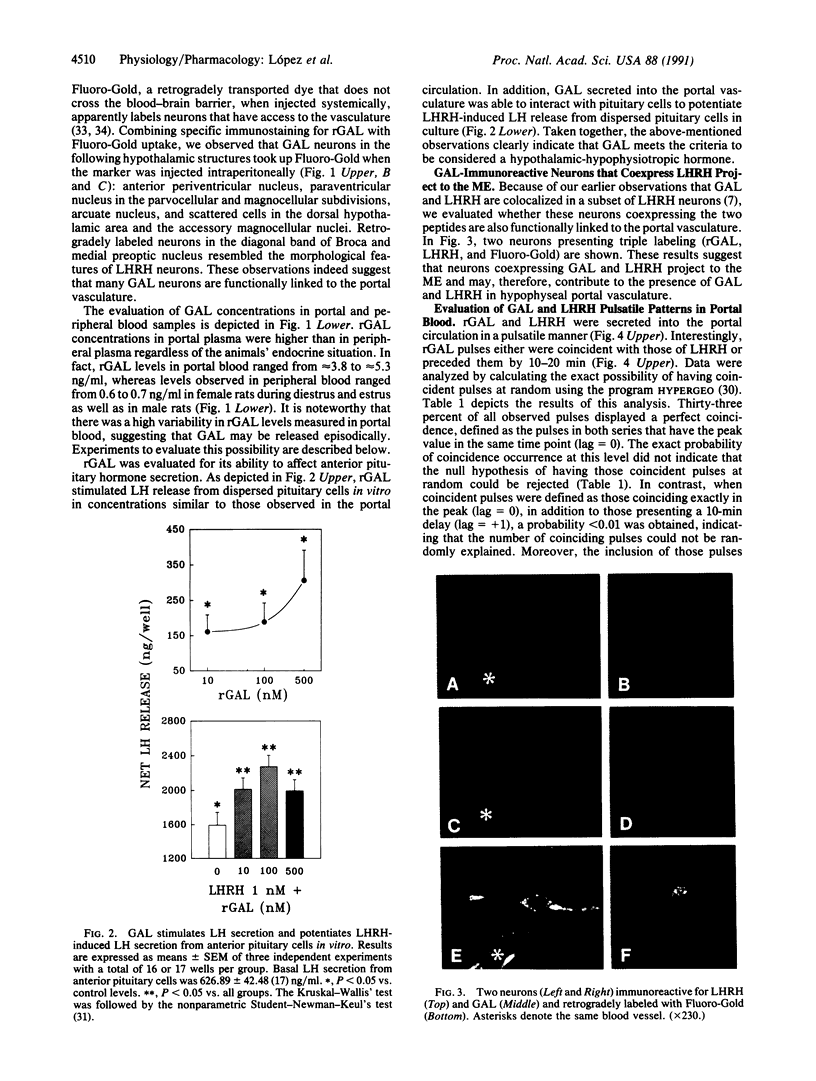
Galanin (GAL) is widely distributed in the peripheral and the central nervous systems. In the brain, the highest GAL concentrations are observed within the hypothalamus and, particularly, in nerve terminals of the median eminence. This location, as well as GAL actions on prolactin, growth hormone, luteinizing hormone (LH), and LH-releasing hormone (LHRH) secretion, suggest the possibility that GAL may act as a putative hypothalamic-hypophysiotropic hormone. To establish this, GAL and LHRH levels were measured in hypophyseal portal plasma samples using specific radioimmunoassays. Rat galanin (rGAL) concentrations in portal blood were approximately 7-fold higher than those observed in peripheral plasma in male and female (estrus, diestrus) rats, indicating an active secretory process of rGAL into the portal vasculature. Frequent (10 min) sampling revealed that rGAL and LHRH were secreted into the portal circulation in a pulsatile manner with a pulse frequency of one pulse per hour. Interestingly, both hormone series depicted a high degree of coincident episodes. In fact, the probability of random coincidence, calculated by the algorithm HYPERGEO, was less than 0.01. Moreover, the retrograde tracer Fluoro-Gold, when given systemically, was taken up by GAL neurons in the hypothalamus, including a subset of neurons expressing rGAL and LHRH, strengthening the notion of the existence of a GAL neuronal system connected to the hypophyseal portal circulation. These observations reinforce the concept that GAL regulates pituitary hormone secretion. To analyze this in further detail, the effects of rGAL on LH secretion were evaluated under basal and stimulated conditions. rGAL induced a small but dose-dependent increase in LH secretion from cultured, dispersed pituitary cells. Interestingly, rGAL enhanced the ability of LHRH to stimulate LH release. The tight link between GAL and LHRH neuronal systems is strengthened by the observation that during the estrous cycle of the rat, rGAL and LHRH contents in the median eminence show an identical profile (r = 1.00). These data indicate that GAL should be considered as a hypothalamic-hypophysiotropic hormone and as an important neuromodulator of LHRH secretion and action. The colocalization and cosecretion of GAL and LHRH and the cooperative action at the level of the anterior pituitary afford important evidence for the functional significance of coexistence of neurotransmitters in neurons of the central nervous system.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Chiappa S. A., Fink G. Hypothalamic luteinizing hormone releasing factor and corticotrophin releasing activity in relation to pituitary and plasma hormone levels in male and female rats. J Endocrinol. 1977 Feb;72(2):195–210. doi: 10.1677/joe.0.0720195. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ching M. Correlative surges of LHRH, LH and FSH in pituitary stalk plasma and systemic plasma of rat during proestrus. Effect of anesthetics. Neuroendocrinology. 1982 Apr;34(4):279–285. doi: 10.1159/000123313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Culler M. D., Kenjo T., Obara N., Arimura A. Stimulation of pituitary cAMP accumulation by human pancreatic GH-releasing factor-(1-44). Am J Physiol. 1984 Nov;247(5 Pt 1):E609–E615. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1984.247.5.E609. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gabriel S. M., MacGarvey U. M., Koenig J. I., Swartz K. J., Martin J. B., Beal M. F. Characterization of galanin-like immunoreactivity in the rat brain: effects of neonatal glutamate treatment. Neurosci Lett. 1988 Apr 22;87(1-2):114–121. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(88)90155-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gabriel S. M., Milbury C. M., Nathanson J. A., Martin J. B. Galanin stimulates rat pituitary growth hormone secretion in vitro. Life Sci. 1988;42(20):1981–1986. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(88)90497-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hedger M. P., Robertson D. M., Browne C. A., de Kretser D. M. The isolation and measurement of luteinizing hormone-releasing hormone (LHRH) from the rat testis. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 1985 Sep;42(2):163–174. doi: 10.1016/0303-7207(85)90104-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan L. M., Gabriel S. M., Koenig J. I., Sunday M. E., Spindel E. R., Martin J. B., Chin W. W. Galanin is an estrogen-inducible, secretory product of the rat anterior pituitary. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Oct;85(19):7408–7412. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.19.7408. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan L. M., Spindel E. R., Isselbacher K. J., Chin W. W. Tissue-specific expression of the rat galanin gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Feb;85(4):1065–1069. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.4.1065. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koshiyama H., Kato Y., Inoue T., Murakami Y., Ishikawa Y., Yanaihara N., Imura H. Central galanin stimulates pituitary prolactin secretion in rats: possible involvement of hypothalamic vasoactive intestinal polypeptide. Neurosci Lett. 1987 Mar 20;75(1):49–54. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(87)90073-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lopez F. J., Negro-Vilar A. Galanin stimulates luteinizing hormone-releasing hormone secretion from arcuate nucleus-median eminence fragments in vitro: involvement of an alpha-adrenergic mechanism. Endocrinology. 1990 Nov;127(5):2431–2436. doi: 10.1210/endo-127-5-2431. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- López F. J., Dominguez J. R., Sánchez-Criado J. E., Negro-Vilar A. Distinct pulsatile prolactin secretory patterns during the estrous cycle: possible encoding for diverse physiological responses. Endocrinology. 1989 Jan;124(1):536–542. doi: 10.1210/endo-124-1-536. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- López F. J., Meade E. H., Jr, Negro-Vilar A. Development and characterization of a specific and sensitive radioimmunoassay for rat galanin: measurement in brain tissue, hypophyseal portal and peripheral serum. Brain Res Bull. 1990 Mar;24(3):395–399. doi: 10.1016/0361-9230(90)90095-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merchenthaler I., Lopez F. J., Negro-Vilar A. Colocalization of galanin and luteinizing hormone-releasing hormone in a subset of preoptic hypothalamic neurons: anatomical and functional correlates. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Aug;87(16):6326–6330. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.16.6326. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merchenthaler I., Vigh S., Petrusz P., Schally A. V. Immunocytochemical localization of corticotropin-releasing factor (CRF) in the rat brain. Am J Anat. 1982 Dec;165(4):385–396. doi: 10.1002/aja.1001650404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murakami Y., Kato Y., Shimatsu A., Koshiyama H., Hattori N., Yanaihara N., Imura H. Possible mechanisms involved in growth hormone secretion induced by galanin in the rat. Endocrinology. 1989 Mar;124(3):1224–1229. doi: 10.1210/endo-124-3-1224. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Negro-Vilar A., Ojeda S. R., McCann S. M. Catecholaminergic modulation of luteinizing hormone-releasing hormone release by median eminence terminals in vitro. Endocrinology. 1979 Jun;104(6):1749–1757. doi: 10.1210/endo-104-6-1749. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oerter K. E., Guardabasso V., Rodbard D. Detection and characterization of peaks and estimation of instantaneous secretory rate for episodic pulsatile hormone secretion. Comput Biomed Res. 1986 Apr;19(2):170–191. doi: 10.1016/0010-4809(86)90014-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ottlecz A., Samson W. K., McCann S. M. Galanin: evidence for a hypothalamic site of action to release growth hormone. Peptides. 1986 Jan-Feb;7(1):51–53. doi: 10.1016/0196-9781(86)90060-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ottlecz A., Snyder G. D., McCann S. M. Regulatory role of galanin in control of hypothalamic-anterior pituitary function. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Dec;85(24):9861–9865. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.24.9861. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rance N., Wise P. M., Selmanoff M. K., Barraclough C. A. Catecholamine turnover rates in discrete hypothalamic areas and associated changes in median eminence luteinizing hormone-releasing hormone and serum gonadotropins on proestrus and diestrous day 1. Endocrinology. 1981 May;108(5):1795–1802. doi: 10.1210/endo-108-5-1795. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rice G. E., Cho G., Barnea A. Aging-related reduced release of LH-releasing hormone from hypothalamic granules. Neurobiol Aging. 1983 Fall;4(3):217–222. doi: 10.1016/0197-4580(83)90023-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rökaeus A., Melander T., Hökfelt T., Lundberg J. M., Tatemoto K., Carlquist M., Mutt V. A galanin-like peptide in the central nervous system and intestine of the rat. Neurosci Lett. 1984 Jun 15;47(2):161–166. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(84)90423-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sahu A., Crowley W. R., Tatemoto K., Balasubramaniam A., Kalra S. P. Effects of neuropeptide Y, NPY analog (norleucine4-NPY), galanin and neuropeptide K on LH release in ovariectomized (ovx) and ovx estrogen, progesterone-treated rats. Peptides. 1987 Sep-Oct;8(5):921–926. doi: 10.1016/0196-9781(87)90081-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmued L. C., Fallon J. H. Fluoro-Gold: a new fluorescent retrograde axonal tracer with numerous unique properties. Brain Res. 1986 Jul 2;377(1):147–154. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(86)91199-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Servin A. L., Amiranoff B., Rouyer-Fessard C., Tatemoto K., Laburthe M. Identification and molecular characterization of galanin receptor sites in rat brain. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1987 Apr 14;144(1):298–306. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(87)80510-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skofitsch G., Jacobowitz D. M. Immunohistochemical mapping of galanin-like neurons in the rat central nervous system. Peptides. 1985 May-Jun;6(3):509–546. doi: 10.1016/0196-9781(85)90118-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tatemoto K., Rökaeus A., Jörnvall H., McDonald T. J., Mutt V. Galanin - a novel biologically active peptide from porcine intestine. FEBS Lett. 1983 Nov 28;164(1):124–128. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(83)80033-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallenstein S., Zucker C. L., Fleiss J. L. Some statistical methods useful in circulation research. Circ Res. 1980 Jul;47(1):1–9. doi: 10.1161/01.res.47.1.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]