Abstract
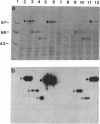
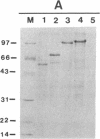
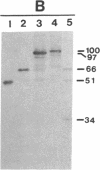
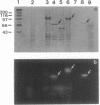
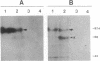
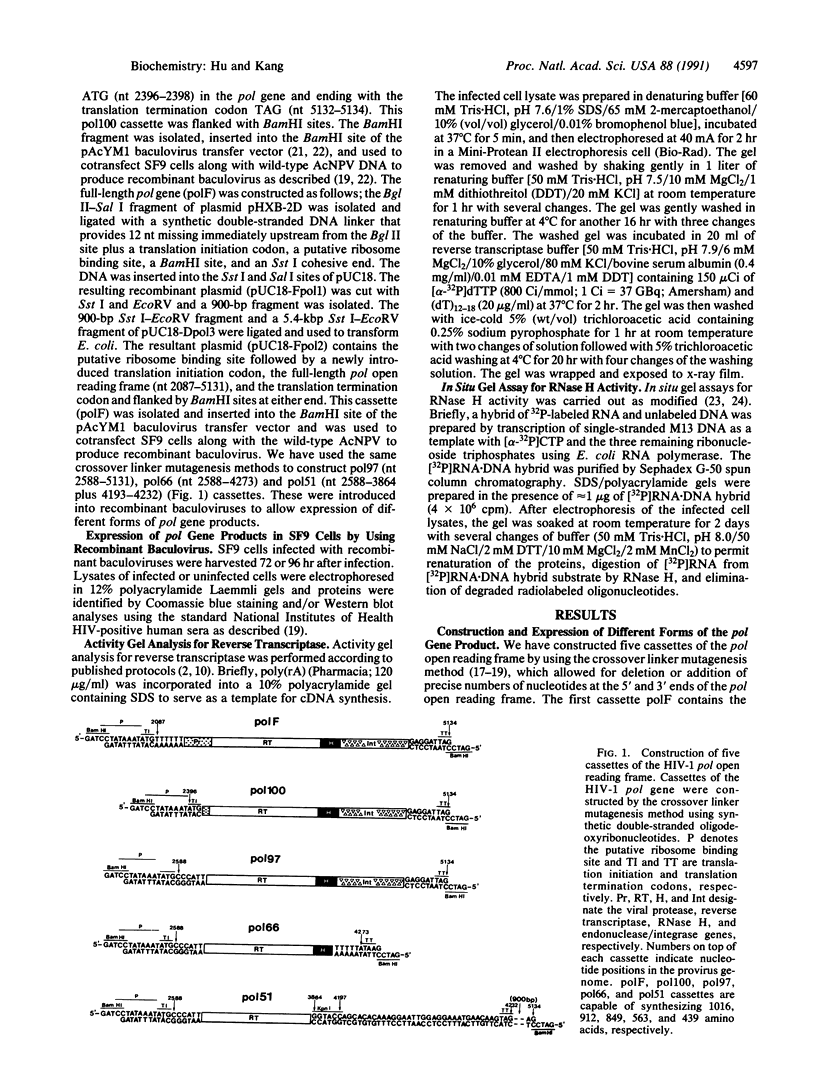
Five cassettes of the pol gene of human immunodeficiency virus 1 were constructed and inserted under the control of the polyhedrin gene promoter of Autographa californica nuclear polyhedrosis virus by homologous recombination. The first cassette polF contains the full-length pol open reading frame; the second cassette pol100 starts with the first AUG codon of the pol gene and deletes 103 amino acids from the amino terminus of the pol gene product; the third cassette pol97 deletes the entire protease coding sequence; the fourth cassette pol66 deletes both the protease and endonuclease/integrase coding sequences; and the fifth cassette pol51 contains the reverse transcriptase coding sequences plus 39 3'-terminal nucleotides of the RNase H coding sequences. We have expressed these five forms of the pol gene in Spodoptera frugiperda SF9 cells and have analyzed for both reverse transcriptase and RNase H activities. The polF construct expressed several processed forms, 66 kDa, 51 kDa, and 34 kDa proteins, that were detected only by Western blot. In contrast, pol100, pol97, pol66, and pol51 products were expressed at high levels and were readily detectable in gels by staining. The levels of expression of these four products were estimated to be greater than 150 mg/liter of culture (5 x 10(8) cells). Activity gel analyses showed that the pol100, pol97, pol66, and pol51 products possess reverse transcriptase activity; however, only pol97 and pol66 have RNase H activity. Our results demonstrate that many forms, including partially cleaved forms of human immunodeficiency virus 1 pol gene products, possess reverse transcriptase activity but only certain forms have RNase H activity.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Chandra A., Gerber T., Chandra P. Biochemical heterogeneity of reverse transcriptase purified from the AIDS virus, HTLV-III. FEBS Lett. 1986 Mar 3;197(1-2):84–88. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(86)80303-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farmerie W. G., Loeb D. D., Casavant N. C., Hutchison C. A., 3rd, Edgell M. H., Swanstrom R. Expression and processing of the AIDS virus reverse transcriptase in Escherichia coli. Science. 1987 Apr 17;236(4799):305–308. doi: 10.1126/science.2436298. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flexner C., Broyles S. S., Earl P., Chakrabarti S., Moss B. Characterization of human immunodeficiency virus gag/pol gene products expressed by recombinant vaccinia viruses. Virology. 1988 Oct;166(2):339–349. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(88)90504-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garson K., Percival H., Kang C. Y. The N-terminal env-derived amino acids of v-rel are required for full transforming activity. Virology. 1990 Jul;177(1):106–115. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(90)90464-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansen J., Schulze T., Mellert W., Moelling K. Identification and characterization of HIV-specific RNase H by monoclonal antibody. EMBO J. 1988 Jan;7(1):239–243. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02805.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hizi A., McGill C., Hughes S. H. Expression of soluble, enzymatically active, human immunodeficiency virus reverse transcriptase in Escherichia coli and analysis of mutants. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Feb;85(4):1218–1222. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.4.1218. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kang C. Y. Baculovirus vectors for expression of foreign genes. Adv Virus Res. 1988;35:177–192. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3527(08)60711-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larder B. A., Purifoy D. J., Powell K. L., Darby G. Site-specific mutagenesis of AIDS virus reverse transcriptase. 1987 Jun 25-Jul 1Nature. 327(6124):716–717. doi: 10.1038/327716a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leuthardt A., Le Grice S. F. Biosynthesis and analysis of a genetically engineered HIV-1 reverse transcriptase/endonuclease polyprotein in Escherichia coli. Gene. 1988 Aug 15;68(1):35–42. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90596-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lightfoote M. M., Coligan J. E., Folks T. M., Fauci A. S., Martin M. A., Venkatesan S. Structural characterization of reverse transcriptase and endonuclease polypeptides of the acquired immunodeficiency syndrome retrovirus. J Virol. 1986 Nov;60(2):771–775. doi: 10.1128/jvi.60.2.771-775.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lori F., Scovassi A. I., Zella D., Achilli G., Cattaneo E., Casoli C., Bertazzoni U. Enzymatically active forms of reverse transcriptase of the human immunodeficiency virus. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 1988 Oct;4(5):393–398. doi: 10.1089/aid.1988.4.393. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowe D. M., Aitken A., Bradley C., Darby G. K., Larder B. A., Powell K. L., Purifoy D. J., Tisdale M., Stammers D. K. HIV-1 reverse transcriptase: crystallization and analysis of domain structure by limited proteolysis. Biochemistry. 1988 Dec 13;27(25):8884–8889. doi: 10.1021/bi00425a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luo L., Li Y., Kang C. Y. Expression of gag precursor protein and secretion of virus-like gag particles of HIV-2 from recombinant baculovirus-infected insect cells. Virology. 1990 Dec;179(2):874–880. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(90)90159-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuura Y., Possee R. D., Overton H. A., Bishop D. H. Baculovirus expression vectors: the requirements for high level expression of proteins, including glycoproteins. J Gen Virol. 1987 May;68(Pt 5):1233–1250. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-68-5-1233. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizrahi V. Analysis of the ribonuclease H activity of HIV-1 reverse transcriptase using RNA.DNA hybrid substrates derived from the gag region of HIV-1. Biochemistry. 1989 Nov 14;28(23):9088–9094. doi: 10.1021/bi00449a020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller B., Restle T., Weiss S., Gautel M., Sczakiel G., Goody R. S. Co-expression of the subunits of the heterodimer of HIV-1 reverse transcriptase in Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1989 Aug 25;264(24):13975–13978. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prasad V. R., Goff S. P. Linker insertion mutagenesis of the human immunodeficiency virus reverse transcriptase expressed in bacteria: definition of the minimal polymerase domain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 May;86(9):3104–3108. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.9.3104. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ratner L., Haseltine W., Patarca R., Livak K. J., Starcich B., Josephs S. F., Doran E. R., Rafalski J. A., Whitehorn E. A., Baumeister K. Complete nucleotide sequence of the AIDS virus, HTLV-III. Nature. 1985 Jan 24;313(6000):277–284. doi: 10.1038/313277a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Restle T., Müller B., Goody R. S. Dimerization of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 reverse transcriptase. A target for chemotherapeutic intervention. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jun 5;265(16):8986–8988. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rucheton M., Lelay M. N., Jeanteur P. Evidence from direct visualization after denaturing gel electrophoresis that RNase H is associated with MSV-MuLV reverse transcripase. Virology. 1979 Aug;97(1):221–223. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(79)90392-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith G. E., Fraser M. J., Summers M. D. Molecular Engineering of the Autographa californica Nuclear Polyhedrosis Virus Genome: Deletion Mutations Within the Polyhedrin Gene. J Virol. 1983 May;46(2):584–593. doi: 10.1128/jvi.46.2.584-593.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Starnes M. C., Cheng Y. C. Human immunodeficiency virus reverse transcriptase-associated RNase H activity. J Biol Chem. 1989 Apr 25;264(12):7073–7077. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Starnes M. C., Gao W. Y., Ting R. Y., Cheng Y. C. Enzyme activity gel analysis of human immunodeficiency virus reverse transcriptase. J Biol Chem. 1988 Apr 15;263(11):5132–5134. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sung W. L., Zahab D. M., MacDonald C. A., Tam C. S. Synthesis of mutant parathyroid hormone genes via site-specific recombination directed by crossover linkers. Gene. 1986;47(2-3):261–267. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(86)90069-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanese N., Goff S. P. Domain structure of the Moloney murine leukemia virus reverse transcriptase: mutational analysis and separate expression of the DNA polymerase and RNase H activities. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Mar;85(6):1777–1781. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.6.1777. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanese N., Roth M. J., Goff S. P. Analysis of retroviral pol gene products with antisera raised against fusion proteins produced in Escherichia coli. J Virol. 1986 Aug;59(2):328–340. doi: 10.1128/jvi.59.2.328-340.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanese N., Sodroski J., Haseltine W. A., Goff S. P. Expression of reverse transcriptase activity of human T-lymphotropic virus type III (HTLV-III/LAV) in Escherichia coli. J Virol. 1986 Sep;59(3):743–745. doi: 10.1128/jvi.59.3.743-745.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tisdale M., Ertl P., Larder B. A., Purifoy D. J., Darby G., Powell K. L. Characterization of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 reverse transcriptase by using monoclonal antibodies: role of the C terminus in antibody reactivity and enzyme function. J Virol. 1988 Oct;62(10):3662–3667. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.10.3662-3667.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]