Abstract
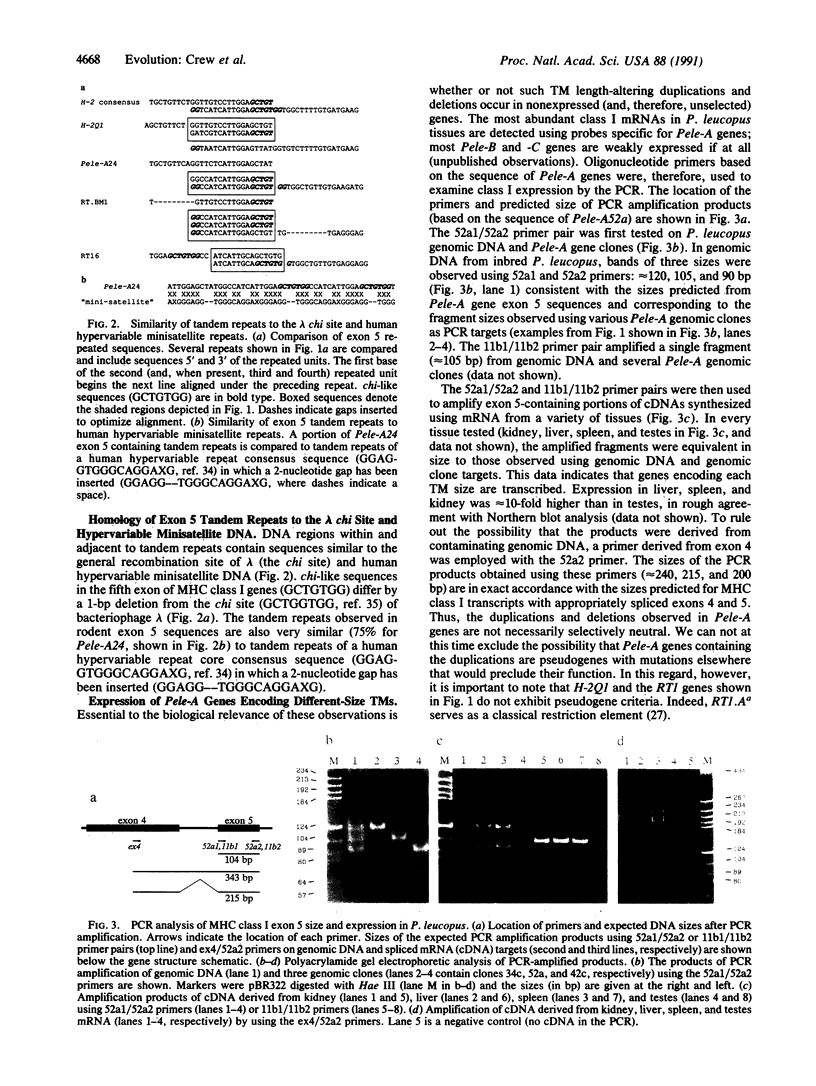
The fifth exons of major histocompatibility complex (MHC) class I genes encode a transmembrane domain (TM) that is largely responsible for class I antigen cell-surface expression usually through conventional hydrophobic amino acid-membrane interactions or, less often, through phosphatidylinositol linkage. In this report we show that Peromyscus leucopus, a Cricetidae rodent, has MHC class I genes (Pele-A genes) encoding three distinct sizes of TMs. Increases in TM lengths were due to tandem duplications of sequences similar to human hypervariable minisatellite repeats and the lambda chi site. We discerned remnants of a similar duplication event in comparable rodent and primate MHC class I genes. Furthermore, several duplications and deletions appear to have occurred independently in H-2, RT1, Pele-A, and ChLA genes in near-identical positions. Accumulated data suggests that sequences in the fifth exon of MHC class I genes may, therefore, constitute a mutational or recombinational hot spot that is mediated by minisatellite- and chi-like sequences imbedded within the coding region. The MHC class I genes may thus have recruited "selfish" DNA in their evolution to encode cell surface proteins. Expression of Pele-A genes was examined by the polymerase chain reaction (PCR) using oligonucleotide primers specific for exon 4 and 5 sequences. The PCR product sizes indicated that genes encoding each TM domain length are ubiquitously transcribed.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brorson K. A., Hunt S. W., 3rd, Hunkapiller T., Sun Y. H., Cheroutre H., Nickerson D. A., Hood L. Comparison of exon 5 sequences from 35 class I genes of the BALB/c mouse. J Exp Med. 1989 Dec 1;170(6):1837–1858. doi: 10.1084/jem.170.6.1837. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crew M. D., Filipowsky M. E., Zeller E. C., Smith G. S., Walford R. L. Major histocompatibility complex class I genes of Peromyscus leucopus. Immunogenetics. 1990;32(6):371–379. doi: 10.1007/BF00241630. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crew M. D., Smith G. S., Zeller E. C., Walford R. L. Polymorphism in the major histocompatibility complex class II genes of Peromyscus leucopus. Immunogenetics. 1989;30(3):214–217. doi: 10.1007/BF02421209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devereux J., Haeberli P., Smithies O. A comprehensive set of sequence analysis programs for the VAX. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 11;12(1 Pt 1):387–395. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.1part1.387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Figueroa F., Günther E., Klein J. MHC polymorphism pre-dating speciation. Nature. 1988 Sep 15;335(6187):265–267. doi: 10.1038/335265a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geraghty D. E., Koller B. H., Orr H. T. A human major histocompatibility complex class I gene that encodes a protein with a shortened cytoplasmic segment. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Dec;84(24):9145–9149. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.24.9145. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geraghty D. E., Wei X. H., Orr H. T., Koller B. H. Human leukocyte antigen F (HLA-F). An expressed HLA gene composed of a class I coding sequence linked to a novel transcribed repetitive element. J Exp Med. 1990 Jan 1;171(1):1–18. doi: 10.1084/jem.171.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gubler U., Hoffman B. J. A simple and very efficient method for generating cDNA libraries. Gene. 1983 Nov;25(2-3):263–269. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(83)90230-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guillemot F., Billault A., Pourquié O., Béhar G., Chaussé A. M., Zoorob R., Kreibich G., Auffray C. A molecular map of the chicken major histocompatibility complex: the class II beta genes are closely linked to the class I genes and the nucleolar organizer. EMBO J. 1988 Sep;7(9):2775–2785. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03132.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes A. L., Nei M. Pattern of nucleotide substitution at major histocompatibility complex class I loci reveals overdominant selection. Nature. 1988 Sep 8;335(6186):167–170. doi: 10.1038/335167a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jeffreys A. J., Royle N. J., Wilson V., Wong Z. Spontaneous mutation rates to new length alleles at tandem-repetitive hypervariable loci in human DNA. Nature. 1988 Mar 17;332(6161):278–281. doi: 10.1038/332278a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jeffreys A. J., Wilson V., Thein S. L. Hypervariable 'minisatellite' regions in human DNA. Nature. 1985 Mar 7;314(6006):67–73. doi: 10.1038/314067a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kastern W. Characterization of two class I major histocompatibility rat cDNA clones, one of which contains a premature termination codon. Gene. 1985;34(2-3):227–233. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90131-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kindt T. J., Singer D. S. Class I major histocompatibility complex genes in vertebrate species: what is the common denominator? Immunol Res. 1987;6(1-2):57–66. doi: 10.1007/BF02918104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein J., Benoist C., David C. S., Demant P., Lindahl K. F., Flaherty L., Flavell R. A., Hämmerling U., Hood L. E., Hunt S. W., 3rd Revised nomenclature of mouse H-2 genes. Immunogenetics. 1990;32(3):147–149. doi: 10.1007/BF02114967. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kroemer G., Zoorob R., Auffray C. Structure and expression of a chicken MHC class I gene. Immunogenetics. 1990;31(5-6):405–409. doi: 10.1007/BF02115020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuhner M. K., Goodenow R. S. DNA sequences of mouse H-2 and Qa genes. Immunogenetics. 1989;30(6):458–464. doi: 10.1007/BF02421178. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawlor D. A., Ward F. E., Ennis P. D., Jackson A. P., Parham P. HLA-A and B polymorphisms predate the divergence of humans and chimpanzees. Nature. 1988 Sep 15;335(6187):268–271. doi: 10.1038/335268a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawlor D. A., Zemmour J., Ennis P. D., Parham P. Evolution of class-I MHC genes and proteins: from natural selection to thymic selection. Annu Rev Immunol. 1990;8:23–63. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.08.040190.000323. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maloy W. L. Comparison of the primary structure of class I molecules. Immunol Res. 1987;6(1-2):11–29. doi: 10.1007/BF02918101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mauxion F., Sobczak J., Kress M. Characterization of five distinct cDNA clones encoding for class I RT1 antigens. Immunogenetics. 1989;29(6):397–401. doi: 10.1007/BF00375868. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayer W. E., Jonker M., Klein D., Ivanyi P., van Seventer G., Klein J. Nucleotide sequences of chimpanzee MHC class I alleles: evidence for trans-species mode of evolution. EMBO J. 1988 Sep;7(9):2765–2774. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03131.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGuire K. L., Duncan W. R., Tucker P. W. Structure of a class I gene from Syrian hamster. J Immunol. 1986 Jul 1;137(1):366–372. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nathenson S. G., Geliebter J., Pfaffenbach G. M., Zeff R. A. Murine major histocompatibility complex class-I mutants: molecular analysis and structure-function implications. Annu Rev Immunol. 1986;4:471–502. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.04.040186.002351. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parham P., Lawlor D. A. Evolution of class I major histocompatibility complex genes and molecules in humans and apes. Hum Immunol. 1991 Feb;30(2):119–128. doi: 10.1016/0198-8859(91)90080-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parham P., Lawlor D. A., Lomen C. E., Ennis P. D. Diversity and diversification of HLA-A,B,C alleles. J Immunol. 1989 Jun 1;142(11):3937–3950. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker K. E., Carter C. A., Fabre J. W. A rat class I cDNA clone with an Alu-like sequence and mapping to two genes in RT1.C/E. Immunogenetics. 1990;31(3):211–214. doi: 10.1007/BF00211559. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ponticelli A. S., Schultz D. W., Taylor A. F., Smith G. R. Chi-dependent DNA strand cleavage by RecBC enzyme. Cell. 1985 May;41(1):145–151. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90069-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rada C., Lorenzi R., Powis S. J., van den Bogaerde J., Parham P., Howard J. C. Concerted evolution of class I genes in the major histocompatibility complex of murine rodents. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Mar;87(6):2167–2171. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.6.2167. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogers J. H. Mouse histocompatibility-related genes are not conserved in other mammals. EMBO J. 1985 Mar;4(3):749–753. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03692.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinmetz M., Stephan D., Fischer Lindahl K. Gene organization and recombinational hotspots in the murine major histocompatibility complex. Cell. 1986 Mar 28;44(6):895–904. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90012-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephan D., Sun H., Lindahl K. F., Meyer E., Hämmerling G., Hood L., Steinmetz M. Organization and evolution of D region class I genes in the mouse major histocompatibility complex. J Exp Med. 1986 May 1;163(5):1227–1244. doi: 10.1084/jem.163.5.1227. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stroynowski I. Molecules related to class-I major histocompatibility complex antigens. Annu Rev Immunol. 1990;8:501–530. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.08.040190.002441. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahls W. P., Wallace L. J., Moore P. D. Hypervariable minisatellite DNA is a hotspot for homologous recombination in human cells. Cell. 1990 Jan 12;60(1):95–103. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90719-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watts S., Wheeler C., Morse R., Goodenow R. S. Amino acid comparison of the class I antigens of mouse major histocompatibility complex. Immunogenetics. 1989;30(5):390–392. doi: 10.1007/BF02425281. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wheeler C. J., Maloney D., Fogel S., Goodenow R. S. Microconversion between murine H-2 genes integrated into yeast. Nature. 1990 Sep 13;347(6289):192–194. doi: 10.1038/347192a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zinkernagel R. M., Doherty P. C. MHC-restricted cytotoxic T cells: studies on the biological role of polymorphic major transplantation antigens determining T-cell restriction-specificity, function, and responsiveness. Adv Immunol. 1979;27:51–177. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60262-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]





