Abstract
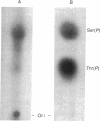
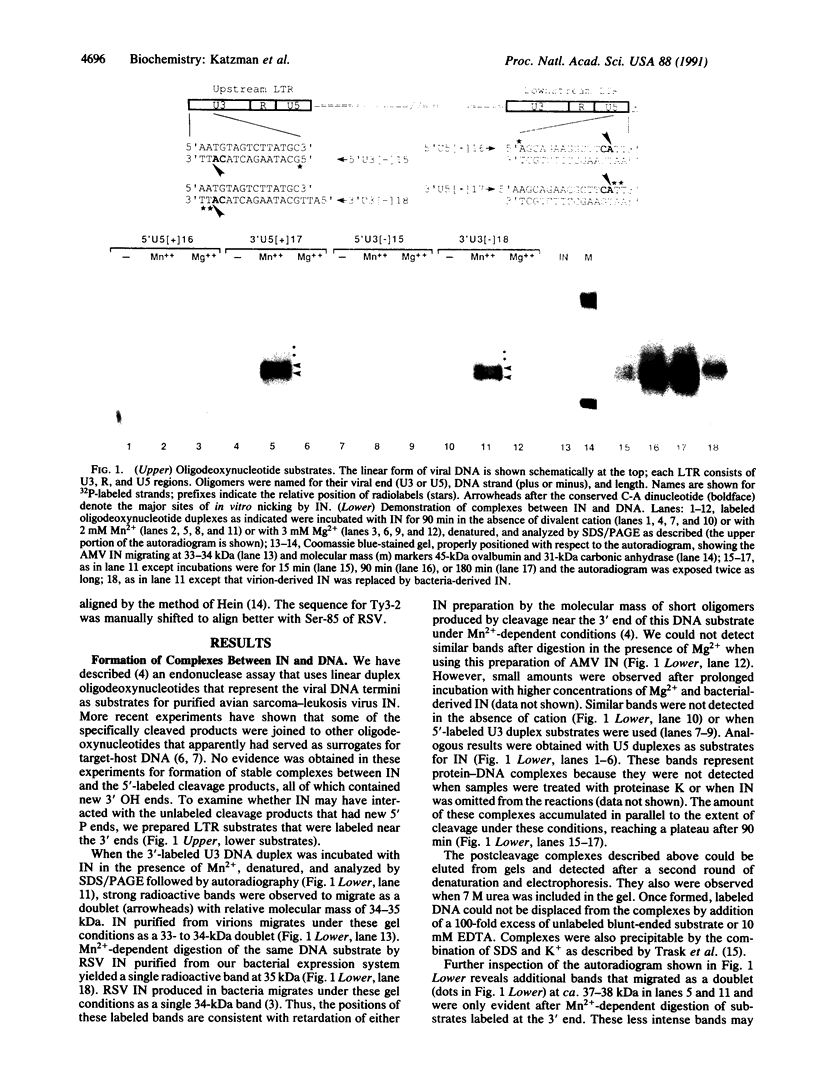
Purified retroviral integrase (IN) from avian sarcoma-leukosis viruses can appropriately process the termini of linear viral DNA, cleave host DNA in a sequence-independent manner, and catalyze integrative recombination; an exogenous source of energy is not required for these reactions. Using DNA substrates containing radioactive phosphate groups, we demonstrate that IN becomes covalently joined to the new 5' phosphate ends of DNA produced at sites of cleavage. Most of the phosphodiester linkages between IN and DNA involve serine, but some involve threonine. Computer-assisted alignment of 80 retroviral and retrotransposon IN sequences identified one serine that is conserved in all of these proteins and three less-conserved threonine residues. These results identify candidate active-site residues and provide support for the participation of a covalent IN-DNA intermediate in retroviral integration.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brown P. O., Bowerman B., Varmus H. E., Bishop J. M. Correct integration of retroviral DNA in vitro. Cell. 1987 May 8;49(3):347–356. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90287-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown P. O., Bowerman B., Varmus H. E., Bishop J. M. Retroviral integration: structure of the initial covalent product and its precursor, and a role for the viral IN protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Apr;86(8):2525–2529. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.8.2525. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bushman F. D., Fujiwara T., Craigie R. Retroviral DNA integration directed by HIV integration protein in vitro. Science. 1990 Sep 28;249(4976):1555–1558. doi: 10.1126/science.2171144. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Champoux J. J. DNA is linked to the rat liver DNA nicking-closing enzyme by a phosphodiester bond to tyrosine. J Biol Chem. 1981 May 25;256(10):4805–4809. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craig N. L., Nash H. A. The mechanism of phage lambda site-specific recombination: site-specific breakage of DNA by Int topoisomerase. Cell. 1983 Dec;35(3 Pt 2):795–803. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90112-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craigie R., Fujiwara T., Bushman F. The IN protein of Moloney murine leukemia virus processes the viral DNA ends and accomplishes their integration in vitro. Cell. 1990 Aug 24;62(4):829–837. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90126-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellison V., Abrams H., Roe T., Lifson J., Brown P. Human immunodeficiency virus integration in a cell-free system. J Virol. 1990 Jun;64(6):2711–2715. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.6.2711-2715.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grandgenett D. P., Vora A. C., Schiff R. D. A 32,000-dalton nucleic acid-binding protein from avian retravirus cores possesses DNA endonuclease activity. Virology. 1978 Aug;89(1):119–132. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(78)90046-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hein J. Unified approach to alignment and phylogenies. Methods Enzymol. 1990;183:626–645. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(90)83041-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson M. S., McClure M. A., Feng D. F., Gray J., Doolittle R. F. Computer analysis of retroviral pol genes: assignment of enzymatic functions to specific sequences and homologies with nonviral enzymes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Oct;83(20):7648–7652. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.20.7648. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz R. A., Merkel G., Kulkosky J., Leis J., Skalka A. M. The avian retroviral IN protein is both necessary and sufficient for integrative recombination in vitro. Cell. 1990 Oct 5;63(1):87–95. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90290-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katzman M., Katz R. A., Skalka A. M., Leis J. The avian retroviral integration protein cleaves the terminal sequences of linear viral DNA at the in vivo sites of integration. J Virol. 1989 Dec;63(12):5319–5327. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.12.5319-5327.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klippel A., Mertens G., Patschinsky T., Kahmann R. The DNA invertase Gin of phage Mu: formation of a covalent complex with DNA via a phosphoserine at amino acid position 9. EMBO J. 1988 Apr;7(4):1229–1237. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02935.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pargellis C. A., Nunes-Düby S. E., de Vargas L. M., Landy A. Suicide recombination substrates yield covalent lambda integrase-DNA complexes and lead to identification of the active site tyrosine. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jun 5;263(16):7678–7685. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pendergast A. M., Traugh J. A. Alteration of aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase activities by phosphorylation with casein kinase I. J Biol Chem. 1985 Sep 25;260(21):11769–11774. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pigiet V., Conley R. R. Isolation and characterization of phosphothioredoxin from Excherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1978 Mar 25;253(6):1910–1920. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed R. R., Moser C. D. Resolvase-mediated recombination intermediates contain a serine residue covalently linked to DNA. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1984;49:245–249. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1984.049.01.028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roth M. J., Brown D. R., Hurwitz J. Analysis of bacteriophage phi X174 gene A protein-mediated termination and reinitiation of phi X DNA synthesis. II. Structural characterization of the covalent phi X A protein-DNA complex. J Biol Chem. 1984 Aug 25;259(16):10556–10568. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terry R., Soltis D. A., Katzman M., Cobrinik D., Leis J., Skalka A. M. Properties of avian sarcoma-leukosis virus pp32-related pol-endonucleases produced in Escherichia coli. J Virol. 1988 Jul;62(7):2358–2365. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.7.2358-2365.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trask D. K., DiDonato J. A., Muller M. T. Rapid detection and isolation of covalent DNA/protein complexes: application to topoisomerase I and II. EMBO J. 1984 Mar;3(3):671–676. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb01865.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang J. C. DNA topoisomerases. Annu Rev Biochem. 1985;54:665–697. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.54.070185.003313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]