Abstract
Premacular sub-internal limiting membrane (sub-ILM) haemorrhage is a known cause of sudden profound loss of vision. Neodymium-doped yttrium aluminium garnet (ND-YAG) posterior hyaloidotomy is an inexpensive, effective and safe treatment modality for rapid drainage of haemorrhage covering the macula. An 18-year-old male patient presented to us with a history of Nd-YAG posterior hyaloidotomy for Valsalva-related premacular bleed. At the posterior pole, a cavity formed by the detached ILM with a central defect in ILM-posterior hyaloid complex was evident. High-definition optical coherence tomography (HD-OCT) showed normal foveal contour with a parafoveal macular hole. Hence, good clinical judgement, appropriate positioning of hyaloidotomy and use of lowest possible energy level is the key to a successful and safe laser drainage of a premacular haemorrhage.
Background
Premacular sub-internal limiting membrane (sub-ILM)/subhyaloid haemorrhage (SHH) is one of the known causes of sudden profound loss of vision. Nd-YAG posterior hyaloidotomy is an established and promising treatment modality for rapid drainage of haemorrhage covering the macula.1 It is an inexpensive, effective and safe outpatient procedure. However, use of high energy and selection of an inappropriate site of hyaloidotomy close to the foveal centre can cause complications. We report a case of an iatrogenic full thickness parafoveal macular hole formation following Nd-YAG posterior hyaloidotomy for Valsalva-related premacular haemorrhage.
Case presentation
An 18-year-old young male presented to us with sudden vision loss in his right eye 15 days before following a bout of severe vomiting. Three days later he underwent Nd-YAG posterior hyaloidotomy for clearing the premacular bleed. On examination he had a best corrected visual acuity (BCVA) of 6/12 in the right eye and 6/6 in the left eye. The anterior segment was normal in either eye. Intraocular pressure was 16 mmHg in the right eye and 14 mmHg in the left eye. Posterior segment examination revealed mild haemorrhage in the inferior vitreous in the right eye. At the posterior pole of right fundus, a cavity formed by the detached ILM with a central defect in the ILM-posterior hyaloid complex was visible. This would have probably been the area of the sub-ILM bleed prior to drainage. A small round area of retinal thinning was noted superior and nasal to the fovea in the area with the defect in the overlying ILM (figure 1). There was no associated intraretinal or subretinal bleed. Left eye fundus was normal.
Figure 1.
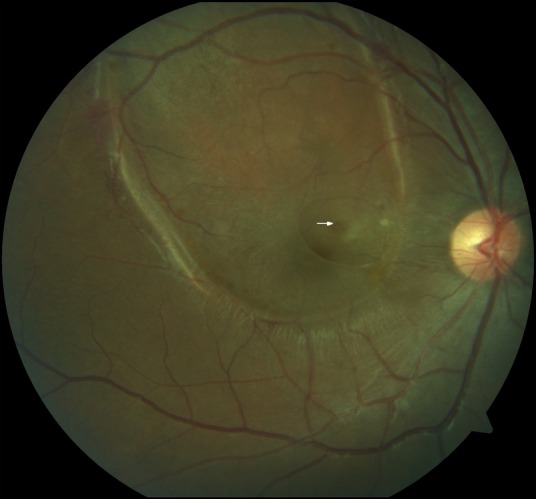
Photograph showing sub-internal limiting membrane (sub-ILM) cavity over the macula with a central defect in the lifted ILM. A small red, parafoveal retinal hole can also be seen in the area of the ILM defect (arrow).
Investigations
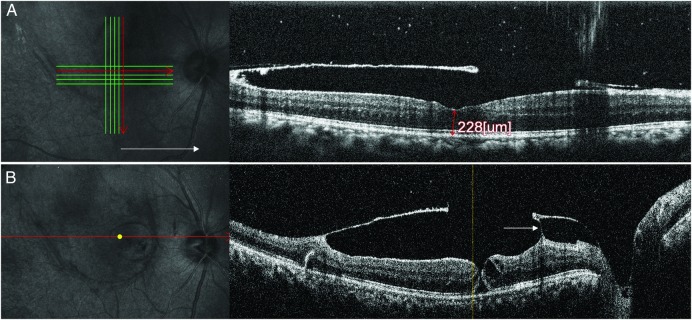
A high-definition optical coherence tomography (HD-OCT, Nidek Advance 3000) scan through the fovea showed a normal foveal contour (figure 2A). A full thickness retinal hole nasal and superior to foveola measuring 293 µ in base diameter was also seen. The nasal margin/wall of the hole had some cystic changes. Overlying the hole a detached, stretched ILM with a central gap/defect could also be clearly seen. In a few scans we could see a thin strand of tissue connecting the ILM to the retinal surface (figure 2B). There was no subretinal fluid around the hole.
Figure 2.
High-definition optical coherence tomography (HD-OCT) showing normal foveal contour (A) along with full thickness retinal hole superonasal to the fovea (B). Intraretinal cystic changes are seen in the nasal wall of the hole. A detached and stretched internal limiting membrane (ILM) with a central defect is seen above the retina overlying the hole. A thin strand of tissue is seen connecting the ILM to the retina nasal to the hole (arrow).
Treatment
Only observation was advised as the BCVA of the patient was 6/12 and it was a small hole at the posterior pole.
Outcome and follow-up
The macular hole remained open at last follow-up (3 months) and his vision was stable at 6/12.
Discussion
Premacular SHH is characterised by a circumscribed, round or dumbbell-shaped, bright red mound of blood beneath the ILM or between ILM and posterior hyaloid face, in or near to the central macular area.2 Various treatment modalities have been described for its management, such as Nd-YAG hyaloidotomy, intravitreal gas-assisted displacement of bleed from macular area, pars plana vitrectomy and observation. Vitrectomy being the most invasive has its inherent risks and complications such as iatrogenic retinal breaks, retinal detachment and glaucoma. Various studies have evaluated and proven the safety and efficacy of Nd-YAG hyaloidotomy. Celebi and Kükner in a study of six patients of SHH reported no retinal damage with laser hyaloidotomy. The maximum follow-up period reported in their study was 42 months.3 Ulbig et al,4 in their case series of 21 patients, reported a success rate of 76.2% with good visualisation of the macula within 1 month and a negligible rate of complications. In their series one myopic patient developed a retinal detachment and one case developed a macular hole.4 However, the photo documentation of the macular hole is lacking. Thach et al5 reported accidental Nd-YAG laser injury to the macula while working in non-medical research laboratory.
In our case we found a parafoveal macular hole following Nd-YAG hyaloidotomy. It is difficult to pin-point the exact cause of the hole. It could be due to the direct impact of the laser beam at the site of the hole or due to the disruption of a detached ILM having some adhesions to the underlying retina. It could also have developed at the time of the bleed due to Valsalva retinopathy. Partial thickness macular holes have been reported earlier following Valsalva retinopathy.4 Absence of surrounding intraretinal or subretinal bleed around the hole points against direct disruptive laser injury. However, the defect in the ILM overlying the parafoveal retinal hole suggests that the major impact of the laser injury was borne by the ILM at this point. A thin strand of tissue connecting the detached ILM to the underlying retina was also seen on the OCT. Following the impact of the laser on the ILM, traction at such pre-existing adhesions could have contributed to the retinal hole formation. Thus, good clinical judgement, appropriate positioning of hyaloidotomy and use of the lowest possible energy level seems prudent for performing successful Nd-YAG laser photodisruption for premacular sub-ILM/SHH.
It has been advocated that if the size of the premacular haemorrhage is <3 disc diameter, Nd-YAG laser should not be performed. Haemorrhages less than this size may not provide adequate cushion effect and this could lead to inadvertent retinal damage by the photodisruptive laser.6 If possible, always drain from a region distant enough from the fovea along the inferior border where there is significant haemorrhagic elevation.7 Khadka et al1 have recently reported an 86% success rate of Nd-YAG laser in management of premacular SHH in a study on 21 eyes with no complications at 6 months follow-up. They recommend that it is better to start with 5 MJ energy and then gradually increase by 1 MJ steps until 12 MJ. If even at this high energy level the ILM/posterior hyaloid does not puncture then it is unlikely that it will perforate with a higher energy level. The location of the bleed in cases of Valsalva retinopathy is mostly sub-ILM rather than sub-hyaloid.8 Sudden disruption and traction on the ILM may inadvertently lead to complications such as a retinal hole formation at the posterior pole as seen in our patient. Thus, we should be cautious in using high laser energy while performing Nd-YAG laser for such cases.
Learning points.
Decision to perform laser hyaloidotomy should be made after careful deliberation with utmost attention to the site of laser application and the laser energy level.
Unexpected complications can occur and need surveillance with careful examination aided by judicious use of optical coherence tomography enabled macular imaging.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank Dr Chaitra C Shekar for her invaluable support in writing this manuscript.
Footnotes
Contributors: RB contributed to the conception and design, acquisition of data or analysis and interpretation of data. RC gave final approval of the version published and agreement to be accountable for the article and to ensure that all questions regarding the accuracy or integrity of the article are investigated and resolved. SVA and BT contributed to the drafting of the article or revising it critically for important intellectual content.
Competing interests: None declared.
Patient consent: Obtained.
Provenance and peer review: Not commissioned; externally peer reviewed.
References
- 1.Khadka D, Bhandari S, Bajimaya S et al. Nd:YAG laser hyaloidotomy in the management of premacular subhyaloid hemorrhage. BMC Ophthalmol 2016;16:41 10.1186/s12886-016-0218-0 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Kwok AKH, Lai TYY, Chan NR. Epiretinal membrane formation with internal limiting membrane wrinkling after Nd:YAG laser membranotomy in Valsalva retinopathy. Am J Ophthalmol 2003;136:763–6. 10.1016/S0002-9394(03)00442-2 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Celebi S, Kükner AS. Photodisruptive Nd:YAG laser in the management of premacular subhyaloid hemorrhage. Eur J Ophthalmol 2001;11:281–6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Ulbig MW, Mangouritsas G, Rothbacher HH et al. Long-term results after drainage of premacular subhyaloid hemorrhage into the vitreous with a pulsed Nd:YAG laser. Arch Ophthalmol 1998;116:1465–9. 10.1001/archopht.116.11.1465 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Thach AB, Lopez PF, Snady-McCoy LC et al. Accidental Nd:YAG laser injuries to the macula. Am J Ophthalmol 1995;119:767–73. 10.1016/S0002-9394(14)72783-7 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Xie Z, Yu S, Chen X et al. Macular hole secondary to Valsalva retinopathy after doing push-up exercise. BMC Ophthalmol 2014;14:98 10.1186/1471-2415-14-98 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Kuruvilla O, Munie M, Shah M et al. Nd:YAG membranotomy for preretinal hemorrhage secondary to Valsalva retinopathy. Saudi J Ophthalmol 2014;28:145–51. 10.1016/j.sjopt.2014.02.006 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Meyer CH, Mennel S, Rodrigues EB et al. Is the location of Valsalva hemorrhages submembranous or subhyaloidal? Am J Ophthalmol 2006;141:231; author reply 231–232 10.1016/j.ajo.2005.08.040 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]