Abstract
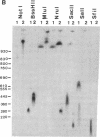
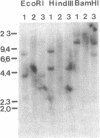
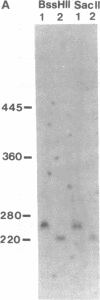
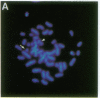
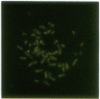
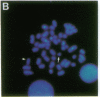
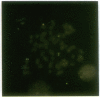
The 8;21 translocation is one of the most common specific rearrangements in acute myelogenous leukemia. We have identified markers (D21S65 and a Not I boundary clone, Not-42, referred to as probe B) flanking the chromosome 21 translocation breakpoint (21q22.3) that demonstrate physical linkage in normal genomic DNA, by using at least three restriction endonucleases (Not I, Sac II, and BssHII), and that are located not more than 250-280 kilobases apart. Pulsed-field gel analysis of DNA from somatic cell hybrids containing the 8;21 translocation chromosomes demonstrates rearrangement of these markers. A 470-kilobase yeast artificial chromosome, YAC-Not-42, has been isolated that contains both probes. Mapping of lambda subclones constructed from YAC-Not-42 suggests that greater than 95% (25/26 probes tested) of the yeast artificial chromosome DNA is located on the proximal (D21S65) side of the breakpoint. In situ hybridization studies using metaphase chromosomes from five acute myelogenous leukemia patients with the 8;21 translocation confirmed these results and demonstrated the translocation of probe B to the derivative chromosome 8. A chromosome walk of approximately 39 kilobases from probe B has allowed identification of the breakpoint in DNA from a somatic cell hybrid containing the derivative chromosome 8. Since probe B contains conserved DNA sequences and is in close proximity to the translocation breakpoint, it may represent a portion of the involved gene on chromosome 21.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brownstein B. H., Silverman G. A., Little R. D., Burke D. T., Korsmeyer S. J., Schlessinger D., Olson M. V. Isolation of single-copy human genes from a library of yeast artificial chromosome clones. Science. 1989 Jun 16;244(4910):1348–1351. doi: 10.1126/science.2544027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burke D. T., Carle G. F., Olson M. V. Cloning of large segments of exogenous DNA into yeast by means of artificial chromosome vectors. Science. 1987 May 15;236(4803):806–812. doi: 10.1126/science.3033825. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diaz M. O., Le Beau M. M., Rowley J. D., Drabkin H. A., Patterson D. The role of the c-mos gene in the 8;21 translocation in human acute myeloblastic leukemia. Science. 1985 Aug 23;229(4715):767–769. doi: 10.1126/science.3860954. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drabkin H. A., Diaz M., Bradley C. M., Le Beau M. M., Rowley J. D., Patterson D. Isolation and analysis of the 21q+ chromosome in the acute myelogenous leukemia 8;21 translocation: evidence that c-mos is not translocated. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jan;82(2):464–468. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.2.464. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ENGEL R. R., HAMMOND D., EITZMAN D. V., PEARSON H., KRIVIT W. TRANSIENT CONGENITAL LEUKEMIA IN 7 INFANTS WITH MONGOLISM. J Pediatr. 1964 Aug;65:303–305. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(64)80535-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans D. I., Steward J. K. Down's syndrome and leukaemia. Lancet. 1972 Dec 16;2(7790):1322–1322. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(72)92704-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferster A., Verhest A., Vamos E., De Maertelaere E., Otten J. Leukemia in a trisomy 21 mosaic: specific involvement of the trisomic cells. Cancer Genet Cytogenet. 1986 Feb 1;20(1-2):109–113. doi: 10.1016/0165-4608(86)90113-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gao J. Z., Erickson P., Patterson D., Jones C., Drabkin H. Isolation and regional mapping of NotI and EagI clones from human chromosome 21. Genomics. 1991 May;10(1):166–172. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(91)90497-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gardiner-Garden M., Frommer M. CpG islands in vertebrate genomes. J Mol Biol. 1987 Jul 20;196(2):261–282. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90689-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gardiner K., Horisberger M., Kraus J., Tantravahi U., Korenberg J., Rao V., Reddy S., Patterson D. Analysis of human chromosome 21: correlation of physical and cytogenetic maps; gene and CpG island distributions. EMBO J. 1990 Jan;9(1):25–34. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08076.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gardiner K., Watkins P., Münke M., Drabkin H., Jones C., Patterson D. Partial physical map of human chromosome 21. Somat Cell Mol Genet. 1988 Nov;14(6):623–637. doi: 10.1007/BF01535316. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gemmill R. M., Coyle-Morris J. F., McPeek F. D., Jr, Ware-Uribe L. F., Hecht F. Construction of long-range restriction maps in human DNA using pulsed field gel electrophoresis. Gene Anal Tech. 1987 Nov-Dec;4(6):119–131. doi: 10.1016/0735-0651(87)90010-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grossberger D. Minipreps of DNA from bacteriophage lambda. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Aug 25;15(16):6737–6737. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.16.6737. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lazarus K. H., Heerema N. A., Palmer C. G., Baehner R. L. The myeloproliferative reaction in a child with Down syndrome: cytological and chromosomal evidence for a transient leukemia. Am J Hematol. 1981 Dec;11(4):417–423. doi: 10.1002/ajh.2830110411. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lichter P., Tang C. J., Call K., Hermanson G., Evans G. A., Housman D., Ward D. C. High-resolution mapping of human chromosome 11 by in situ hybridization with cosmid clones. Science. 1990 Jan 5;247(4938):64–69. doi: 10.1126/science.2294592. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindgren V., Rowley J. D. Comparable complex rearrangements involving 8;21 and 9;22 translocations in leukaemia. Nature. 1977 Apr 21;266(5604):744–745. doi: 10.1038/266744a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCormick M. K., Schinzel A., Petersen M. B., Stetten G., Driscoll D. J., Cantu E. S., Tranebjaerg L., Mikkelsen M., Watkins P. C., Antonarakis S. E. Molecular genetic approach to the characterization of the "Down syndrome region" of chromosome 21. Genomics. 1989 Aug;5(2):325–331. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(89)90065-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rahmani Z., Blouin J. L., Creau-Goldberg N., Watkins P. C., Mattei J. F., Poissonnier M., Prieur M., Chettouh Z., Nicole A., Aurias A. Critical role of the D21S55 region on chromosome 21 in the pathogenesis of Down syndrome. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Aug;86(15):5958–5962. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.15.5958. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rao V. N., Modi W. S., Drabkin H. D., Patterson D., O'Brien S. J., Papas T. S., Reddy E. S. The human erg gene maps to chromosome 21, band q22: relationship to the 8; 21 translocation of acute myelogenous leukemia. Oncogene. 1988 Nov;3(5):497–500. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowley J. D., Diaz M. O., Espinosa R., 3rd, Patel Y. D., van Melle E., Ziemin S., Taillon-Miller P., Lichter P., Evans G. A., Kersey J. H. Mapping chromosome band 11q23 in human acute leukemia with biotinylated probes: identification of 11q23 translocation breakpoints with a yeast artificial chromosome. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Dec;87(23):9358–9362. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.23.9358. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowley J. D. Down Syndrome and acute leukaemia: increased risk may be due to trisomy 21. Lancet. 1981 Nov 7;2(8254):1020–1022. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(81)91218-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowley J. D. Identification of the constant chromosome regions involved in human hematologic malignant disease. Science. 1982 May 14;216(4547):749–751. doi: 10.1126/science.7079737. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowley J. D. Identificaton of a translocation with quinacrine fluorescence in a patient with acute leukemia. Ann Genet. 1973 Jun;16(2):109–112. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sacchi N., Cheng S. V., Tanzi R. E., Gusella J. F., Drabkin H. A., Patterson D., Haines J. H., Papas T. S. The ETS genes on chromosome 21 are distal to the breakpoint of the acute myelogenous leukemia translocation (8;21). Genomics. 1988 Aug;3(2):110–116. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(88)90140-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sacchi N., Watson D. K., Guerts van Kessel A. H., Hagemeijer A., Kersey J., Drabkin H. D., Patterson D., Papas T. S. Hu-ets-1 and Hu-ets-2 genes are transposed in acute leukemias with (4;11) and (8;21) translocations. Science. 1986 Jan 24;231(4736):379–382. doi: 10.1126/science.3941901. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sealey P. G., Whittaker P. A., Southern E. M. Removal of repeated sequences from hybridisation probes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Mar 25;13(6):1905–1922. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.6.1905. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suda J., Eguchi M., Akiyama Y., Iwama Y., Furukawa T., Sato Y., Miura Y., Suda T., Saito M. Differentiation of blast cells from a Down's syndrome patient with transient myeloproliferative disorder. Blood. 1987 Feb;69(2):508–512. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swirsky D. M., Li Y. S., Matthews J. G., Flemans R. J., Rees J. K., Hayhoe F. G. 8;21 translocation in acute granulocytic leukaemia: cytological, cytochemical and clinical features. Br J Haematol. 1984 Feb;56(2):199–213. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1984.tb03948.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Keuren M. L., Watkins P. C., Drabkin H. A., Jabs E. W., Gusella J. F., Patterson D. Regional localization of DNA sequences on chromosome 21 using somatic cell hybrids. Am J Hum Genet. 1986 Jun;38(6):793–804. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whittaker P. A., Campbell A. J., Southern E. M., Murray N. E. Enhanced recovery and restriction mapping of DNA fragments cloned in a new lambda vector. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Jul 25;16(14B):6725–6736. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.14.6725. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong C., Kazazian H. H., Jr, Stetten G., Earnshaw W. C., Van Keuren M. L., Antonarakis S. E. Molecular mechanism in the formation of a human ring chromosome 21. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Mar;86(6):1914–1918. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.6.1914. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]