Abstract
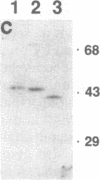
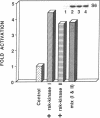
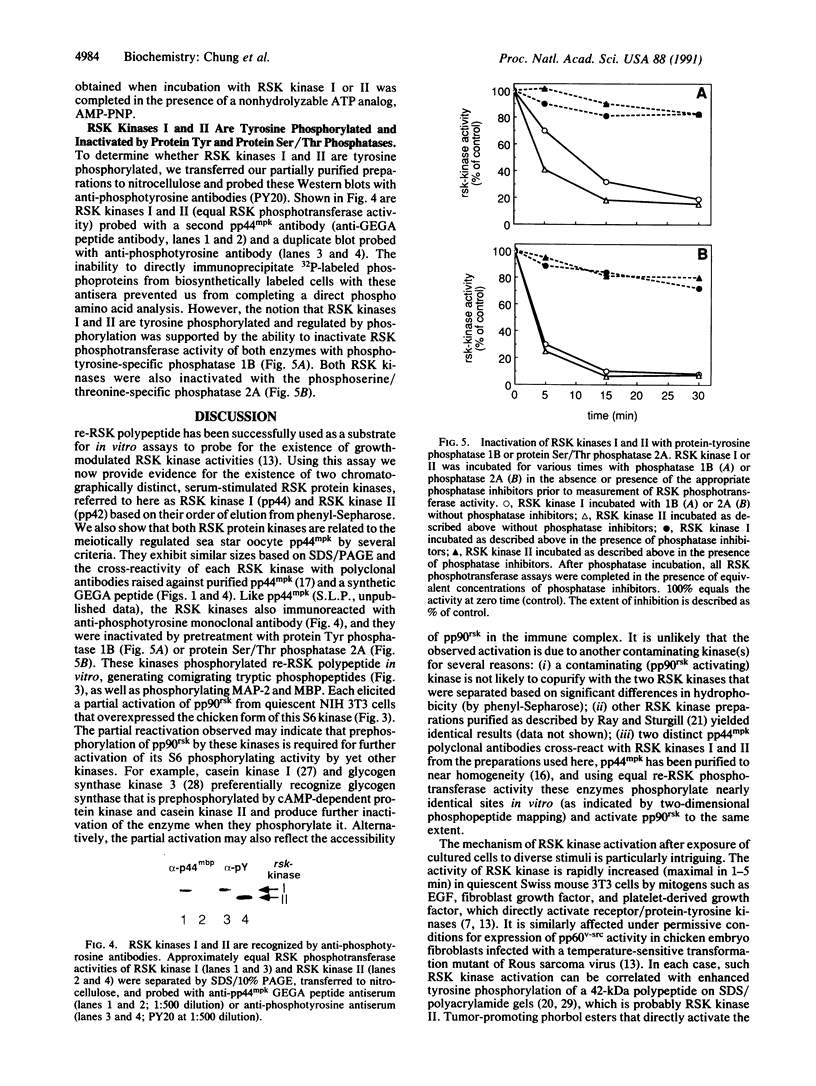
Using a recombinant rsk gene product as a substrate for in vitro kinase assays, we have identified two mitogen-activated Swiss 3T3 RSK protein kinase activities (referred to as RSK kinase I and RSK kinase II, based on their order of elution from phenyl-Sepharose). Polyclonal antisera prepared against maturation-regulated 44-kDa myelin basic protein (MBP) kinase (pp44mpk) purified from sea star oocytes demonstrated immunocrossreactivity with polypeptides of approximately 44 kDa in the RSK kinase I preparation and approximately 42 kDa in the RSK kinase II preparation, respectively. These polypeptides were also recognized by anti-phosphotyrosine antibodies, and either phosphatase 1B or 2A (tyrosine- and serine/threonine-specific phosphatases, respectively) separately inactivated RSK phosphotransferase activity supporting the notion that tyrosine and serine/threonine phosphorylation are required for activity. In vitro, both RSK kinases and MBP kinase phosphorylated recombinant RSK and generated nearly identical two-dimensional tryptic phosphopeptide maps. They also phosphorylated MBP and microtubule-associated protein 2 but not 40S ribosomal protein S6. Furthermore, these protein kinases phosphorylated and partially activated pp90rsk in immune complexes obtained from quiescent cells.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ahn N. G., Krebs E. G. Evidence for an epidermal growth factor-stimulated protein kinase cascade in Swiss 3T3 cells. Activation of serine peptide kinase activity by myelin basic protein kinases in vitro. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jul 15;265(20):11495–11501. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alcorta D. A., Crews C. M., Sweet L. J., Bankston L., Jones S. W., Erikson R. L. Sequence and expression of chicken and mouse rsk: homologs of Xenopus laevis ribosomal S6 kinase. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Sep;9(9):3850–3859. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.9.3850. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson N. G., Maller J. L., Tonks N. K., Sturgill T. W. Requirement for integration of signals from two distinct phosphorylation pathways for activation of MAP kinase. Nature. 1990 Feb 15;343(6259):651–653. doi: 10.1038/343651a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Banerjee P., Ahmad M. F., Grove J. R., Kozlosky C., Price D. J., Avruch J. Molecular structure of a major insulin/mitogen-activated 70-kDa S6 protein kinase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Nov;87(21):8550–8554. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.21.8550. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blenis J., Kuo C. J., Erikson R. L. Identification of a ribosomal protein S6 kinase regulated by transformation and growth-promoting stimuli. J Biol Chem. 1987 Oct 25;262(30):14373–14376. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boulton T. G., Yancopoulos G. D., Gregory J. S., Slaughter C., Moomaw C., Hsu J., Cobb M. H. An insulin-stimulated protein kinase similar to yeast kinases involved in cell cycle control. Science. 1990 Jul 6;249(4964):64–67. doi: 10.1126/science.2164259. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen R. H., Blenis J. Identification of Xenopus S6 protein kinase homologs (pp90rsk) in somatic cells: phosphorylation and activation during initiation of cell proliferation. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Jun;10(6):3204–3215. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.6.3204. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen R. H., Chung J., Blenis J. Regulation of pp90rsk phosphorylation and S6 phosphotransferase activity in Swiss 3T3 cells by growth factor-, phorbol ester-, and cyclic AMP-mediated signal transduction. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Apr;11(4):1861–1867. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.4.1861. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chung J., Chen R. H., Blenis J. Coordinate regulation of pp90rsk and a distinct protein-serine/threonine kinase activity that phosphorylates recombinant pp90rsk in vitro. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Apr;11(4):1868–1874. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.4.1868. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cicirelli M. F., Pelech S. L., Krebs E. G. Activation of multiple protein kinases during the burst in protein phosphorylation that precedes the first meiotic cell division in Xenopus oocytes. J Biol Chem. 1988 Feb 5;263(4):2009–2019. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper J. A., Bowen-Pope D. F., Raines E., Ross R., Hunter T. Similar effects of platelet-derived growth factor and epidermal growth factor on the phosphorylation of tyrosine in cellular proteins. Cell. 1982 Nov;31(1):263–273. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90426-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper J. A., Sefton B. M., Hunter T. Detection and quantification of phosphotyrosine in proteins. Methods Enzymol. 1983;99:387–402. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)99075-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper J. A., Sefton B. M., Hunter T. Diverse mitogenic agents induce the phosphorylation of two related 42,000-dalton proteins on tyrosine in quiescent chick cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Jan;4(1):30–37. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.1.30. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ely C. M., Oddie K. M., Litz J. S., Rossomando A. J., Kanner S. B., Sturgill T. W., Parsons S. J. A 42-kD tyrosine kinase substrate linked to chromaffin cell secretion exhibits an associated MAP kinase activity and is highly related to a 42-kD mitogen-stimulated protein in fibroblasts. J Cell Biol. 1990 Mar;110(3):731–742. doi: 10.1083/jcb.110.3.731. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erikson E., Maller J. L. Biochemical characterization of the p34cdc2 protein kinase component of purified maturation-promoting factor from Xenopus eggs. J Biol Chem. 1989 Nov 25;264(33):19577–19582. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erikson E., Maller J. L. Substrate specificity of ribosomal protein S6 kinase II from Xenopus eggs. Second Messengers Phosphoproteins. 1988;12(2-3):135–143. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erikson R. L. Structure, expression, and regulation of protein kinases involved in the phosphorylation of ribosomal protein S6. J Biol Chem. 1991 Apr 5;266(10):6007–6010. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fiol C. J., Mahrenholz A. M., Wang Y., Roeske R. W., Roach P. J. Formation of protein kinase recognition sites by covalent modification of the substrate. Molecular mechanism for the synergistic action of casein kinase II and glycogen synthase kinase 3. J Biol Chem. 1987 Oct 15;262(29):14042–14048. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flotow H., Graves P. R., Wang A. Q., Fiol C. J., Roeske R. W., Roach P. J. Phosphate groups as substrate determinants for casein kinase I action. J Biol Chem. 1990 Aug 25;265(24):14264–14269. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilmore T., Martin G. S. Phorbol ester and diacylglycerol induce protein phosphorylation at tyrosine. Nature. 1983 Dec 1;306(5942):487–490. doi: 10.1038/306487a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanks S. K., Quinn A. M., Hunter T. The protein kinase family: conserved features and deduced phylogeny of the catalytic domains. Science. 1988 Jul 1;241(4861):42–52. doi: 10.1126/science.3291115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones S. W., Erikson E., Blenis J., Maller J. L., Erikson R. L. A Xenopus ribosomal protein S6 kinase has two apparent kinase domains that are each similar to distinct protein kinases. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 May;85(10):3377–3381. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.10.3377. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozma S. C., Ferrari S., Bassand P., Siegmann M., Totty N., Thomas G. Cloning of the mitogen-activated S6 kinase from rat liver reveals an enzyme of the second messenger subfamily. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Oct;87(19):7365–7369. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.19.7365. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maller J. L. Xenopus oocytes and the biochemistry of cell division. Biochemistry. 1990 Apr 3;29(13):3157–3166. doi: 10.1021/bi00465a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura K. D., Martinez R., Weber M. J. Tyrosine phosphorylation of specific proteins after mitogen stimulation of chicken embryo fibroblasts. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Mar;3(3):380–390. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.3.380. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelech S. L., Sanghera J. S., Daya-Makin M. Protein kinase cascades in meiotic and mitotic cell cycle control. Biochem Cell Biol. 1990 Dec;68(12):1297–1330. doi: 10.1139/o90-194. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelech S. L., Tombes R. M., Meijer L., Krebs E. G. Activation of myelin basic protein kinases during echinoderm oocyte maturation and egg fertilization. Dev Biol. 1988 Nov;130(1):28–36. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(88)90410-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ray L. B., Sturgill T. W. Characterization of insulin-stimulated microtubule-associated protein kinase. Rapid isolation and stabilization of a novel serine/threonine kinase from 3T3-L1 cells. J Biol Chem. 1988 Sep 5;263(25):12721–12727. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ray L. B., Sturgill T. W. Insulin-stimulated microtubule-associated protein kinase is phosphorylated on tyrosine and threonine in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jun;85(11):3753–3757. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.11.3753. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ray L. B., Sturgill T. W. Rapid stimulation by insulin of a serine/threonine kinase in 3T3-L1 adipocytes that phosphorylates microtubule-associated protein 2 in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Mar;84(6):1502–1506. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.6.1502. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rossomando A. J., Payne D. M., Weber M. J., Sturgill T. W. Evidence that pp42, a major tyrosine kinase target protein, is a mitogen-activated serine/threonine protein kinase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Sep;86(18):6940–6943. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.18.6940. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanghera J. S., Paddon H. B., Bader S. A., Pelech S. L. Purification and characterization of a maturation-activated myelin basic protein kinase from sea star oocytes. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jan 5;265(1):52–57. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanghera J. S., Paddon H. B., Pelech S. L. Role of protein phosphorylation in the maturation-induced activation of a myelin basic protein kinase from sea star oocytes. J Biol Chem. 1991 Apr 15;266(11):6700–6707. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sturgill T. W., Ray L. B., Erikson E., Maller J. L. Insulin-stimulated MAP-2 kinase phosphorylates and activates ribosomal protein S6 kinase II. Nature. 1988 Aug 25;334(6184):715–718. doi: 10.1038/334715a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sweet L. J., Alcorta D. A., Erikson R. L. Two distinct enzymes contribute to biphasic S6 phosphorylation in serum-stimulated chicken embryo fibroblasts. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Jun;10(6):2787–2792. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.6.2787. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sweet L. J., Alcorta D. A., Jones S. W., Erikson E., Erikson R. L. Identification of mitogen-responsive ribosomal protein S6 kinase pp90rsk, a homolog of Xenopus S6 kinase II, in chicken embryo fibroblasts. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 May;10(5):2413–2417. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.5.2413. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]