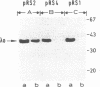
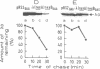
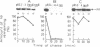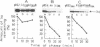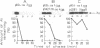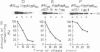Abstract
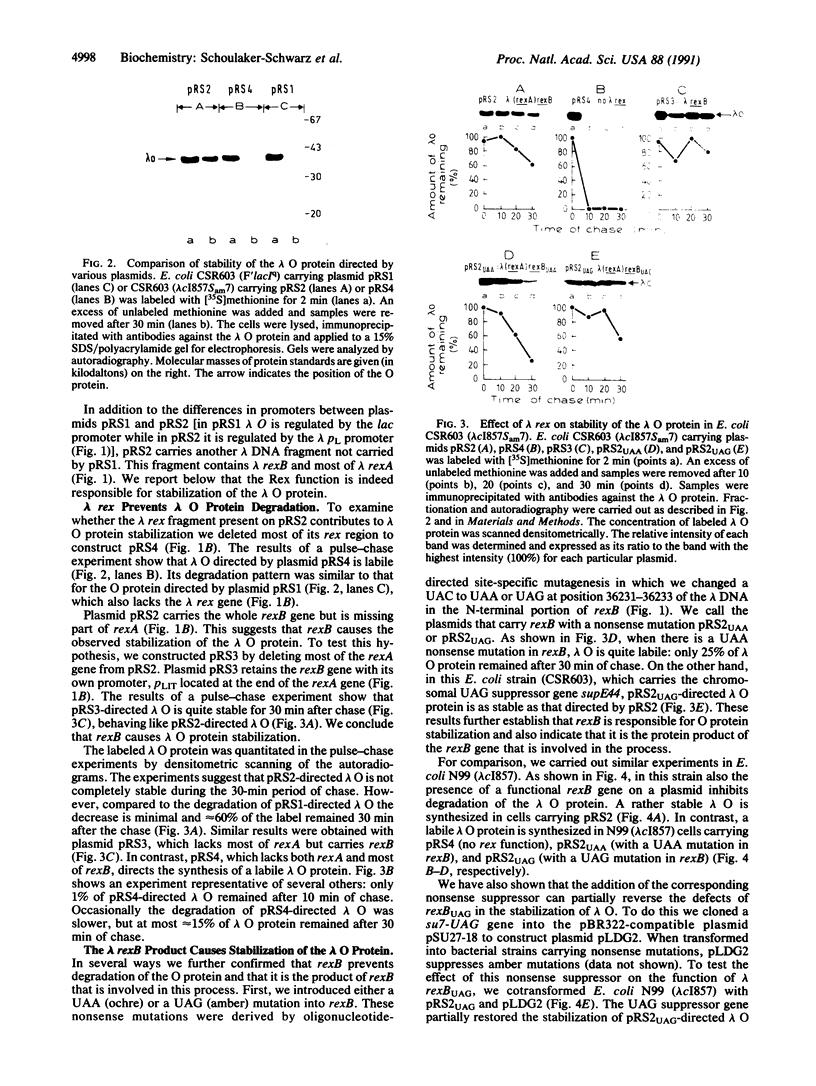
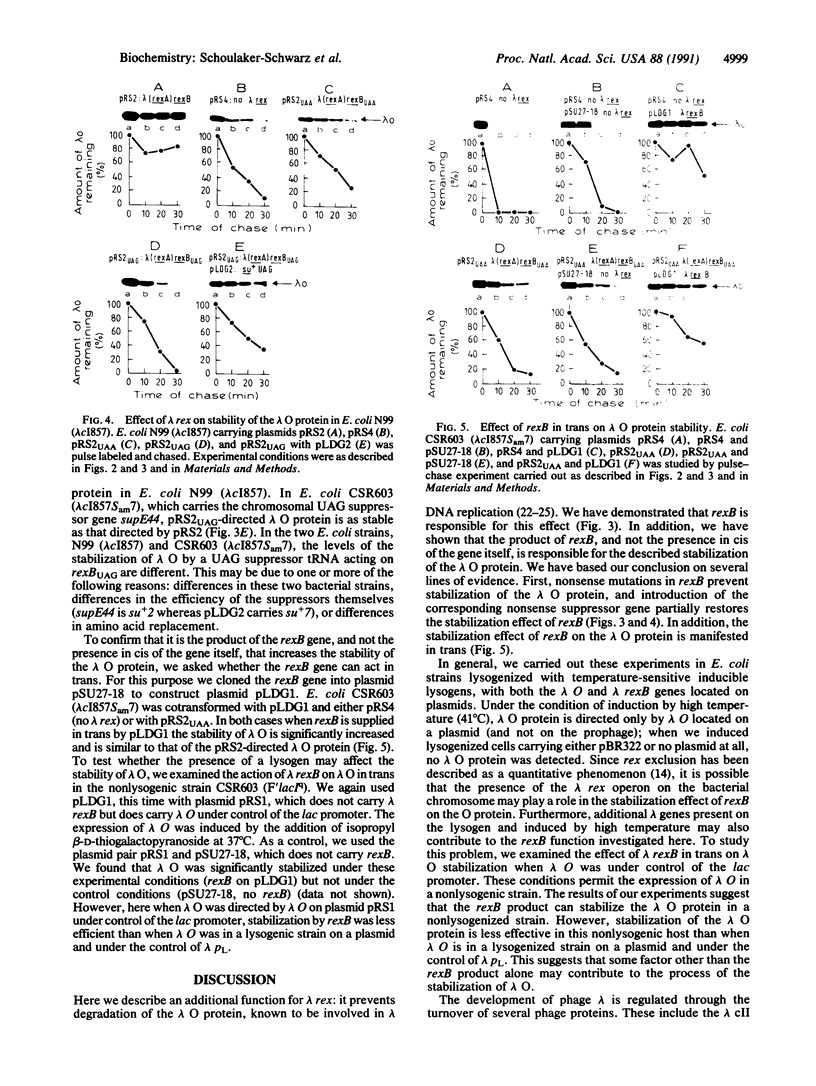
The rex operon of bacteriophage lambda excludes the development of several unrelated bacteriophages. Here we present an additional lambda rexB function: it prevents degradation of the short-lived protein lambda O known to be involved in lambda DNA replication. We have shown that it is the product of rexB that is responsible for the stabilization of lambda O: when a nonsense mutation is present in rexB, lambda O protein is labile; suppression of the mutation by the corresponding nonsense suppressor causes partial restabilization of lambda O. lambda rexB also stabilizes lambda O in trans. We discuss our results in relation to the function of rexB in lambda DNA replication and its role in the protein degradation pathways of bacteriophage lambda.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alfano C., McMacken R. Heat shock protein-mediated disassembly of nucleoprotein structures is required for the initiation of bacteriophage lambda DNA replication. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jun 25;264(18):10709–10718. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Banuett F., Hoyt M. A., McFarlane L., Echols H., Herskowitz I. hflB, a new Escherichia coli locus regulating lysogeny and the level of bacteriophage lambda cII protein. J Mol Biol. 1986 Jan 20;187(2):213–224. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90229-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Belfort M. Anomalous behavior of bacteriophage lambda polypeptides in polyacrylamide gels: resolution, identification, and control of the lambda rex gene product. J Virol. 1978 Oct;28(1):270–278. doi: 10.1128/jvi.28.1.270-278.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Belfort M., Wulff D. L. An analysis of the processes of infection and induction of E. coli mutant hfl-1 by bacteriophage lambda. Virology. 1973 Sep;55(1):183–192. doi: 10.1016/s0042-6822(73)81020-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Belfort M., Wulff D. The roles of the lambda c3 gene and the Escherichia coli catabolite gene activation system in the establishment of lysogeny by bacteriophage lambda. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Mar;71(3):779–782. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.3.779. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benzer S. FINE STRUCTURE OF A GENETIC REGION IN BACTERIOPHAGE. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1955 Jun 15;41(6):344–354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.41.6.344. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CRICK F. H., BARNETT L., BRENNER S., WATTS-TOBIN R. J. General nature of the genetic code for proteins. Nature. 1961 Dec 30;192:1227–1232. doi: 10.1038/1921227a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheng H. H., Muhlrad P. J., Hoyt M. A., Echols H. Cleavage of the cII protein of phage lambda by purified HflA protease: control of the switch between lysis and lysogeny. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Nov;85(21):7882–7886. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.21.7882. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christensen J. R., Geiman J. M. A new effect of the rex gene of phage lambda: premature lysis after infection by phage T1. Virology. 1973 Nov;56(1):285–290. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90306-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dekel-Gorodetsky L., Schoulaker-Schwarz R., Engelberg-Kulka H. Escherichia coli tryptophan operon directs the in vivo synthesis of a leader peptide. J Bacteriol. 1986 Mar;165(3):1046–1048. doi: 10.1128/jb.165.3.1046-1048.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dodson M., McMacken R., Echols H. Specialized nucleoprotein structures at the origin of replication of bacteriophage lambda. Protein association and disassociation reactions responsible for localized initiation of replication. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jun 25;264(18):10719–10725. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gottesman S., Gottesman M., Shaw J. E., Pearson M. L. Protein degradation in E. coli: the lon mutation and bacteriophage lambda N and cII protein stability. Cell. 1981 Apr;24(1):225–233. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90518-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenblatt J. Regulation of the expression of the N gene of bacteriophage lambda. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Feb;70(2):421–424. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.2.421. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gussin G. N., Peterson V. Isolation and properties of rex - mutants of bacteriophage lambda. J Virol. 1972 Oct;10(4):760–765. doi: 10.1128/jvi.10.4.760-765.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayes S., Szybalski W. Control of short leftward transcripts from the immunity and ori regions in induced coliphage lambda. Mol Gen Genet. 1973 Nov 22;126(4):275–290. doi: 10.1007/BF00269438. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herskowitz I., Hagen D. The lysis-lysogeny decision of phage lambda: explicit programming and responsiveness. Annu Rev Genet. 1980;14:399–445. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.14.120180.002151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howard B. D. Phage lambda mutants deficient in r-II exclusion. Science. 1967 Dec 22;158(3808):1588–1589. doi: 10.1126/science.158.3808.1588. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoyt M. A., Knight D. M., Das A., Miller H. I., Echols H. Control of phage lambda development by stability and synthesis of cII protein: role of the viral cIII and host hflA, himA and himD genes. Cell. 1982 Dec;31(3 Pt 2):565–573. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90312-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacquemin-Sablon A., Lanni Y. T. Lambda-repressed mutants of bacteriophage T5. I. Isolation and genetical characterization. Virology. 1973 Nov;56(1):230–237. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90302-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konrad M. W. Dependence of "early" lambda bacteriophage RNA synthesis on bacteriophage-directed protein synthesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 Jan;59(1):171–178. doi: 10.1073/pnas.59.1.171. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuypers B., Reiser W., Klein A. Cloning of the replication gene O of E. coli bacteriophage lambda and its expression under the control of the lac promoter. Gene. 1980 Aug;10(3):195–203. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(80)90049-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landsmann J., Kröger M., Hobom G. The rex region of bacteriophage lambda: two genes under three-way control. Gene. 1982 Nov;20(1):11–24. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90083-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipińska B., Podhajska A., Taylor K. Synthesis and decay of lambda DNA replication proteins in minicells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1980 Jan 15;92(1):120–126. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(80)91528-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martinez E., Bartolomé B., de la Cruz F. pACYC184-derived cloning vectors containing the multiple cloning site and lacZ alpha reporter gene of pUC8/9 and pUC18/19 plasmids. Gene. 1988 Aug 15;68(1):159–162. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90608-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matz K., Schmandt M., Gussin G. N. The rex gene of bacteriophage lambda is really two genes. Genetics. 1982 Nov;102(3):319–327. doi: 10.1093/genetics/102.3.319. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neidhardt F. C., Bloch P. L., Smith D. F. Culture medium for enterobacteria. J Bacteriol. 1974 Sep;119(3):736–747. doi: 10.1128/jb.119.3.736-747.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oliver D. B., Beckwith J. Regulation of a membrane component required for protein secretion in Escherichia coli. Cell. 1982 Aug;30(1):311–319. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90037-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pao C. C., Speyer J. F. Mutants of T7 bacteriophage inhibited by lambda prophage. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Sep;72(9):3642–3646. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.9.3642. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raftery L. A., Egan J. B., Cline S. W., Yarus M. Defined set of cloned termination suppressors: in vivo activity of isogenetic UAG, UAA, and UGA suppressor tRNAs. J Bacteriol. 1984 Jun;158(3):849–859. doi: 10.1128/jb.158.3.849-859.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rattray A., Altuvia S., Mahajna G., Oppenheim A. B., Gottesman M. Control of bacteriophage lambda CII activity by bacteriophage and host functions. J Bacteriol. 1984 Jul;159(1):238–242. doi: 10.1128/jb.159.1.238-242.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sancar A., Hack A. M., Rupp W. D. Simple method for identification of plasmid-coded proteins. J Bacteriol. 1979 Jan;137(1):692–693. doi: 10.1128/jb.137.1.692-693.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz M. On the function of the N cistron in phage lambda. Virology. 1970 Jan;40(1):23–33. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(70)90375-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shinedling S., Parma D., Gold L. Wild-type bacteriophage T4 is restricted by the lambda rex genes. J Virol. 1987 Dec;61(12):3790–3794. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.12.3790-3794.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simatake H., Rosenberg M. Purified lambda regulatory protein cII positively activates promoters for lysogenic development. Nature. 1981 Jul 9;292(5819):128–132. doi: 10.1038/292128a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snyder L., McWilliams K. The rex genes of bacteriophage lambda can inhibit cell function without phage superinfection. Gene. 1989 Sep 1;81(1):17–24. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(89)90332-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toothman P., Herskowitz I. Rex-dependent exclusion of lambdoid phages. I. Prophage requirements for exclusion. Virology. 1980 Apr 15;102(1):133–146. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(80)90076-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toothman P., Herskowitz I. Rex-dependent exclusion of lambdoid phages. II. Determinants of sensitivity to exclusion. Virology. 1980 Apr 15;102(1):147–160. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(80)90077-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toothman P., Herskowitz I. Rex-dependent exclusion of lambdoid phages. III. Physiology of the abortive infection. Virology. 1980 Apr 15;102(1):161–171. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(80)90078-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wold M. S., Mallory J. B., Roberts J. D., LeBowitz J. H., McMacken R. Initiation of bacteriophage lambda DNA replication in vitro with purified lambda replication proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Oct;79(20):6176–6180. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.20.6176. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wyatt W. M., Inokuchi H. Stability of lambda O and P replication functions. Virology. 1974 Mar;58(1):313–315. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(74)90168-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]