Abstract
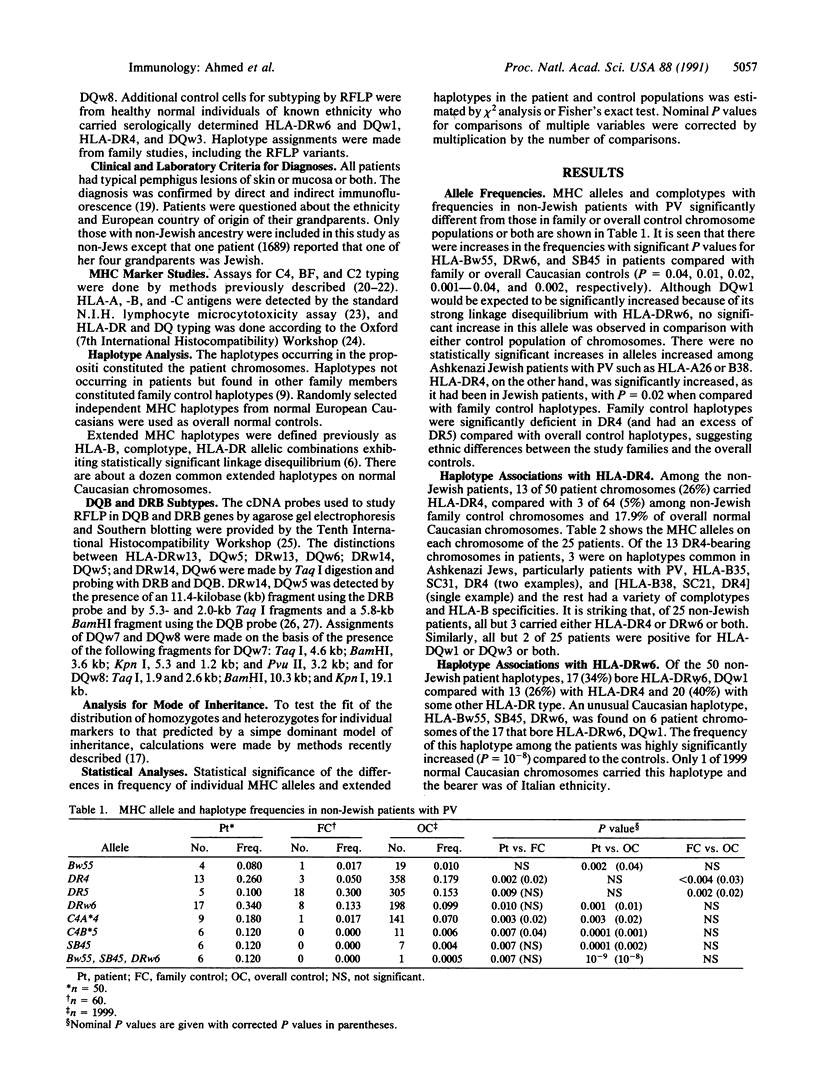
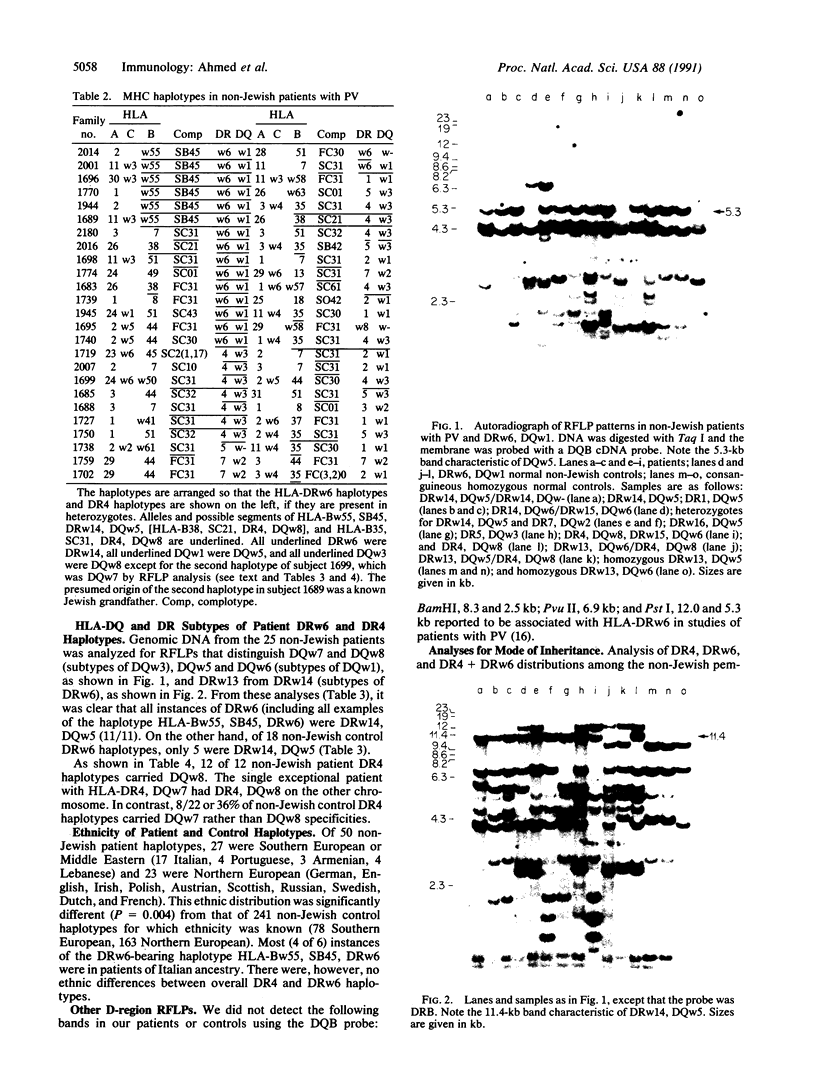
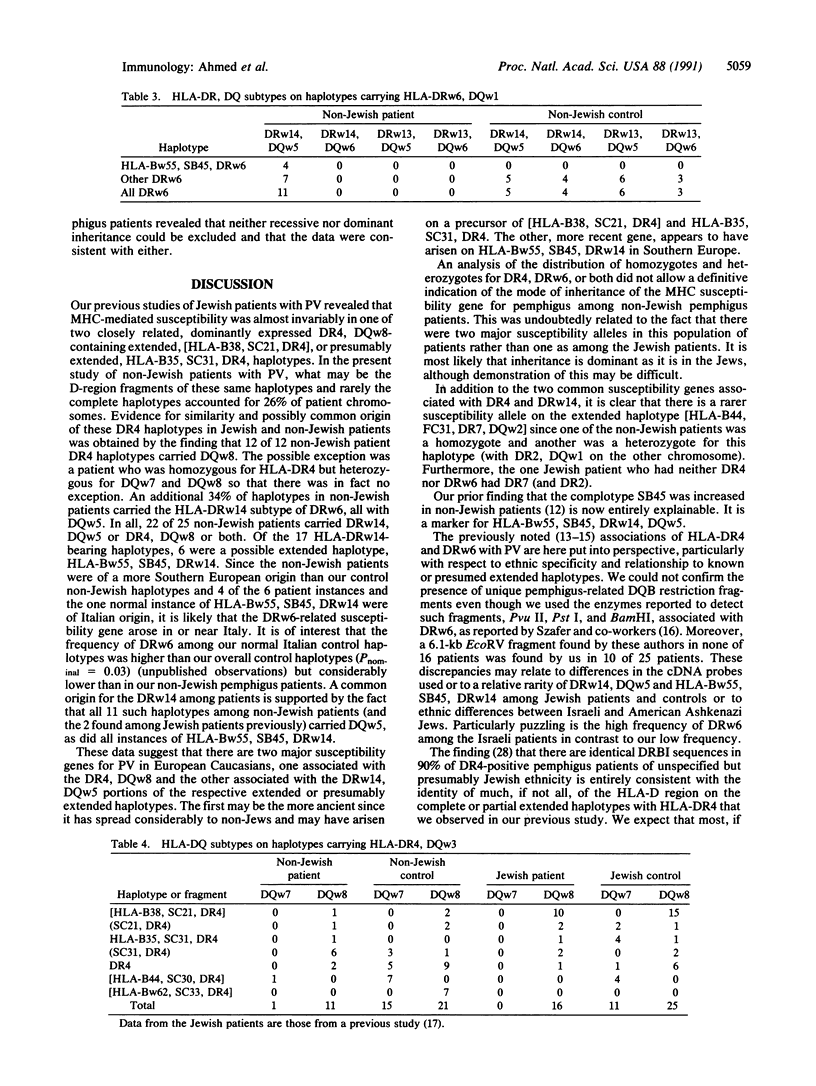
Previous studies demonstrated that HLA-DR4 was markedly increased among Ashkenazi Jewish patients with pemphigus vulgaris (PV), almost entirely as the common Jewish extended haplotype [HLA-B38, SC21, DR4, DQw8] or as the haplotype HLA-B35, SC31, DR4, DQw8, and that HLA-DR4, DQw8 was distributed among patients in a manner consistent with dominant expression of a class II (D-region or D-region-linked) susceptibility gene. In the present study of major histocompatibility complex (MHC) haplotypes in 25 non-Jewish PV patients, DR4, DQw8 was found in 12 of the patients and DRw6, DQw5 was found in 15. Only 3 patients had neither. Only 1 of the DR4, DQw8 haplotypes was [HLA-B38, SC21, DR4, DQw8] and 2 were HLA-B35, SC31, DR4, DQw8; most were the presumed fragments (SC31, DR4, DQw8) or (SC21, DR4, DQw8) or DR4, DQw8 with some other complotype. Of the patients with DRw6, DQw5, all were DRw14, DQw5, and 6 had a rare Caucasian haplotype, HLA-Bw55, SB45, DRw14, DQw5. Four of 6 of these were found in patients of Italian extraction, as was the 1 normal example. The non-Jewish patients were of more Southern European extraction than our controls. This suggests that there are two major MHC susceptibility alleles in American patients with PV. The more ancient apparently arose on a haplotype in the Jews, HLA-B38(35), SC21(SC31), DR4, DQw8, and spread to other populations largely as D-region segments. The other arose in or near Italy on the haplotype HLA-Bw55, SB45, DRw14, DQw5 and has also partially fragmented so that many patients carry only DRw14, DQw5. The available data do not permit the specific localization of either the DR4, DQw8- or the DRw14, DQw5-linked susceptibility genes.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ahmed A. R., Workman S. Anti-intercellular substance antibodies. Presence in serum samples of 14 patients without pemphigus. Arch Dermatol. 1983 Jan;119(1):17–21. doi: 10.1001/archderm.119.1.17. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ahmed A. R., Yunis E. J., Alper C. A. Complotypes in pemphigus vulgaris: differences between Jewish and non-Jewish patients. Hum Immunol. 1990 Apr;27(4):298–304. doi: 10.1016/0198-8859(90)90081-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ahmed A. R., Yunis E. J., Khatri K., Wagner R., Notani G., Awdeh Z., Alper C. A. Major histocompatibility complex haplotype studies in Ashkenazi Jewish patients with pemphigus vulgaris. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Oct;87(19):7658–7662. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.19.7658. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alper C. A., Boenisch T., Watson L. Genetic polymorphism in human glycine-rich beta-glycoprotein. J Exp Med. 1972 Jan;135(1):68–80. doi: 10.1084/jem.135.1.68. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alper C. A., Fleischnick E., Awdeh Z., Katz A. J., Yunis E. J. Extended major histocompatibility complex haplotypes in patients with gluten-sensitive enteropathy. J Clin Invest. 1987 Jan;79(1):251–256. doi: 10.1172/JCI112791. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alper C. A. Inherited structural polymorphism in human C2: evidence for genetic linkage between C2 and Bf. J Exp Med. 1976 Oct 1;144(4):1111–1115. doi: 10.1084/jem.144.4.1111. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alper C. A., Raum D., Karp S., Awdeh Z. L., Yunis E. J. Serum complement 'supergenes' of the major histocompatibility complex in man (complotypes). Vox Sang. 1983;45(1):62–67. doi: 10.1111/j.1423-0410.1983.tb04124.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anhalt G. J., Labib R. S., Voorhees J. J., Beals T. F., Diaz L. A. Induction of pemphigus in neonatal mice by passive transfer of IgG from patients with the disease. N Engl J Med. 1982 May 20;306(20):1189–1196. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198205203062001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Awdeh Z. L., Alper C. A. Inherited structural polymorphism of the fourth component of human complement. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jun;77(6):3576–3580. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.6.3576. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Awdeh Z. L., Raum D., Yunis E. J., Alper C. A. Extended HLA/complement allele haplotypes: evidence for T/t-like complex in man. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jan;80(1):259–263. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.1.259. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benacerraf B., McDevitt H. O. Histocompatibility-linked immune response genes. Science. 1972 Jan 21;175(4019):273–279. doi: 10.1126/science.175.4019.273. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brautbar C., Moscovitz M., Livshits T., Haim S., Hacham-Zadeh S., Cohen H. A., Sharon R., Nelken D., Cohen T. HLA-DRw4 in pemphigus vulgaris patients in Israel. Tissue Antigens. 1980 Sep;16(3):238–243. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0039.1980.tb00299.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlsson B., Wallin J., Böhme J., Möller E. HLA-DR-DQ haplotypes defined by restriction fragment analysis. Correlation to serology. Hum Immunol. 1987 Oct;20(2):95–113. doi: 10.1016/0198-8859(87)90025-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korman A. J., Boss J. M., Spies T., Sorrentino R., Okada K., Strominger J. L. Genetic complexity and expression of human class II histocompatibility antigens. Immunol Rev. 1985 Jul;85:45–86. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1985.tb01130.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korman N. Pemphigus. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1988 Jun;18(6):1219–1238. doi: 10.1016/s0190-9622(88)70128-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krain L. S., Terasaki P. I., Newcomer V. D., Mickey M. R. Increased frequency of HL-A10 in pemphigus vulgaris. Arch Dermatol. 1973 Dec;108(6):803–805. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Park M. S., Terasaki P. I., Ahmed A. R., Tiwari J. L. HLA-DRW4 in 91% of Jewish pemphigus vulgaris patients. Lancet. 1979 Sep 1;2(8140):441–442. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(79)91493-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raum D., Awdeh Z., Yunis E. J., Alper C. A., Gabbay K. H. Extended major histocompatibility complex haplotypes in type I diabetes mellitus. J Clin Invest. 1984 Aug;74(2):449–454. doi: 10.1172/JCI111441. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scharf S. J., Friedmann A., Brautbar C., Szafer F., Steinman L., Horn G., Gyllensten U., Erlich H. A. HLA class II allelic variation and susceptibility to pemphigus vulgaris. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 May;85(10):3504–3508. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.10.3504. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sinha A. A., Brautbar C., Szafer F., Friedmann A., Tzfoni E., Todd J. A., Steinman L., McDevitt H. O. A newly characterized HLA DQ beta allele associated with pemphigus vulgaris. Science. 1988 Feb 26;239(4843):1026–1029. doi: 10.1126/science.2894075. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szafer F., Brautbar C., Tzfoni E., Frankel G., Sherman L., Cohen I., Hacham-Zadeh S., Aberer W., Tappeiner G., Holubar K. Detection of disease-specific restriction fragment length polymorphisms in pemphigus vulgaris linked to the DQw1 and DQw3 alleles of the HLA-D region. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Sep;84(18):6542–6545. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.18.6542. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wasserstrum N., Laros R. K., Jr Transplacental transmission of pemphigus. JAMA. 1983 Mar 18;249(11):1480–1482. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zervas J., Tosca A., Apostolakis I., Varelzidis A. HLA and pemphigus. Br J Dermatol. 1979 Sep;101(3):357–358. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2133.1979.tb05633.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]