Abstract
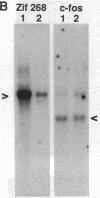
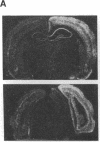
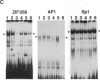
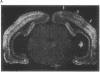
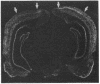
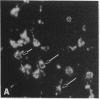
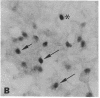
Transcription factors are rapidly and transiently induced in brain by excitatory stimuli and may be important in coordinating changes in gene expression underlying neuronal plasticity. In contrast to their transient induction after stimulation, certain transcription factors display stable, relatively high basal levels of expression in brain. Here we demonstrate that this "constitutive" expression of the transcription factor zif268 in cortex is driven by natural synaptic activity. Blockade of afferent visual activity with intraocular injections of tetrodotoxin results in rapid, dramatic reductions of Zif268 mRNA and immunoreactivity in visual cortex. Moreover, dark-adaptation for several days lowers zif268 expression in visual cortex, and expression rapidly returns to control levels upon subsequent light exposure. Several other transcription factors, which are induced in cortical neurons by excitatory stimuli, appear less responsive to changes in natural sensory input. These studies suggest that transcription factors play a role not only in responses to artificial stimuli but also in the normal maintenance of cortical physiology. Anatomic markers for zif268 may be useful in mapping normal cortical activity in brain.
Full text
PDF
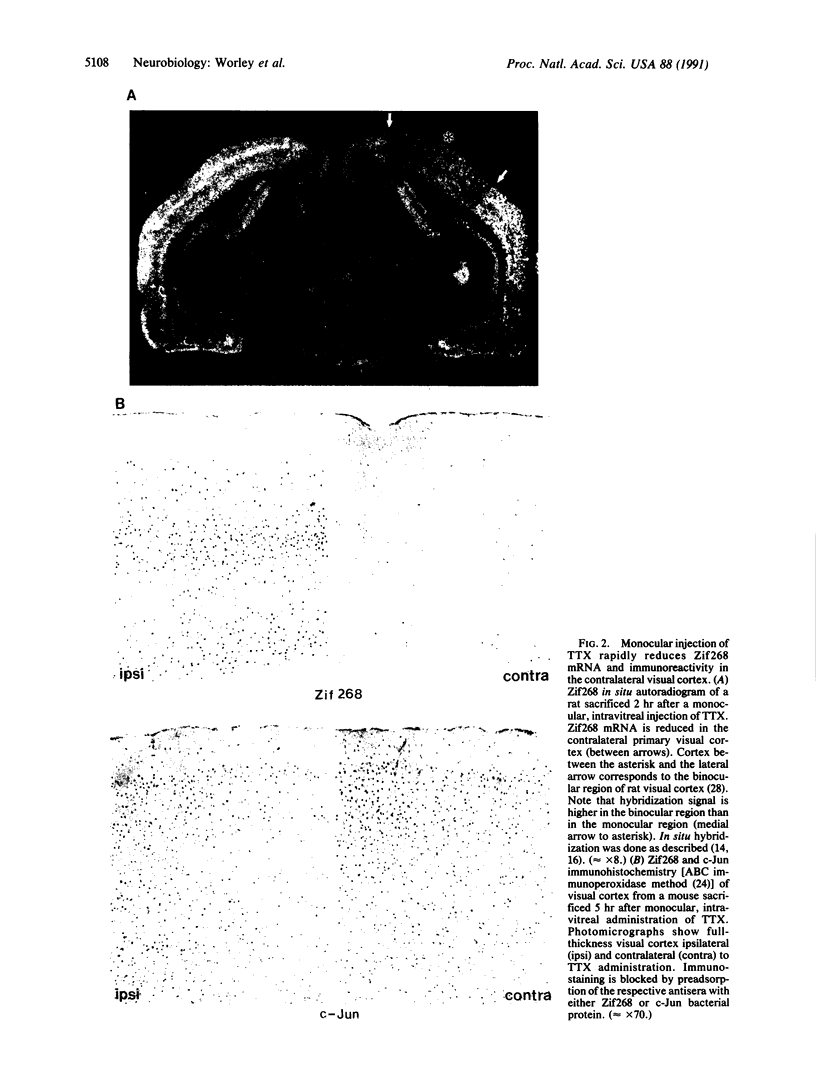
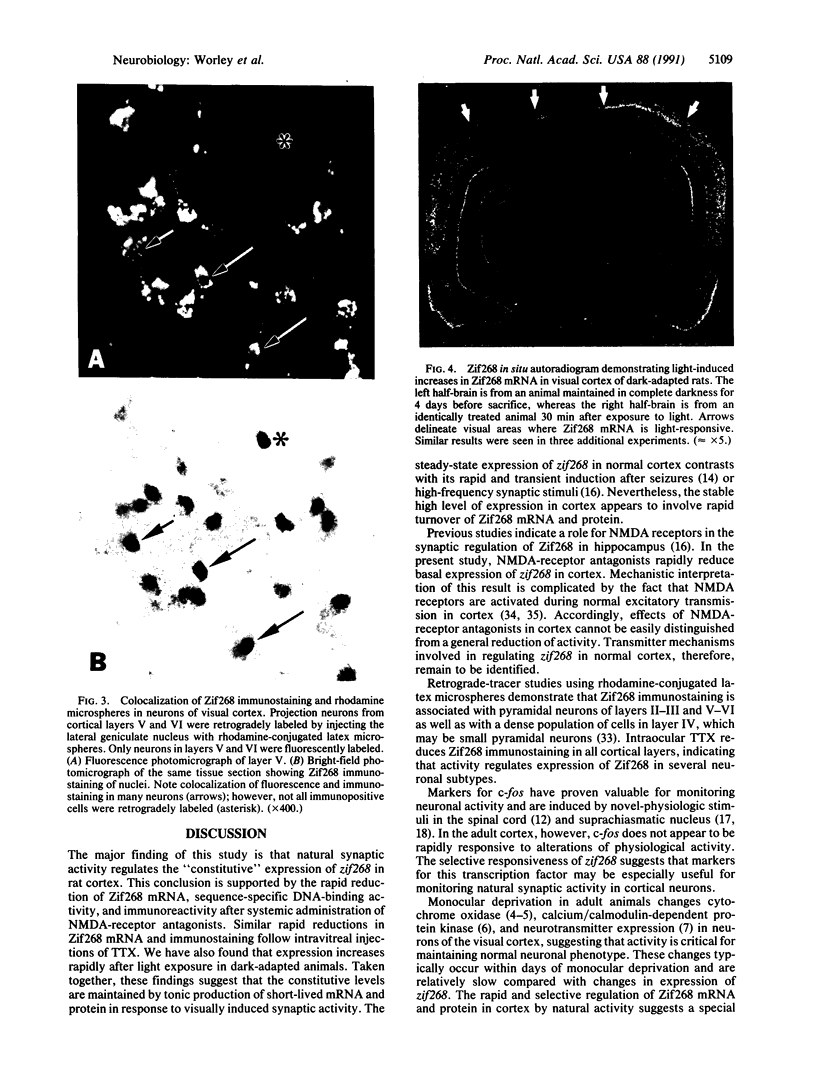

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aronin N., Sagar S. M., Sharp F. R., Schwartz W. J. Light regulates expression of a Fos-related protein in rat suprachiasmatic nuclei. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Aug;87(15):5959–5962. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.15.5959. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chavrier P., Vesque C., Galliot B., Vigneron M., Dollé P., Duboule D., Charnay P. The segment-specific gene Krox-20 encodes a transcription factor with binding sites in the promoter region of the Hox-1.4 gene. EMBO J. 1990 Apr;9(4):1209–1218. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08228.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christy B. A., Lau L. F., Nathans D. A gene activated in mouse 3T3 cells by serum growth factors encodes a protein with "zinc finger" sequences. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Nov;85(21):7857–7861. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.21.7857. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christy B., Nathans D. DNA binding site of the growth factor-inducible protein Zif268. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Nov;86(22):8737–8741. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.22.8737. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cole A. J., Saffen D. W., Baraban J. M., Worley P. F. Rapid increase of an immediate early gene messenger RNA in hippocampal neurons by synaptic NMDA receptor activation. Nature. 1989 Aug 10;340(6233):474–476. doi: 10.1038/340474a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dignam J. D., Lebovitz R. M., Roeder R. G. Accurate transcription initiation by RNA polymerase II in a soluble extract from isolated mammalian nuclei. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Mar 11;11(5):1475–1489. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.5.1475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dubin M. W., Stark L. A., Archer S. M. A role for action-potential activity in the development of neuronal connections in the kitten retinogeniculate pathway. J Neurosci. 1986 Apr;6(4):1021–1036. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.06-04-01021.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellis R. W., Defeo D., Shih T. Y., Gonda M. A., Young H. A., Tsuchida N., Lowy D. R., Scolnick E. M. The p21 src genes of Harvey and Kirsten sarcoma viruses originate from divergent members of a family of normal vertebrate genes. Nature. 1981 Aug 6;292(5823):506–511. doi: 10.1038/292506a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goelet P., Castellucci V. F., Schacher S., Kandel E. R. The long and the short of long-term memory--a molecular framework. 1986 Jul 31-Aug 6Nature. 322(6078):419–422. doi: 10.1038/322419a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUBEL D. H., WIESEL T. N. Shape and arrangement of columns in cat's striate cortex. J Physiol. 1963 Mar;165:559–568. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1963.sp007079. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagihara K., Tsumoto T., Sato H., Hata Y. Actions of excitatory amino acid antagonists on geniculo-cortical transmission in the cat's visual cortex. Exp Brain Res. 1988;69(2):407–416. doi: 10.1007/BF00247586. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hendry S. H., Jones E. G. Reduction in number of immunostained GABAergic neurones in deprived-eye dominance columns of monkey area 17. Nature. 1986 Apr 24;320(6064):750–753. doi: 10.1038/320750a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hendry S. H., Kennedy M. B. Immunoreactivity for a calmodulin-dependent protein kinase is selectively increased in macaque striate cortex after monocular deprivation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Mar;83(5):1536–1540. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.5.1536. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hubel D. H., Wiesel T. N. The period of susceptibility to the physiological effects of unilateral eye closure in kittens. J Physiol. 1970 Feb;206(2):419–436. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1970.sp009022. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunt S. P., Pini A., Evan G. Induction of c-fos-like protein in spinal cord neurons following sensory stimulation. Nature. 1987 Aug 13;328(6131):632–634. doi: 10.1038/328632a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaas J. H., Krubitzer L. A., Chino Y. M., Langston A. L., Polley E. H., Blair N. Reorganization of retinotopic cortical maps in adult mammals after lesions of the retina. Science. 1990 Apr 13;248(4952):229–231. doi: 10.1126/science.2326637. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz L. C., Burkhalter A., Dreyer W. J. Fluorescent latex microspheres as a retrograde neuronal marker for in vivo and in vitro studies of visual cortex. Nature. 1984 Aug 9;310(5977):498–500. doi: 10.1038/310498a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lodge D., Davies S. N., Jones M. G., Millar J., Manallack D. T., Ornstein P. L., Verberne A. J., Young N., Beart P. M. A comparison between the in vivo and in vitro activity of five potent and competitive NMDA antagonists. Br J Pharmacol. 1988 Nov;95(3):957–965. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1988.tb11726.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mastronarde D. N. Correlated firing of cat retinal ganglion cells. I. Spontaneously active inputs to X- and Y-cells. J Neurophysiol. 1983 Feb;49(2):303–324. doi: 10.1152/jn.1983.49.2.303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller K. D., Chapman B., Stryker M. P. Visual responses in adult cat visual cortex depend on N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jul;86(13):5183–5187. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.13.5183. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan J. I., Cohen D. R., Hempstead J. L., Curran T. Mapping patterns of c-fos expression in the central nervous system after seizure. Science. 1987 Jul 10;237(4811):192–197. doi: 10.1126/science.3037702. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakabeppu Y., Ryder K., Nathans D. DNA binding activities of three murine Jun proteins: stimulation by Fos. Cell. 1988 Dec 2;55(5):907–915. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90146-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rusak B., Robertson H. A., Wisden W., Hunt S. P. Light pulses that shift rhythms induce gene expression in the suprachiasmatic nucleus. Science. 1990 Jun 8;248(4960):1237–1240. doi: 10.1126/science.2112267. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saffen D. W., Cole A. J., Worley P. F., Christy B. A., Ryder K., Baraban J. M. Convulsant-induced increase in transcription factor messenger RNAs in rat brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Oct;85(20):7795–7799. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.20.7795. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheng M., Greenberg M. E. The regulation and function of c-fos and other immediate early genes in the nervous system. Neuron. 1990 Apr;4(4):477–485. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(90)90106-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sonnenberg J. L., Macgregor-Leon P. F., Curran T., Morgan J. I. Dynamic alterations occur in the levels and composition of transcription factor AP-1 complexes after seizure. Neuron. 1989 Sep;3(3):359–365. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(89)90260-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stryker M. P., Harris W. A. Binocular impulse blockade prevents the formation of ocular dominance columns in cat visual cortex. J Neurosci. 1986 Aug;6(8):2117–2133. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.06-08-02117.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson M. A., Milbrandt J. The NGFI-B gene, a transcriptionally inducible member of the steroid receptor gene superfamily: genomic structure and expression in rat brain after seizure induction. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Oct;9(10):4213–4219. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.10.4213. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiesel T. N., Hubel D. H. Comparison of the effects of unilateral and bilateral eye closure on cortical unit responses in kittens. J Neurophysiol. 1965 Nov;28(6):1029–1040. doi: 10.1152/jn.1965.28.6.1029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong E. H., Kemp J. A., Priestley T., Knight A. R., Woodruff G. N., Iversen L. L. The anticonvulsant MK-801 is a potent N-methyl-D-aspartate antagonist. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Sep;83(18):7104–7108. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.18.7104. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Worley P. F., Baraban J. M., Van Dop C., Neer E. J., Snyder S. H. Go, a guanine nucleotide-binding protein: immunohistochemical localization in rat brain resembles distribution of second messenger systems. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jun;83(12):4561–4565. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.12.4561. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zilles K., Wree A., Schleicher A., Divac I. The monocular and binocular subfields of the rat's primary visual cortex: a quantitative morphological approach. J Comp Neurol. 1984 Jul 1;226(3):391–402. doi: 10.1002/cne.902260308. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]