Abstract
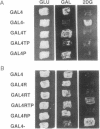
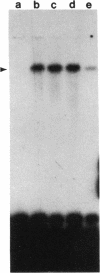
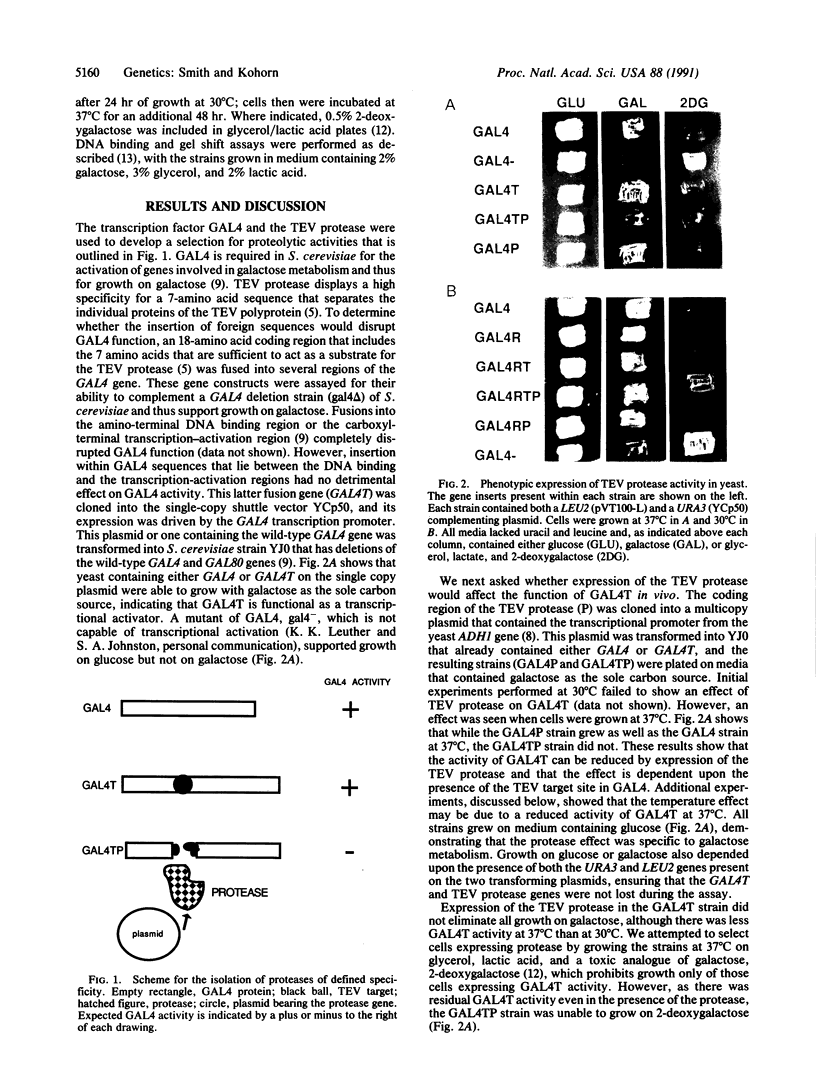
We have developed a simple genetic selection that could be used to isolate eukaryotic cDNAs encoding proteases that cleave within a defined amino acid sequence. The selection was developed by using the transcription factor GAL4 from Saccharomyces cerevisiae as a selectable marker, a cloned protease from tobacco etch virus (TEV), and an 18-amino acid TEV protease target sequence. In yeast, TEV protease cleaves its target even when the target is fused to internal regions of the GAL4 protein. This cleavage separates the DNA binding domain from the transcription activation domain of GAL4, rendering it transcriptionally inactive. The proteolytic cleavage can be detected phenotypically by the inability of cells to metabolize galactose. Cells expressing the TEV protease can also be selected on the suicide substrate 2-deoxygalactose. DNA binding studies show that the TEV protease decreases the activity of the GAL4/target fusion protein. Because another protease target sequence of 55 amino acids can be inserted into GAL4 without any loss of transcriptional activity, this assay offers the opportunity to use high-efficiency cDNA cloning and expression vectors to select coding sequences of other proteases from various species. The assay could also be used to help define both target specificities and functional domains of proteases.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Corton J. C., Johnston S. A. Altering DNA-binding specificity of GAL4 requires sequences adjacent to the zinc finger. Nature. 1989 Aug 31;340(6236):724–727. doi: 10.1038/340724a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dougherty W. G., Carrington J. C., Cary S. M., Parks T. D. Biochemical and mutational analysis of a plant virus polyprotein cleavage site. EMBO J. 1988 May;7(5):1281–1287. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02942.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elledge S. J., Mulligan J. T., Ramer S. W., Spottswood M., Davis R. W. Lambda YES: a multifunctional cDNA expression vector for the isolation of genes by complementation of yeast and Escherichia coli mutations. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Mar 1;88(5):1731–1735. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.5.1731. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito H., Fukuda Y., Murata K., Kimura A. Transformation of intact yeast cells treated with alkali cations. J Bacteriol. 1983 Jan;153(1):163–168. doi: 10.1128/jb.153.1.163-168.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnston M., Davis R. W. Sequences that regulate the divergent GAL1-GAL10 promoter in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Aug;4(8):1440–1448. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.8.1440. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keegstra K. Transport and routing of proteins into chloroplasts. Cell. 1989 Jan 27;56(2):247–253. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90898-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laughon A., Gesteland R. F. Primary structure of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae GAL4 gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Feb;4(2):260–267. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.2.260. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matrisian L. M. Metalloproteinases and their inhibitors in matrix remodeling. Trends Genet. 1990 Apr;6(4):121–125. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(90)90126-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray A. W., Solomon M. J., Kirschner M. W. The role of cyclin synthesis and degradation in the control of maturation promoting factor activity. Nature. 1989 May 25;339(6222):280–286. doi: 10.1038/339280a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Platt T. Toxicity of 2-deoxygalactose to Saccharomyces cerevisiae cells constitutively synthesizing galactose-metabolizing enzymes. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 May;4(5):994–996. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.5.994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salmeron J. M., Jr, Langdon S. D., Johnston S. A. Interaction between transcriptional activator protein LAC9 and negative regulatory protein GAL80. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Jul;9(7):2950–2956. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.7.2950. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vernet T., Dignard D., Thomas D. Y. A family of yeast expression vectors containing the phage f1 intergenic region. Gene. 1987;52(2-3):225–233. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(87)90049-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]