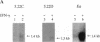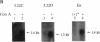Abstract
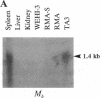
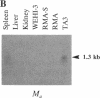
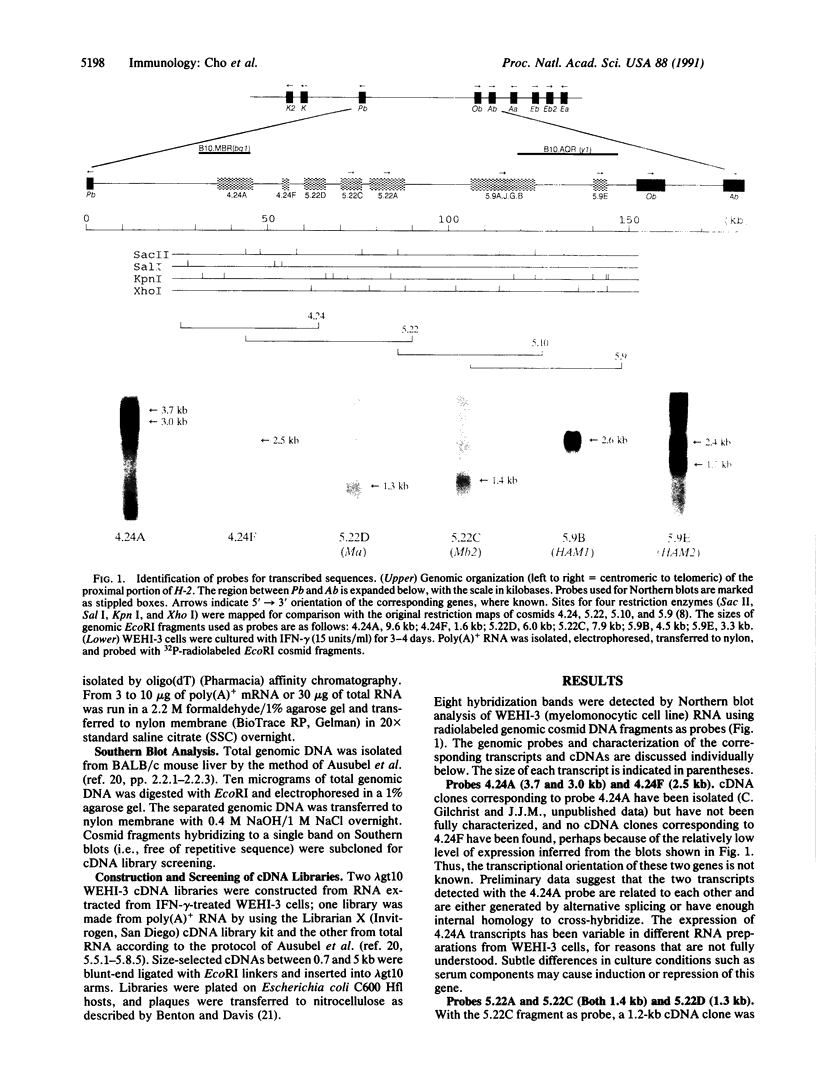
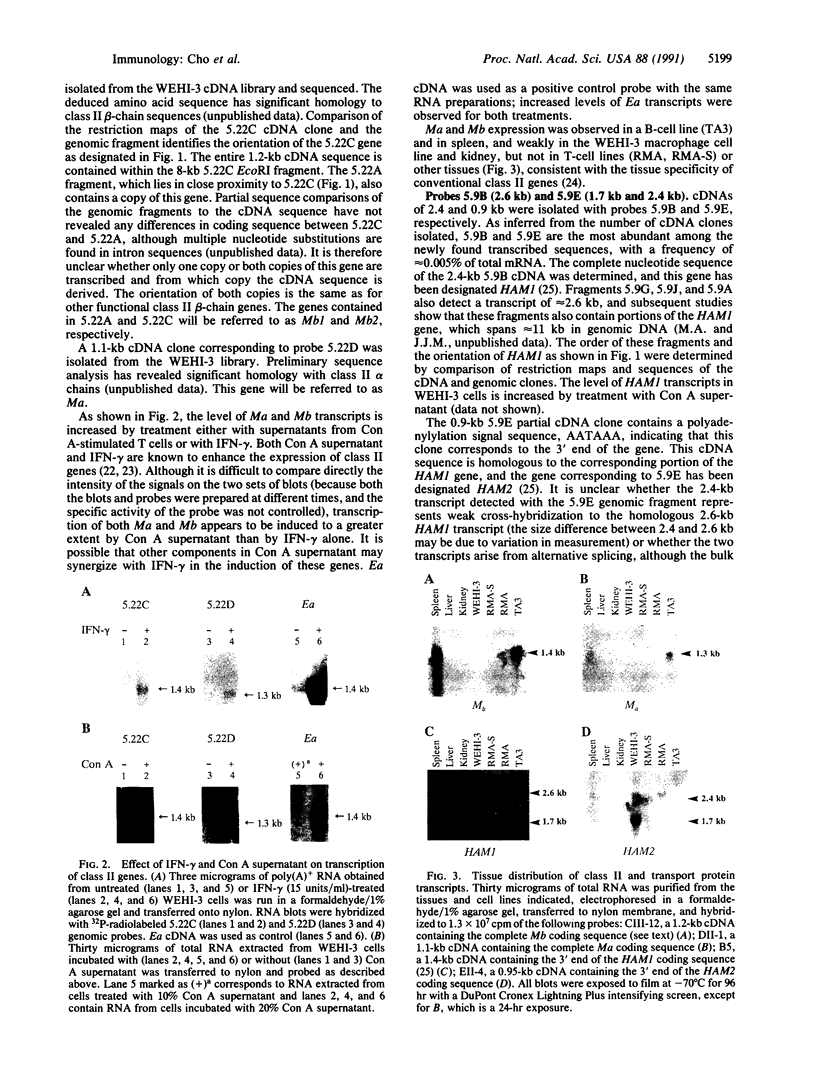
The region of the murine major histocompatibility complex (MHC) between the Pb (A beta 3) and Ob (A beta 2) genes controls the expression of an intracellular complex named the LMP (low molecular weight polypeptide) complex. DNA probes for at least seven different genes mapping to this region were isolated. These hybridize to a minimum of eight different transcripts ranging from approximately 1.3 to 3.7 kilobases (kb). The deduced amino acid sequences of the corresponding cDNAs indicate that three of these genes are new members of the MHC class II gene family. These genes are transcribed in a tissue-specific pattern similar to that of the traditional class II genes. Two of the remaining four genes, HAM1 and HAM2, are homologous to one another and to a family of eukaryotic and prokaryotic transport proteins and may be involved in antigen processing. The tissue distribution of HAM1 transcripts is consistent with its proposed role in class I-restricted antigen processing, whereas HAM2 transcription appears more restricted and may be involved in antigen processing for class II-restricted T cells. The HAM2 gene may produce two differentially spliced transcripts. The identity of the remaining two genes is not known. Analyses of transcript sizes, tissue distribution, sequence, and genetic mapping data suggest that none of these genes code for LMP antigens.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bell J. I., Denny D. W., Jr, McDevitt H. O. Structure and polymorphism of murine and human class II major histocompatibility antigens. Immunol Rev. 1985 Jul;84:51–71. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1985.tb01125.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benton W. D., Davis R. W. Screening lambdagt recombinant clones by hybridization to single plaques in situ. Science. 1977 Apr 8;196(4286):180–182. doi: 10.1126/science.322279. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chaplin D. D. Molecular organization and in vitro expression of murine class III genes. Immunol Rev. 1985 Oct;87:61–80. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1985.tb01145.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Favaloro J., Treisman R., Kamen R. Transcription maps of polyoma virus-specific RNA: analysis by two-dimensional nuclease S1 gel mapping. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):718–749. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65070-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. "A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity". Addendum. Anal Biochem. 1984 Feb;137(1):266–267. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90381-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flavell R. A., Allen H., Huber B., Wake C., Widera G. Organization and expression of the MHC of the C57 black/10 mouse. Immunol Rev. 1985 Jul;84:29–50. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1985.tb01124.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glimcher L. H., Hamano T., Asofsky R., Sachs D. H., Pierres M., Samelson L. E., Sharrow S. O., Paul W. E. IA mutant functional antigen-presenting cell lines. J Immunol. 1983 May;130(5):2287–2294. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kärre K., Ljunggren H. G., Piontek G., Kiessling R. Selective rejection of H-2-deficient lymphoma variants suggests alternative immune defence strategy. Nature. 1986 Feb 20;319(6055):675–678. doi: 10.1038/319675a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le Meur M., Gerlinger P., Benoist C., Mathis D. Correcting an immune-response deficiency by creating E alpha gene transgenic mice. Nature. 1985 Jul 4;316(6023):38–42. doi: 10.1038/316038a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathis D. J., Benoist C. O., Williams V. E., 2nd, Kanter M. R., McDevitt H. O. The murine E alpha immune response gene. Cell. 1983 Mar;32(3):745–754. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90060-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mellins E., Smith L., Arp B., Cotner T., Celis E., Pious D. Defective processing and presentation of exogenous antigens in mutants with normal HLA class II genes. Nature. 1990 Jan 4;343(6253):71–74. doi: 10.1038/343071a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monaco J. J., Cho S., Attaya M. Transport protein genes in the murine MHC: possible implications for antigen processing. Science. 1990 Dec 21;250(4988):1723–1726. doi: 10.1126/science.2270487. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monaco J. J., McDevitt H. O. H-2-linked low-molecular weight polypeptide antigens assemble into an unusual macromolecular complex. 1984 Jun 28-Jul 4Nature. 309(5971):797–799. doi: 10.1038/309797a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monaco J. J., McDevitt H. O. Identification of a fourth class of proteins linked to the murine major histocompatibility complex. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 May;79(9):3001–3005. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.9.3001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monaco J. J., McDevitt H. O. The LMP antigens: a stable MHC-controlled multisubunit protein complex. Hum Immunol. 1986 Apr;15(4):416–426. doi: 10.1016/0198-8859(86)90019-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller U., Jongeneel C. V., Nedospasov S. A., Lindahl K. F., Steinmetz M. Tumour necrosis factor and lymphotoxin genes map close to H-2D in the mouse major histocompatibility complex. Nature. 1987 Jan 15;325(6101):265–267. doi: 10.1038/325265a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura M., Manser T., Pearson G. D., Daley M. J., Gefter M. L. Effect of IFN-gamma on the immune response in vivo and on gene expression in vitro. 1984 Jan 26-Feb 1Nature. 307(5949):381–382. doi: 10.1038/307381a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosa F., Hatat D., Abadie A., Fellous M. Regulation of histocompatibility antigens by interferon. Ann Inst Pasteur Immunol. 1985 Jan-Feb;136C(1):103–119. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steeg P. S., Moore R. N., Oppenheim J. J. Regulation of murine macrophage Ia-antigen expression by products of activated spleen cells. J Exp Med. 1980 Dec 1;152(6):1734–1744. doi: 10.1084/jem.152.6.1734. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinmetz M., Stephan D., Fischer Lindahl K. Gene organization and recombinational hotspots in the murine major histocompatibility complex. Cell. 1986 Mar 28;44(6):895–904. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90012-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strunk R. C., Cole F. S., Perlmutter D. H., Colten H. R. gamma-Interferon increases expression of class III complement genes C2 and factor B in human monocytes and in murine fibroblasts transfected with human C2 and factor B genes. J Biol Chem. 1985 Dec 5;260(28):15280–15285. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uematsu Y., Fischer Lindahl K., Steinmetz M. The same MHC recombinational hot spots are active in crossing-over between wild/wild and wild/inbred mouse chromosomes. Immunogenetics. 1988;27(2):96–101. doi: 10.1007/BF00351082. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White P. C., Chaplin D. D., Weis J. H., Dupont B., New M. I., Seidman J. G. Two steroid 21-hydroxylase genes are located in the murine S region. 1984 Nov 29-Dec 5Nature. 312(5993):465–467. doi: 10.1038/312465a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Widera G., Flavell R. A. The I region of the C57BL/10 mouse: characterization and physical linkage to H-2K of an SB beta-like class II pseudogene, psi A beta 3. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Aug;82(16):5500–5504. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.16.5500. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong G. H., Clark-Lewis I., Harris A. W., Schrader J. W. Effect of cloned interferon-gamma on expression of H-2 and Ia antigens on cell lines of hemopoietic, lymphoid, epithelial, fibroblastic and neuronal origin. Eur J Immunol. 1984 Jan;14(1):52–56. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830140110. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]