Abstract
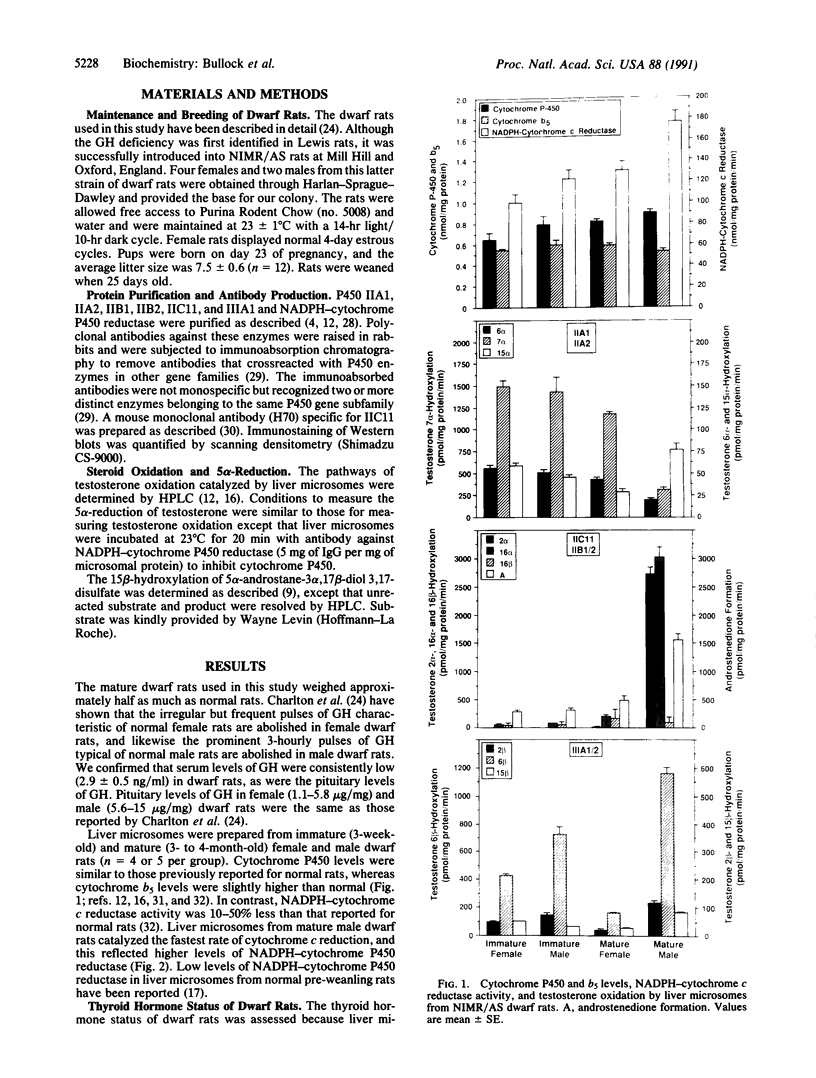
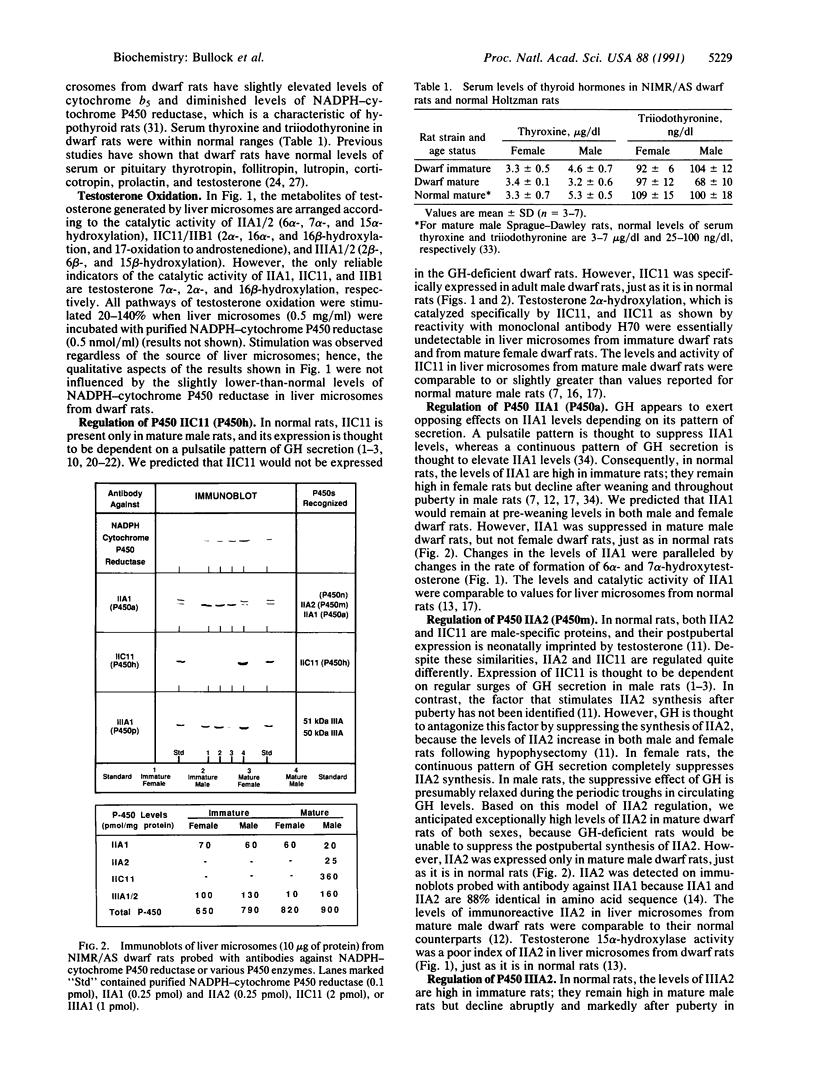
Differences in the pattern of growth hormone (GH) secretion in mature rats (i.e., "continuous" secretion in females versus "pulsatile" secretion in males) are thought to be the underlying cause of sex-dependent differences in a subpopulation of liver microsomal P450 enzymes and steroid 5 alpha-reductase. A new strain of dwarf rats (NIMR/AS) has recently been shown to have low or undetectable levels of circulating GH due to a selective defect in pituitary GH synthesis. We have measured the levels and/or activity of IIA1 (P450a), IIA2 (P450m), IIC11 (P450h), IIC12 (P450i), IIIA2 (a P450p isozyme), and steroid 5 alpha-reductase in liver microsomes from male and female dwarf rats, to test the hypothesis that the expression of these sexually dimorphic enzymes is regulated by GH. In mature rats, the levels of liver microsomal IIA2, IIC11, and IIIA2 were higher in male than in female dwarf rats, whereas the levels of activity of IIA1, IIC12, and steroid 5 alpha-reductase were greater in female than in male dwarf rats. These sex differences resulted from age-related changes in either male dwarf rats (i.e., an increase in IIC11 and IIA2 and a decrease in IIA1) or female dwarf rats (i.e., an increase in IIC12 and 5 alpha-reductase and a decrease in IIIA2). The magnitudes of these sex-dependent, age-related changes were essentially indistinguishable from those observed in normal rats. These unexpected results suggest that GH is not the pituitary factor responsible for regulating the levels of sexually dimorphic, steroid-metabolizing enzymes in rat liver. Alternatively, it is possible that these enzymes are regulated by extremely low levels of GH. In either case, the current model of how steroid-metabolizing enzymes are regulated in rats must be revised to account for the normal sexual differentiation of these enzymes in dwarf rats.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arlotto M. P., Greenway D. J., Parkinson A. Purification of two isozymes of rat liver microsomal cytochrome P450 with testosterone 7 alpha-hydroxylase activity. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1989 May 1;270(2):441–457. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(89)90526-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arlotto M. P., Parkinson A. Identification of cytochrome P450a (P450IIA1) as the principal testosterone 7 alpha-hydroxylase in rat liver microsomes and its regulation by thyroid hormones. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1989 May 1;270(2):458–471. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(89)90527-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bartlett J. M., Charlton H. M., Robinson I. C., Nieschlag E. Pubertal development and testicular function in the male growth hormone-deficient rat. J Endocrinol. 1990 Aug;126(2):193–201. doi: 10.1677/joe.0.1260193. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carmignac D. F., Robinson I. C. Growth hormone (GH) secretion in the dwarf rat: release, clearance and responsiveness to GH-releasing factor and somatostatin. J Endocrinol. 1990 Oct;127(1):69–75. doi: 10.1677/joe.0.1270069. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Charlton H. M., Clark R. G., Robinson I. C., Goff A. E., Cox B. S., Bugnon C., Bloch B. A. Growth hormone-deficient dwarfism in the rat: a new mutation. J Endocrinol. 1988 Oct;119(1):51–58. doi: 10.1677/joe.0.1190051. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonzalez F. J., Song B. J., Hardwick J. P. Pregnenolone 16 alpha-carbonitrile-inducible P-450 gene family: gene conversion and differential regulation. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Aug;6(8):2969–2976. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.8.2969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonzalez F. J. The molecular biology of cytochrome P450s. Pharmacol Rev. 1988 Dec;40(4):243–288. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorski J. R., Arlotto M. P., Klaassen C. D., Parkinson A. Age- and sex-dependent induction of liver microsomal benzo[a]pyrene hydroxylase activity in rats treated with pregnenolone-16 alpha-carbonitrile (PCN). Carcinogenesis. 1985 Apr;6(4):617–624. doi: 10.1093/carcin/6.4.617. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guzelian P. S., Li D., Schuetz E. G., Thomas P., Levin W., Mode A., Gustafsson J. A. Sex change in cytochrome P-450 phenotype by growth hormone treatment of adult rat hepatocytes maintained in a culture system on matrigel. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Dec;85(24):9783–9787. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.24.9783. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halvorson M., Greenway D., Eberhart D., Fitzgerald K., Parkinson A. Reconstitution of testosterone oxidation by purified rat cytochrome P450p (IIIA1). Arch Biochem Biophys. 1990 Feb 15;277(1):166–180. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(90)90566-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jansson J. O., Edén S., Isaksson O. Sexual dimorphism in the control of growth hormone secretion. Endocr Rev. 1985 Spring;6(2):128–150. doi: 10.1210/edrv-6-2-128. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jeffery S., Carter N. D., Clark R. G., Robinson I. C. The episodic secretory pattern of growth hormone regulates liver carbonic anhydrase III. Studies in normal and mutant growth-hormone-deficient dwarf rats. Biochem J. 1990 Feb 15;266(1):69–74. doi: 10.1042/bj2660069. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamataki T., Maeda K., Yamazoe Y., Nagai T., Kato R. Sex difference of cytochrome P-450 in the rat: purification, characterization, and quantitation of constitutive forms of cytochrome P-450 from liver microsomes of male and female rats. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1983 Sep;225(2):758–770. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(83)90087-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsunaga T., Nagata K., Holsztynska E. J., Lapenson D. P., Smith A., Kato R., Gelboin H. V., Waxman D. J., Gonzalez F. J. Gene conversion and differential regulation in the rat P-450 IIA gene subfamily. Purification, catalytic activity, cDNA and deduced amino acid sequence, and regulation of an adult male-specific hepatic testosterone 15 alpha-hydroxylase. J Biol Chem. 1988 Dec 5;263(34):17995–18002. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mode A., Norstedt G., Eneroth P., Gustafsson J. A. Purification of liver feminizing factor from rat pituitaries and demonstration of its identity with growth hormone. Endocrinology. 1983 Oct;113(4):1250–1260. doi: 10.1210/endo-113-4-1250. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mode A., Norstedt G., Simic B., Eneroth P., Gustafsson J. A. Continuous infusion of growth hormone feminizes hepatic steroid metabolism in the rat. Endocrinology. 1981 Jun;108(6):2103–2108. doi: 10.1210/endo-108-6-2103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mode A., Wiersma-Larsson E., Ström A., Zaphiropoulos P. G., Gustafsson J. A. A dual role of growth hormone as a feminizing and masculinizing factor in the control of sex-specific cytochrome P-450 isozymes in rat liver. J Endocrinol. 1989 Feb;120(2):311–317. doi: 10.1677/joe.0.1200311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan E. T., MacGeoch C., Gustafsson J. A. Hormonal and developmental regulation of expression of the hepatic microsomal steroid 16 alpha-hydroxylase cytochrome P-450 apoprotein in the rat. J Biol Chem. 1985 Oct 5;260(22):11895–11898. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagata K., Gonzalez F. J., Yamazoe Y., Kato R. Purification and characterization of four catalytically active testosterone 6 beta-hydroxylase P-450s from rat liver microsomes: comparison of a novel form with three structurally and functionally related forms. J Biochem. 1990 May;107(5):718–725. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a123115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norstedt G., Mode A., Eneroth P., Gustafsson J. A. Induction of prolactin receptors in rat liver after the administration of growth hormone. Endocrinology. 1981 May;108(5):1855–1861. doi: 10.1210/endo-108-5-1855. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norstedt G., Mode A., Hökfelt T., Eneroth P., Elde R., Ferland L., Labrie F., Gustafsson J. A. Possible role of somatostatin in the regulation of the sexually differentiated steroid metabolism and prolactin receptor in rat liver. Endocrinology. 1983 Mar;112(3):1076–1090. doi: 10.1210/endo-112-3-1076. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reik L. M., Maines S. L., Ryan D. E., Levin W., Bandiera S., Thomas P. E. A simple, non-chromatographic purification procedure for monoclonal antibodies. Isolation of monoclonal antibodies against cytochrome P450 isozymes. J Immunol Methods. 1987 Jun 26;100(1-2):123–130. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(87)90180-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rozman K., Hazelton G. A., Klaassen C. D., Arlotto M. P., Parkinson A. Effect of thyroid hormones on liver microsomal enzyme induction in rats exposed to 2,3,7,8,-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin. Toxicology. 1985 Oct;37(1-2):51–63. doi: 10.1016/0300-483x(85)90112-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell S. M., Vodian M. A., Hughes J. P., Nicoll C. S. Electrophoretic separation of forms of rat growth hormone with different bioassay and radioimmunoassay activities: comparison of intraglandular and secreted forms. Life Sci. 1978 Dec 11;23(24):2373–2382. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(78)90295-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryan D. E., Dixon R., Evans R. H., Ramanathan L., Thomas P. E., Wood A. W., Levin W. Rat hepatic cytochrome P-450 isozyme specificity for the metabolism of the steroid sulfate, 5 alpha-androstane-3 alpha, 17 beta-diol-3,17-disulfate. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1984 Sep;233(2):636–642. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(84)90489-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryan D. E., Levin W. Purification and characterization of hepatic microsomal cytochrome P-450. Pharmacol Ther. 1990;45(2):153–239. doi: 10.1016/0163-7258(90)90029-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapiro B. H., MacLeod J. N., Pampori N. A., Morrissey J. J., Lapenson D. P., Waxman D. J. Signalling elements in the ultradian rhythm of circulating growth hormone regulating expression of sex-dependent forms of hepatic cytochrome P450. Endocrinology. 1989 Dec;125(6):2935–2944. doi: 10.1210/endo-125-6-2935. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skett P. Biochemical basis of sex differences in drug metabolism. Pharmacol Ther. 1988;38(3):269–304. doi: 10.1016/0163-7258(88)90007-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skottner A., Clark R. G., Fryklund L., Robinson I. C. Growth responses in a mutant dwarf rat to human growth hormone and recombinant human insulin-like growth factor I. Endocrinology. 1989 May;124(5):2519–2526. doi: 10.1210/endo-124-5-2519. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sonderfan A. J., Arlotto M. P., Dutton D. R., McMillen S. K., Parkinson A. Regulation of testosterone hydroxylation by rat liver microsomal cytochrome P-450. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1987 May 15;255(1):27–41. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(87)90291-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas P. E., Reik L. M., Ryan D. E., Levin W. Regulation of three forms of cytochrome P-450 and epoxide hydrolase in rat liver microsomes. Effects of age, sex, and induction. J Biol Chem. 1981 Jan 25;256(2):1044–1052. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waxman D. J., Dannan G. A., Guengerich F. P. Regulation of rat hepatic cytochrome P-450: age-dependent expression, hormonal imprinting, and xenobiotic inducibility of sex-specific isoenzymes. Biochemistry. 1985 Jul 30;24(16):4409–4417. doi: 10.1021/bi00337a023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waxman D. J. Interactions of hepatic cytochromes P-450 with steroid hormones. Regioselectivity and stereospecificity of steroid metabolism and hormonal regulation of rat P-450 enzyme expression. Biochem Pharmacol. 1988 Jan 1;37(1):71–84. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(88)90756-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waxman D. J., LeBlanc G. A., Morrissey J. J., Staunton J., Lapenson D. P. Adult male-specific and neonatally programmed rat hepatic P-450 forms RLM2 and 2a are not dependent on pulsatile plasma growth hormone for expression. J Biol Chem. 1988 Aug 15;263(23):11396–11406. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waxman D. J., Morrissey J. J., LeBlanc G. A. Female-predominant rat hepatic P-450 forms j (IIE1) and 3 (IIA1) are under hormonal regulatory controls distinct from those of the sex-specific P-450 forms. Endocrinology. 1989 Jun;124(6):2954–2966. doi: 10.1210/endo-124-6-2954. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waxman D. J., Morrissey J. J., Leblanc G. A. Hypophysectomy differentially alters P-450 protein levels and enzyme activities in rat liver: pituitary control of hepatic NADPH cytochrome P-450 reductase. Mol Pharmacol. 1989 Apr;35(4):519–525. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waxman D. J., Morrissey J. J., MacLeod J. N., Shapiro B. H. Depletion of serum growth hormone in adult female rats by neonatal monosodium glutamate treatment without loss of female-specific hepatic enzymes P450 2d (IIC12) and steroid 5 alpha-reductase. Endocrinology. 1990 Feb;126(2):712–720. doi: 10.1210/endo-126-2-712. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waxman D. J., Ram P. A., Notani G., LeBlanc G. A., Alberta J. A., Morrissey J. J., Sundseth S. S. Pituitary regulation of the male-specific steroid 6 beta-hydroxylase P-450 2a (gene product IIIA2) in adult rat liver. Suppressive influence of growth hormone and thyroxine acting at a pretranslational leve;. Mol Endocrinol. 1990 Mar;4(3):447–454. doi: 10.1210/mend-4-3-447. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamazoe Y., Murayama N., Shimada M., Yamauchi K., Nagata K., Imaoka S., Funae Y., Kato R. A sex-specific form of cytochrome P-450 catalyzing propoxycoumarin O-depropylation and its identity with testosterone 6 beta-hydroxylase in untreated rat livers: reconstitution of the activity with microsomal lipids. J Biochem. 1988 Nov;104(5):785–790. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a122550. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamazoe Y., Shimada M., Kamataki T., Kato R. Effects of hypophysectomy and growth hormone treatment on sex-specific forms of cytochrome P-450 in relation to drug and steroid metabolisms in rat liver microsomes. Jpn J Pharmacol. 1986 Nov;42(3):371–382. doi: 10.1254/jjp.42.371. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamazoe Y., Shimada M., Murayama N., Kato R. Suppression of levels of phenobarbital-inducible rat liver cytochrome P-450 by pituitary hormone. J Biol Chem. 1987 May 25;262(15):7423–7428. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zaphiropoulos P. G., Mode A., Norstedt G., Gustafsson J. A. Regulation of sexual differentiation in drug and steroid metabolism. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1989 Apr;10(4):149–153. doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(89)90167-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zaphiropoulos P. G., Mode A., Ström A., Möller C., Fernandez C., Gustafsson J. A. cDNA cloning, sequence, and regulation of a major female-specific and growth hormone-inducible rat liver cytochrome P-450 active in 15 beta-hydroxylation of steroid sulfates. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jun;85(12):4214–4217. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.12.4214. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]