Abstract
Attenuated Vibrio cholerae vaccine strains specifically mutated in genes encoding cholera toxin (CT) are still capable of causing mild to moderate diarrhea. Culture supernatants of V. cholerae strains, both CT-positive and CT-negative, were examined in Ussing chambers, and a toxin was found that increases the permeability of the small intestinal mucosa by affecting the structure of the intercellular tight junction, or zonula occludens. The activity of this toxin is reversible, heat-labile, sensitive to protease digestion, and found in culture supernatant fractions containing molecules between 10 and 30 kDa in size. Production of this factor (named ZOT for zonula occludens toxin) correlates with diarrheagenicity of V. cholerae strains in volunteers and may represent another virulence factor of infectious diarrhea that must be eliminated to achieve a safe and effective live oral vaccine against cholera.
Full text
PDF
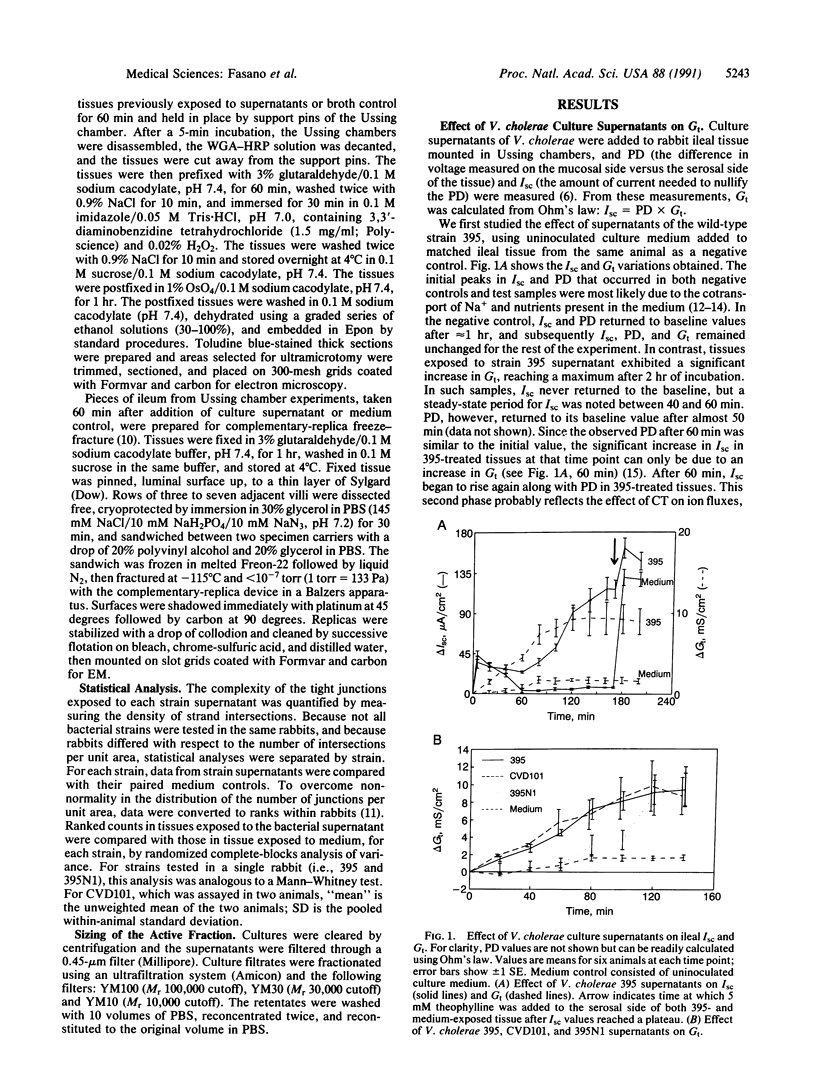
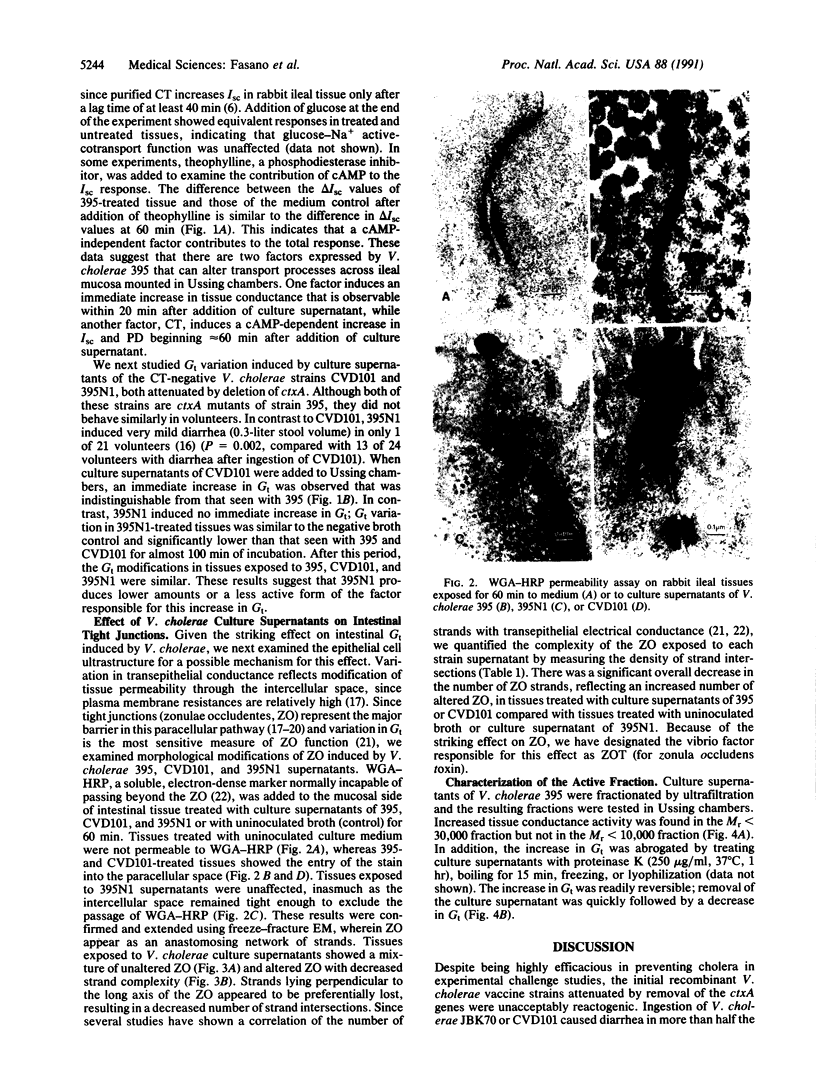
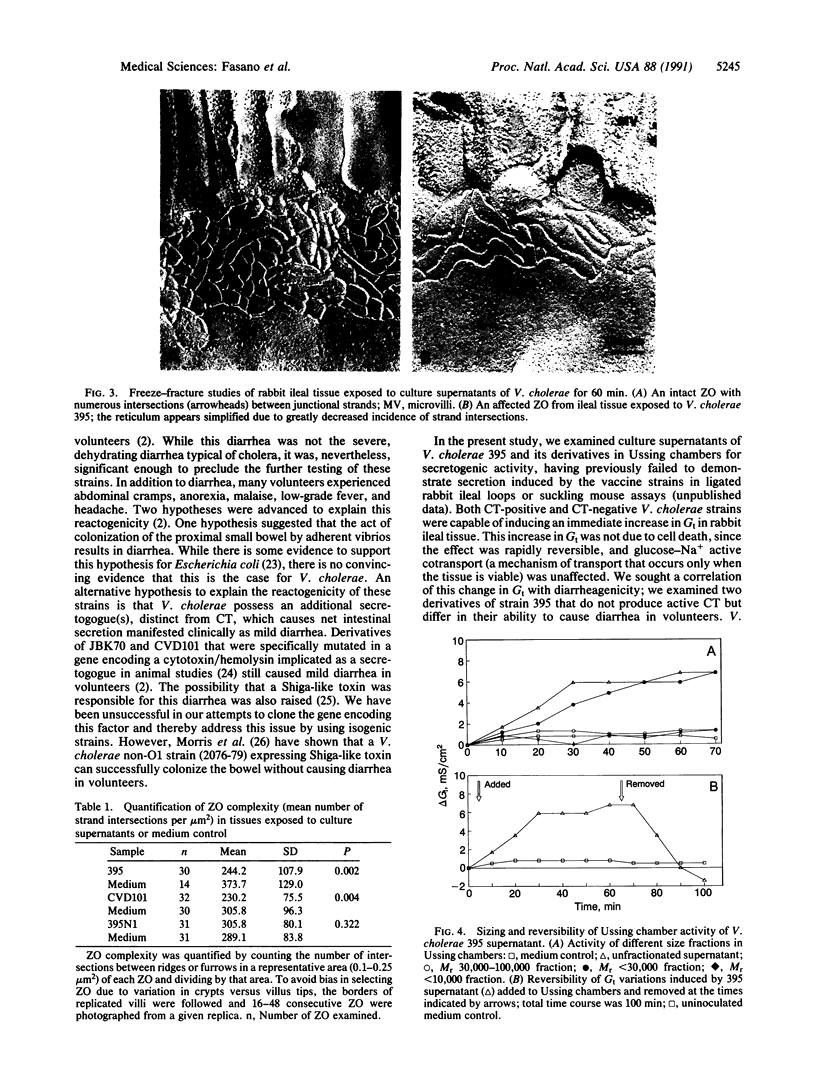

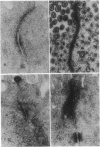
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- CRANE R. K. Hypothesis for mechanism of intestinal active transport of sugars. Fed Proc. 1962 Nov-Dec;21:891–895. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crane R. K. Na+ -dependent transport in the intestine and other animal tissues. Fed Proc. 1965 Sep-Oct;24(5):1000–1006. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curci S., Frömter F. Micropuncture of lateral intercellular spaces of Necturus gallbladder to determine space fluid K+ concentration. Nature. 1979 Mar 22;278(5702):355–357. doi: 10.1038/278355a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diamond J. M. Twenty-first Bowditch lecture. The epithelial junction: bridge, gate, and fence. Physiologist. 1977 Feb;20(1):10–18. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dove C. H., Wang S. Z., Price S. B., Phelps C. J., Lyerly D. M., Wilkins T. D., Johnson J. L. Molecular characterization of the Clostridium difficile toxin A gene. Infect Immun. 1990 Feb;58(2):480–488. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.2.480-488.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ewe K. Intestinal transport in constipation and diarrhoea. Pharmacology. 1988;36 (Suppl 1):73–84. doi: 10.1159/000138424. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Field M., Fromm D., al-Awqati Q., Greenough W. B., 3rd Effect of cholera enterotoxin on ion transport across isolated ileal mucosa. J Clin Invest. 1972 Apr;51(4):796–804. doi: 10.1172/JCI106874. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frömter E., Diamond J. Route of passive ion permeation in epithelia. Nat New Biol. 1972 Jan 5;235(53):9–13. doi: 10.1038/newbio235009a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furie M. B., Cramer E. B., Naprstek B. L., Silverstein S. C. Cultured endothelial cell monolayers that restrict the transendothelial passage of macromolecules and electrical current. J Cell Biol. 1984 Mar;98(3):1033–1041. doi: 10.1083/jcb.98.3.1033. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gill D. M. Mechanism of action of cholera toxin. Adv Cyclic Nucleotide Res. 1977;8:85–118. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guandalini S., Fasano A., Migliavacca M., Verga M. C., Mastrantonio Gianfrilli P., Ferrara A., Alessio M., Malamisura B., Galati P., Pantosti A. Pathogenesis of postantibiotic diarrhoea caused by Clostridium difficile: an in vitro study in the rabbit intestine. Gut. 1988 May;29(5):598–602. doi: 10.1136/gut.29.5.598. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guandalini S., Kachur J. F., Smith P. L., Miller R. J., Field M. In vitro effects of somatostatin on ion transport in rabbit intestine. Am J Physiol. 1980 Feb;238(2):G67–G74. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1980.238.2.G67. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gumbiner B. Structure, biochemistry, and assembly of epithelial tight junctions. Am J Physiol. 1987 Dec;253(6 Pt 1):C749–C758. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1987.253.6.C749. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hecht G., Pothoulakis C., LaMont J. T., Madara J. L. Clostridium difficile toxin A perturbs cytoskeletal structure and tight junction permeability of cultured human intestinal epithelial monolayers. J Clin Invest. 1988 Nov;82(5):1516–1524. doi: 10.1172/JCI113760. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herrington D. A., Hall R. H., Losonsky G., Mekalanos J. J., Taylor R. K., Levine M. M. Toxin, toxin-coregulated pili, and the toxR regulon are essential for Vibrio cholerae pathogenesis in humans. J Exp Med. 1988 Oct 1;168(4):1487–1492. doi: 10.1084/jem.168.4.1487. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine M. M., Kaper J. B., Herrington D., Losonsky G., Morris J. G., Clements M. L., Black R. E., Tall B., Hall R. Volunteer studies of deletion mutants of Vibrio cholerae O1 prepared by recombinant techniques. Infect Immun. 1988 Jan;56(1):161–167. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.1.161-167.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- López-Vancell R., Beaty G., Stefani E., Rodríguez-Boulan E. E., Cereijido M. Changes in paracellular and cellular ionic permeabilities of monolayers of MDCK cells infected with influenza or vesicular stomatitis viruses. J Membr Biol. 1984;81(3):171–180. doi: 10.1007/BF01868711. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madara J. L. Loosening tight junctions. Lessons from the intestine. J Clin Invest. 1989 Apr;83(4):1089–1094. doi: 10.1172/JCI113987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mekalanos J. J., Swartz D. J., Pearson G. D., Harford N., Groyne F., de Wilde M. Cholera toxin genes: nucleotide sequence, deletion analysis and vaccine development. Nature. 1983 Dec 8;306(5943):551–557. doi: 10.1038/306551a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore R., Pothoulakis C., LaMont J. T., Carlson S., Madara J. L. C. difficile toxin A increases intestinal permeability and induces Cl- secretion. Am J Physiol. 1990 Aug;259(2 Pt 1):G165–G172. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1990.259.2.G165. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morris J. G., Jr, Takeda T., Tall B. D., Losonsky G. A., Bhattacharya S. K., Forrest B. D., Kay B. A., Nishibuchi M. Experimental non-O group 1 Vibrio cholerae gastroenteritis in humans. J Clin Invest. 1990 Mar;85(3):697–705. doi: 10.1172/JCI114494. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Brien A. D., Chen M. E., Holmes R. K., Kaper J., Levine M. M. Environmental and human isolates of Vibrio cholerae and Vibrio parahaemolyticus produce a Shigella dysenteriae 1 (Shiga)-like cytotoxin. Lancet. 1984 Jan 14;1(8368):77–78. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(84)90006-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pumplin D. W. Normal variations in presynaptic active zones of frog neuromuscular junctions. J Neurocytol. 1983 Apr;12(2):317–323. doi: 10.1007/BF01148467. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tucker K. D., Carrig P. E., Wilkins T. D. Toxin A of Clostridium difficile is a potent cytotoxin. J Clin Microbiol. 1990 May;28(5):869–871. doi: 10.1128/jcm.28.5.869-871.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wanke C. A., Guerrant R. L. Small-bowel colonization alone is a cause of diarrhea. Infect Immun. 1987 Aug;55(8):1924–1926. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.8.1924-1926.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright E. M. Electrophysiology of plasma membrane vesicles. Am J Physiol. 1984 Apr;246(4 Pt 2):F363–F372. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1984.246.4.F363. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]