Abstract
Treatment options for patients with hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) are limited, in particular in advanced and drug resistant HCC. MicroRNAs (miRNA) are non-coding small RNAs that are emerging as novel drugs for the treatment of cancer. The aim of this study was to assess treatment effects of two complementary miRNAs (sense miRNA-122, and antisense antimiR-21) encapsulated in biodegradable poly (lactic-co-glycolic acid) nanoparticles (PLGA-NP), administered by an ultrasound-guided and microbubble-enhanced delivery approach in doxorubicin-resistant and non-resistant human HCC xenografts. Proliferation and invasiveness of human HCC cells after miRNA-122/antimiR-21 and doxorubicin treatment were assessed in vitro. Confocal microscopy and qRT-PCR were used to visualize and quantitate successful intracellular miRNA-loaded PLGA-NP delivery. Up and down-regulation of miRNA downstream targets and multidrug resistance proteins and extent of apoptosis were assessed in vivo in treated human HCC xenografts in mice. Compared to single miRNA therapy, combination therapy with the two complementary miRNAs resulted in significantly (P < 0.05) stronger decrease in cell proliferation, invasion, and migration of HCC cells as well as higher resensitization to doxorubicin. Ultrasound-guided delivery significantly increased in vivo miRNA-loaded PLGA-NP delivery in human HCC xenografts compared to control conditions by 5–9 fold (P < 0.001). miRNA-loaded PLGA-NP were internalized in HCC cells and anti-apoptotic proteins were down regulated with apoptosis in ~27% of the tumor volume of doxorubicin-resistant human HCC after a single treatment with complementary miRNAs and doxorubicin. Thus, ultrasound-guided delivery of complementary miRNAs is highly efficient in the treatment of doxorubicin- resistant and non-resistant HCC. Further development of this new treatment approach could aid in better treatment of patients with HCC.
Keywords: Hepatocellular carcinoma, Cancer therapy, Drug resistance, Complementary miRNA, Ultrasound
1. Introduction
HCC is the sixth most common cancer and the third most common cause of cancer-related deaths worldwide [1]. The current treatment paradigm for HCC has significant limitations. Early stage HCC is treatable by surgical resection or liver transplantation, with local thermal ablation as an alternative [2,3]. However, only 10–30% of patients qualify for surgical management [4]; recurrence is common after resection (up to 70%) [5], and transplantation is limited by a shortage of donor organs [6]. For intermediate stage HCC, transarterial chemoembolization (TACE) is the standard of care [7], with transarterial radioembolization emerging as a complementary liver-directed therapy [8]. Unfortunately, both are often contraindicated in cirrhotic patients due to poor baseline liver function and treatment response can be variable. Patients with advanced HCC and those who fail or are ineligible for liver-directed therapies are left with extremely limited treatment options and dismal prognosis. Moreover, HCC is commonly resistant to systemic chemotherapies such as doxorubicin [9]. Novel therapeutic strategies are therefore critically needed in particular in drug resistant HCC.
miRNAs are non-coding small RNAs that regulate the expression of genes involved in various cellular processes [10,11]. Aberrant expression of miRNAs plays a critical role in tumor initiation, progression, and metastasis. In HCC, miRNA-122 and miRNA-21 have been identified to play pivotal roles in HCC progression, migration, and chemo-resistance [12–14]. miRNA-122 has tumor suppressive effects and is significantly down-regulated in all stages of HCC development [13,15]. This downregulation causes chemo-resistance to doxorubicin [16]. Therefore, therapeutic restoration of miRNA-122 activity has the potential to not only slow HCC growth but also render these tumors sensitive to doxorubicin. In contrast, miRNA-21 is highly over-expressed in HCC and plays an important role in tumor initiation, progression [17,18], and chemoresistance [19–21]. Therefore, therapeutic silencing of miRNA-21 using antisense antimiR-21 can inhibit HCC cell proliferation, migration, and invasion while also mitigating drug resistance.
However, the lack of safe and efficient approaches to deliver miRNA to the diseased sites hinders clinical translation of miRNA modulation therapy. Intravenously injected miRNAs are rapidly degraded by nucleases and therefore need to be protected to extend their circulation lifetime in the blood. Food and Drug Administration (FDA)-approved biodegradable PLGA-NP can be used to protect miRNAs from degradation [22]. However, due to the size of PLGA-NP, usually ranging between 100 and 150 nm [23], intravenous administration results in minimal tumor tissue penetration as delivery depends on the enhanced permeability and retention (EPR) effect [24] that is often weak in human tumors [25–27]. Using therapeutic ultrasound, PLGA-NP can be actively delivered into cancer using image-guidance, overcoming the limitations of passive tumor accumulation and delivering miRNA deeply into tumors, even in less vascularized portions of the tumor [28,29]. Through a process termed “sonoporation,” local perforations can be formed on vessel walls, facilitating the delivery of therapeutic agents into cancer [30–32,55–57]. The putative primary mechanism for sonoporation is cavitation, whereby gas bodies oscillate and eventually collapse to induce perforations. Ultrasound-mediated drug delivery has shown to be markedly potentiated in the presence of contrast microbubbles [33, 34]. Recently, our group has optimized the acoustic parameters to maximize PLGA-NP delivery in human cancer xenografts in mice [35].
In this study, we hypothesized that co-delivery of the two complementary miRNAs (miRNA-122 and antimiR-21) loaded into PLGA-NP using an optimized ultrasound-guided delivery protocol can significantly decrease tumor cell viability and proliferation associated with HCC in vitro and in vivo and resensitize resistant HCC cells to doxorubicin chemotherapy (Fig. 1). In vitro experiments on human HCC cells were used to investigate and establish the anti-tumorigenic cellular and molecular effects of complementary miRNA-122 and antimiR-21 treatment. We then assessed the in vivo therapeutic effects of miRNA-loaded PLGA-NP in doxorubicin-resistant and non-resistant human HCC xenografts in mice.
Fig. 1.
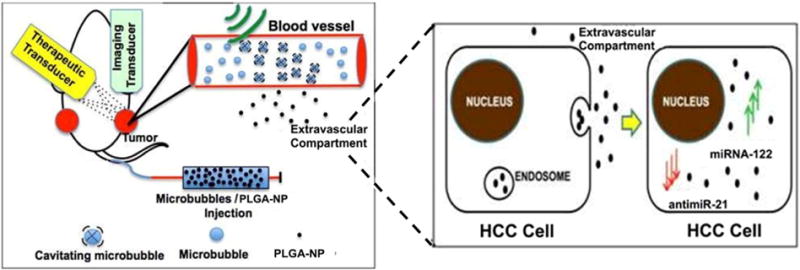
Schematic shows experimental setting and transducer arrangement in mouse bearing two human HCC xenografts. One xenograft was used as non-insonated control tumor, one was treated with ultrasound and microbubble mediated sonoporation, causing leakage of miRNA-loaded PLGA-NP into the extravascular compartment. PLGA-NP are taken up by HCC cells via endocytosis and their miRNA cargo is released into the cytoplasm of HCC cells.
2. Materials and methods
2.1. Synthesis and characterization of miRNA-122 and antimiR-21 loaded PLGA-NP
PLGA-NP were synthesized and loaded with both miRNAs as described previously [22,35](see details in Supplementary section).
2.2. Cell culture
Human HepG2 HCC cells (ATCC, Manassas, VA) were grown in high glucose (4.5 g/L) Dulbecco’s modified Eagle’s medium (Invitrogen, Carlsbad, CA), supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum, L-glutamine (2 mM), penicillin (100 U/mL), and streptomycin (100 μg/mL). Cells were incubated at 37 °C in a humidified atmosphere of 5% CO2, and 95% air.
2.3. Doxorubicin-resistant HCC cell line development
Two HepG2 cell lines with two different levels of resistance to doxorubicin (1 μM doxorubicin and 5 μM doxorubicin) were created by exposure of non-resistant HepG2 cells to increasing concentrations of doxorubicin as described previously [36]. In brief, 1 × 104 non-resistant cells were treated with 0.045 μM doxorubicin for 48 h and surviving cells were sub-cultured. This was repeated with increasing doxorubicin concentrations (multiples of 0.045 μM) till a resistance of 1 μM (~550 ng/mL) was reached. A subgroup of cells was further treated with increasing doxorubicin concentrations (multiples of 0.18 μM) till a resistance of 5 μM was reached.
2.4. Endogenous expression of miRNA-122 and miRNA-21
The endogenous expression levels of miRNA-122 and miRNA-21 in doxorubicin-resistant and non-resistant HepG2 cells were analyzed using qRT-PCR as described [22,35](see details in Supplementary section).
2.5. Multi drug resistance protein activity and expression
Multi drug resistance protein activity and cell membrane expression in resistant and non-resistant HCC cell lines before and after miRNA treatment was assessed using fluorescence microscopy and western blot analysis using standard protocols (see details in Supplementary section).
2.6. Intracellular uptake of miRNA-loaded PLGA-NP in human HCC cells
Uptake of PLGA-NP into human HepG2 HCC cells was assessed by using quantitative RT-PCR and fluorescence microscopy following standard protocols (see details in Supplementary section).
2.7. In vitro treatment response assessment
Treatment response following administration of miRNA-loaded PLGA-NP either individually or in combination was assessed in resistant and non-resistant HCC cells (resistant up to 5 μM doxorubicin) using several standard assays, including MTT cell viability assay, live cell counting cell proliferation assay, migration assay, and invasion assay (see details in Supplementary section).
2.8. Human HCC xenografts in mice
All in vivo experiments were performed in nude mice (Charles River, Hollister, CA) with prior approval from the Institutional Administrative Panel on Laboratory Animal Care. Cells at ~70% confluence were collected by trypsinization. Human HCC xenografts were established on the mouse flanks by subcutaneously injecting 5 × 106 HepG2 cells mixed in 50 μL low growth factor matrigel membrane matrix (BD Biosciences, Billerica, MA). Two tumors were established in all animals (one on the right and one on the left flank of hind limbs). Only one tumor (on the right leg) was treated with the ultrasound-guided drug delivery system (see below), whereas the contralateral tumor served as intra-animal control without ultrasound treatment in all animals. Tumors were allowed to grow for 3–4 weeks until they reached a mean maximum diameter of 8 mm (range, 6–10 mm). A total of 47 mice with 94 non-resistant tumors and 21 mice with 42 doxorubicin-resistant tumors were used in this study.
2.9. Microbubble and ultrasound-guided drug delivery platform apparatus
Clinical grade lipid-shelled perfluorobutane and nitrogen-filled microbubbles (BR38; Bracco Research, Geneva, Switzerland) were used. An ultrasound-guided drug delivery platform apparatus optimized previously [35] for PLGA-NP delivery in cancers was used (see details in Supplementary section) [35].
2.10. Ultrasound-guided delivery of miRNA-loaded PLGA-NP into human HCC xenografts in mice
Mice were anesthetized with 2% isoflurane in 2 L of oxygen per minute. A catheter (MicroMarker Tail Vein Access Cannulation kit; VisualSonics, Toronto, Ontario) was placed into a lateral tail vein for administration of MB and PLGA-NP. A total of 350 μL (3.5 × 108) microbubbles and 200 μl of PLGA-NP (100 μL or ~14 nmol/kg body weight of each miRNA modulator, miRNA-122 and antimiR-21, in 25 mg/kg body weight PLGA-NP) were mixed into a total solution of 550 μL prior to tumor treatment. The treatment consisted of 5 repetitive cycles of microbubble/PLGA-NP administrations combined with ultrasound exposures as previously optimized and described [35]. In each cycle, the microbubbles/PLGA-NP were first administered for 1 min at a constant rate of 110 μL/min using an automated infusion pump (GeniePlus, Kent Scientific, Torrington, CT) to achieve steady state. The microbubble/PLGA-NP infusion was then stopped and ultrasound pulses were then delivered to the target tumor sites for 1 min [35]. The ultrasound focal beam was electronically steered across 6 locations, 1.5 mm apart each, to allow complete anatomical coverage of the tumors. The following ultrasound parameters were used, which were optimized previously [35] to maximize PLGA-NP delivery into HCC tumors in mice while minimizing tissue damage: acoustic pressure, 5.4 MPa; ultrasound frequency, 1.8 MHz; pulse length: 5 cycles; pulse repetition frequency, 100 Hz.
2.11. Ex vivo assessment of PLGA-NP delivery into HCC xenografts and of successful miRNA treatment
Successful delivery of PLGA-NP into HCC cells in human HCC xenografts was visualized using TEM and quantified using RT-PCR. Downstream therapeutic effects in HCC xenografts were assessed by a TUNEL apoptosis assay. Details are provided in the Supplementary method section.
2.12. Statistical analysis
Continuous measures were summarized with their sample mean and standard deviation. For all two-group comparisons, we used the two-sided nonparametric Wilcoxon rank sum test except for comparing intracellular protein expression using western blot analysis and invasion and migration assays where we used a t-test due to small sample sizes (n = 3 per group). The statistical significance level was set at 0.05 and the analysis was performed using R3.2.2 (The R foundation for statistical computing).
3. Results
3.1. Characterization of miRNA-122 and antimiR-21-loaded PLGA-NP and cell lines
PLGA-NP were spherical in shape with a mean diameter of 120 nm (range, 80–140 nm) as measured by TEM (Fig. 2A). The hydrodynamic radius obtained from DLS measurements further corroborated TEM results (Fig. 2B; Table S1).
Fig. 2.
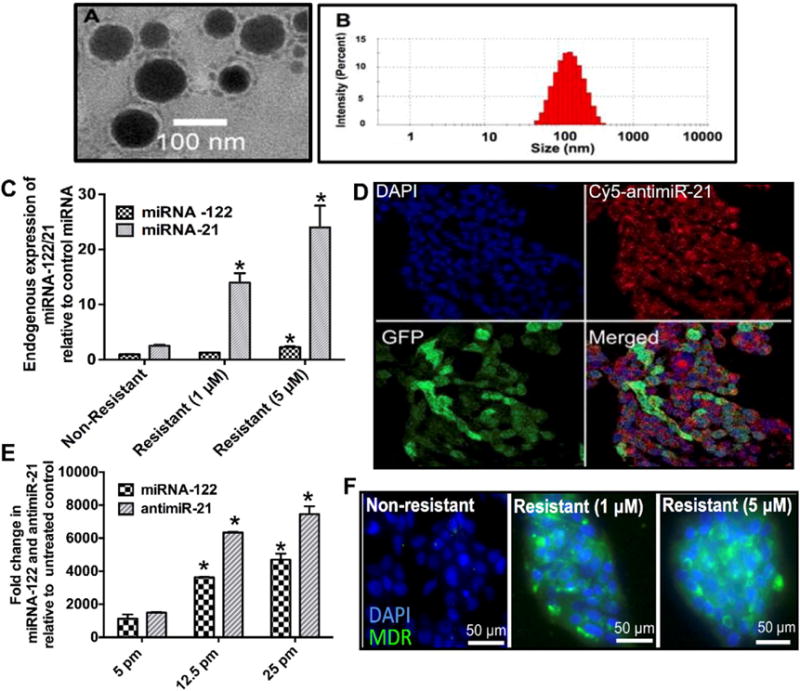
(A) Representative TEM images of PLGA-NP. (B) Distribution of the hydrodynamic diameter of PLGA-NP assessed by Dynamic Light Scattering (DLS). (C) Quantification of endogenous miRNA-122 and miRNA-21 expression levels in non-resistant and two doxorubicin-resistant HCC cells shows increased miRNA-21 levels with increased resistance while miRNA-122 levels remain relatively lower in all three cell lines. *, P < 0.05 compared to non-resistant cells; n = 6 each. (D) Confocal microscopy images confirm intracellular delivery of Cy5-labelled antimiR-21 in GFP expressing (green) HCC cells. (E) Dose-dependent intracellular uptake of miRNA-122- and antimiR-21-loaded PLGA-NP in HCC cells. *, P < 0.05 compared to untreated control cells; n = 6 each. (F) Confocal microscopy images show increasing Multi-drug Resistant (MDR) protein expression levels (green) in non-resistant and doxorubicin-resistant HCC cells.
Endogenous miRNA-122 expression as quantified by RT-PCR was less in non-resistant HCC cells (~0.9 ± 0.15 fold compared to control miRNA-10b) and increased in doxorubicin-resistant cells (1.25 ± 0.11 fold in 1 μM resistant cells and 2.25 ± 0.19 fold in 5 μM resistant cells). Similarly, miRNA-21 expression level was higher than endogenous control miRNA in non-resistant HCC cells (2.5 ± 0.2 fold). Expression significantly increased in doxorubicin-resistant cells (14 ± 1.6 fold in 1 μM resistant cells; P = 0.01) and 24 ± 3.95 fold in 5 μM resistant cells; P = 0.0021), supporting the role of miRNA-21 in drug resistance (Fig. 2C). Resistant and non-resistant HCC cells were further characterized in terms of MDR protein expression known to be directly related to miRNA-21 expression and doxorubicin resistance in cancer [37]. Nonresistant HCC cells showed very little MDR expression (green fluorescence) while doxorubicin resistant cells demonstrated high MDR protein expression levels (Fig. 2F).
3.2. PLGA-NP uptake into HCC cells
HCC cells were incubated with increasing concentrations of miRNA-loaded PLGA-NP and cell uptake of miRNA-122 and antimiR-21 was assessed by RT-PCR (Fig. 2E). Incubating cells with 5 picomoles of miRNA-loaded PLGA-NP resulted in a 1078 ± 246 and 1499 ± 29 fold increase, respectively, in miRNA-122 and antimiR-21 levels compared to endogenous control miRNA. Also, intracellular miRNA-122/antimiR-21 levels increased in a dose-dependent manner (Fig. 2E). Fluorescence microscopy of Cy5-labelled antimiR-21 loaded in PLGA-NP further confirmed efficient uptake of PLGA-NP into HepG2 cells (Fig. 2D). Since cellular uptake of PLGA-NP occurs mostly via clathrin mediated endocytosis [38], an endocytosis inhibition assay was performed to confirm uptake of miRNA-loaded PLGA-NP via endocytosis in HCC cells (Fig. S1).
3.3. Effects of miRNA combination therapy on proliferation and invasion of HCC cells
To assess whether a synergistic combination therapy of miRNA-122 and antimiR-21 has a stronger therapeutic effect than single miRNA treatments, treatment response was quantified in non-resistant HCC cells. Cell viability experiments using the MTT assay showed that all treatment conditions (miRNA-122 alone, antimiR-21 alone, combination of the two) resulted in similar decreases in cell viability at a dose of 10 picomoles (76.9 ± 4.65%, 84.3 ± 4.36%, 78.2 ± 6.26%, respectively; Fig. 3A). However, at higher doses, the combination therapy resulted in significantly increased treatment effects (P = 0.024; Fig. 3A) with an IC50 of 36 picomoles for single miRNA-122 treatment and an IC50 of 29 picomoles for single antimiR-21 treatments. The IC50 was 21 picomoles for the miRNA combination therapy (P = 0.006). The combination therapy was also significantly more effective than the single treatments in decreasing HCC migration (Fig. 3B; P = 0.001) and HCC invasion (Fig. 3C; P = 0.001). Taken together, these results indicated that the miRNA combination therapy was more effective in decreasing HCC cell proliferation and invasion than single miRNA treatments.
Fig. 3.
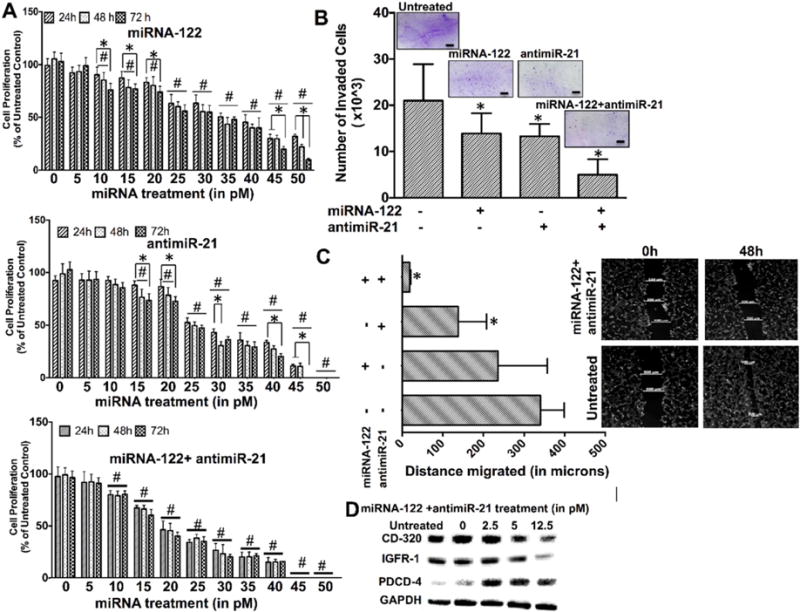
(A) Cell proliferation assays of non-resistant HCC cells treated with miRNA-122 (upper row), antimiR-21 (middle row), and miRNA-122/antimiR-21 combination (lower row) for 24, 48, and 72 h show dose dependent decrease in proliferation with the miRNA combination treatment resulting in strongest anti-proliferation effects. *, P < 0.05 among time points for the same treatment concentration. #, P < 0.05 compared to untreated control; n = 6. (B) Cell invasion assays show strongest decrease of HCC cell invasion following the miRNA combination treatment. Inserts show crystal violet stained invaded HCC cells for the different treatments. *, P < 0.05 compared to untreated control cells; n = 3 each. (C) Cell migration assays show smallest migration distance when HCC cells were treated with the miRNA combination treatment. *, P < 0.05 compared to untreated control cells; n = 3. (D) Western blots shows strongest decrease of the two anti-apoptotic proteins CD-320 and IGFR-1 and strongest increase of the pro-apoptotic protein PDCD4 with the miRNA combination treatment in HCC cells. GAPDH was used as loading control.
Further effects of miRNA treatments on downstream anti-apoptotic and pro-apoptotic proteins in non-resistant HCC cells were assessed by western blotting. While CD320 and Insulin like growth factor 1 expression (both anti-apoptotic proteins upregulated in HCC) decreased in a miRNA dose dependent manner (Fig. 3D), expression of Programmed Cell Death Protein 4 (PDCD4, a pro-apoptotic protein down-regulated in HCC) showed a dose dependent increase in HCC cells (Fig. 3D).
3.4. Effects of miRNA combination therapy on doxorubicin resistance in HCC cells
In doxorubicin-resistant HCC cells with resistance up to 5 μM, the combined miRNA-122/antimiR-21 therapy showed strongest therapeutic effects compared to single treatments with 32% of cells dying at the highest tested dose (Fig. 4A). When cells were treated with an additional dose of 1 μM of doxorubicin, therapeutic effects further increased with 100% of HCC cells dying at a dose of 50 picomoles of the miRNA combination therapy (Fig. 4A). As expected, MDR protein activity (measured by the doxorubicin uptake in HCC cells) significantly (P = 0.001) decreased in miRNA treated cells with the strongest effect in cells pretreated with the miRNA combination therapy before doxorubicin administration (Fig. 4B; S2 shows doxorubicin fluorescence images). Similarly, the miRNA combination therapy resulted in the strongest increase (P = 0.007) in Rho-123 (MDR substrate) fluorescence in resistant HCC cells (Fig. 4B; S3 shows Rho-123 fluorescence images). Both doxorubicin and Rho-123 fluorescence were not significantly (P > 0.3) different in non-resistant HCC cells because the MDR protein was down-regulated in these cells.
Fig. 4.
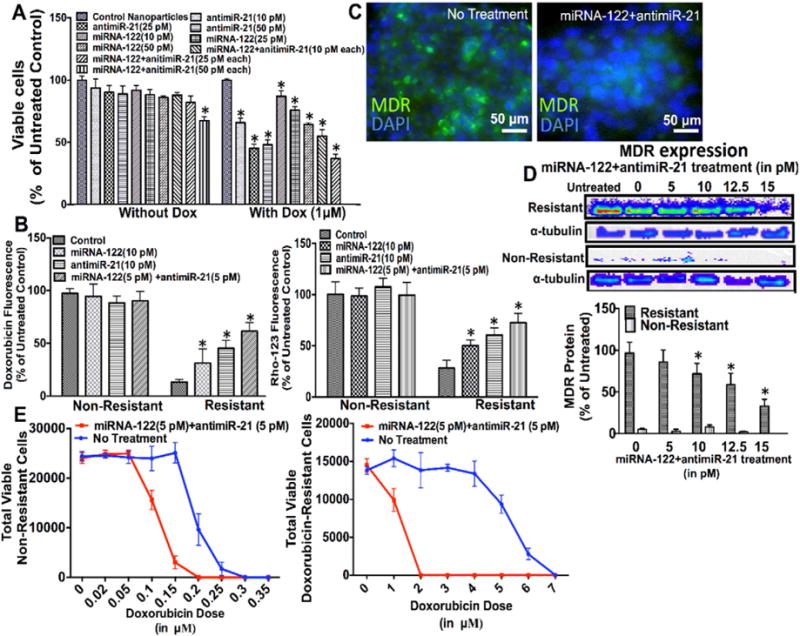
(A) Cell proliferation assay of HCC cells with strong doxorubicin resistance (5 μM) treated with different doses of miRNA-122 and antimiR-21 (10, 25, 50 picomoles), either individually or in combination, shows that the miRNA combination therapy resulted in the strongest inhibition of cell proliferation. *, P < 0.05 compared to untreated control cells; n = 6 each. When HCC cells were treated with the miRNA combination treatment and doxorubicin, all cells died at a miRNA dose of 50 picomoles each. *, P < 0.05 compared to untreated control cells; n = 6 each. α tubulin was used as loading control. (B) Treatment with the miRNA combination therapy increased both doxorubicin and Rho-123 uptake in resistant HCC cells, suggesting decreased multi drug resistance (MDR) protein expression following miRNA treatment. *, P < 0.05 compared to untreated control cells; n = 12 each. This was confirmed by fluorescence imaging (C), and western blotting (D) showing decreased MDR protein expression in doxorubicin resistant HCC cells after treatment with the miRNA combination therapy. *, P < 0.05 compared to untreated control cells; n = 3 each. α tubulin was used as loading control. (E) Cell viability of non-resistant (left) and doxorubicin resistant (right) HCC cells treated with the miRNA combination therapy for 18 h followed by increasing doxorubicin doses shows increased therapeutic effects of doxorubicin in both cell types; n = 6 each.
Significant dose dependent decrease of MDR protein expression in resistant versus non-resistant cells (P < 0.01) following the miRNA combination therapy was further shown by fluorescence imaging (Fig. 4C) and western blotting (Fig. 4D), further supporting that the miRNA combination therapy decreased drug resistance in HCC most efficiently.
Finally, the minimum doxorubicin dose resulting in complete cell death in both non-resistant and resistant HCC cells was determined with and without pretreatment of the miRNA combination therapy (Fig. 4E). While non-resistant HCC cells withstand a doxorubicin dose up to 0.3 μM, miRNA combination pretreatment decreased this value to 0.2 μM (Fig. 4E, left). Doxorubicin-resistant HCC cells could normally survive a doxorubicin dose up to 6.5 μM. However, with the miRNA combination pretreatment this value was reduced to a dose of 1.5 μM doxorubicin (Fig. 4E, right). This suggests that the miRNA combination treatment improves therapeutic effects of doxorubicin in both non-resistant and resistant HCC cells.
3.5. Ultrasound-guided delivery and intracellular uptake of miRNA-122 and antimiR-21-loaded PLGA-NP into human HCC xenografts
Experiments were then translated to in vivo studies in human HCC xenografts in mice. A toxicity study was performed first which showed no animal death and no signs of toxicity in any of the examined organs.
In vivo delivery efficiency of miRNA-loaded PLGA-NP into human HCC xenografts was then assessed for both miRNA-122 and antimiR-21 separately using quantitative RT-PCR at two time points (Fig. 5). At 4 h, miRNA-122 concentrations increased by 88.5 ± 18.4 fold (Fig. 5A) and antimiR-21 concentration increased by 221.2 ± 78.1 fold (Fig. 5A) compared to control PLGA-NP treatment. Ultrasound treatment increased miRNA-122 and antimiR-21 concentrations by 5- and 9-fold, respectively (Fig. 5A). Similar results were observed for the 24 h time point (Fig. 5B). Human HCC xenografts treated with control non-loaded PLGA-NP (with and without ultrasound) did not show significant changes in miRNA concentrations (P = 0.7; Fig. 5B).
Fig. 5.
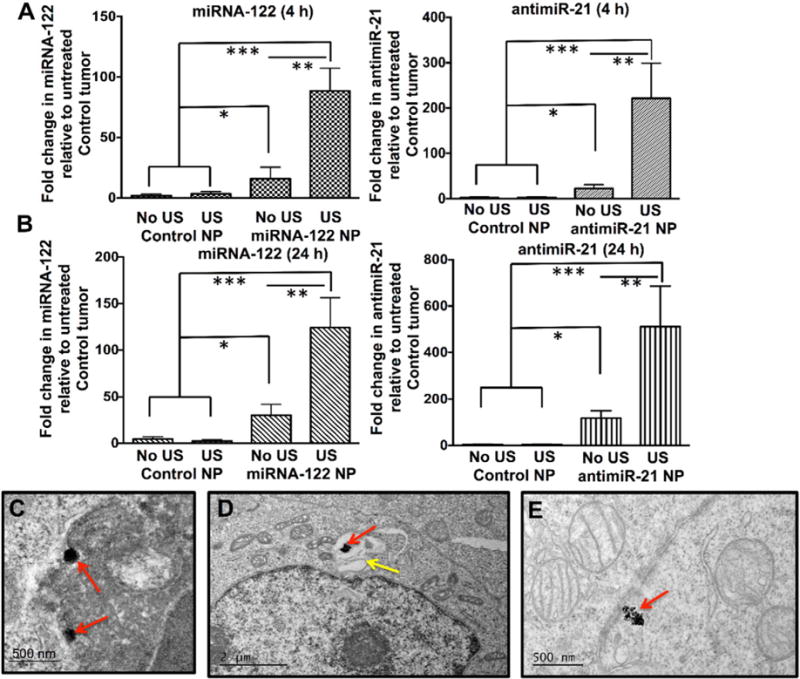
Quantitative RT-PCR assessment of non-resistant human HCC xenografts in mice intravenously injected with either control PLGA-NP (no miRNA loading) or with miRNA-loaded PLGA-NP that were either treated or not treated with ultrasound (US). (A) shows fold increase of respective miRNA levels at 4 h, (B) shows them at 24 h following treatment. *, P = 0.005, **, P = 0.002; ***, P = 0.001, all compared to untreated control tumors; n = 5 each. Representative TEM image shows internalization of PLGA-NP (red arrows) into a HCC cell (C) through endocytosis. (D) PLGA-NP (red arrow) is shown within a vesicular structure (yellow arrow) in a HCC cell by TEM. (E) Degrading PLGA-NP (red arrow) aggregates in the cytoplasm of a HCC cell (red arrow).
Successful intracellular delivery of PLGA-NP into HCC cells in vivo was further confirmed by direct visualization with TEM (Fig. 5C–E). TEM showed that PLGA-NP were internalized into vesicular structures (Fig. 5C, D) and released into the cytoplasm (Fig. 5E). In vivo intracellular uptake of PLGA-NP was further confirmed quantitatively by flow cytometry of Cy5-labelled antimiR-21 in HCC cells isolated from treated HCC xenografts (Fig. S4).
3.6. Tumor response following a single treatment with miRNA-loaded PLGA-NP, delivered by ultrasound guidance
Fig. 6A shows bar graphs summarizing TUNEL stained non-resistant and doxorubicin-resistant HCC xenografts treated with various combinations of miRNA-loaded PLGA-NP and doxorubicin, with and without ultrasound. For both non-resistant and resistant HCC xenografts, tumor cell apoptosis measured in the entire tumor volumes significantly increased (P < 0.01) following ultrasound-guided delivery of the miRNA combination therapy (Fig. 6A), which further increased by additional doxorubicin treatment (Fig. 6A). In non-resistant HCC xenografts, an average ~24% of the tumor volume was apoptotic after a single treatment with the miRNA combination therapy and doxorubicin (1.5-fold higher compared to treatment with doxorubicin alone). In resistant HCC xenografts, an average ~27% of the tumor volumes were apoptotic after a single treatment with the miRNA combination therapy and doxorubicin, which was 6-fold higher compared to treatment with doxorubicin alone (Fig. 6A). Positive treatment response with signs of apoptosis was further confirmed using TEM (Fig. 6D–E).
Fig. 6.
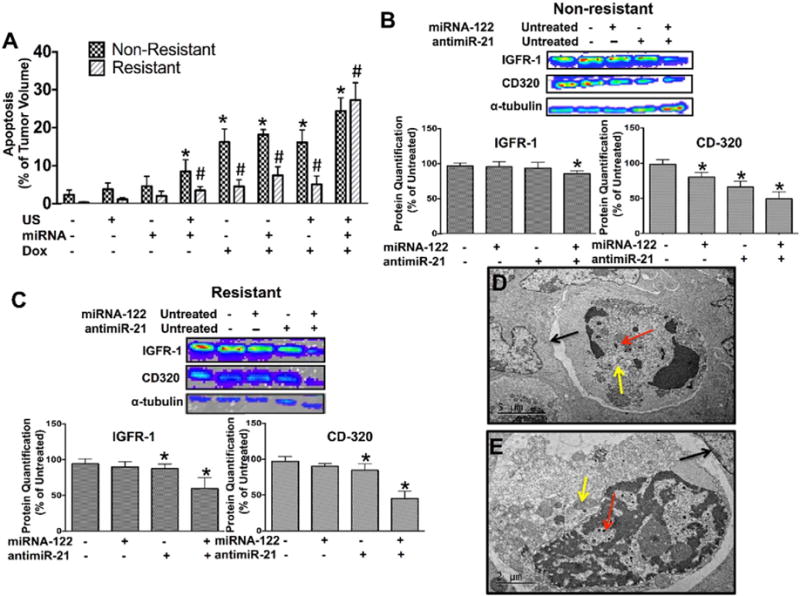
(A) Bar graphs summarizing mean and standard deviations of % tumor volume apoptosis calculated from TUNEL stained non-resistant and doxorubicin-resistant HCC xenograft sections show highest extent of apoptosis in tumors treated with the miRNA combination therapy. * and #, P < 0.05 compared to untreated control tumors; n = 5 each. Western blotting and quantitative bar graph summary (mean ± standard deviations) of treatment effects on down-stream anti-apoptotic proteins, IGFR-1 and CD320, in non–resistant (B) and resistant (C) human HCC xenografts treated with miRNA-122 and antimiR-21, either isolated or in combination. *, P < 0.05 compared to control tumors; n = 3 each. α tubulin was used as loading control. (D and E) TEM images show HCC cells with multiple internalized PLGA-NP (red arrows), double layered vacuolar structures in the cytoplasm (yellow arrows) and evidence of detachment from surrounding HCC cells (black arrows), indicating apoptosis.
Treatment effects on two downstream anti-apoptotic proteins (CD-320 and IGFR-1) was further assessed using western blotting which showed that in non-resistant HCC, only the miRNA combination therapy resulted in significant (P = 0.02) down-regulation of IGFR-1 levels while isolated treatments with the respective miRNAs did no significantly (P > 0.6) change expression levels (Fig. 6B). Expression of CD-320 was significantly (P < 0.03) decreased for both isolated and combined miRNA therapies, with the combination resulting in strongest effects (Fig. 6B). In resistant cells, similar results were observed with the combination therapy resulting in strongest reduction in expression levels of both IGFR-1 and CD-320 (P = 0.001), while isolated treatments with respective miRNAs resulted in significantly lower (P = 0.04 and 0.03) protein levels (Fig. 6C).
4. Discussion
Our results show that a combined miRNA-122 and antimiR-21 therapy results in improved therapeutic effects compared to targeting a single miRNA in doxorubicin-resistant and non-resistant human HCC cells in vitro and human HCC xenografts in vivo. Ultrasound-guided delivery substantially increases uptake of miRNA-loaded PLGA-NP in human HCC xenografts. Our study lays the foundation to further develop imaging-guided delivery of complementary miRNA-loaded PLGA-NP for improved treatment of HCC.
Previous studies have suggested an emerging role of miRNA based therapy in HCC treatment [39,40]. Those studies have focused on either supplementing anti-oncogenic miRNAs down-regulated in HCC or inhibiting overexpressed oncogenic miRNAs [40]. To our knowledge, our study is the first to leverage the complementary potential of both treatment strategies to maximize treatment effects in HCC. Supplementation of miRNA-122, which is significantly down-regulated in HCC, can inhibit uncontrolled proliferation of oncogenic HCC cells [14] while antimiR-21 plays an important role in blocking endogenous miRNA-21 function and preventing invasion and metastasis of HCC along with suppressing drug resistance [41]. Thus, the molecular functions of both miRNAs complement each other in arresting HCC progression while resensitizing resistant HCC cells to drugs such as doxorubicin.
However, intravenously injected miRNA is degraded almost immediately by nucleases [42]. Therefore, a delivery vehicle was needed to protect and carry these miRNAs into HCC. Biodegradable vehicles such as PLGA-NP are advantageous as they not only protect miRNAs from degradation, but also facilitate internalization into cancer cells. Following internalization, miRNAs are slowly released into the cytoplasm, thereby providing sustained and prolonged therapeutic effects in vivo [43]. Smaller size with improved tissue leakage and the fact that PLGA-NP are already FDA approved facilitating clinical translation are additional advantages over other experimental biodegradable nanoparticles that have been previously explored for in vivo delivery of small RNA (both siRNA and miRNA) into HCC [44–46] or HCC cancer stem cells [47].
Characterization of doxorubicin-resistant and non-resistant HCC cell lines using quantitative RT-PCR and fluorescence microscopy in our study provided evidence of low miRNA-122 expression in all HCC cells and increased miRNA-21 and MDR expression in resistant cells compared to non-resistant cells. This supported our hypothesis that two complementary miRNA may maximize treatment effects by not only directly decreasing tumor proliferation but also mitigating drug resistance. This hypothesis was confirmed by our in vitro experiments showing normalization of aberrantly expressed proteins in HCC including the MDR protein responsible for drug resistance using the two complementary miRNAs. Previous studies have explored several other miRNAs as therapeutic agents for HCC including miRNA-26a [48], miRNA-124 [49] and miRNA-143 [50], and miRNA-181b [51]. However, those studies focused on the treatment with one single miRNA with the intention to treat either tumor proliferation or drug resistance. Since both tumor properties are interlinked with each other in the progression of HCC, our results suggest that administering two complementary miRNAs with functional overlap have stronger therapeutic effects than treating HCC with single miRNAs only.
However, miRNAs can only show in vivo therapeutic effects when a high enough dose can be delivered into HCC cells in vivo. Previous studies have either relied on passive delivery by the enhanced permeability and retention (EPR) effect which is minimal in most tumors or have tried to increase tumor uptake of nanoparticles by attaching ligands onto the nanoparticle surface that can attach to overexpressed receptors on tumors cells [52]. However, to allow receptor-mediated uptake of nanoparticles by tumor cells, they first need to penetrate into the extravascular space which is challenging as the EPR is minimal in most tumors often leading to heterogeneous drug delivery in tumors [53] [54]. To address the challenge of limited passive tumor delivery, we utilized a non-invasive delivery approach using ultrasound and microbubble-mediated sonoporation to actively deliver PLGA-NP into the extravascular compartment by using a custom delivery platform previously optimized for an efficient delivery of PLGA-NP into cancer tissues [35]. We hypothesized that the optimized ultrasound-guided drug delivery strategy results in high enough intratumoral delivery of miRNA-loaded PLGA-NP to cause substantial downstream therapeutic effects in human HCC xenografts. We could show that intratumoral miRNA concentrations increased 5–9-fold in HCC through the help of ultrasound and microbubble-mediated sonoporation and TEM directly visualized accumulation of substantial amounts of PLGA-NP in HCC cells. Furthermore, strong therapeutic effects with increased apoptosis and down-regulation of anti-apoptotic proteins could be seen after a single treatment cycle in vivo in our study. As expected, in particular in doxorubicin-resistant human HCCs, pretreatment of miRNA efficiently resensitized the tumors with as much as 27% of the tumor volume showing apoptosis following a single treatment cycle.
We acknowledge the following limitations of our study. In this proof of principle study human HCC xenografts were only treated by a single dose of miRNA-loaded PLGA-NP with and without doxorubicin. Repetitive treatments similar to chemotherapeutic cycles will likely result in increased therapeutic effects and possibly complete HCC eradication; future longitudinal studies are warranted to test this hypothesis. Also, we assessed miRNA treatment effects on overcoming HCC resistance to a single chemotherapeutic drug (doxorubicin) only; additional studies are needed to explore whether this new treatment strategy can also overcome multi-drug resistance in HCC.
In conclusion, our study suggests that a combined miRNA-122 and antimiR-21 therapy results in substantial cell death in doxorubicin-resistant and non-resistant HCC both in vitro and in human HCC xenografts in mice. Ultrasound combined with microbubbles substantially increases successful intra-tumoral delivery and treatment effects of miRNA-loaded PLGA-NP in vivo compared to passive delivery. Since the liver is well accessible for ultrasound imaging in patients, ultrasound-guided delivery of miRNA-loaded PLGA-NP is a promising new and clinically translatable therapeutic strategy for treating HCC in patients.
Supplementary Material
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by the NIH grants R01 CA155289 (JKW), R01 DK092509 (JKW), R21 EB022298-01(JKW), 5T32CA009695 (TYW), and R25T CA118681 training grant (SMC). We also thank Cell Sciences Imaging Facility (CSIF), Stanford University for their help with Transmission Electron Microscopy.
Appendix A. Supplementary data
Supplementary data to this article can be found online at http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jconrel.2016.08.005.
Footnotes
Author contributions
SMC, TYW, SB, DSW, BKY, RP, JKW designed the experiments for this study, SMC, TYW, SB, RD, JWC, LAE, RP, JKW carried out the experiments and were involved in data acquisition. SMC, DSW, RP, JKW wrote and edited the manuscript. LT, SMC, JKW did the statistical analysis.
Disclosure of potential conflicts of interest
There is no actual or potential conflicts of interest with regard to this paper.
References
- 1.Forner A, Llovet JM, Bruix J. Hepatocellular carcinoma. Lancet. 2012;379:1245–1255. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(11)61347-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.E.A.f.S.o. Liver. EASL-EORTC clinical practice guidelines: management of hepatocellular carcinoma. Eur J Cancer. 2012;48:599. doi: 10.1016/j.ejca.2011.12.021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Lencioni R, Cioni D, Crocetti L, Bartolozzi C. Percutaneous ablation of hepatocellular carcinoma: state-of-the-art. Liver Transpl. 2004;10:S91–S97. doi: 10.1002/lt.20043. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Yang T, Zhang J, Lu JH, Yang LQ, Yang GS, Wu MC, Yu WF. A new staging system for resectable hepatocellular carcinoma: comparison with six existing staging systems in a large Chinese cohort. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2011;137:739–750. doi: 10.1007/s00432-010-0935-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Llovet JM, Fuster J, Bruix J. Intention-to-treat analysis of surgical treatment for early hepatocellular carcinoma: resection versus transplantation. Hepatology. 1999;30:1434–1440. doi: 10.1002/hep.510300629. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Manns MP. Liver cirrhosis, transplantation and organ shortage. Dtsch Arztebl Int. 2013;110:83. doi: 10.3238/arztebl.2013.0083. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Llovet JM, Bruix J. Systematic review of randomized trials for unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma: chemoembolization improves survival. Hepatology. 2003;37:429–442. doi: 10.1053/jhep.2003.50047. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Raoul JL, Sangro B, Forner A, Mazzaferro V, Piscaglia F, Bolondi L, Lencioni R. Evolving strategies for the management of intermediate-stage hepatocellular carcinoma: available evidence and expert opinion on the use of transarterial chemoembolization. Cancer Treat Rev. 2011;37:212–220. doi: 10.1016/j.ctrv.2010.07.006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Giglia JL, Antonia SJ, Berk LB, Bruno S, Dessureault S, Finkelstein SE. Systemic therapy for advanced hepatocellular carcinoma: past, present, and future. Cancer Control. 2010;17:120. doi: 10.1177/107327481001700207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Carthew RW, Sontheimer EJ. Origins and mechanisms of miRNAs and siRNAs. Cell. 2009;136:642–655. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2009.01.035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Pereira DM, Rodrigues PM, Borralho PM, Rodrigues CM. Delivering the promise of miRNA cancer therapeutics. Drug Discov Today. 2013;18:282–289. doi: 10.1016/j.drudis.2012.10.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Meng F, Henson R, Wehbe-Janek H, Ghoshal K, Jacob ST, Patel T. MicroRNA-21 regulates expression of the PTEN tumor suppressor gene in human hepatocellular cancer. Gastroenterology. 2007;133:647–658. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2007.05.022. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Kutay H, Bai S, Datta J, Motiwala T, Pogribny I, Frankel W, Jacob ST, Ghoshal K. Downregulation of miR-122 in the rodent and human hepatocellular carcinomas. J Cell Biochem. 2006;99:671–678. doi: 10.1002/jcb.20982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Girard M, Jacquemin E, Munnich A, Lyonnet S, Henrion-Caude A. miR-122, a paradigm for the role of microRNAs in the liver. J Hepatol. 2008;48:648–656. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2008.01.019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Tsai WC, Hsu SD, Hsu CS, Lai TC, Chen SJ, Shen R, Huang Y, Chen HC, Lee CH, Tsai TF. MicroRNA-122 plays a critical role in liver homeostasis and hepatocarcinogenesis. J Clin Invest. 2012;122:2884. doi: 10.1172/JCI63455. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Xu Y, Xia F, Ma L, Shan J, Shen J, Yang Z, Liu J, Cui Y, Bian X, Bie P. MicroRNA-122 sensitizes HCC cancer cells to adriamycin and vincristine through modulating expression of MDR and inducing cell cycle arrest. Cancer Lett. 2011;310:160–169. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2011.06.027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Xu G, Zhang Y, Wei J, Jia W, Ge Z, Zhang Z, Liu X. MicroRNA-21 promotes hepatocellular carcinoma HepG2 cell proliferation through repression of mitogen-activated protein kinase-kinase 3. BMC Cancer. 2013;13:469. doi: 10.1186/1471-2407-13-469. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Zhu Q, Wang Z, Hu Y, Li J, Li X, Zhou L, Huang Y. miR-21 promotes migration and invasion by the miR-21-PDCD4-AP-1 feedback loop in human hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncol Rep. 2012;27:1660–1668. doi: 10.3892/or.2012.1682. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Pan X, Wang ZX, Wang R. MicroRNA-21: a novel therapeutic target in human cancer. Cancer Biol Ther. 2010;10:1224–1232. doi: 10.4161/cbt.10.12.14252. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Sarkar FH, Li Y, Wang Z, Kong D, Ali S. Implication of microRNAs in drug resistance for designing novel cancer therapy. Drug Resist Updat. 2010;13:57–66. doi: 10.1016/j.drup.2010.02.001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Mei M, Ren Y, Zhou X, Yuan XB, Han L, Wang GX, Jia Z, Pu PY, Kang CS, Yao Z. Downregulation of miR-21 enhances chemotherapeutic effect of taxol in breast carcinoma cells. Technol Cancer Res Treat. 2010;9:77–86. doi: 10.1177/153303461000900109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Devulapally R, Sekar NM, Sekar TV, Foygel K, Massoud TF, Willmann JK, Paulmurugan R. Polymer nanoparticles mediated codelivery of antimiR-10b and antimiR-21 for achieving triple negative breast cancer therapy. ACS Nano. 2015;9:2290–2302. doi: 10.1021/nn507465d. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Dinarvand R, Sepehri N, Manoochehri S, Rouhani H, Atyabi F. Polylactide-co-glycolide nanoparticles for controlled delivery of anticancer agents. Int J Nanomedicine. 2011;6:877–895. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S18905. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Yhee JY, Son S, Son S, Joo MK, Kwon IC. Cancer Targeted Drug Delivery. Springer; 2013. The EPR effect in cancer therapy; pp. 621–632. [Google Scholar]
- 25.Maeda H, Wu J, Sawa T, Matsumura Y, Hori K. Tumor vascular permeability and the EPR effect in macromolecular therapeutics: a review. J Control Release. 2000;65:271–284. doi: 10.1016/s0168-3659(99)00248-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Iyer AK, Khaled G, Fang J, Maeda H. Exploiting the enhanced permeability and retention effect for tumor targeting. Drug Discov Today. 2006;11:812–818. doi: 10.1016/j.drudis.2006.07.005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Sugahara KN, Teesalu T, Karmali PP, Kotamraju VR, Agemy L, Girard OM, Hanahan D, Mattrey RF, Ruoslahti E. Tissue-penetrating delivery of compounds and nanoparticles into tumors. Cancer Cell. 2009;16:510–520. doi: 10.1016/j.ccr.2009.10.013. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Chumakova OV, Liopo AV, Andreev VG, Cicenaite I, Evers BM, Chakrabarty S, Pappas TC, Esenaliev RO. Composition of PLGA and PEI/DNA nanoparticles improves ultrasound-mediated gene delivery in solid tumors in vivo. Cancer Lett. 2008;261:215–225. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2007.11.023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Teng Y, Bai M, Sun Y, Wang Q, Li F, Xing J, Du L, Gong T, Duan Y. Enhanced delivery of PEAL nanoparticles with ultrasound targeted microbubble destruction mediated siRNA transfection in human MCF-7/S and MCF-7/ADR cells in vitro. Int J Nanomedicine. 2015;10:5447. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S81172. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Delalande A, Kotopoulis S, Postema M, Midoux P, Pichon C. Sonoporation: mechanistic insights and ongoing challenges for gene transfer. Gene. 2013;525:191–199. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2013.03.095. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Lentacker I, De Cock I, Deckers R, De Smedt S, Moonen C. Understanding ultrasound induced sonoporation: definitions and underlying mechanisms. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2014;72:49–64. doi: 10.1016/j.addr.2013.11.008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Wang TY, Wilson KE, Machtaler S, Willmann JK. Ultrasound and microbubble guided drug delivery: mechanistic understanding and clinical implications. Curr Pharm Biotechnol. 2013;14:743–752. doi: 10.2174/1389201014666131226114611. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Karshafian R, Bevan PD, Williams R, Samac S, Burns PN. Sonoporation by ultrasound-activated microbubble contrast agents: effect of acoustic exposure parameters on cell membrane permeability and cell viability. Ultrasound Med Biol. 2009;35:847–860. doi: 10.1016/j.ultrasmedbio.2008.10.013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Forbes MM, Steinberg RL. Examination of inertial cavitation of optison in producing sonoporation of Chinese hamster ovary cells. Ultrasound Med Biol. 2008;34:2009–2018. doi: 10.1016/j.ultrasmedbio.2008.05.003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Wang TY, Choe JW, Pu K, Devulapally R, Bachawal S, Machtaler S, Chowdhury SM, Luong R, Tian L, Khuri-Yakub B, Rao J, Paulmurugan R, Willmann JK. Ultrasound-guided delivery of microRNA loaded nanoparticles into cancer. J Control Release. 2015;203:99–108. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2015.02.018. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Smith L, Watson MB, O’Kane SL, Drew PJ, Lind MJ, Cawkwell L. The analysis of doxorubicin resistance in human breast cancer cells using antibody microarrays. Mol Cancer Ther. 2006;5:2115–2120. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-06-0190. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Dong Z, Ren L, Lin L, Li J, Huang Y, Li J. Effect of microRNA-21 on multidrug resistance reversal in A549/DDP human lung cancer cells. Mol Med Rep. 2015;11:682–690. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2014.2662. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Mahato RI. Biomaterials for Delivery and Targeting of Proteins and Nucleic Acids. CRC Press; 2004. [Google Scholar]
- 39.Shibata C, Otsuka M, Kishikawa T, Yoshikawa T, Ohno M, Takata A, Koike K. Current status of miRNA-targeting therapeutics and preclinical studies against gastroenterological carcinoma. Mol Cell Ther. 2013;1 doi: 10.1186/2052-8426-1-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Aravalli RN. Development of microRNA therapeutics for hepatocellular carcinoma. Diagnostics. 2013;3:170–191. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics3010170. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Hong L, Han Y, Zhang Y, Zhang H, Zhao Q, Wu K, Fan D. MicroRNA-21: a therapeutic target for reversing drug resistance in cancer. Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2013;17:1073–1080. doi: 10.1517/14728222.2013.819853. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Boado RJ, Pardridge WM. Complete protection of antisense oligonucleotides against serum nuclease degradation by an avidin-biotin system. Bioconjug Chem. 1992;3:519–523. doi: 10.1021/bc00018a010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Danhier F, Ansorena E, Silva JM, Coco R, Le Breton A, Préat V. PLGA-based nanoparticles: an overview of biomedical applications. J Control Release. 2012;161:505–522. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2012.01.043. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Hsu S-h, Yu B, Wang X, Lu Y, Schmidt CR, Lee RJ, Lee LJ, Jacob ST, Ghoshal K. Cationic lipid nanoparticles for therapeutic delivery of siRNA and miRNA to murine liver tumor. Nanomed Nanotechnol Biol Med. 2013;9:1169–1180. doi: 10.1016/j.nano.2013.05.007. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Yang T, Zhao P, Rong Z, Li B, Xue H, You J, He C, Li W, He X, Lee RJ. Anti-tumor efficiency of lipid-coated cisplatin nanoparticles co-loaded with microRNA-375. Theranostics. 2016;6:142. doi: 10.7150/thno.13130. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Liu JY, Chiang T, Liu CH, Chern GG, Lin TT, Gao DY, Chen Y. Delivery of siRNA using CXCR4-targeted nanoparticles modulates tumor microenvironment and achieves a potent antitumor response in liver cancer. Mol Ther. 2015;23(11):1772–1782. doi: 10.1038/mt.2015.147. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Wang L, Su W, Liu Z, Zhou M, Chen S, Chen Y, Lu D, Liu Y, Fan Y, Zheng Y. CD44 antibody-targeted liposomal nanoparticles for molecular imaging and therapy of hepatocellular carcinoma. Biomaterials. 2012;33:5107–5114. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2012.03.067. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Kota J, Chivukula RR, O’Donnell KA, Wentzel EA, Montgomery CL, Hwang H-W, Chang T-C, Vivekanandan P, Torbenson M, Clark KR, Mendell JR, Mendell JT. Therapeutic microRNA delivery suppresses tumorigenesis in a murine liver cancer model. Cell. 2009;137:1005–1017. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2009.04.021. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Lang Q, Ling C. MiR-124 suppresses cell proliferation in hepatocellular carcinoma by targeting PIK3CA. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2012;426:247–252. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2012.08.075. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Zhang X, Liu S, Hu T, Liu S, He Y, Sun S. Up-regulated microRNA-143 transcribed by nuclear factor kappa B enhances hepatocarcinoma metastasis by repressing fibronectin expression. Hepatology. 2009;50:490–499. doi: 10.1002/hep.23008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Liu J, Shi W, Wu C, Ju J, Jiang J. miR-181b as a key regulator of the oncogenic process and its clinical implications in cancer (review) Biomed Rep. 2014;2:7–11. doi: 10.3892/br.2013.199. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Kocbek P, Obermajer N, Cegnar M, Kos J, Kristl J. Targeting cancer cells using PLGA nanoparticles surface modified with monoclonal antibody. J Control Release. 2007;120:18–26. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2007.03.012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Bae YH, Park K. Targeted drug delivery to tumors: myths, reality and possibility. J Control Release. 2011;153:198. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2011.06.001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Maity AR, Stepensky D. Limited efficiency of drug delivery to specific intracellular organelles using subcellularly “targeted” drug delivery systems. Mol Pharm. 2015;13:1–7. doi: 10.1021/acs.molpharmaceut.5b00697. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Wang DS, Panje C, Pysz MA, Paulmurugan R, Rosenberg J, Gambhir SS, Schneider M, Willmann JK. Cationic versus neutral microbubbles for ultrasound-mediated gene delivery in cancer. Radiology. 2012 Sep;264(3):721–732. doi: 10.1148/radiol.12112368. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Panje CM, Wang DS, Willmann JK. Ultrasound and Microbubble–Mediated Gene Delivery in Cancer: Progress and Perspectives. Investigative radiology. 2013;48(11):755–769. doi: 10.1097/RLI.0b013e3182982cc1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Panje CM, Wang DS, Pysz MA, Paulmurugan R, Ren Y, Tranquart F, Tian L, Willmann JK. Ultrasound-mediated gene delivery with cationic versus neutral microbubbles: effect of DNA and microbubble dose on in vivo transfection efficiency. Theranostics. 2012;2(11):1078–1091. doi: 10.7150/thno.4240. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.


