Abstract
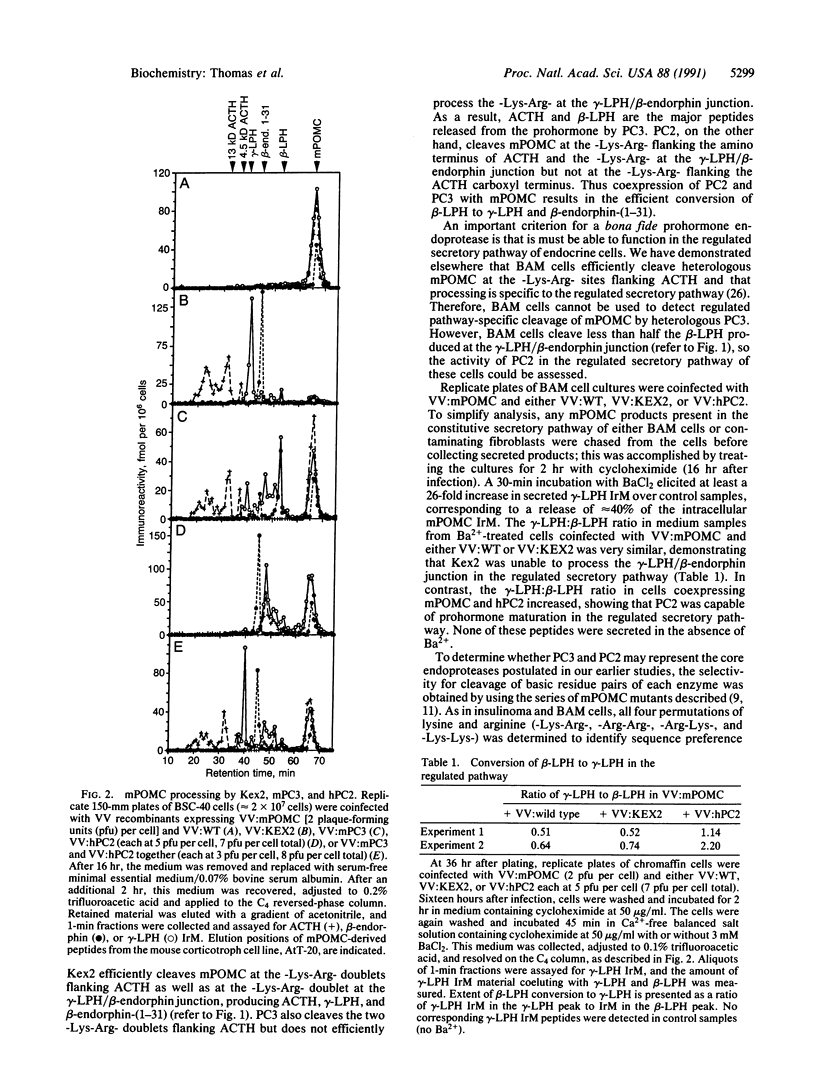
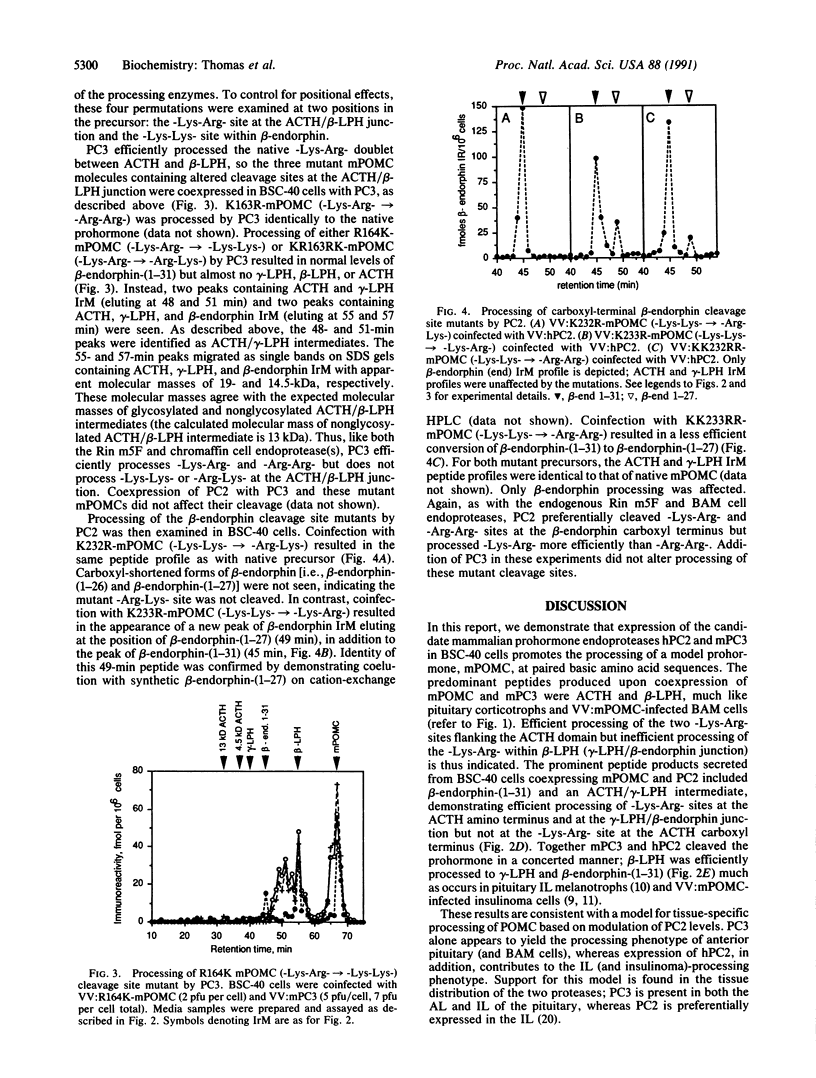
Two mammalian gene products, PC2 and PC3, have been proposed as candidate neuroendocrine-precursor processing enzymes based on the structural similarity of their catalytic domains to that of the yeast precursor-processing endoprotease Kex2. In this report we demonstrate that these two proteases can cleave proopiomelanocortin (POMC) in the secretory pathway of mammalian cells. Similarly to pituitary corticotrophs, PC3 expressed in processing-deficient BSC-40 cells cleaved native mouse POMC at the -Lys-Arg- sites flanking corticotropin. The -Lys-Arg- within beta-lipotropin was less efficiently cleaved to release beta-endorphin. Expression of PC2 together with PC3 resulted in efficient conversion of beta-lipotropin, as occurs in pituitary melanotrophs. Furthermore, coexpression of PC2 together with mouse POMC in bovine adrenomedullary chromaffin cells resulted in conversion of beta-lipotropin to gamma-lipotropin and beta-endorphin in the regulated secretory pathway. Finally, the processing selectivities of PC3 and PC2 expressed together in BSC-40 cells were determined by using a series of mutant mouse POMCs containing all possible pairs of basic residues at certain sites. The observed pattern of cleavage site selectivities mimicked that of the endogenous endoproteases of the insulinoma and bovine adrenomedullary chromaffin cells, suggesting that PC2 and PC3 may represent important core endoproteases in the catalysis of prohormone processing in many neuroendocrine cell types.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berger E. A., Shooter E. M. Evidence for pro-beta-nerve growth factor, a biosynthetic precursor to beta-nerve growth factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Sep;74(9):3647–3651. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.9.3647. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bresnahan P. A., Leduc R., Thomas L., Thorner J., Gibson H. L., Brake A. J., Barr P. J., Thomas G. Human fur gene encodes a yeast KEX2-like endoprotease that cleaves pro-beta-NGF in vivo. J Cell Biol. 1990 Dec;111(6 Pt 2):2851–2859. doi: 10.1083/jcb.111.6.2851. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgess T. L., Kelly R. B. Constitutive and regulated secretion of proteins. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1987;3:243–293. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.03.110187.001331. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chance R. E., Ellis R. M., Bromer W. W. Porcine proinsulin: characterization and amino acid sequence. Science. 1968 Jul 12;161(3837):165–167. doi: 10.1126/science.161.3837.165. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chrétien M., Li C. H. Isolation, purification, and characterization of gamma-lipotropic hormone from sheep pituitary glands. Can J Biochem. 1967 Jul;45(7):1163–1174. doi: 10.1139/o67-133. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davidson H. W., Rhodes C. J., Hutton J. C. Intraorganellar calcium and pH control proinsulin cleavage in the pancreatic beta cell via two distinct site-specific endopeptidases. Nature. 1988 May 5;333(6168):93–96. doi: 10.1038/333093a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuller R. S., Brake A., Thorner J. Yeast prohormone processing enzyme (KEX2 gene product) is a Ca2+-dependent serine protease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Mar;86(5):1434–1438. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.5.1434. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hruby D. E., Thomas G., Herbert E., Franke C. A. Use of vaccinia virus as a neuropeptide expression vector. Methods Enzymol. 1986;124:295–309. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(86)24022-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Julius D., Schekman R., Thorner J. Glycosylation and processing of prepro-alpha-factor through the yeast secretory pathway. Cell. 1984 Feb;36(2):309–318. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90224-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCune J. M., Rabin L. B., Feinberg M. B., Lieberman M., Kosek J. C., Reyes G. R., Weissman I. L. Endoproteolytic cleavage of gp160 is required for the activation of human immunodeficiency virus. Cell. 1988 Apr 8;53(1):55–67. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90487-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roebroek A. J., Schalken J. A., Leunissen J. A., Onnekink C., Bloemers H. P., Van de Ven W. J. Evolutionary conserved close linkage of the c-fes/fps proto-oncogene and genetic sequences encoding a receptor-like protein. EMBO J. 1986 Sep;5(9):2197–2202. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04484.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seidah N. G., Gaspar L., Mion P., Marcinkiewicz M., Mbikay M., Chrétien M. cDNA sequence of two distinct pituitary proteins homologous to Kex2 and furin gene products: tissue-specific mRNAs encoding candidates for pro-hormone processing proteinases. DNA Cell Biol. 1990 Jul-Aug;9(6):415–424. doi: 10.1089/dna.1990.9.415. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seidah N. G., Marcinkiewicz M., Benjannet S., Gaspar L., Beaubien G., Mattei M. G., Lazure C., Mbikay M., Chrétien M. Cloning and primary sequence of a mouse candidate prohormone convertase PC1 homologous to PC2, Furin, and Kex2: distinct chromosomal localization and messenger RNA distribution in brain and pituitary compared to PC2. Mol Endocrinol. 1991 Jan;5(1):111–122. doi: 10.1210/mend-5-1-111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smeekens S. P., Avruch A. S., LaMendola J., Chan S. J., Steiner D. F. Identification of a cDNA encoding a second putative prohormone convertase related to PC2 in AtT20 cells and islets of Langerhans. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jan 15;88(2):340–344. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.2.340. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smeekens S. P., Steiner D. F. Identification of a human insulinoma cDNA encoding a novel mammalian protein structurally related to the yeast dibasic processing protease Kex2. J Biol Chem. 1990 Feb 25;265(6):2997–3000. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith A. I., Funder J. W. Proopiomelanocortin processing in the pituitary, central nervous system, and peripheral tissues. Endocr Rev. 1988 Feb;9(1):159–179. doi: 10.1210/edrv-9-1-159. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sossin W. S., Fisher J. M., Scheller R. H. Cellular and molecular biology of neuropeptide processing and packaging. Neuron. 1989 May;2(5):1407–1417. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(89)90186-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steiner D. F., Cunningham D., Spigelman L., Aten B. Insulin biosynthesis: evidence for a precursor. Science. 1967 Aug 11;157(3789):697–700. doi: 10.1126/science.157.3789.697. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas G., Thorne B. A., Thomas L., Allen R. G., Hruby D. E., Fuller R., Thorner J. Yeast KEX2 endopeptidase correctly cleaves a neuroendocrine prohormone in mammalian cells. Science. 1988 Jul 8;241(4862):226–230. doi: 10.1126/science.3291117. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thorne B. A., Caton L. W., Thomas G. Expression of mouse proopiomelanocortin in an insulinoma cell line. Requirements for beta-endorphin processing. J Biol Chem. 1989 Feb 25;264(6):3545–3552. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thorne B. A., Thomas G. An in vivo characterization of the cleavage site specificity of the insulin cell prohormone processing enzymes. J Biol Chem. 1990 May 25;265(15):8436–8443. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wise R. J., Barr P. J., Wong P. A., Kiefer M. C., Brake A. J., Kaufman R. J. Expression of a human proprotein processing enzyme: correct cleavage of the von Willebrand factor precursor at a paired basic amino acid site. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Dec;87(23):9378–9382. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.23.9378. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshimasa Y., Seino S., Whittaker J., Kakehi T., Kosaki A., Kuzuya H., Imura H., Bell G. I., Steiner D. F. Insulin-resistant diabetes due to a point mutation that prevents insulin proreceptor processing. Science. 1988 May 6;240(4853):784–787. doi: 10.1126/science.3283938. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van de Ven W. J., Voorberg J., Fontijn R., Pannekoek H., van den Ouweland A. M., van Duijnhoven H. L., Roebroek A. J., Siezen R. J. Furin is a subtilisin-like proprotein processing enzyme in higher eukaryotes. Mol Biol Rep. 1990 Nov;14(4):265–275. doi: 10.1007/BF00429896. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van den Ouweland A. M., van Duijnhoven H. L., Keizer G. D., Dorssers L. C., Van de Ven W. J. Structural homology between the human fur gene product and the subtilisin-like protease encoded by yeast KEX2. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Feb 11;18(3):664–664. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.3.664. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



