Abstract
Using phylogenomic and gene compositional analyses, five highly conserved gene families have been detected in the core genome of the phylogenetically coherent genus Acidithiobacillus of the class Acidithiobacillia. These core gene families are absent in the closest extant genus Thermithiobacillus tepidarius that subtends the Acidithiobacillus genus and roots the deepest in this class. The predicted proteins encoded by these core gene families are not detected by a BLAST search in the NCBI non-redundant database of more than 90 million proteins using a relaxed cut-off of 1.0e−5. None of the five families has a clear functional prediction. However, bioinformatic scrutiny, using pI prediction, motif/domain searches, cellular location predictions, genomic context analyses, and chromosome topology studies together with previously published transcriptomic and proteomic data, suggests that some may have functions associated with membrane remodeling during cell division perhaps in response to pH stress. Despite the high level of amino acid sequence conservation within each family, there is sufficient nucleotide variation of the respective genes to permit the use of the DNA sequences to distinguish different species of Acidithiobacillus, making them useful additions to the armamentarium of tools for phylogenetic analysis. Since the protein families are unique to the Acidithiobacillus genus, they can also be leveraged as probes to detect the genus in environmental metagenomes and metatranscriptomes, including industrial biomining operations, and acid mine drainage (AMD).
Keywords: Acidithiobacillus, Thermithiobacillus, extreme acidophile, Orphan (ORFan) genes, horizontal gene transfer (HGT), biomining bioleaching and acid mine drainage (AMD), acid resistance, metagenome and metatranscriptome
Introduction
The power of comparative genomics to enlighten evolutionary processes through hypotheses has emerged based on the enormous availability of complete and partial genome sequences from both early and late branching lineages at different taxonomic levels (MacLean et al., 2009). At present, we are able to exploit the powerful analytical methods of molecular evolution and population genomics to determine the relative contribution of the different evolutionary forces that shape genome organization, structure, and diversity. These methods also offer an exceptional opportunity to explore the genetic and genomic determinants of lifestyle diversity in bacteria, especially for polyextremophiles including those that thrive in extremely acidic environments and for which there are genome sequences available (Cárdenas et al., 2016a,b).
The genus Acidithiobacillus (termed Acidithiobacilli) consists of seven recognized species; Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans, A. ferridurans, A. ferrivorans, A. ferriphilus, A. thiooxidans, A. caldus and A. albertensis (reviewed in Nuñez et al., 2016). The Acidithiobacilli together with Thermithiobacillus tepidarius constitute the class Acidithiobacillia (Williams and Kelly, 2013; Hudson et al., 2014).
The Acidithiobacilli have been found principally in industrial biomining and coal processing operations, the deep subsurface of the Spanish pyritic belt and in natural and man-made acid drainages including acid mine drainage (AMD; Méndez-García et al., 2015; Hedrich, 2016). All are extreme acidophiles with a pH optima for growth of 3.5 or less (Barrie Johnson and Quatrini, 2016). In contrast, T. tepidarius is a neutrophile that was recovered from a terrestrial thermal spring (Wood and Kelly, 1985). All the other extant bacterial lineages phylogenetically closely related to T. tepidarius are also neutrophiles, making it likely that the last common ancestor before the split between T. tepidarius and the Acidithiobacilli was also a neutrophile. This raises questions about the origin and evolution of genes and mechanisms that allowed the transition to be made from a neutral pH environment to an extremely acidic environment eventually giving rise to the Acidithiobacilli.
Mechanisms used by extreme acidophiles to mitigate the effect of low pH have been extensively investigated (Baker-Austin and Dopson, 2007). However, there are no studies that use comparative genomics to discover new genetic determinants of pH homeostasis in the Acidithiobacilli, although one study used multiple strains of A. thiooxidans to confirm known acid resistant determinants and assign them to the core or accessory genome (Zhang et al., 2016).
The study of unique gene families from extreme acidophile representatives could provide evidence about events of protein lineage specification involving many structural rearrangements needed to survive under extreme life conditions. Gene tree analyses suggest recent, lineage-specific expansion, and diversification among homologs encoding yet unknown functions for pathway and processes that might be unique requirements in Acidithiobacilli. Their analysis could help close gaps in our understanding of genetic and metabolic requirements that support extremophile lifestyles and they could also provide novel candidate sequences for prospecting for new DNA-based screenings and other production avenues (Sabir et al., 2016).
In the present study, we perform an extensive bioinformatic characterization of five protein families taxonomically restricted to the Acidithiobacilli. Analyses of their fundamental properties combined with comparative genomics and phylogenomics suggest potential functional roles and allow evolutionary models to be built. The sequences of the five families are also exploited as molecular probes for phylogenetic scrutiny and interrogation of metagenomes and metatranscriptomes including AMD and biomining operations.
Materials and methods
Genomes used
Table 1 provides information about the genomes.
Table 1.
Genomes used in this study.
| Microorganism | Genome size (Mbp) | Predicted protein coding sequences | Genome G+C (%) | Genome accession number (NCBI) | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans ATCC 23270T | 2.98 | 3147 | 58.8 | CP001219 | Valdés et al., 2008 |
| Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans ATCC 53993 | 2.88 | 2826 | 58.9 | CP001132 | Lucas et al., 2008, Unpublished |
| Acidithiobacillus ferrivorans SS3T | 3.2 | 3093 | 56.6 | CP002985 | Liljeqvist et al., 2011 |
| Acidithiobacillus ferrivorans CF27 | 3.42 | 3854 | 56.4 | CCCS020000000 | Talla et al., 2014 |
| Acidithiobacillus thiooxidans A01 | 3.82 | 3826 | 53.1 | AZMO00000000 | Yin et al., 2014 |
| Acidithiobacillus thiooxidans ATCC 19377T | 3.01 | 3041 | 53.1 | AFOH00000000 | Valdés et al., 2011 |
| Acidithiobacillus thiooxidans Licanantay | 3.93 | 4191 | 52.8 | JMEB00000000 | Travisany et al., 2014 |
| Acidithiobacillus caldus ATCC 51756T | 2.77 | 2681 (0.21)P | 61.4 | CP005986-CP005989 | Valdes et al., 2009 |
| Acidithiobacillus caldus SM-1 | 2.93 | 2881 (0.31)P | 61.3 | CP002573-CP002577 | You et al., 2011 |
| Thermithiobacillus tepidarius DSM 3134T | 2.96 | 2750 | 66.8 | AUIS00000000 | Kelly and Wood, 2000 |
| Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans strain BY0502 | 2.97 | 2822 | 56.8 | LVXZ00000000 | Zhou, 2016, Unpublished |
| Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans strain DLC-5 | 4.23 | 5600 | 57.6 | JNNH00000000* | Chen et al., 2015 |
| Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans strain YQH-1 | 3.11 | 2949 | 58.6 | LJBT00000000 | Yan et al., 2015 |
| Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans strain Hel18 | 3.11 | 2939 | 58.6 | LQRJ00000000 | Schopf, 2016, Unpublished |
| Acidithiobacillus caldus strain MTH-04 | 2.87 | 2646 | 61.4 | LXQG00000000 | Mi et al., 2006, Unpublished |
| Acidithiobacillus thiooxidans DMC | 3.85 | 3768 | 53.1 | LWSB00000000 | Zhang et al., 2016 |
denotes type strain;
denotes plasmid information.
Denotes JGI accession number.
Pipeline used for compiling and analyzing the data set
Predicted protein sequences corresponding to all Acidithiobacilli proteomes were sorted using an all-vs.-all BLASTP script based on Best Bidirectional BLAST Hit (BBBH; Altschul et al., 1997) with an E-value of 1e-5. Protein families were constructed based on 50% of identity and 50% of coverage in the alignments (Altschul et al., 1997), assigning each protein to one protein family. The families with predicted proteins shared by all strains were selected and denominated the core-genome (Williams and Kelly, 2013; Hudson et al., 2014). The Acidithiobacillus core-genome was compared using BLASTP version 2.2.26 (Altschul et al., 1997) against NCBI non-redundant (NR) database in August of 2015, using a minimal E-value of 1e-5. Core families with exclusive similarity with Acidithiobacillus members, and not associated with any other microorganism, were selected and denominated unique (orphan) core genes. The selected unique protein families were checked manually using BLASTP, Psi-BLAST (Altschul et al., 1997) and HMMer version 3.0 (Eddy, 1998) against NR database with an E-value of 1e-4 to confirm their exclusive association with the Acidithiobacillus genus. The locus tags of the respective genes are provided in Table 2.
Table 2.
Predicted properties of the proteins of families I–V.
| Microorganism | Locus tag or contig | pI | Size (aa) | TM regions | Signal peptide | Subcellular location | Lipoprotein signature | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Family I | A. ferrooxidans ATCC 23270 | AFE_0294 | 8.06 | 250 | 5 | – | IM | – |
| A. ferrooxidans ATCC 53993 | Lferr_0470 | 8.06 | 251 | 5 | – | IM | – | |
| A. ferrivorans SS3 | Acife_2737 | 9.47 | 259 | 5 | – | IM | – | |
| A. ferrivorans CF27 | CDQ10770.1 | 9.26 | 259 | 5 | – | IM | – | |
| A. thiooxidans ATCC 19377 | AFOH01000117 | 8.21 | 261 | 5 | – | IM | – | |
| A. thiooxidans A01 | AZMO01000067 | 8.06 | 263 | 5 | – | IM | – | |
| A. thiooxidans Licanantay | JMEB01000250 | 8.21 | 261 | 5 | – | IM | – | |
| A. caldus SM-1 | Atc_0578 | 9.25 | 257 | 5 | – | IM | – | |
| A. caldus ATCC 51756 | Acaty_c0588 | 8.85 | 249 | 5 | – | IM | – | |
| Family II | A. ferrooxidans ATCC 23270 | AFE_2894 | 9.52 | 103 | 1 | – | IM/P/C | – |
| A. ferrooxidans ATCC 53993 | Lferr_2514 | 9.52 | 103 | 1 | – | IM | – | |
| A. ferrivorans SS3 | Acife_0262 | 10.26 | 103 | 1 | – | IM/P/C | – | |
| A. ferrivorans CF27 | CDQ10832.1 | 9.98 | 103 | 1 | – | IM/P/C | – | |
| A. thiooxidans ATCC 19377 | AFOH01000056 | 10.94 | 103 | 1 | – | IM/P/C | – | |
| A. thiooxidans A01 | AZMO01000007 | 10.63 | 103 | 1 | – | IM/P/C | – | |
| A. thiooxidans Licanantay | JMEB01000152 | 10.90 | 103 | 1 | – | IM/P/C | – | |
| A. caldus SM-1 | Atc_0665 | 10.37 | 103 | 1 | – | IM/P/C | – | |
| A. caldus ATCC 51756 | Acaty_c0696 | 9.97 | 91 | 1 | – | IM/P/C | – | |
| Family III | A. ferrooxidans ATCC 23270 | AFE_2918 | 6.82 | 128 | 1 | Yes | P | Yes |
| A. ferrooxidans ATCC 53993 | Lferr_2533 | 6.82 | 128 | 1 | Yes | P | Yes | |
| A. ferrivorans SS3 | Acife_0237 | 8.79 | 128 | 1 | Yes | P/C | Yes | |
| A. ferrivorans CF27 | CDQ10857.1 | 7.88 | 128 | 1 | Yes | P | Yes | |
| A. thiooxidans ATCC 19377 | AFOH01000056 | 8.76 | 128 | 1 | Yes | P | Yes | |
| A. thiooxidans A01 | AZMO01000007 | 8.07 | 128 | 1 | Yes | P | Yes | |
| A. thiooxidans Licanantay | JMEB01000332 | 8.76 | 128 | 1 | Yes | P | Yes | |
| A. caldus SM-1 | Atc_2682 | 8.58 | 129 | 1 | Yes | P/C | Yes | |
| A. caldus ATCC 51756 | Acaty_c2529 | 8.59 | 129 | 1 | Yes | P/C | Yes | |
| Family IV | A. ferrooxidans ATCC 23270 | AFE_3261 | 6.33 | 172 | – | Yes | P/IM | Yes |
| A. ferrooxidans ATCC 53993 | Lferr_2861 | 6.48 | 172 | – | Yes | P | Yes | |
| A. ferrivorans SS3 | Acife_0197 | 8.80 | 170 | – | Yes | P/E | Yes | |
| A. ferrivorans CF27 | CDQ11656.1 | 8.80 | 170 | – | Yes | P/E | Yes | |
| A. thiooxidans ATCC 19377 | AFOH01000137 | 6.33 | 172 | – | Yes | P | Yes | |
| A. thiooxidans A01 | AZMO01000008 | 8.21 | 171 | – | Yes | P | Yes | |
| A. thiooxidans Licanantay | JMEB01000258 | 8.22 | 171 | – | Yes | P | Yes | |
| A. caldus SM-1 | Atc_0064 | 8.80 | 170 | – | Yes | P/IM | Yes | |
| A. caldus ATCC 51756 | Acaty_c0059 | 8.80 | 170 | – | Yes | P | Yes | |
| Family V | A. ferrooxidans ATCC 23270 | AFE_2816 | 9.30 | 146 | 1 | – | P/IM | – |
| A. ferrooxidans ATCC 53993 | Lferr_2439 | 9.31 | 146 | 1 | – | P/IM | – | |
| A. ferrivorans SS3 | Acife_0333 | 9.75 | 145 | 1 | – | P | – | |
| A. ferrivorans CF27 | CDQ09308.1 | 9.70 | 145 | 1 | – | P | – | |
| A. thiooxidans ATCC 19377 | AFOH01000029 | 9.52 | 86 | 1 | – | C/P | – | |
| A. thiooxidans A01 | AZMO01000004 | 9.56 | 119 | 1 | – | P | – | |
| A. thiooxidans Licanantay | JMEB01000081 | 9.40 | 119 | 1 | Yes | P | – | |
| A. caldus SM-1 | Atc_0233 | 9.21 | 128 | 1 | – | P | – | |
| A. caldus ATCC 51756 | Acaty_c0260 | 9.21 | 128 | 1 | – | P | – |
IM, inner membrane; C, cytoplasm; P, periplasm.
Genomic contexts of unique core genes
Collinear blocks between the genomes and conservation of gene neighbors were determined by MAUVE (Darling et al., 2010), RAST (Aziz et al., 2008; Overbeek et al., 2014; Markowitz et al., 2014a) and IMG-JGI (Markowitz et al., 2014b; Dhillon et al., 2015). Genomic contexts were visualized using Artemis of Sanger (Brettin et al., 2015).
Evaluation of HGT
IslandViewer (Rutherford et al., 2000) was used to predict genomic islands.
Annotation of unique core genes (families I–V)
Protein coding sequences were annotated using an integrated pipeline consisting of BLASTP (Altschul et al., 1997) searches against NR database of NCBI with an E-value cutoff of 1e-3, Pfam (Punta et al., 2012), TigrFAM (Consortium, 2014), and Uniprot (Hofmann and Stoffel, 1993) database comparisons. Transmembrane regions in protein sequences were predicted with TMHMM (Haft et al., 2003) and TMPRED (Krogh et al., 2001). Computation of isoelectric point and molecular weight were made with ExPASy web tool (Bjellqvist et al., 1993; Nakai and Horton, 1999; Gasteiger et al., 2005).
Estimation of mutation rates
Synonymous and non-synonymous substitution rates were calculated as follows: amino acid alignments of unique (orphan) core genes were constructed using MUSCLE (Edgar, 2004), and used as input for PAL2NAL (Suyama et al., 2006) with the nucleotide sequences to create the codon alignments of gene core families. The ratio of non-synonymous (Ka) to synonymous (Ks) nucleotide substitution rates (Ka/Ks ratios) were calculated using SeqinR package of R project (Charif and Lobry, 2007). Mean Ka/Ks ratios were assigned for individual unique (orphan) core genes (families I–V) by averaging all pairwise ratios within each family.
Signal peptide and subcellular location predictions
A combination of computational prediction tools PSORTb (Nakai and Horton, 1999; Yu et al., 2010), CELLO (Yu et al., 2006) and ProtCompB1 (Yu et al., 2004) were used to perform whole genome analysis of unique core protein subcellular localization via the Sec Mechanism and Tat signal prediction (Natale et al., 2008; Bagos et al., 2010). The results derived from three prediction algorithms tools were combined according to majority to obtain a more accurate protein subcellular localization prediction.
Lipoproteins signal prediction
Prediction of lipoproteins signals was made with LipoP Server (Juncker et al., 2003).
Phylogenetic analyses
16S rRNA sequences from Acidithiobacillus genomes were identified by BLASTN-based script using an E-value threshold of 1e-5 and the databases GREENGENES (DeSantis et al., 2006), RDP (Cole et al., 2009) and SILVA (Pruesse et al., 2007) and were aligned using MAFFT (Katoh et al., 2002, 2005) alignment tool with L-INS strategy. Phylogenetic trees were constructed with MrBayes (Huelsenbeck and Ronquist, 2001; Ronquist and Huelsenbeck, 2003) and PHYML (Guindon et al., 2010), using the substitution model predicted for jModelTest2 (Guindon and Gascuel, 2003; Darriba et al., 2012).
Mapping of genes for families I–V onto circular genomes
The genes encoding families I–V were mapped onto the genomes A. ferrooxidans ATCC 23270, A. ferrivorans SS3, A. caldus ATCC 51756, and A. caldus SM-1 using DNAplotter (Carver et al., 2009). The origin of replication (Ori) of each genome was predicted between dnaN and dnaA as previously described (Valdés et al., 2008) and was used as the zero coordinate to orient the genome maps.
Metagenomic analysis
Metagenomic and metatranscriptomic sequences were downloaded from NCBI, JGI (Nordberg et al., 2014), and MG-RAST (Meyer et al., 2008; additional information can be found in Table 4) and were interrogated by BLASTX (Altschul et al., 1997) against the five core protein families with an E-value cut-off of 1e-5. The percent identity and coverage of sequences were analyzed for each alignment.
Results and discussion
Pipeline for discovery of protein families unique to the core genome of the genus Acidithiobacillus
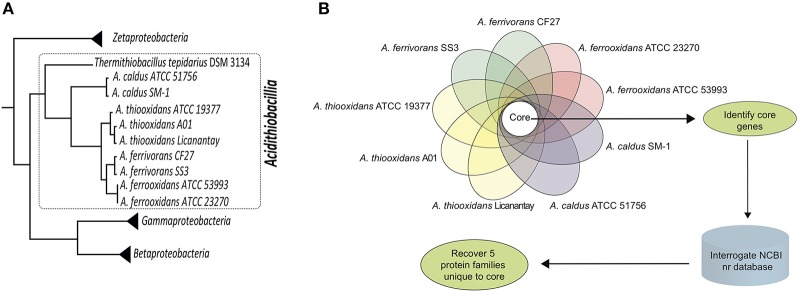
Figure 1 summarizes the bioinformatics pipeline used to recover five families of proteins and their corresponding genes that are taxonomically restricted to the genus Acidithiobacillus. Using a relaxed cutoff (1e-5) in a BLAST search, they were not detected in the NCBI nr database of more than 90 million proteins that includes the predicted proteins of Thermithiobacillus tepidarius, the nearest extant relative of the Acidithiobacilli.
Figure 1.
Work Flow. (A) Phylogenetic tree of the class Acidithiobacillia (within the dotted line) showing the clustering of the acidophilic Acidithiobacillus genus (Acidithiobacilli) subtended by the neutrophilic Thermithiobacillus tepidarius. The tree is based on genome-scale maximum-likelihood analysis of 98 universal protein families (housekeeping) conserved in Zeta-, Gamma-, Betaproteobacteria, and Acidithiobacillia class according to references Williams and Kelly (2013) and Hudson et al. (2014). (B) Pipeline for the identification and recovery of five protein families (termed I-V) unique to the genus Acidithiobacillus.
Integrative bioinformatics approaches can suggest functions for the unique Acidithiobacillus gene families I–V
Since Acidithiobacilli-specific protein families have almost no similarity with known proteins for other non-Acidithiobacilli representatives, we used a collection of bioinformatics resources in order to gain insights into potential protein functions based on hydrophobicity profiles, secondary structure predictions, predicted protein cell localizations and the comparison of consensus and profile sequences to pattern and domain databases (see Section Materials and Methods). Protein function predictions of the five Acidithiobacilli-specific protein families were examined using an analysis of their genomic contexts. Their differential expression was linked to previously published proteomic data derived from cells subjected to changes of pH, which is known to be a major selective pressure for members of the Acidithiobacillus genus (Baker-Austin and Dopson, 2007; see Table 3).
Table 3.
Gene expression evidence.
| Microorganism | Locus tag or contig | Gene expresseda | Protein abundance with pH changeb | Meta-transcriptomic evidencec | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Family I | A. ferrooxidans ATCC 23270 | AFE_0294 | ND | ND | Family I | AFE sp. Yes |
| A. ferrooxidans ATCC 53993 | Lferr_0470 | ND | ND | |||
| A. ferrivorans SS3 | Acife_2737 | Yes | ND | |||
| A. ferrivorans CF27 | CDQ10770.1 | ND | ND | AFV sp. Yes | ||
| A. thiooxidans ATCC 19377 | AFOH01000117 | ND | ND | |||
| A. thiooxidans A01 | AZMO01000067 | ND | ND | |||
| A. thiooxidans Licanantay | JMEB01000250 | ND | ND | ATHIO sp. Yes | ||
| A. caldus SM-1 | Atc_0578 | ND | ND | |||
| A. caldus ATCC 51756 | Acaty_c0588 | Yes | Up at pH 1 | |||
| Family II | A. ferrooxidans ATCC 23270 | AFE_2894 | ND | ND | Family II | AFE sp. Yes |
| A. ferrooxidans ATCC 53993 | Lferr_2514 | ND | ND | |||
| A. ferrivorans SS3 | Acife_0262 | Yes | ND | |||
| A. ferrivorans CF27 | CDQ10832.1 | ND | ND | AFV sp. Yes | ||
| A. thiooxidans ATCC 19377 | AFOH01000056 | ND | ND | |||
| A. thiooxidans A01 | AZMO01000007 | ND | ND | |||
| A. thiooxidans Licanantay | JMEB01000152 | ND | ND | ATHIO sp. Yes | ||
| A. caldus SM-1 | Atc_0665 | ND | ND | |||
| A. caldus ATCC 51756 | Acaty_c0696 | Yes | No change | |||
| Family III | A. ferrooxidans ATCC 23270 | AFE_2918 | Yes | ND | Family III | AFE sp. Yes |
| A. ferrooxidans ATCC 53993 | Lferr_2533 | ND | ND | |||
| A. ferrivorans SS3 | Acife_0237 | Yes | ND | |||
| A. ferrivorans CF27 | CDQ10857.1 | ND | ND | AFV sp. Yes | ||
| A. thiooxidans ATCC 19377 | AFOH01000056 | ND | ND | |||
| A. thiooxidans A01 | AZMO01000007 | ND | ND | |||
| A. thiooxidans Licanantay | JMEB01000332 | ND | ND | ATHIO sp. Yes | ||
| A. caldus SM-1 | Atc_2682 | ND | ND | |||
| A. caldus ATCC 51756 | Acaty_c2529 | Yes | Up at pH 1 | |||
| Family IV | A. ferrooxidans ATCC 23270 | AFE_3261 | ND | ND | Family IV | AFE sp. Yes |
| A. ferrooxidans ATCC 53993 | Lferr_2861 | ND | ND | |||
| A. ferrivorans SS3 | Acife_0197 | Yes | ND | |||
| A. ferrivorans CF27 | CDQ11656.1 | ND | ND | AFV sp. Yes | ||
| A. thiooxidans ATCC 19377 | AFOH01000137 | ND | ND | |||
| A. thiooxidans A01 | AZMO01000008 | ND | ND | |||
| A. thiooxidans Licanantay | JMEB01000258 | ND | ND | ATHIO sp. Yes | ||
| A. caldus SM-1 | Atc_0064 | ND | ND | |||
| A. caldus ATCC 51756 | Acaty_c0059 | Yes | Up at pH 1 | |||
| Family V | A. ferrooxidans ATCC 23270 | AFE_2816 | ND | ND | Family V | AFE sp. Yes |
| A. ferrooxidans ATCC 53993 | Lferr_2439 | ND | ND | |||
| A. ferrivorans SS3 | Acife_0333 | Yes | ND | |||
| A. ferrivorans CF27 | CDQ09308.1 | ND | ND | AFV sp. Yes | ||
| A. thiooxidans ATCC 19377 | AFOH01000029 | ND | ND | |||
| A. thiooxidans A01 | AZMO01000004 | ND | ND | |||
| A. thiooxidans Licanantay | JMEB01000081 | ND | ND | ATHIO sp. Yes | ||
| A. caldus SM-1 | Atc_0233 | ND | ND | |||
| A. caldus ATCC 51756 | Acaty_c0260 | Yes | Up at pH 4 |
Expression of members of the five orphan families in different environmental conditions. Locus tags for the five families are provided.
Gene expression for families I–V was extracted from Christel et al. (2016a,b) and Osorio et al. (2013).
Information regarding protein abundance levels when A. caldus was subjected to growth at pH 1, 2, or 4 was taken from Mangold et al. (2013). Abundance of proteins is expressed as “up in low pH” or “up in high pH” relative to protein levels found at pH 2 (Mangold et al., 2013). Note that the gene accession numbers in Mangold et al. (2013) have been replaced recently by the locus tags provided in this Table.
RNA transcript expression as determined by examination of published metatranscriptomics data (Chen et al., 2015) using the families I–V as probes (see Table 4 for details).
AFE, Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans; AFV, Acidithiobacillus ferrivorans; ATHIO, Acidithiobacillus thiooxidans; ND, Not detected.
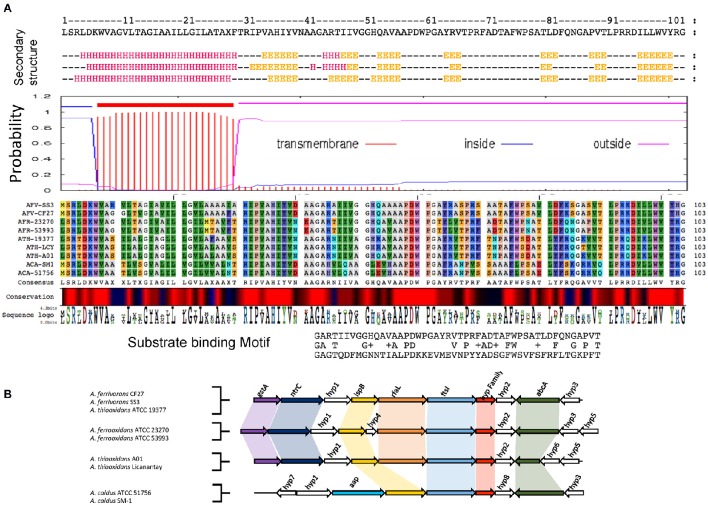
Figure 2 provides an example of the predicted protein properties deduced with bioinformatics tools and comparative genomic analysis for members of family II. Additional information for all five families I–V can be found in Supplemental Files 1, 2. In silico predictions demonstrate the power of integrative genomics approaches to gain insights into gene function. A significant prediction was made for an integral membrane segment with a moderate conservation profile within the family II. From the non-membrane associated portion of the protein, profile sequences were generated that have similarity to a pattern present in periplasmic binding proteins (Dwyer and Hellinga, 2004) and also solute carrier organic anion transporter family member 4A1 (Pizzagalli et al., 2003).
Figure 2.
Example of functional prediction based on multiple bioinformatics and genome-based evidence for members of family II. (A) Bioinformatics analysis of members of family II based on secondary structure prediction, hydrophobicity profiles and transmembrane segments prediction, multiple alignments and conservation profiles for the generation of consensus and profile sequences and their comparison to specific substrate binding protein profiles found in public databases. (B) Genomic context analysis of members of family II including functional annotations of the closest neighborhood genes for functional association. gstA, Glutathione S-transferase; ntrC, Nitrogen assimilation regulatory protein; ispB, Octaprenyl-diphosphate synthase; rfaL, O-antigen ligase; ftsI, Cell division protein; Hyp family II, Hypothetical protein; abcA, ABC transporter A family; app, Amino acid permease; Hyp (1–8), Hypothetical protein (1–8). Table 2 provides a complete overview of the predicted properties from amino acid sequences for member of the five families.
Comparative genome organization data demonstrated that there is conservation of gene neighborhood profiles that include genes predicted for cell division, surface proteins and ABC transport systems (Figure 2 and Supplemental File 3). Table 2 shows a detailed overview of the predicted properties based on amino acid sequences for families I–V.
Gene expression of families I–V
Information regarding the expression of the genes encoding the five families was extracted from the literature and is presented in Table 3. RNA transcript analysis indicates that all five family genes are expressed in A. ferrivorans SS3 in two different conditions: continuous culture at 20°C (Christel et al., 2016a) and at 8°C (Christel et al., 2016b), adjusted to pH 2.5 with sulfuric acid plus trace elements. A proteomic study of A. ferrooxidans ATCC 23270 on elemental sulfur as electron donor under aerobic and anaerobic conditions (Osorio et al., 2013) showed that family III was expressed in this strain. A proteomic study of A. caldus ATCC 51756 using cells grown at pH 2.5 (optimum growth pH) vs. pH 1 and 4, demonstrated up-regulation of core families I, III, and IV when cells were shifted from pH 2.5 to 1 and that family V was upregulated when cells were shifted from pH 2.5 to 4 (Table 3; Mangold et al., 2013). These data show that the genes for the five families (i) are expressed and thus are unlikely to be mis-annotated open reading frames with no coding capacity and (ii) provide evidence that families I, III, IV, and V could be involved in responses to acid stress at least in A. caldus. It remains to be determined if changes in RNA levels are associated with these genes in the other Acidithiobacilli.
In addition, RNA transcripts in metatranscriptomes of the Dabaoshan and Yunfu Pond mines in China (Chen et al., 2015) were detected that exhibited sequences similar to families I–V (Table 3, right hand side) from A. ferrooxidans, A. ferrivorans, and A. thiooxidans, although no strain specificity could be determined. This supports the idea that the five families are bona fide genes.
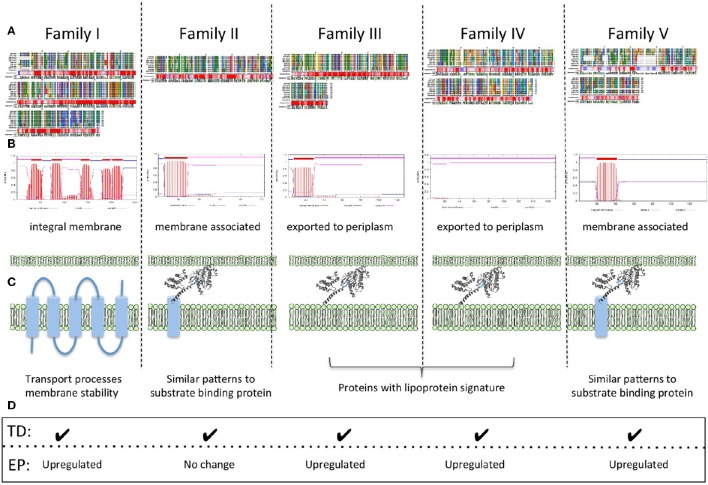
Insights into protein functions
In order to make a comprehensive summary of the potential gene function inferred from all the evidence presented, a schematic summary is presented in Figure 3. Families I, II, and V, have predicted transmembrane segments that, in conjunction with protein sorting signal identification, provide preliminary information about their cellular location. Profile and consensus sequences comparisons against public databases only provided information about family II. Family II sequences have motifs similar to those of periplasmic binding proteins, usually associated with ABC transport for the substrate specific incorporation of nutrients and scarce molecules or beneficial solutes under extreme environmental conditions (Cuneo et al., 2008). We suggest that members of family II could be distant relatives of periplasmic binding proteins whose specific substrate(s) and functional role remains to be investigated.
Figure 3.
Schematic summary of functional associations found in families I–V. (A) Multiple alignments, conservation profiles and consensus sequences. (B) Transmembrane topology predictions. (C) Predicted protein localization and deduced general functions. (D) Expression data TD: RNA transcript detected; EP: protein expression profile.
Families III and IV have predicted protein localizations associated with inner membrane and periplasmic spaces and their strong lipoprotein signatures, in addition to genomic context information, provide clues for their potential role in key physiological processes, such as lipid metabolism. We hypothesize a potential connection between membrane associated lipoproteins, lipid metabolism and membrane stability as a requirement for low pH lifestyle (Baker-Austin and Dopson, 2007; Liljeqvist et al., 2015).
Predicted protein properties of all families I–V, suggest a general involvement in functions associated with membrane processes perhaps involving roles in membrane stability, transport processes, and/or the generation of molecular components to allow the synthesis and incorporation of hydrophobic molecules into the membrane increasing its stability in low pH.
Chromosome architecture is consistent with functional inferences (involvement in cell envelope remodeling during cell division)
It has been observed in many bacteria that the gene order relative to OriC is highly conserved along the chromosomal replicores (Sobetzko et al., 2012). Also, essential and highly expressed genes tend to be encoded close to oriC (Rocha, 2004). This heightened activity can be attributed to gene dosage effects during chromosome replication especially in rapidly dividing cells, but underlying physical properties of the circular chromosome, including an inferred gradient of DNA superhelical density from the origin to the terminus, are also known to be involved in influencing gene expression (Sobetzko et al., 2012).
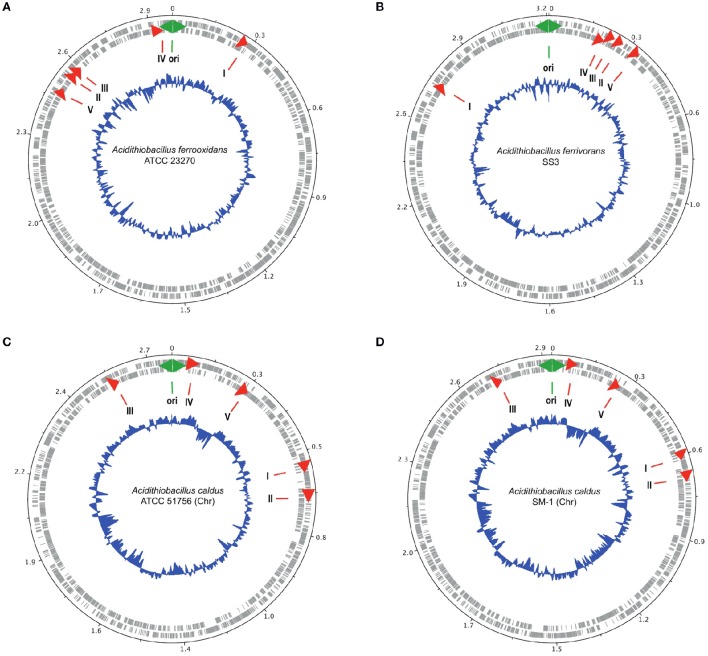
In particular, it has been observed that several genes involved in acid stress, including envelope remodeling, are located close to oriC in the gammaproteobacterium Dickeya dadantii (Jiang et al., 2015). Given the possibility that genes of families I–V could be involved in acid stress response and that this response might be associated with chromosome topology, we determine their chromosomal locations on the closed circular chromosomes of A. ferrooxidans ATCC 23270T, A. ferrivorans SS3T, A. caldus ATCC 51756T, and A. caldus SM-1 using DNAplotter (Carver et al., 2009; Figure 4). In all these chromosomes, the five family genes exhibit a tendency to be located nearer Ori rather than the terminus, especially in the cases of A. ferrooxidans and A. ferrivorans. In the latter two chromosomes, the gene order relative to Ori is conserved but is inverted, perhaps due to inter-replicore translocation that is known to be common around Ori in other microorganisms (Eisen et al., 2000; Khedkar and Seshasayee, 2016). Three of the families have genes predicted to DNA handling functions in their gene neighborhoods ordered in tightly clustered associations that could be operons; for example, rmuC (DNA recombination) near family IV, and dnaB and radA (DNA helicase and DNA repair, respectively) near family V. These genes are usually associated with DNA replication and cell division (Figure 4). The juxtaposition of ftsL, an essential cell division protein (Guzman et al., 1992), to the gene encoding family II and its closeness to the family III gene (Figure 4) strongly suggests that family II and III are involved in cell division perhaps through cell envelope remodeling. Their proximity to Ori could enhance the ability of the Acidithiobacilli to respond to changes in environmental acidity at early stages of cell division. Such changes might be more difficult to accomplish during later stages of cell division or at the resting stage.
Figure 4.
Location of the genes encoding families I–V (red arrows) in the genomes of (A) A. ferrooxidans ATCC 23270, (B) A. ferrivorans SS3, (C) A. caldus ATCC 51756, and (D) A. caldus SM-1. The outer two circles show the genes on both strands of DNA of the chromosome. The inner blue circle indicates the G+C content. The green two-headed arrow indicates the predicted origin of replication of the chromosome. The red arrows indicate the position of the families I–V genes.
Families I–V are protein coding genes
Taxonomically restricted genes, such as families I–V, are referred to as orphans genes or ORFans (orphan open reading frames; Fischer and Eisenberg, 1999; Pedroso et al., 2008; Tautz and Domazet-Loso, 2011). ORFans can be artifacts of annotation, non-coding RNA genes or protein encoding genes (Prabh and Rodelsperger, 2016). In the case of families I–V, there is evidence that those from A. caldus encode proteins and that families I–V from A. ferrooxidans, A. ferrivorans, and A. thiooxidans express RNA (Table 3). Given the highly conserved sequences similarity between the respective families from the different Acidithiobacillus species, it is reasonable to suggest that all are protein coding genes, as observed for the A. caldus families and are not “merely” RNA genes. However, in order to provide additional evidence for protein coding capacity, selection pressure was measured as the ratio of the synonymous and non-synonymous rates of amino acid substitution (dN/dS), also called omega (ω) for all families. The omega values for families I–V are 0.07, 0.05, 0.03, 0.05, and 0.08 respectively. An ω <1 can be interpreted as evidence for negative selection and most likely such a sequence would correspond to a protein encoding gene (Prabh and Rodelsperger, 2016). The omega values are considerably <1 for all five families providing compelling evidence that they are protein-encoding genes.
Origin of families I–V
The genes encoding families I–V are not found in T. tepidarius that subtends the genus Acidithiobacillus and shares the last common ancestor with it, nor are they found in any other organism that has sequence information in the NCBI nr database. So questions arise as to the origin and evolution of the five families.
We propose three main hypotheses.
The genes arose de novo in the Acidithiobacillus genus, after its split with T. tepidarius perhaps by gene duplication and divergence (Long et al., 2003; Tautz and Domazet-Loso, 2011; Klasberg et al., 2016). If this happened, then the duplication events occurred so long ago and/or involved such fast divergence that sequence similarities to the original genes have been blurred by subsequent evolutionary events.
The genes entered the last common ancestor of the Acidithiobacillus genus by horizontal gene transfer (HGT). IslandViewer (Rutherford et al., 2000) was employed to search for evidence of HGT with no positive results. Also, the annotated gene neighborhoods of families I–V were searched by hand for evidence of signatures of HGT such as transposases (Riadi et al., 2012; Acuña et al., 2013), integrases, conjugative and viral functions, and tRNAs but only one transposase was detected in the vicinity of family IV, (Supplemental File 3). Although little evidence of HGT could be found, it can be argued that it occurred so long ago that its molecular signatures have been lost. If HGT occurred, who were the donor organisms? There is no obvious donor lineage represented in the NCBI nr database, but other organisms could remain to be discovered whose study could help shed light on the evolutionary history of the genes of families I–V genes. The increasing metagenomic sequencing efforts offer the best opportunities for discovering such potential donors.
Other lineages of Bacteria and Archaea including the ancestors of T. tepidarius, once contained the genes but all subsequently lost them except the Acidithiobacillus genus. We think that this is the least likely explanation because it requires many independent gene loss events to have occurred. Also, if the proposed association of families I–V with functions involved in acid related response is correct, it would suggest that many ancestral lineages of the Acidithiobacillus genus were acidophiles for which there is no evidence.
Although a lack of definitive evidence leaves all three hypothesis unimpaired, we speculate that the emergence of families I–V could have helped promote by whatever means (direct activity of the encoded proteins, or via sensing or regulatory mechanisms) the ability of the last common ancestor of the Acidithiobacillus genus and T. tepidarius to transition from a neutral pH environment to one that was increasingly acidic and finally to one that was extremely acidic. In this scenario, the transition process could have provided opportunities for the Acidithiobacillus genus to diverge from the T. tepidarius lineage. This hypothesis requires additional evidence, especially experimental evidence, to clearly pinpoint the specific functions and physiological roles of the five families.
Use of families I–V as genetic probes for Acidithiobacillus genus and species identification
In order to evaluate the sensitivity and specificity of the families to discriminate between Acidithiobacillus species, the DNA sequences of families I–V were concatenated for each Acidithiobacillus species and compared by BLASTN against each Acidithiobacillus species. The results are reported as % nucleotide identity between the concatenated probe and each Acidithiobacillus species (Figure 5). The dark blue diagonal indicates high nucleotide identity, as expected, between the concatenated probe and its respective sequences in the corresponding genome. Importantly, the concatenated probes from one species have lower levels of sequence identity when compared to other species. For example, the concatenated probe from A. caldus has only 69% identity (white cell) when compared to sequences present in the genome of A. ferrivorans.
Figure 5.
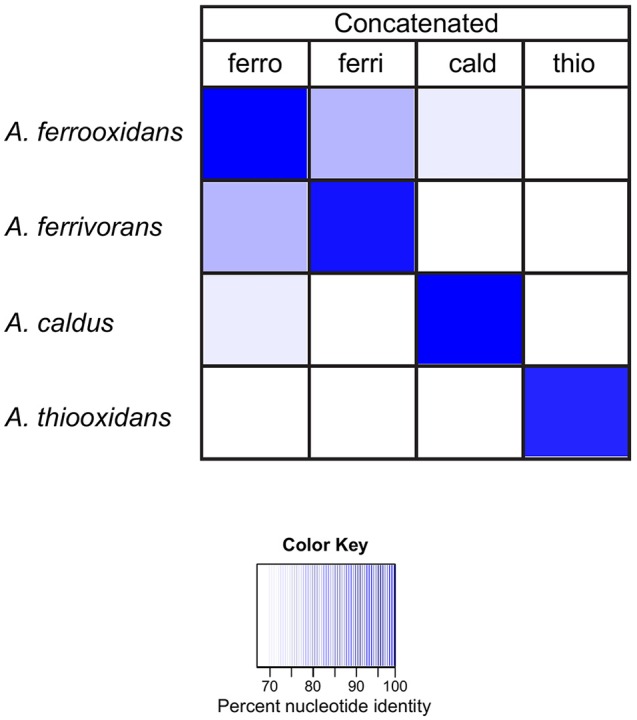
Heat map showing the percent nucleotide similarity (from 100% to <70%, see color key) between families I–V genes, concatenated for each Acidithiobacillus species (top row) vs. families I–V in each genome (left). ferro: A. ferrooxidans; ferri: A. ferrivorans; thio: A. thiooxidans and cald: A. caldus.
These data indicate that the concatenated families are capable of discriminating between the different Acidithiobacilli species used to build the concatenated probes, but are they capable of phylotyping new genomes that did not contribute to building the probes?
During the course of this investigation four new genomes of A. ferrooxidans (strains BY0502, DLC-5, YQH-1, and Hel18), one A. caldus genome (strain MTH-04) and six genomes of A. thiooxidans were released (Table 1), providing an opportunity to test the discriminatory powers of the family probes on new genomes.
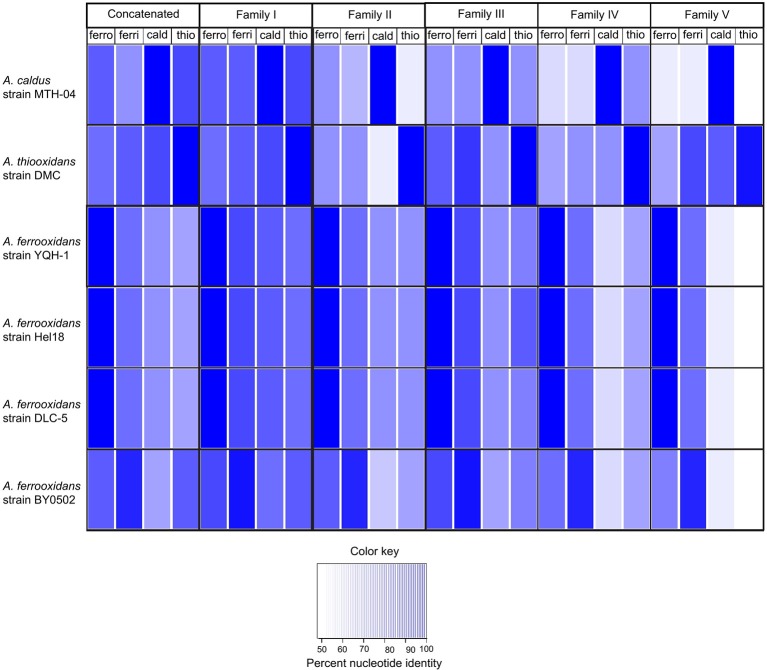
First, the concatenated family probes, described in the previous experiment, were used in BLASTN comparisons with the new genomes. The results are reported as % nucleotide identity between the concatenated probe and each Acidithiobacillus species (leftmost four columns, Figure 6). The concatenated probes clearly have the ability to discriminate between A. caldus MTH-04, A. thiooxidans DMC, A. ferrooxidans BY0502, A. ferrooxidans YQH-1, and A. ferrooxidans Hel18, indicated by the dark blue color (close to 100% sequence identity). However, there is one anomalous identification. A. ferrooxidans BY0502 exhibits the best match with the A. ferrivorans concatenated probe (bottom row), suggesting that this species might not be A. ferrooxidans.
Figure 6.
Heat map illustrating the percent nucleotide similarity (from 100% to <50%, see color key) between families I–V genes and the best BLAST hit of four newly identified A. ferrooxidans genomes (strain BY0502, strain DLC-5, strain YQH-1, and strain Hel18) and one A. caldus genome (strain MTH-04).
In order to determine if this anomaly could be attributed to one (or more) of the families in particular, the experiment was repeated with each individual family (Figure 6). Each family correctly identified the new genomes of A. ferrooxidans, A. thiooxidans and A. caldus with the exception of A. ferrooxidans BY0502. The highest percentage matches of all five families to A. ferrooxidans BY0502 were to the probes built from A. ferrivorans, confirming the results using the concatenated family probe.
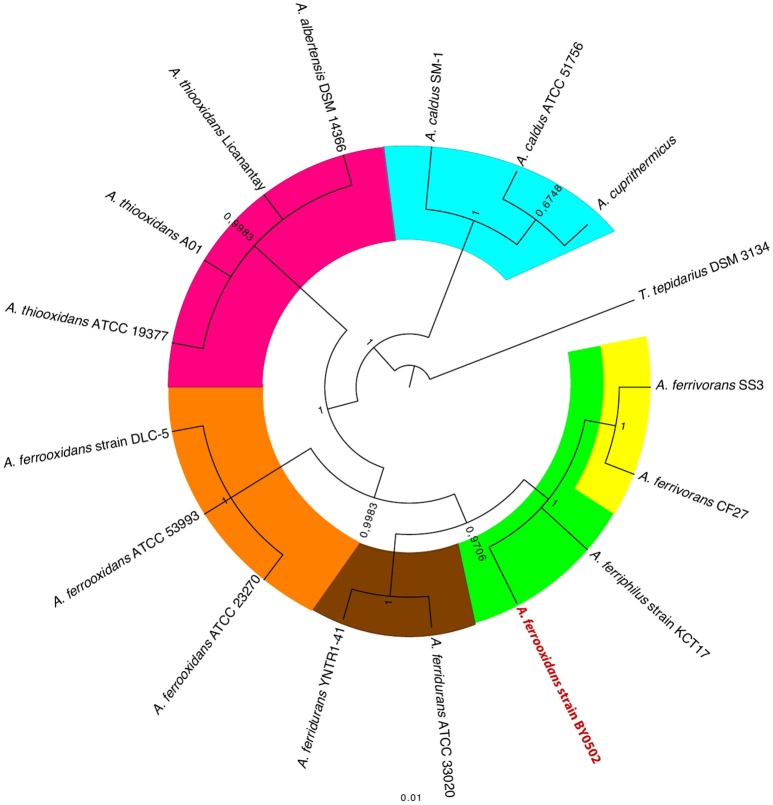
Because of the vexing problem of the anomalous A. ferrooxidans BY0502 in which the family I–V probes place it closer to A. ferrivorans than A. ferrooxidans, it was decided to use other approaches to investigate its phylogeny using ANI (Goris et al., 2007) and TETRA (Richter and Rosselló-Móra, 2009). Both approaches indicate that A. ferrooxidans BY0502 is not related to A. ferrooxidans because of the low values of ANI and TETRA, 83.4 and 0.988, respectively, between the two genomes. Nor can it be classified in the A. ferrivorans clade, with low values of 91.7/0.996 (ANI/TETRA values), although it is more closely related to A. ferrivorans than A. ferrooxidans. In order to investigate further the phylogeny of A. ferrooxidans BY0502, 16S rRNA sequence analysis was carried out that placed it in a clade with A. ferriphilus, subtended by the clade A. ferrivorans with a bayesian posterior probability node support of 1 that strongly endorses the proposed phylogeny (Figure 7). Therefore, we suggest that A. ferrooxidans BY0502 is more likely to be an A. ferriphilus-like microorganism; an hypothesis that requires confirmation using other phylogenetic approaches. This example demonstrates the power of the family probes to aid in the identification of the Acidithiobacillus genus with discriminatory powers to suggest species at least for those under interrogation in the present study.
Figure 7.
16S rRNA gene tree of selected Acidithiobacilli showing the anomalous location of A. ferrooxidans BY0502 within the A. ferriphilus clade. The tree was constructed using bayesian inference with MrBayes (Huelsenbeck and Ronquist, 2001). The posterior probability node support is given for all nodes.
Use of families I–V as genetic probes for interrogation of metagenomes and metatranscriptomes
Gaining insight into the structure, organization, and function of microbial communities (microbiomes) has been proposed as one of the major research challenges of the current decade (2020 visions, 2010) and metagenomic and metatranscriptomic approaches present major opportunities for advancing our knowledge in this area. One of the most promising areas of metagenomics research is the use of shotgun methods to sequence random fragments of DNA (or RNA) in an environmental sample. This information can then be analyzed for microbial diversity, prediction of gene functions and biochemical pathway model building. Many bioinformatic approaches have been developed to handle the typically enormous amounts of data generated by metagenomics investigations (e.g., reviewed in Hiraoka et al., 2016).
One of the most straightforward and computationally less demanding approaches to estimate microbial diversity in a microbiome is the use of marker genes (molecular probes; Wu and Eisen, 2008; Liu et al., 2011; Wu and Scott, 2012; Kim et al., 2013; Darling et al., 2014). For example, rRNA sequences from known organisms can be used to computationally search the shotgun sequences for similar sequences or can be coupled with rRNA-PCR to pull out and extend specific sequences. These methods provide an overview of the phylogenetic distribution (phylotyping) of the cell-based life present in a sample but they have their limitations (reviewed in Fabrice and Didier, 2009).
Taxonomically restricted protein encoding genes have been used for phylotyping, including the recombinase A gene family and the RNA polymerase beta subunit (Wu et al., 2011), genes specifically targeting the Acidithiobacilli (Nieto et al., 2009; Nuñez et al., 2014, 2016) and many other examples (Liu et al., 2011; Segata et al., 2011; Wu et al., 2013; Darling et al., 2014). However, such marker genes are subject to HGT and evolutionary rate differences that can exacerbate the interpretation of phylogenies. Since the five families are taxonomically restricted to the Acidithiobacilli and do not appear to be prone to HGT, we decided to examine their ability to identify the Acidithiobacillus genus and to discriminate between different species of the Acidithiobacilli (Figures 6, 7) in environmental metagenomic and metatranscriptomic samples. For the first objective, the amino acid sequence of all five families from all participating Acidithiobacillus species (A. ferrooxidans, A. ferrivorans, A. thiooxidans, and A. caldus) was concatenated (five families × nine species). This was considered as a general probe for the Acidithiobacillus genus (genus-level probe). A second series of probes was constructed where the protein sequences of the five families was concatenated according to species, generating five different probes each one specific for an Acidithiobacillus species (e.g., A. ferrooxidans probe = the concatenation of families I–V of A. ferrooxidans). These probes were then used in a BLASTX searches to interrogate several environmental metagenomes and metatranscriptomes listed in Table 4.
Table 4.
Detection of Acidithiobacilli in (A) various metagenomes and (B) metatranscriptomes using families I–V as molecular probes.
| (A) Study name | Sample type | Source | pH | Database source | ID | Acidithiobacilli reported | Acidithiobacilli detected using Families I–V (this study) in reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Kristineberg Mine | P | Malå, Sweden | 2.5–2.7 | NCBI nr | AOMQ00000000 | AFV, AFE, ATHIO, ACAL (Liljeqvist et al., 2015) | AFV, AFE, ATHIO, ACAL |
| Kristineberg Mine | B | Malå, Sweden | 2.5–2.7 | NCBI nr | AOMP00000000 | AFV, AFE, ATHIO, ACAL (Liljeqvist et al., 2015) | AFV, AFE, ATHIO, ACAL |
| Pink biofilm Richmond Mine | AMD | California, USA | 0.83 | NCBI nr | AADL00000000 | None (Tyson et al., 2004) | Not detected |
| Carnoulès Mine (bin 5) | AMD | Gard, France | 3.5–3.8 | NCBI nr | PRJNA62261 | AFE (Bertin et al., 2011) | AFE, ATHIO, ACAL |
| Snottites in Frasassi Cave | AMD | Ancona, Italy | 0–1 | NCBI nr | SRP006444 | ATHIO, AT (Jones et al., 2012) | ATHIO |
| Acquasanta Terme AS5 | SB | Grotta Nuova di Rio Garrafo, Italy | 0–1.5 | IMG/M | 3300000825 | ATHIO (Jones et al., 2016) | ATHIO |
| Black Soud Mine | AMD | Minnesota, USA | 6.7 | NCBI nr | ABLV00000000 | None (Edwards et al., 2006) | Not detected |
| Black smokers (Tui Malila) | HVP | Lau Basin, Pacific Ocean | 3.8–5.7 | IMG/M | 3300001676 | None (Sheik et al., 2015) | Not detected |
| Hydrothermal vent (Guaymas Basin) | HVP | Guaymas Basin, Pacific Ocean | 6.5–8 | IMG/M | 3300003086 | None (Li et al., 2016) | Not detected |
| Marine Microbial communities (Loihi) | HVP | Loihi Seamount, Hawaii | 8 | IMG/M | 3300000327 | None (Singer et al., 2013) | Not detected |
| Deep Oceanic Microbial Communities (Juan de Fuca) | HVP | Juan de Fuca, Pacific Ocean | 4.2 | IMG/M | 3300002481 | None (Jungbluth et al., 2013) | Not detected |
| Marine Microbial communities (Lost City) | HVP | Lost City, Atlantic Ocean | 9–11 | IMG/M | 3300003136 | None (Anantharaman et al., 2014) | Not detected |
| (B) Study | Sample type | Origin | pH | Database source | ID | Acidithiobacillus reported | Acidithiobacillus detected with family probes in reference |
| Dabaoshan Mine | AMD | Guangdong, China | 1.9–2.3 | MG-RAST | 4481316.3 | AFE, AFV (Chen et al., 2015) | AFE, AFV, ATHIO |
| Yunfu Mine | AMD | Guangdong, China | 2.5 | MG-RAST | 4481318.3 | AFE, AFV (Chen et al., 2015) | AFE, AFV, ATHIO |
AMD, Acid Mine Drainage; ACAL, A. caldus; AFV, A. ferrivorans; AFE, A. ferrooxidans; ATHIO, A. thiooxidans; AT, Acidithiobacillus genus; P, Planktonic; B, Biofilm; SB, Subaerial biofilm; HVP, Hydrothermal vent plume; NCBI nr, National Center for Biotechnology Information, non-redundant database; IMG/M, Integrated Microbial Genomes/ Metagenomes; MG-RAST, Metagenomes- Rapid Annotation using Subsystem Technology.
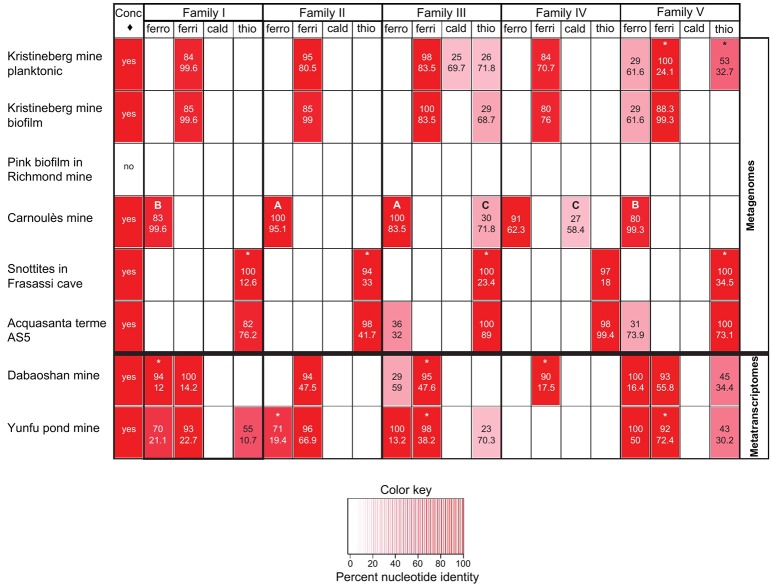
The metagenomes were chosen to include low pH environments such as mining operations and AMD, where Acidithiobacilli have previously been reported, and also environments of intermediate acidity (e.g., Black Smokers, Tui Malila), neutral pH (e.g., Hydrothermal vent, Guaymas Basin), and high pH (e.g., Marine Microbial Communities, Lost City) where Acidithiobacilli have not been detected. Two low pH metatranscriptomes were also included in the analysis. The results of the BLASTX interrogations are shown in Figure 8 and the results are summarized in Table 4.
Figure 8.
Heat map indicating the percent nucleotide identity (top number in respective cells) and sequence coverage (lower number in respective cells) between families I–V and environmental metagenomes and metatranscriptomes as assayed by BLASTX. The figure also shows (leftmost column, ♢ = concatenated probe) the presence or absence of the Acidithiobacillus genus in the metagenomes and metatranscriptomes determined by BLASTX, using as a probe the concatenated sequences of all five families of all Acidithiobacilli used in the study (5 families × 9 Acidithiobacilli species = 45 concatenated sequences), where positive matching is indicated with a “yes.” The letters A to C refer to specific cases described in the text. The * refers to sequences that are truncated in the respective metagenome/transcriptome databases.
Inspection of the left hand column of Figure 8 indicates that the genus-level probe detects sequence similarity in all the samples except for the Pink Biofilm from the Richmond mine. This is in agreement with the report that no Acidithiobacilli were detected in the Pink Biofilm but were detected in all the other samples (references provided in Table 4). The absence of Acidithiobacilli in the Pink Biofilm sample could be due to its extremely low pH (pH 0.83) which is thought to be too acidic to support their growth (Tyson et al., 2004). In addition no Acidithiobacilli were detected in samples from the Black Soud Mine, Black Smokers (Tui Malila), Hydrothermal Vent (Guaymas Basin), Marine Microbial Communities (Loihi), Deep Ocean Microbial Communities (Juan de Fuca), Marine Microbial Communities (Lost City), which is also in agreement with the published literature (references found in Table 4). The conclusion is that the Acidithiobacilli genus-level probe appears to have good specificity and sensitivity in detecting Acidithiobacilli in environmental metagenomes but more samples are required to develop statistical support for this assertion.
Table 4 also indicates that the families can be used to interrogate metatranscriptomes and provides additional evidence that the genes of family I–V are transcribed. This evidence was used to construct the right hand column presented earlier in Table 3.
However, caution is required in the interpretation of the use of the species-specific probes. In case A (see Figure 8), both the sequence identity (100%) and sequence coverage (83.5–95.1%) of the A. ferrooxidans probes of families II and III strongly support the contention that sequences corresponding to them are present in the Carnoulès metagenome. However, in case B, although there is good coverage of the A. ferrooxidans family I and V probes (99.3–99.6%), the sequence identity is lower (80–83%). This suggests that these families probably belong to A. ferrooxidans in the metagenome but that they have diverged somewhat from the probe sequences. Recovery of such sequences would expand the number and diversity of such sequences that could be helpful for elucidating their function and shedding light on their evolution. In case C, both the coverage and identity are lower and the hits are to probes developed for A. thiooxidans and A. caldus family III and family IV. This suggests that the Carnoulès metagenome contains A. thiooxidans-like and A. caldus-like organisms that exhibit low sequence similarity to families III and IV, but not to the other families. As in case B, these sequences could be helpful for later studies to help unravel sequence function and evolution. A final case marked by asterisks in Figure 8 illustrates the common finding of sequence similarity to metagenomic reads that are truncated. Truncated sequences that have high similarity to the probes could potentially be extended by PCR using primers designed from the probes and subsequently analyzed.
With these caveats in mind, families I–V satisfy a number of criteria for use as identification markers for Acidithiobacilli in genomic, metagenomic/metatranscriptomic investigations. They are universally present in the genus, not present in other genera and are not subject to HGT. Preliminary evidence also points to association of at least three of the families (Families I, III, and IV) in envelope remodeling and lipid metabolism possibly associated with acid stress response and so could serve as PhyEco (for phylogenetic and phylogenetic ecology; Wu et al., 2013) markers for certain acidic environments including AMD and biomining operations.
Conclusions
This study:
Used comparative genomics approaches to discover five protein families that are taxonomically restricted to the genus Acidithiobacillus (Acidithiobacilli), a group of extreme acidophiles.
Highlighted and examined the potential functions of the five families. Although functional assignments could not be made with confidence for any of the families, it was hypothesized that they are involved in cell envelope restructuring that in four families may be associated with responses to changing pH conditions, at least in A. caldus.
Reflected on the possible evolution of the five families. It was suggested that the five families emerged after the split of the Acidithiobacilli lineage from the neutrophile T. tepidarius, allowing the Acidithiobacilli lineage to colonize acidic econiches.
Considered how the five families can be used as molecular probes to interrogate genomic and metagenomic/metatranscriptomic data.
Served as a springboard for testing hypotheses and for guiding future research, for example to: (i) investigate experimentally the hypothesis that some of the orphan family genes could be involved in acid stress response(s) and/or membrane remodeling, (ii) explore further the concept that the orphan family genes have played a role in the evolution of the Acidithiobacilli from neutral ancestors to modern day extreme acidophiles, and (iii) use additional tools to investigate the phylogeny of A. ferrooxidans BY0502 that our study suggests is more likely to be a Ferriphilus-like microorganism.
Future perspectives
As more data become available from genomic and metagenome sequencing projects, it will be possible to determine if families I–V maintain their ability to be specific probes for the genus Acidithiobacillus. The availability of additional examples of families I–V could advance our understanding of their function, origin and evolutionary trajectory.
Author contributions
DH and JV conceived the project. DH and CG designed the experiments. ML and CG carried out the experiments. All authors analyzed the data. DH drafted the manuscript. All authors contributed to subsequent drafts of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Acknowledgments
Fondecyt 1130683 and Conicyt Basal CCTE PFB16 (DH, CG, and ML), FIDUM OI101002 (JV), CONICYT doctoral fellowship (CG). We thank Dr. Mark Dopson for drawing our attention to the proteomic data for A. caldus and the transcriptomic data for A. ferrivorans.
Footnotes
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: http://journal.frontiersin.org/article/10.3389/fmicb.2016.02035/full#supplementary-material
References
- 2020 visions (2010). Nature 463, 26–32. 10.1038/463026a [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Acuña L. G., Cárdenas J. P., Covarrubias P. C., Haristoy J. J., Flores R., Nunez H., et al. (2013). Architecture and gene repertoire of the flexible genome of the extreme acidophile Acidithiobacillus caldus. PLoS ONE 8:e78237. 10.1371/journal.pone.0078237 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Altschul S. F., Madden T. L., Schäffer A. A., Zhang J., Zhang Z., Miller W., et al. (1997). Gapped BLAST and PSI-BLAST: a new generation of protein database search programs. Nucleic Acids Res. 25, 3389–3402. 10.1093/nar/25.17.3389 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anantharaman K., Duhaime M. B., Breier J. A., Wendt K. A., Toner B. M., Dick G. J. (2014). Sulfur oxidation genes in diverse deep-sea viruses. Science 344, 757–760. 10.1126/science.1252229 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aziz R. K., Bartels D., Best A. A., DeJongh M., Disz T., Edwards R. A., et al. (2008). The RAST server: rapid annotations using subsystems technology. BMC Genomics 9:75. 10.1186/1471-2164-9-75 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bagos P. G., Nikolaou E. P., Liakopoulos T. D., Tsirigos K. D. (2010). Combined prediction of Tat and Sec signal peptides with hidden Markov models. Bioinformatics 26, 2811–2817. 10.1093/bioinformatics/btq530 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker-Austin C., Dopson M. (2007). Life in acid: pH homeostasis in acidophiles. Trends Microbiol. 15, 165–171. 10.1016/j.tim.2007.02.005 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barrie Johnson D., Quatrini R. (2016). Acidophile microbiology in space and tim, in Acidophile Life in Extremely Acidic Environment, eds Quatrini R., Barrie Johnson D. (Norfolk, VA: Caister Academic Press; ), 3–16. [Google Scholar]
- Bertin P. N., Heinrich-Salmeron A., Pelletier E., Goulhen-Chollet F., Arsène-Ploetze F., Gallien S., et al. (2011). Metabolic diversity among main microorganisms inside an arsenic-rich ecosystem revealed by meta- and proteo-genomics. ISME J. 5, 1735–1747. 10.1038/ismej.2011.51 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bjellqvist B., Hughes G. J., Pasquali C., Paquet N., Ravier F., Sanchez J. C., et al. (1993). The focusing positions of polypeptides in immobilized pH gradients can be predicted from their amino acid sequences. Electrophoresis 14, 1023–1031. 10.1002/elps.11501401163 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brettin T., Davis J. J., Disz T., Edwards R. A., Gerdes S., Olsen G. J., et al. (2015). RASTtk: a modular and extensible implementation of the RAST algorithm for building custom annotation pipelines and annotating batches of genomes. Sci. Rep. 5:8365. 10.1038/srep08365 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cárdenas J. P., Quatrini R., Holmes D. S. (2016a). Genomic and metagenomic challenges and opportunities for bioleaching: a mini-review. Res. Microbiol. 167, 529–538. 10.1016/j.resmic.2016.06.007 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cárdenas J. P., Quatrini R., Holmes D. S. (2016b). The Genomics of Acidophile, in Acidophile Life in Extremely Acidic Environment, eds Quatrini R., Johnson D. B. (Norfolk, VA: Caister Academic Press; ), 179–197. [Google Scholar]
- Carver T., Thomson N., Bleasby A., Berriman M., Parkhill J. (2009). DNAPlotter: circular and linear interactive genome visualization. Bioinformatics 25, 119–120. 10.1093/bioinformatics/btn578 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Charif D., Lobry J. R. (2007). A Contributed package to the R Project for statistical computing devoted to biological sequences retrieval and analysi, in Structural Approaches to Sequence Evolution, eds Bastoll U., Port M., Roma H. E., Vendruscolo M. (Berlin; Heidelberg: Springer; ), 207–232. [Google Scholar]
- Chen L. X., Hu M., Huang L. N., Hua Z. S., Kuang J. L., Li S. J., et al. (2015). Comparative metagenomic and metatranscriptomic analyses of microbial communities in acid mine drainage. ISME J. 9, 1579–1592. 10.1038/ismej.2014.245 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christel S., Fridlund J., Buetti-Dinh A., Buck M., Watkin E. L., Dopson M. (2016a). RNA transcript sequencing reveals inorganic sulfur compound oxidation pathways in the acidophile Acidithiobacillus ferrivorans. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 363:fnw057. 10.1093/femsle/fnw057 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christel S., Fridlund J., Watkin E. L., Dopson M. (2016b). Acidithiobacillus ferrivorans SS3 presents little RNA transcript response related to cold shock during growth at 8°C suggesting it is a eurypsychrophile. Extremophiles 20, 903–913. 10.1007/s00792-016-0882-2 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cole J. R., Wang Q., Cardenas E., Fish J., Chai B., Farris R. J., et al. (2009). The Ribosomal Database Project: improved alignments and new tools for rRNA analysis. Nucleic Acids Res. 37(Suppl. 1), D141–D145. 10.1093/nar/gkn879 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Consortium T. U. (2014). Activities at the Universal Protein Resource (UniProt). Nucleic Acids Res. 42, D191–D198. 10.1093/nar/gkt1140 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cuneo M. J., Beese L. S., Hellinga H. W. (2008). Ligand-induced conformational changes in a thermophilic ribose-binding protein. BMC Struct. Biol. 8:50. 10.1186/1472-6807-8-50 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darling A. E., Jospin G., Lowe E., Matsen F. A., IV., Bi H. M., Eisen J. A. (2014). PhyloSift: phylogenetic analysis of genomes and metagenomes. PeerJ. 2:e243. 10.7717/peerj.243 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darling A. E., Mau B., Perna N. T. (2010). Progressivemauve: multiple genome alignment with gene gai loss and rearrangement. PLoS ONE 5:e11147. 10.1371/journal.pone.0011147 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darriba D., Taboada G. L., Doallo R., Posada D. (2012). jModelTest 2: more model new heuristics and parallel computing. Nat. Methods 9, 772. 10.1038/nmeth.2109 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeSantis T. Z., Hugenholtz P., Larsen N., Rojas M., Brodie E. L., Keller K., et al. (2006). Greengene a chimera-checked 16S rRNA gene database and workbench compatible with ARB. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 72, 5069–5072. 10.1128/AEM.03006-05 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dhillon B. K., Laird M. R., Shay J. A., Winsor G. L., Lo R., Nizam F., et al. (2015). IslandViewer 3: more flexibl interactive genomic island discover visualization and analysis. Nucleic Acids Res. 43, W104–W108. 10.1093/nar/gkv401 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dwyer M. A., Hellinga H. W. (2004). Periplasmic binding proteins: a versatile superfamily for protein engineering. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 14, 495–504. 10.1016/j.sbi.2004.07.004 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eddy S. R. (1998). Profile hidden Markov models. Bioinformatics 14, 755–763. 10.1093/bioinformatics/14.9.755 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edgar R. C. (2004). MUSCLE: multiple sequence alignment with high accuracy and high throughput. Nucleic Acids Res. 32, 1792–1797. 10.1093/nar/gkh340 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edwards R. A., Rodriguez-Brito B., Wegley L., Haynes M., Breitbart M., Peterson D. M., et al. (2006). Using pyrosequencing to shed light on deep mine microbial ecology. BMC Genomics 7:57. 10.1186/1471-2164-7-57 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisen J. A., Heidelberg J. F., White O., Salzberg S. L. (2000). Evidence for symmetric chromosomal inversions around the replication origin in bacteria. Genome Biol. 1:RESEARCH0011. 10.1186/gb-2000-1-6-research0011 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fabrice A., Didier R. (2009). Exploring Microbial Diversity Using 16S rRNA High-Throughput Methods. J. Comput. Sci. Syst. Biol. 2, 074–092. 10.4172/jcsb.100001910498776 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Fischer D., Eisenberg D. (1999). Finding families for genomic ORFans. Bioinformatics 15, 759–762. 10.1093/bioinformatics/15.9.759 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gasteiger E., Hoogland C., Gattiker A., Duvaud S., Wilkins M. R., Appel R. D., et al. (2005). Protein identification and analysis tools on the ExPASy Serve in The Proteomics Protocols Handbook, eds Walke J. M., Totowa N. J. (New York, NY: Humana Press; ), 571–607. [Google Scholar]
- Goris J., Konstantinidis K. T., Klappenbach J. A., Coenye T., Vandamme P., Tiedje J. M. (2007). DNA-DNA hybridization values and their relationship to whole-genome sequence similarities. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 57, 81–91. 10.1099/ijs.0.64483-0 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guindon S., Dufayard J.-F., Lefort V., Anisimova M., Hordijk W., Gascuel O. (2010). New algorithms and methods to estimate maximum-likelihood phylogenies: assessing the performance of PhyML 3.0. Syst. Biol. 59, 307–321. 10.1093/sysbio/syq010 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guindon S., Gascuel O. (2003). A simple, fast and accurate algorithm to estimate large phylogenies by maximum likelihood. Syst. Biol. 52, 696–704. 10.1080/10635150390235520 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guzman L. M., Barondess J. J., Beckwith J. (1992). Fts an essential cytoplasmic membrane protein involved in cell division in Escherichia coli. J. Bacteriol. 174, 7716–7728. 10.1128/jb.174.23.7717.1992 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haft D. H., Selengut J. D., White O. (2003). The TIGRFAMs database of protein families. Nucleic Acids Res. 31, 371–373. 10.1093/nar/gkg128 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hedrich S. S. A. (2016). Distribution of acidophilic microorganisms in natural and man-made acidic environment in Acidophile Life in Extremely Acidic Environment, ed Quatrini R. J. D. B. (Norfolk, VA: Caister Academic Press; ), 153–176. [Google Scholar]
- Hiraoka S., Yang C. C., Iwasaki W. (2016). Metagenomics and bioinformatics in microbial ecology: current status and beyond. Microbes Environ. 31, 204–212. 10.1264/jsme2.ME16024 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hofmann K., Stoffel W. (1993). TMbase - A database of membrane spanning proteins segments. Biol Chem Hoppe-Seyler. 374. 26134144 [Google Scholar]
- Hudson C. M., Williams K. P., Kelly D. P. (2014). Definitive assignment by multigenome analysis of the gammaproteobacterial genus Thermithiobacillus to the class Acidithiobacillia. Pol. J. Microbiol. 63, 245–247. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huelsenbeck J. P., Ronquist F. (2001). MRBAYES: Bayesian inference of phylogenetic trees. Bioinformatics 17, 754–755. 10.1093/bioinformatics/17.8.754 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jiang X., Sobetzko P., Nasser W., Reverchon S., Muskhelishvili G. (2015). Chromosomal “stress-response” domains govern the spatiotemporal expression of the bacterial virulence program. Mbio 6, e00353–e00315. 10.1128/mBio.00353-15 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones D. S., Albrecht H. L., Dawson K. S., Schaperdoth I., Freeman K. H., Pi Y., et al. (2012). Community genomic analysis of an extremely acidophilic sulfur-oxidizing biofilm. ISME J. 6, 158–170. 10.1038/ismej.2011.75 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones D. S., Schaperdoth I., Macalady J. L. (2016). Biogeography of sulfur-oxidizing Acidithiobacillus populations in extremely acidic cave biofilms. ISME J. 10, 2879–2891. 10.1038/ismej.2016.74 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Juncker A. S., Willenbrock H., Von Heijne G., Brunak S., Nielsen H., Krogh A. (2003). Prediction of lipoprotein signal peptides in Gram-negative bacteria. Protein Sci. 12, 1652–1662. 10.1110/ps.0303703 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jungbluth S. P., Grote J., Lin H. T., Cowen J. P., Rappé M. S. (2013). Microbial diversity within basement fluids of the sediment-buried Juan de Fuca Ridge flank. ISME J. 7, 161–172. 10.1038/ismej.2012.73 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katoh K., Kuma K., Toh H., Miyata T. (2005). MAFFT version 5: improvement in accuracy of multiple sequence alignment. Nucleic Acids Res. 33, 511–518. 10.1093/nar/gki198 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katoh K., Misawa K., Kuma K. Ä., Miyata T. (2002). MAFFT: a novel method for rapid multiple sequence alignment based on fast Fourier transform. Nucleic Acids Res. 30, 3059–3066. 10.1093/nar/gkf436 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly D. P., Wood A. P. (2000). Reclassification of some species of Thiobacillus to the newly designated genera Acidithiobacillus gen. nov., Halothiobacillus gen. nov. and Thermithiobacillus gen. nov. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 50(Pt 2), 511–516. 10.1099/00207713-50-2-511 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khedkar S., Seshasayee A. S. (2016). Comparative genomics of interreplichore translocations in bacteria: a measure of chromosome topology? G3 (Bethesda) 6, 1597–1606. 10.1534/g3.116.028274 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim M., Lee K. H., Yoon S. W., Kim B. S., Chun J., Yi H. (2013). Analytical tools and databases for metagenomics in the next-generation sequencing era. Genomics Inform. 11, 102–113. 10.5808/GI.2013.11.3.102 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klasberg S., Bitard-Feildel T., Mallet L. (2016). Computational identification of novel genes: current and future perspectives. Bioinform. Biol. Insights 10, 121–131. 10.4137/BBI.S39950 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krogh A., Larsson B., von Heijne G., Sonnhammer E. L. (2001). Predicting transmembrane protein topology with a hidden markov model: application to complete genomes. J. Mol. Biol. 305, 567–580. 10.1006/jmbi.2000.4315 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li M., Jain S., Dick G. J. (2016). Genomic and transcriptomic resolution of organic matter utilization among deep-sea bacteria in guaymas basin hydrothermal plumes. Front. Microbiol. 7:1125. 10.3389/fmicb.2016.01125 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liljeqvist M., Ossandon F. J., Gonzalez C., Rajan S., Stell A., Valdes J., et al. (2015). Metagenomic analysis reveals adaptations to a cold adapted lifestyle in a low temperature acid mine drainage stream. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 91:fiv011. 10.1093/femsec/fiv011 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liljeqvist M., Valdes J., Holmes D. S., Dopson M. (2011). Draft genome of the psychrotolerant acidophile Acidithiobacillus ferrivorans SS3. J. Bacteriol. 193, 4304–4305. 10.1128/JB.05373-11 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu B., Gibbons T., Ghodsi M., Treangen T., Pop M. (2011). Accurate and fast estimation of taxonomic profiles from metagenomic shotgun sequences. BMC Genomics. 12(Suppl. 2):S4. 10.1186/1471-2164-12-S2-S4 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Long M., Betran E., Thornton K., Wang W. (2003). The origin of new genes: glimpses from the young and old. Nat. Rev. Genet. 4, 865–875. 10.1038/nrg1204 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacLean D., Jones J. D., Studholme D. J. (2009). Application of ‘next-generation’ sequencing technologies to microbial genetics. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 7, 287–296. 10.1038/nrmicro2122 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mangold S., Rao Jonna V., Dopson M. (2013). Response of Acidithiobacillus caldus toward suboptimal pH conditions. Extremophiles 17, 689–696. 10.1007/s00792-013-0553-5 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Markowitz V. M., Chen I. M., Chu K., Szeto E., Palaniappan K., Pillay M., et al. (2014a). IMG/M 4 version of the integrated metagenome comparative analysis system. Nucleic Acids Res. 42, D568–D573. 10.1093/nar/gkt919 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Markowitz V. M., Chen I. M., Palaniappan K., Chu K., Szeto E., Pillay M., Ratner A., et al. (2014b). IMG 4 version of the integrated microbial genomes comparative analysis system. Nucleic Acids Res. 42, D560–D567. 10.1093/nar/gkt963 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Méndez-García C., Peláez A. I., Mesa V., Sánchez J., Golyshina O. V., Ferrer M. (2015). Microbial diversity and metabolic networks in acid mine drainage habitats. Front. Microbiol. 6:475. 10.3389/fmicb.2015.00475 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer F., Paarmann D., D'Souza M., Olson R., Glass E. M., Kubal M., et al. (2008). The metagenomics RAST server - a public resource for the automatic phylogenetic and functional analysis of metagenomes. BMC Bioinformatics 9:386. 10.1186/1471-2105-9-386 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakai K., Horton P. (1999). PSORT: a program for detecting sorting signals in proteins and predicting their subcellular localization. Trends Biochem. Sci. 24, 34–35. 10.1016/S0968-0004(98)01336-X [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Natale P., Brüser T., Driessen A. J. (2008). Sec- and Tat-mediated protein secretion across the bacterial cytoplasmic membranÄîDistinct translocases and mechanisms. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1778, 1735–1756. 10.1016/j.bbamem.2007.07.015 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nieto P. A., Covarrubias P. C., Jedlicki E., Holmes D. S., Quatrini R. (2009). Selection and evaluation of reference genes for improved interrogation of microbial transcriptomes: case study with the extremophile Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans. BMC Mol. Biol. 10:63. 10.1186/1471-2199-10-63 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nordberg H., Cantor M., Dusheyko S., Hua S., Poliakov A., Shabalov I., et al. (2014). The genome portal of the Department of Energy Joint Genome Institute: 2014 updates. Nucleic Acids Res. 42, D26–D31. 10.1093/nar/gkt1069 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nuñez H., Covarrubias P. C., Moya-Beltrán A., Issotta F., Atavales J., Acuna L. G., et al. (2016). Detectio identification and typing of Acidithiobacillus species and strains: a review. Res. Microbiol. 167, 555–567. 10.1016/j.resmic.2016.05.006 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nuñez H., Loyola D., Cárdenas J. P., Holmes D. S., Johnson D. B., Quatrini R. (2014). Multi locus sequence typing scheme for Acidithiobacillus caldus strain evaluation and differentiation. Res. Microbiol. 165, 735–742. 10.1016/j.resmic.2014.07.014 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osorio H., Mangold S., Denis Y., Ñancucheo I., Esparza M., Johnson D. B., et al. (2013). Anaerobic sulfur metabolism coupled to dissimilatory iron reduction in the extremophile Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 79, 2172–2181. 10.1128/AEM.03057-12 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Overbeek R., Olson R., Pusch G. D., Olsen G. J., Davis J. J., Disz T., et al. (2014). The SEED and the Rapid Annotation of microbial genomes using Subsystems Technology (RAST). Nucleic Acids Res. 42, D206–D214. 10.1093/nar/gkt1226 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pedroso I., Rivera G., Lazo F., Chacón M., Ossandon F., Veloso F. A., et al. (2008). AlterORF: a database of alternate open reading frames. Nucleic Acids Res. 36, D517–D518. 10.1093/nar/gkm886 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pizzagalli F., Varga Z., Huber R. D., Folkers G., Meier P. J., St-Pierre M. V. (2003). Identification of steroid sulfate transport processes in the human mammary gland. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 88, 3902–3912. 10.1210/jc.2003-030174 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prabh N., Rodelsperger C. (2016). Are orphan genes protein-codin prediction artifact or non-coding RNAs? BMC Bioinformatics 17:226. 10.1186/s12859-016-1102-x [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pruesse E., Quast C., Knittel K., Fuchs B. M., Ludwig W., Peplies J., et al. (2007). SILVA: a comprehensive online resource for quality checked and aligned ribosomal RNA sequence data compatible with ARB. Nucleic Acids Res. 35, 7188–7196. 10.1093/nar/gkm864 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Punta M., Coggill P. C., Eberhardt R. Y., Mistry J., Tate J., Boursnell C., et al. (2012). The Pfam protein families database. Nucleic Acids Res. 40, D290–D301. 10.1093/nar/gkr1065 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riadi G., Medina-Moenne C., Holmes D. S. (2012). TnpPred: a web service for the robust prediction of prokaryotic transposases. Comp. Funct. Genomics. 2012:678761. 10.1155/2012/678761 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richter M., Rosselló-Móra R. (2009). Shifting the genomic gold standard for the prokaryotic species definition. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 106, 19126–19131. 10.1073/pnas.0906412106 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rocha E. P. (2004). The replication-related organization of bacterial genomes. Microbiology 150, 1609–1627. 10.1099/mic.0.26974-0 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ronquist F., Huelsenbeck J. P. (2003). MrBayes 3: Bayesian phylogenetic inference under mixed models. Bioinformatics 19, 1572–1574. 10.1093/bioinformatics/btg180 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rutherford K., Parkhill J., Crook J., Horsnell T., Rice P., Rajandream M. A., et al. (2000). Artemis: sequence visualization and annotation. Bioinformatics 16, 944–945. 10.1093/bioinformatics/16.10.944 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sabir J. S., Jansen R. K., Arasappan D., Calderon V., Noutahi E., Zheng C., et al. (2016). The nuclear genome of Rhazya stricta and the evolution of alkaloid diversity in a medically relevant clade of Apocynaceae. Sci. Rep. 6:33782. 10.1038/srep33782 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Segata N., Izard J., Waldron L., Gevers D., Miropolsky L., Garrett W. S., et al. (2011). Metagenomic biomarker discovery and explanation. Genome Biol. 12:R60. 10.1186/gb-2011-12-6-r60 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheik C. S., Anantharaman K., Breier J. A., Sylvan J. B., Edwards K. J., Dick G. J. (2015). Spatially resolved sampling reveals dynamic microbial communities in rising hydrothermal plumes across a back-arc basin. ISME J. 9, 1434–1445. 10.1038/ismej.2014.228 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singer E., Heidelberg J. F., Dhillon A., Edwards K. J. (2013). Metagenomic insights into the dominant Fe(II) oxidizing Zetaproteobacteria from an iron mat at Lo ih Hawai l. Front. Microbiol. 4:52. 10.3389/fmicb.2013.00052 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sobetzko P., Travers A., Muskhelishvili G. (2012). Gene order and chromosome dynamics coordinate spatiotemporal gene expression during the bacterial growth cycle. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 109, E42–E50. 10.1073/pnas.1108229109 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suyama M., Torrents D., Bork P. (2006). PAL2NAL: robust conversion of protein sequence alignments into the corresponding codon alignments. Nucleic Acids Res. 34(Suppl. 2), W609–W612. 10.1093/nar/gkl315 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Talla E., Hedrich S., Mangenot S., Ji B., Johnson D. B., Barbe V., et al. (2014). Insights into the pathways of iron- and sulfur-oxidatio and biofilm formation from the chemolithotrophic acidophile Acidithiobacillus ferrivorans CF27. Res. Microbiol. 165, 753–760. 10.1016/j.resmic.2014.08.002 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tautz D., Domazet-Loso T. (2011). The evolutionary origin of orphan genes. Nat. Rev. Genet. 12, 692–702. 10.1038/nrg3053 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Travisany D., Cortés M. P., Latorre M., Di Genova A., Budinich M., Bobadilla-Fazzini R. A., et al. (2014). A new genome of Acidithiobacillus thiooxidans provides insights into adaptation to a bioleaching environment. Res. Microbiol. 165, 743–752. 10.1016/j.resmic.2014.08.004 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tyson G. W., Chapman J., Hugenholtz P., Allen E. E., Ram R. J., Richardson P. M., et al. (2004). Community structure and metabolism through reconstruction of microbial genomes from the environment. Nature 428, 37–43. 10.1038/nature02340 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valdés J., Ossandon F., Quatrini R., Dopson M., Holmes D. S. (2011). Draft genome sequence of the extremely acidophilic biomining bacterium Acidithiobacillus thiooxidans ATCC 19377 provides insights into the evolution of the Acidithiobacillus genus. J. Bacteriol. 193, 7003–7004. 10.1128/JB.06281-11 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valdés J., Pedroso I., Quatrini R., Dodson R. J., Tettelin H., Blake R., et al. (2008). Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans metabolism: from genome sequence to industrial applications. BMC Genomics 9:597. 10.1186/1471-2164-9-597 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valdes J., Quatrini R., Hallberg K., Dopson M., Valenzuela P. D., Holmes D. S. (2009). Draft genome sequence of the extremely Acidophilic Bacterium Acidithiobacillus caldus ATCC 51756 reveals metabolic versatility in the genus Acidithiobacillus. J. Bacteriol. 191, 5877–5878. 10.1128/JB.00843-09 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams K. P., Kelly D. P. (2013). Proposal for a new class within the phylum Proteobacteri Acidithiobacillia classis nov., with the type order Acidithiobacillale and emended description of the class Gammaproteobacteria. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 63(Pt 8), 2901–2906. 10.1099/ijs.0.049270-0 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood A. P., Kelly D. P. (1985). Physiological characteristics of a new thermophilic obligately chemolithotrophic Thiobacillus Species Thiobacillus tepidarius. Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol. 35, 434–437. 10.1099/00207713-35-4-434 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Wu D., Jospin G., Eisen J. A. (2013). Systematic identification of gene families for use as “markers” for phylogenetic and phylogeny-driven ecological studies of bacteria and archaea and their major subgroups. PLoS ONE 8:e77033. 10.1371/journal.pone.0077033 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu D., Wu M., Halpern A., Rusch D. B., Yooseph S., Frazier M., et al. (2011). Stalking the fourth domain in metagenomic data: searching fo discoverin and interpreting nove deep branches in marker gene phylogenetic trees. PLoS ONE 6:e18011. 10.1371/journal.pone.0018011 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu M., Eisen J. A. (2008). A simpl fas and accurate method of phylogenomic inference. Genome Biol. 9:R151. 10.1186/gb-2008-9-10-r151 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu M., Scott A. J. (2012). Phylogenomic analysis of bacterial and archaeal sequences with AMPHORA2. Bioinformatics 28, 1033–1034. 10.1093/bioinformatics/bts079 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yan L., Zhang S., Wang W., Hu H., Wang Y., Yu G., et al. (2015). Draft genome sequence of Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans YQH-1. Genom Data 6, 269–270. 10.1016/j.gdata.2015.10.009 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yin H., Zhang X., Liang Y., Xiao Y., Niu J., Li X. (2014). Draft Genome sequence of the extremophile Acidithiobacillus thiooxidans A01, isolated from the wastewater of a coal dump. Genome Announc. 2:e00222-14. 10.1128/genomeA.00222-14 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- You X. Y., Guo X., Zheng H. J., Zhang M. J., Liu L. J., Zhu Y. Q., et al. (2011). Unraveling the Acidithiobacillus caldus complete genome and its central metabolisms for carbon assimilation. J. Genet. Genomics 38, 243–252. 10.1016/j.jgg.2011.04.006 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu C. S., Che Y. C., Lu C. H., Hwan J. K. (2006). Prediction of protein subcellular localization. Proteins 64, 643–651. 10.1002/prot.21018 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu C. S., Li C. J., Hwan J. K. (2004). Predicting subcellular localization of proteins for Gram-negative bacteria by support vector machines based on n-peptide compositions. Protein Sci. 13, 1402–1406. 10.1110/ps.03479604 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu N. Y., Wagner J. R., Laird M. R., Melli G., Rey S., Lo R., et al. (2010). PSORTb 3.0: improved protein subcellular localization prediction with refined localization subcategories and predictive capabilities for all prokaryotes. Bioinformatics 26, 1608–1615. 10.1093/bioinformatics/btq249 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang X., Feng X., Tao J., Ma L., Xiao Y., Liang Y., et al. (2016). Comparative genomics of the extreme acidophile Acidithiobacillus thiooxidans reveals intraspecific divergence and niche adaptation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 17:1355. 10.3390/ijms17081355 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.