Significance
Many aquatic microorganisms have evolved CO2-concentration mechanisms (CCMs) to boost photosynthesis. The green algae Chlamydomonas reinhardtii has the best-characterized eukaryotic CCM model. Mutants lacking the limiting CO2-inducible B protein (LCIB) protein are unable to survive in air. To investigate the molecular underpinnings of this effect, we biochemically and structurally characterized a number of LCIB homologues from diverse organisms, including constitutively carbonic anhydrase (CA)-active proteins. We discovered that LCIB proteins structurally resemble β-CAs in both overall fold and active site architecture. Our results provide insight into the molecular mechanism of the LCIB family involved in microalgal CCMs.
Keywords: LCIB, limiting-CO2 inducible protein, CO2-concentrating mechanism, photosynthesis, carbonic anhydrases
Abstract
Aquatic microalgae have evolved diverse CO2-concentrating mechanisms (CCMs) to saturate the carboxylase with its substrate, to compensate for the slow kinetics and competing oxygenation reaction of the key photosynthetic CO2-fixing enzyme rubisco. The limiting CO2-inducible B protein (LCIB) is known to be essential for CCM function in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. To assign a function to this previously uncharacterized protein family, we purified and characterized a phylogenetically diverse set of LCIB homologs. Three of the six homologs are functional carbonic anhydrases (CAs). We determined the crystal structures of LCIB and limiting CO2-inducible C protein (LCIC) from C. reinhardtii and a CA-functional homolog from Phaeodactylum tricornutum, all of which harbor motifs bearing close resemblance to the active site of canonical β-CAs. Our results identify the LCIB family as a previously unidentified group of β-CAs, and provide a biochemical foundation for their function in the microalgal CCMs.
Photosynthesis powers the biosphere, and aquatic photosynthetic microorganisms contribute to ∼50% of global photosynthesis (1); however, this process is intrinsically hampered by the biophysical properties of inorganic carbon (Ci) and the poor kinetics of the enzyme ribulose 1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase (rubisco) (2), which catalyzes the critical reaction of fixing carbon dioxide (CO2) into organic molecules. To supply sufficient CO2 to the active site of rubisco, most photosynthetic aquatic microeukaryotes have evolved a myriad of syndromes collectively known as CO2-concentrating mechanisms (CCMs) (3–5).
The best-characterized eukaryotic CCM is the one found in the green algae Chlamydomonas reinhardtii (6, 7). Ci in the form of bicarbonate (HCO3−) is pumped into the chloroplast by active transport (8, 9), where it is converted to CO2 by the carbonic anhydrase (CA) CAH3, which is localized in the thylakoid lumen (10, 11). This mechanism elevates the CO2 concentration in the rubisco-containing compartment, the pyrenoid (12–14). A critical component of the CCM required at air levels of CO2 is the stromal soluble protein complex CrLCIB-LCIC (limiting CO2-inducible B and C protein in C. reinhardtii) (15, 16).
The air-dier phenotype of a CrLCIB lesion was discovered more than 30 years ago (17), and the mutant C. reinhardtii was found to be unable to accumulate Ci in air. In addition, the gene encoding the CrLCIB protein, LCIB, is one of the most up-regulated genes when CO2 is limiting (9, 18, 19). CrLCIB has no sequence homology to any of the previously characterized proteins, and its detailed functional characterization has so far remained elusive. Nonetheless, it clearly forms a high molecular weight complex of 1:1 stoichiometry (possibly hetero-hexameric) with its homolog CrLCIC, and localization studies using CrLCIB-GFP fusions have shown CO2 concentration-dependent shifts from the chloroplast stroma to a region surrounding the pyrenoid (15, 16). Key functional information has been gleaned from the discovery of mutants that suppress the air-dier phenotype (20). An additional mutation in the pyrenoidal CAH3 restores the ability of the CrLCIB mutant to grow at air levels of CO2, and implicates its function as operating downstream of CAH3. Thus, current working hypotheses propose that the CrLCIB-LCIC complex recaptures or prevents the leakage of CO2 generated by CAH3 and not fixed by rubisco. Theoretically, this function could be fulfilled by a unidirectional CO2 hydration function (21), by formation of a physical CO2 barrier around the pyrenoid, or by regulation of other CAs, such as the stromal CAH6 (22).
Here we discovered that microalgal LCIB structurally resembles β-CAs. We describe a number of constitutively CA-active LCIB homologs from the diatom Phaeodactylum tricornutum and the bacteroidete Flavobacterium johnsoniae. Although the well-studied C. reinhardtii homologs also appear to have the required structural attributes of a functional CA, their biochemical activities are absent. Consistent with this finding, we reason that to perform the hypothesized unidirectional CO2 capture function, a CA needs to be tightly regulated.
Results
Several LCIB Homologs Exhibit CA Activity.
The leading hypothesis for LCIB function proposes a unidirectional CO2 hydration activity, which would trap HCO3− anions in the chloroplast, thereby preventing CO2 leakage (7). To test this hypothesis, we produced a number of recombinant LCIB homologs in Escherichia coli, including the C. reinhardtii proteins CrLCIB, CrLCIC, and the CrLCIB-LCIC complex. The constructs used exclude the N-terminal chloroplast-targeting peptide (16). LCIB homologs also have been identified in diatoms, cyanobacteria, and other bacteria (15). The genome of the diatom P. tricornutum, which also has a pyrenoid-based CCM (23), contains a cluster of four genes homologous to the C. reinhardtii LCIB (SI Appendix, Fig. S1) (24); herein, their gene products (UniProt accession nos. B7FR26–29) are referred to as PtLCIB1–4. Therefore, we prepared recombinant PtLCIB3, PtLCIB4, and CsLCIB from the cyanobacterium Cyanothece sp. PCC 7425 and FjLCIB from the bacteroidete F. johnsoniae (SI Appendix, Fig. S1). The sequence comparison and key residues of these proteins are depicted in SI Appendix, Fig. S2.
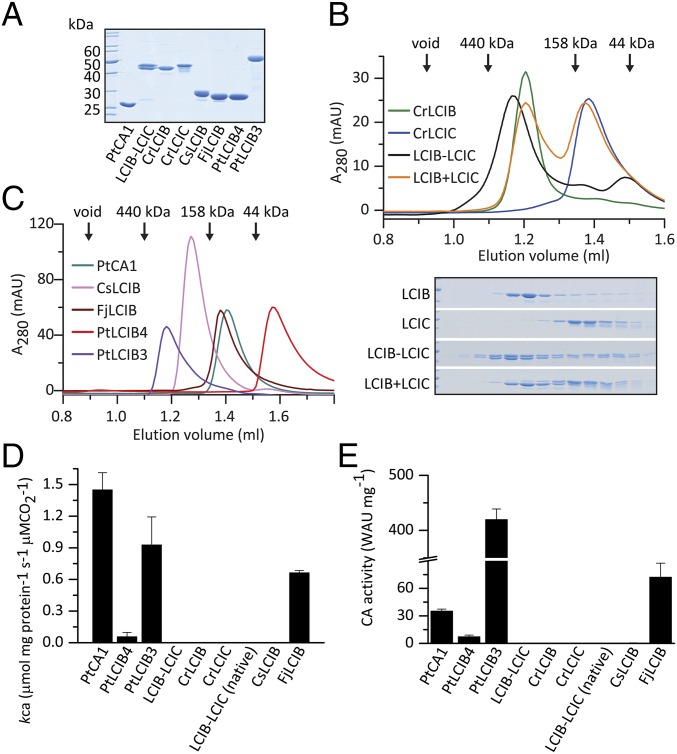
All recombinant proteins were soluble and could be purified to homogeneity using a combination of affinity, anion-exchange, and gel filtration chromatography (Fig. 1A). The native CrLCIB-LCIC complex was purified from C. reinhardtii cells by anion-exchange and gel filtration chromatography, and behaved similarly to the recombinant complex as assessed by gel filtration (SI Appendix, Fig. S3 A–D). Coexpression of CrLCIB and CrLCIC resulted in a high molecular weight (∼440 kDa) complex of 1:1 stoichiometry (Fig. 1B), consistent with the complex found in vivo (15) (SI Appendix, Fig. S3D). Gel filtration chromatography exhibited a broad elution profile indicating significant polydispersity. In contrast, the isolated CrLCIB and CrLCIC eluted as monodisperse populations, with CrLCIB forming a high molecular weight complex (∼390 kDa) and CrLCIC eluting at a later position corresponding to a dimer. Mixing of the purified CrLCIB and CrLCIC in vitro did not reconstitute the high molecular weight complex (Fig. 1B). All of the LCIB homologs except PtLCIB4 presented as higher-order complexes (tetramers or larger) with trailing shoulders, indicating polydispersity (Fig. 1C). PtLCIB4 eluted relatively late, indicating a possible interaction with the column material.
Fig. 1.
Purification and characterization of LCIB homologs. (A) SDS/PAGE analysis. (B) Gel filtration analysis of recombinant CrLCIB and CrLCIC complexes. LCIB-LCIC was prepared by recombinantly coexpressing CrLCIB and CrLCIC. LCIB+LCIC was prepared by mixing and incubating separately expressed CrLCIB and CrLCIC in vitro. In each experiment, a total of 25 μg per sample was loaded, and the corresponding fractions were separated by SDS/PAGE and are shown below the chromatograph. (C) Gel filtration analysis of diatom and prokaryotic LCIB homologs, with 50 μg per isoform loaded in each experiment. (D) MIMS CA activity assay for LCIB homologs reported as the first-order rate constant for the hydration of CO2 (kCA), μmol mg protein−1 s−1 μM CO2−1 at 25 °C. LCIB-LCIC (native), CrLCIB-LCIC complex purified from C. reinhardtii cells. (E) Wilbur–Anderson CA activity assay of the LCIB proteins. Error bars indicate the mean and SD of at least three independent repeats.
We tested the hypothesized conversion of CO2 to HCO3− by performing CA activity assays using isotope-exchange membrane-inlet mass spectrometry (MIMS). We found that PtLCIB3, PtLCIB4, and FjLCIB exhibited diverse levels of CA activity, measured as a first-order rate constant for the hydration of CO2 per milligram of protein (∼0.06–0.9 μmol mg protein−1 s−1 μM CO2−1), whereas CsLCIB, CrLCIB, CrLCIC, recombinant CrLCIB-LCIC complex, and native CrLCIB-LCIC complex were inactive under all conditions tested (Fig. 1D). In comparison, the activity of the classic β-type CA PtCA1 (25) used as the positive control was 1.45 μmol mg protein−1 s−1 μM CO2−1.
To confirm our findings, we also measured the CA activities using the Wilbur–Anderson method (26) (Fig. 1E). Differences in relative activities observed between proteins using the two methods are likely due to the very different substrate concentrations used. The CA-inhibitor acetazolamide (AZM) was found to inhibit the activity of all CA-active LCIB proteins (SI Appendix, Fig. S3F), providing further evidence for a specific CA function. PtLCIB3 and FjLCIB4 were more sensitive to AZM inhibition than the less CA-active PtLCIB4. This indicates that the difference in their activity is likely a result of substrate binding or accessibility of the active site, considering the competitive nature of the inhibitor. Recently, Matsuda et al. (27) also demonstrated that PtLCIB3 (designated in their work as Pt43233) has CA activity and is localized to the thylakoid membrane spanning the pyrenoid. To understand the molecular basis of the observed biochemical results, we set out to structurally characterize the various LCIB proteins.
PtLCIB4 Exhibits a Typical β-CA Fold.
We generated expression constructs for CrLCIB (residues 53–346; CrLCIB-ΔC) and CrLCIC (residues 40–344; CrLCIC-ΔC), excluding the N-terminal chloroplast targeting peptide (16) and the C-terminal disordered region of both proteins as predicted by DISOPRED3 (28). The crystal structures of these two constructs were determined at 2.59-Å and 2.51-Å resolution, respectively. In addition, the structure of the full-length PtLCIB4 was determined at 1.75-Å resolution. The structure of CrLCIC-ΔC was solved by the single-wavelength anomalous dispersion method using a Pt-derived CrLCIC-ΔC crystal with SHELX (29), and was subsequently used as a search model to determine the structures of CrLCIB-ΔC and PtLCIB4, using the molecular replacement program PHASER (30). Data collection and final refinement statistics are summarized in SI Appendix, Table S1.
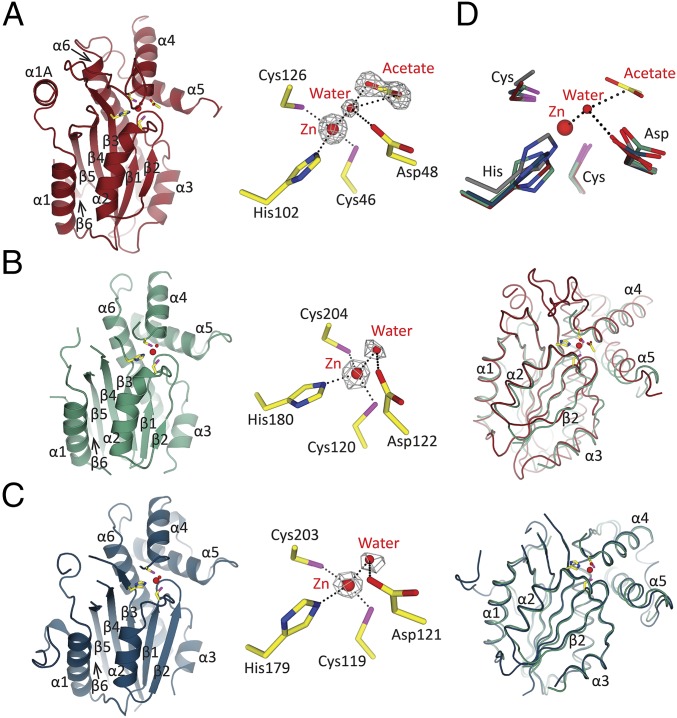
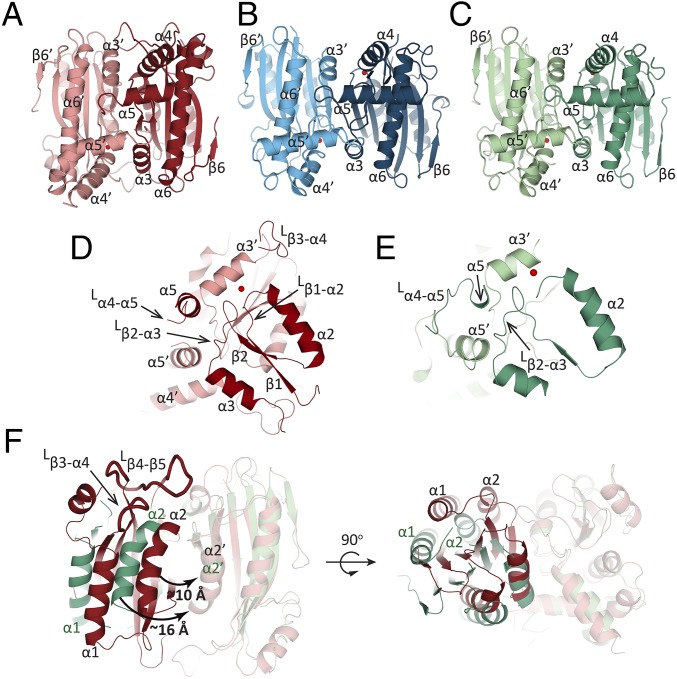
The PtLCIB4 molecule has an α/β fold with six mixed β-strands forming a twisted sheet flanked by two α-helices on the concave side and four α-helices on the opposite side (Fig. 2A). The central core is composed of four parallel β-strands in a 2-1-3-4 arrangement, which is a typical feature of β-CAs (31). In addition, two more β-strands (β5 and β6) are positioned in an antiparallel manner adjacent to β4, extending the compact β-sheet core (Fig. 2A). An area of substantial electron density was observed at the C terminus of β1. Combining our X-ray absorption spectroscopic scanning results with the arrangement of the surrounding residues, a zinc ion was assigned. This zinc ion is coordinated by Cys46, His102, Cys126, and a water molecule (Fig. 2A). PtLCIB4 forms a dimer with the dimeric axis coinciding with a crystallographic twofold axis (Fig. 3A). At the dimeric interface, the buried surface area is 1,997 Å2, and the theoretical interaction energy (ΔiG) is −15.6 kcal/mol, as calculated with PISA (32). At the dimeric interface, α3, α5 (and their N-terminal loops), Lβ3-α4 (loop connecting β3 and α4, same as below), Lβ1-α2, and β2 harbor residues forming interactions with the adjacent subunit (Fig. 3D and SI Appendix, Fig. S4A).
Fig. 2.
Overall structures, active sites, and comparison of CrLCIB-ΔC, CrLCIC-ΔC, and PtLCIB4 subunits. Zn ion and water are colored in bright red and represented as larger and smaller spheres, respectively. The active site residues are in yellow. The Fo-Fc electron density maps are calculated with omission of the enveloped atoms. The side chains of the residues involved in Zn and water binding are shown as sticks, with C, O, and N atoms colored in yellow, red, and blue, respectively (same as below). Coordination of the Zn ion and polar interactions are indicated by dashed lines. (A) The structure of the PtLCIB4 (red, same as below) and the Zn-binding site. The acetate molecule is shown as sticks, with O atom colored in red. (B) The structure of the CrLCIB-ΔC subunit (green, same as below), an enlarged view of the Zn-binding site and the CrLCIB-ΔC subunit overlaid with PtLCIB4. (C) The structure of the CrLCIC-ΔC subunit (blue, same as below), the Zn-binding site, and the CrLCIC-ΔC subunit overlaid with CrLCIB-ΔC. (D) Active site residue superposition of CrLCIB-ΔC (green), CrLCIC-ΔC (blue), PtCIB4 (red), and PSCA (gray). Zn, water, and acetate are from the PtLCIB4 structure. The dashed lines indicate that those atoms are within interacting distance of the water molecule.
Fig. 3.
Comparison of dimerization among CrLCIB-ΔC, CrLCIC-ΔC and PtLCIB4. (A–C) The two subunits of the PtLCIB4 dimer (red and pale red), CrLCIC-ΔC dimer (blue and pale blue), and CrLCIB-ΔC (green and pale green) are depicted with one zinc ion per subunit. (D and E) The secondary structure elements of PtLCIB4 (D) and CrLCIB-ΔC (E) involved in dimerization are shown. (F) Comparison of CrLCIB-ΔC and PtLCIB4 dimers by alignment based on one subunit (shown in transparency). Secondary structure elements of CrLCIB-ΔC and PtLCIB4 are labeled in dark green and black, respectively. The intersubunit gap distance is measured as the distance between α2 and α2′ and is highlighted by a curved arrow with the distance indicated. The two loops (Lβ3-α4 and Lβ4-β5) that are clearly defined in PtLCIB4 but disordered in CrLCIB/C-ΔC are shown as ribbons with a thicker radius. An alternative view is also depicted with the dimer rotated 90 degrees around an axis perpendicular to the dimeric axis.
A Dali server (33) search based on structural similarity to PtLCIB4 identified numerous CAs with a z-score of ∼11, whereas conventional sequence-based bioinformatic tools failed to detect any homologs. Indeed, the pseudotetrahedral (Cys2HisWater) network and the coordinated zinc ion demonstrated a typical β-CA active site architecture (34, 35) (Fig. 2 A and D).
The Active Site Arrangement in PtLCIB4 Supports CA Activity.
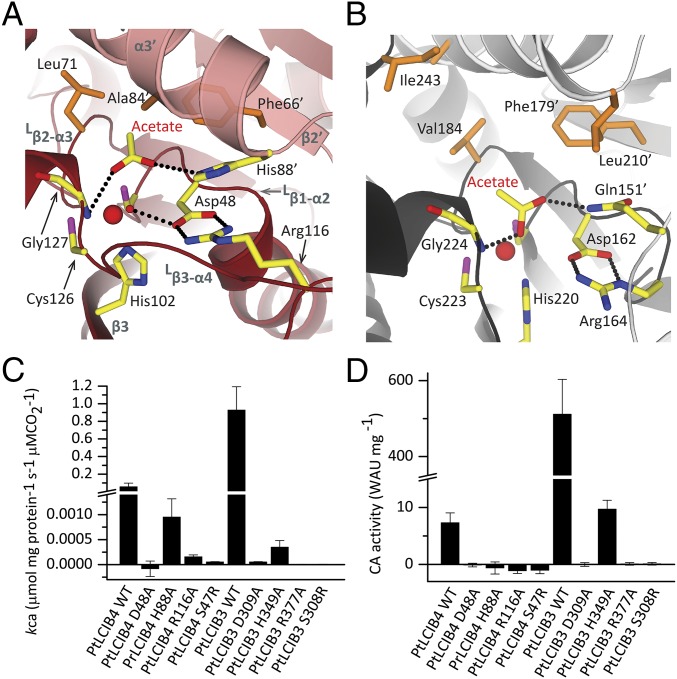
Both active sites of the PtLCIB4 dimer are located at the dimer interface and are formed by secondary structure elements from both halves of the dimer (Lβ1-α2, β3, Lβ3-α4, Lβ2-α3, β2′, and α3′) (Fig. 4A). The crystallization condition of PtLCIB4 contains 200 mM acetate, and the unbiased difference electron density map (Fo-Fc) clearly shows an acetate molecule located in the active site (Fig. 2A). As an analog of the substrate CO2, acetate has been observed in many previously solved CA structures (36–39). The three zinc-binding residues (Cys46, His102, and Cys126) are located at the bottom (nearer to the central core of each subunit) of each active site. One highly conserved aspartate (Asp48) is proposed to be the catalytic residue and is in direct contact with the zinc-bound water. The proper orientation of Asp48 is maintained by forming salt bridges with Arg116. In addition, His88′ (where ′ indicates residues on the neighboring subunit within a dimer, same as below) forms a stacking interaction with Arg116, stabilizing the Asp48-Arg116 dyad (Fig. 4A). Consistent with these observations, substituting Asp48, His88, or Arg116 in PtLCIB4 (and the corresponding Asp309, His349, and Arg377 in PtLCIB3) with alanine renders the enzymes inactive (Fig. 4 C and D).
Fig. 4.
Detailed view of the active site in PtLCIB4 and PSCA, and activity assay. (A and B) The detailed view of the active site in PtLCIB4 (A) and PSCA (B). The two subunits of PSCA from pea P. sativum are colored dark gray and light gray. The side chains of the polar residues at the active site of the two structures are shown as yellow sticks. The hydrophobic residues involved in acetate binding at the active site are shown as orange sticks. (C and D) MIMS (C) and Wilbur–Anderson (D) CA activity assays of PtLCIB4, PtLCIB3, and their mutants are shown. Error bars indicate the mean and SD of at least three independent repeats.
The binding of the acetate molecule is enhanced through shape and charge complementarity with the pocket. O1 of the acetate interacts with both the amide nitrogen of Gly127 and a zinc-bound water molecule. In addition, the interaction of the zinc ion with O1 stabilizes acetate binding. O2 is within hydrogen-bonding distance to His88′, which is presumably critical for retaining acetate in the active site. Indeed, mutating His88 in PtLCIB4 and the corresponding His349 in PtLCIB3 to alanine significantly impede this activity (Fig. 4 C and D). The structure of the PtLCIB4 His88A mutant lacks acetate in the active site, despite the presence of 200 mM sodium acetate in the crystallization buffer as well (SI Appendix, Fig. S5). Furthermore, the methyl group of acetate contacts the side chains of Leu71, Phe66′, and Ala84′ through hydrophobic interactions (Fig. 4A). These surrounding hydrophobic residues could facilitate the binding of the authentic substrate CO2, which, because of its hydrophobicity, is presumably positioned closer to the zinc ion compared with acetate.
The Catalytic Core of PtLCIB4 Is Conserved Among Classic β-CAs.
PSCA, a canonical and highly active β-CA from the pea Pisum sativum (37), has a z-score of 10.6 for 151 Cα atoms with PtLCIB4 based on a DALI server search (33); however, the sequence identity is only ∼11%. A structural comparison shows that the central β-sheet cores superpose well, but the helices on both sides pack against the central β-sheet differently, most profoundly in the N-terminal regions (SI Appendix, Fig. S6A). The two N-terminal helices in PtLCIB4 wrap around β5 of the central core. In PSCA, these elements have an “L”-like arrangement extending toward the neighboring subunit and pack against a cleft formed by β5 and its flanking helix (SI Appendix, Fig. S6E). In PtLCIB4, the N-terminal regions appear to contribute little to dimerization (SI Appendix, Fig. S6C). The buried surface area of the PSCA dimer (3,255 Å2) is also substantially larger than that of PtLCIB4 (1,997 Å2).
In both structures, the zinc ion and a trio of residues (Cys-His-Cys) are arranged similarly. A zinc-bound water molecule is clearly defined in our PtLCIB4 structure. In contrast to its interaction with His88′ in PtLCIB4, the O2 of the acetate molecule forms a hydrogen bond with the side chain amide of Gln151′ in PSCA (Fig. 4 A and B). A similar role for the corresponding Gln residue is also seen in other β-CA structures, such as in the enzyme from A. thaliana (40). Therefore, His88 in PtLCIB4 mimics the role of the Gln residue in other β-CAs. Interestingly, the catalytic residues Asp48/162 and Arg116/164 in PtLCIB4/PSCA both form salt bridges, although the arginine atoms involved in the interaction are different (Fig. 4 A and B). In the formation of this Asp-Arg dyad, the two residues are separated by a gap of only one residue in PSCA (Asp162 and Arg164), as well as in the Cab type β-CA from M. thermoautotrophicum (Asp34 and Arg36) (41), whereas in PtLCIB4 they are separated in primary sequence (Asp48 and Arg116). This finding clearly demonstrates the theme of functional replacement often observed in β-CAs: the critical residues are replaced by similar residues from a different part of the structure. In addition, it is often observed that in CAs from different species, the protein sequences are diverse, whereas the active sites are well conserved (42).
CrLCIB/C-ΔC Resembles PtLCIB4 in the Overall Structure and Zinc-Binding Site.
CrLCIB/C-ΔC structures contain one zinc ion per molecule, coordinated by a water molecule and a conserved trio of residues, namely Cys120/119, His180/179, and Cys204/203, in CrLCIB/C-ΔC (Fig. 2 B and C). The subunit of CrLCIB-ΔC differs from the subunits of CrLCIC-ΔC and PtLCIB4 by an rmsd of only 0.6 Å and 1.59 Å, respectively, for all atoms. Thus, CrLCIB/C-ΔC closely resembles PtLCIB4 in secondary structure topology and overall architecture (Fig. 2 B and C). In particular, the residues at the zinc-binding site of CrLCIB/C-ΔC adopt nearly the same position as seen in PtLCIB4 and the classic β-CA PSCA (Fig. 2D). Both zinc-binding sites superpose closely with those found in the CA-active PtLCIB4. In contrast, the C-terminal ends of α3 and Lβ3-α4, which harbor the conserved His88 and Arg116 (His162/161 and Arg194/193 in CrLCIB/C-ΔC) essential for the activity of PtLCIB4, are disordered in CrLCIB and CrLCIC (Figs. 3F and 4A).
Oligomerization in CrLCIB/C-ΔC Differs from That in PtLCIB4.
CrLCIB/C-ΔC both form dimers, with a buried surface area of 1,094 Å2/1,118 Å2 (1,997 Å2 in PtLCIB4) and a ΔiG value of −7.9 kcal/mol/−9.9 kcal/mol (−15.6 kcal/mol in PtLCIB4), respectively (Fig. 3 B and C). Similar to PtLCIB4, CrLCIB-ΔC also lacks the N-terminal extension found in PSCA (SI Appendix, Fig. S6 B, D, and E). The dimeric association in CrLCIB-ΔC involves fewer contacting secondary structure elements compared with that in PtLCIB4 (Fig. 3 D and E and SI Appendix, Fig. S4B). Furthermore, the mature forms of the isolated proteins with intact C termini, CrLCIB/C, appear larger than those of CrLCIB/C-ΔC in the gel filtration profile (SI Appendix, Fig. S3E), implying a possible role for the C-terminal extensions in forming higher order homo-oligomers.
In PtLCIB4, the opening of the zinc-binding pocket is essentially shielded from the solvent by Lβ4-β5 and Lβ3-α4. The corresponding loops in CrLCIB/C-ΔC are presumably flexible, given the fact that they cannot be traced in the corresponding electron density maps (Fig. 3F). The major difference between the PtLCIB4 and CrLCIB/C-ΔC dimers is caused predominantly by rigid body rotation of one subunit around an axis orthogonal to the molecular twofold axis (Fig. 3F). Consequently, the intersubunit gap is considerably widened in CrLCIB-ΔC, as revealed by an ∼6-Å increase in the distance between α2 and α2′.
To investigate whether the CrLCIB-ΔC dimer is able to adopt the presumed active conformation with shortened intersubunit distance, we modeled the CrLCIB-ΔC dimer on the PtLCIB4 dimer and relaxed the structure using Rosetta3.4 (43). The resulting structure has a dimeric interface area of 1,542 Å2, compared with 1,094 Å2 in the original dimer, along with a considerably narrower intersubunit gap. Furthermore, mass spectroscopy analysis of the native CrLCIB-LCIC complex identified a phosphorylation site on Ser163/160 in CrLCIB/C (SI Appendix, Fig. S7 B and C). Phosphorylation of both isoforms has been shown previously, but not precisely mapped (15, 16). These two serine residues are directly adjacent to His162/161 in CrLCIB/C (SI Appendix, Fig. S2). Given that the corresponding residue in PtLCIB4, H88, is deemed important for the activity of the enzyme, phosphorylation occurring next to this residue might be implicated in the activity regulation of the CrLCIB-LCIC complex. Specifically, a number of positively charged residues (especially Arg194/193 in CrLCIB/C) on the adjacent disordered loop from the neighboring subunit (Lβ3-α4′) could form electrostatic interactions with the phosphorylated serine. This could stabilize the structure of the loop and properly orient the histidine residue toward the putative substrate binding pocket, as is the case in the PtLCIB4 dimer (SI Appendix, Fig. S7 D and E).
One glycerophosphorylation site was also identified with high confidence in the mass spectroscopy analysis (SI Appendix, Fig. S7A). As discussed above, the highly active PSCA has an N-terminal extension that wraps around the neighboring subunit. In CrLCIB/C, the hydroxyl groups added by glycerophosphorylation may enhance the interaction of the N-terminal disordered region with the neighboring subunit through additional hydrogen bonds. This could strengthen the dimer association.
The Integrity of the Active Site Is Perturbed in CrLCIB/C-ΔC.
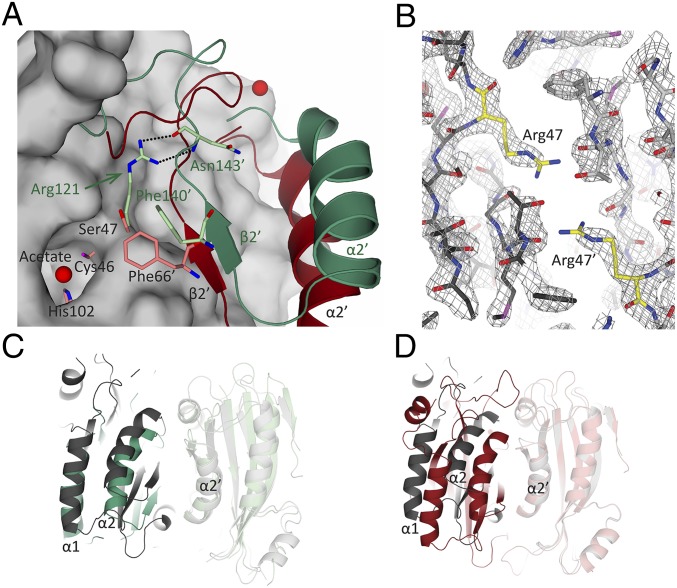
Apart from the aforementioned disorder of the important conserved residues His162/161 and Arg194/193 in CrLCIB/C-ΔC, the large side chain of Arg121/120 in CrLCIB/C-ΔC protrudes into the intersubunit cleft and pushes away the β2 strand, thereby perturbing the substrate binding pocket (Fig. 5A). Interestingly, we also found that the corresponding residue Ser47/Ser308 in PtLCIB4/3 is essential for the catalytic activity; missense mutation to arginine (the same as that in CrLCIB/C-ΔC) renders the enzymes inactive (Fig. 4 C and D). In addition, the presence of Arg121 in CrLCIB-ΔC prevents the highly conserved Phe140′ (Phe66′ in PtLCIB4) from accessing the putative active site, thereby presumably interfering with substrate binding (Fig. 5A).
Fig. 5.
Comparison of the positioning of Arg121 and Ser47 in CrLCIB-ΔC, PtLCIB4, and PtLCIB4 S47R mutant. (A) The CrLCIB-ΔC dimer (green) and PtLCIB4 dimer (red) are aligned based on one subunit. The subunit used for alignment in the PtLCIB4 dimer is shown as a gray surface, excluding Zn, its binding residues (Cys46, His102, and Cys126), and Ser47. The residues from the other subunit in proximity to Arg121 (CrLCIB-ΔC) and Ser47 (PtLCIB4) are shown as sticks. The secondary structure elements are labeled in dark green (CrLCIB-ΔC) and black (PtLCIB). (B) Structure of the PtLCIB4 S47R dimer at the mutation site. The two subunits of the mutant dimer are depicted in dark gray and light gray, respectively. Arg47 from both subunits are colored yellow. The 2Fo-Fc electron density map (gray mesh) clearly shows the mutation of Ser47 to arginine. (C and D) The dimer of PtLCIB4 S47R (gray) compared with CrLCIB-ΔC (C, green) and PtLCIB4 (D, red) by alignment based on one subunit (shown in transparency).
Comparison of PtLCIB4 with CrLCIB-ΔC also shows that the presence of the bulky Arg121 residue in CrLCIB appears to prevent the dimer from adopting the more closely packed conformation seen in the PtLCIB4 structure (Fig. 5A). Indeed, the structure of the PtLCIB4 S47R mutant exhibits a dimer assembly that is significantly more similar to CrLCIB-ΔC compared with the wild-type PtLCIB4 (Fig. 5 B–D), demonstrating the pivotal importance of Ser47 for the integrity of the dimeric association. However, “back-mutation” of the Arg121 to Ser in CrLCIB did not restore its β-CA activity. This suggests that mutating Arg121 is insufficient to switch on CA activity in this family of proteins, and that additional factors are likely required for this activity. In addition, whether the (nonfunctional) high molecular weight CrLCIB-LCIC complex consists of homodimers or heterodimers is currently unclear. Thus, whether the observed dimer interface is physiologically relevant requires further investigation. Nevertheless, the dimer interface and the interference of Arg121/120 with dimer assembly within the CrLCIB-ΔC and CrLCIC-ΔC homodimer are predicted to be similar to those in a CrLCIB-LCIC heterodimer, given the high sequence identity and structural similarity (SI Appendix, Fig. S8).
In the LCIB protein family, residues corresponding to Ser47 in PtLCIB4 are mainly divided into two types: arginine and small side chain residues (cysteine, serine, and alanine) (SI Appendix, Fig. S9). Among the LCIB homologs that we have tested, those with arginine at this position are not CA-functional, whereas those with small side chain residues exhibit CA activity under our experimental conditions (Fig. 1 D and E and SI Appendix, Fig. S9). Results related to this hypothesis are shown in SI Appendix, Results.
Discussion
The three proteins CrLCIB-ΔC, CrLCIC-ΔC, and PtLCIB4 structurally resemble β-CAs with striking similarities in overall fold, zinc-binding motif, and especially putative active site architecture. The lack of activity in CrLCIB, CrLCIC, and the CrLCIB-LCIC complex is likely caused by widening of the intersubunit cleft, which affects active site integrity by causing disordering of the important His162/161 and Arg194/193 residues in CrLCIB/C-ΔC (His88 and Arg116 in PtLCIB4). Similar observations have been reported in the redox regulation of carboxysomal γ-CA, CcmM, in Thermosynechococcus elongatus BP-1 (44). Reduction breaks a disulfide bond in CcmM and consequently causes a relative domain movement, which displaces a number of catalytically important residues, rendering the enzyme inactive (44). Thus, the correct positioning of the subunit within the oligomer seems to be critical for catalytic activity. Collectively, our findings provide insight into the molecular mechanisms of the LCIB protein family and implicate them as a previously unidentified group of β-CAs essential for the C. reinhardtii CCM.
Ser47/Ser308 in PtLCIB4/3 was found to be a key residue that affects the CA activity of the four LCIB proteins studied. A bulky arginine side chain at this position results in loss of activity by restricting intersubunit gap closure. This finding was confirmed in the evolutionarily related homologs of LCIB, underlying the divergent evolution of limiting CO2-inducible proteins in different species. It is plausible that the function of the proteins in the LCIB family bifurcated during evolution: those with constitutive CA activity (such as PtLCIB4/3) vs. those with a tightly regulated CA function (such as CrLCIB/C). Activity-regulating mechanisms have been observed in a number of CAs. Apart from the aforementioned redox regulation in CcmM (44), HICA, a β-CA found in Haemophilus influenzae, contains an allosteric binding site for bicarbonate, which acts as both a substrate and a regulator of the enzyme (45); however, the structure alignment revealed that the allosteric site in HICA corresponds to an area occupied mainly by hydrophobic residues in CrLCIB/C-ΔC and PtLCIB4. Thus, the bicarbonate-dependent activation mechanism is unlikely to be present in these proteins. Regarding the function of the non-C. reinhardtii proteins analyzed here, Kikutani et al. (27) recently published a key study regarding the localization and function of PtLCIB3. They reported that in the diatom, this gene product localizes to the lumen of pyrenoid-penetrating thylakoid and is essential for the CCM function of the algae. The algal protein is CA-active, and thus PtLCIB3 appears to fulfill an analogous function to the luminal CAH3 CA in C. reinhardtii.
Based on our current understanding of the C. reinhardtii CCM, it appears that the stromal CrLCIB-LCIC complex is required for the uptake of external CO2 into the stromal bicarbonate pool and the prevention of CO2 (generated by CAH3) leakage from the pyrenoid. In this context, it would be important to deactivate the CA activity of the CrLCIB-LCIC complex when the HCO3−/CO2 ratio is high, to permit Ci buildup in the lumen. Once this ratio has decreased (as a result of CO2 leakage from the pyrenoid), the complex would become functional. This scenario would require preferential activation of the proposed CO2 hydration activity when CO2 is in excess (16), rather than promotion of constant equilibration of Ci species in the stroma, which would result from a highly active nonregulated CA. Such a situation would uncouple the CCM, as seen in cyanobacteria (46). Both the peripyrenoidal and stromal localization (15, 16) observed for the CrLCIB-LCIC complex are consistent with such a function. In addition to the posttranslational modifications observed here, many other regulatory mechanisms can be envisaged, and future work will focus on carefully characterizing the protein complex purified from the native source. Considering the data at hand, we are unable to definitely rule out other proposed functions for the CrLCIB-LCIC complex, such as a noncatalytic structural barrier for CO2.
Methods
Cloning, protein preparation, crystallization, data collection and structure determination, CA assays, and posttranslational modification analysis are described in detail in SI Appendix, Methods.
Supplementary Material
Acknowledgments
We thank the beamline scientists at Swiss Light Source, Advanced Light Source (United States), National Synchrotron Radiation Research Center (Taiwan), and Australian Synchrotron for technical assistance; Dr. Liew Chong Wai (Nanyang Technological University) for assistance with data collection; Dexter Tan for experimental assistance; and Dr. Rya Ero for comments on the manuscript. This work was supported by the Singapore National Research Foundation Grant NRF-RF2009-RF001-267 (to Y.-G.G.), a Tier II grant from the Ministry of Education of Singapore MOE2015-T2-1-078 (to Y.-G.G.), and a Nanyang Technological University Start-Up grant (to O.M.-C.).
Footnotes
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
This article is a PNAS Direct Submission.
Data deposition: The atomic coordinates and structure factors have been deposited in the Protein Data Bank, www.pdb.org (PDB ID codes 5K5W, 5B5X, 5B5Y, 5B5Z, and 5B60).
This article contains supporting information online at www.pnas.org/lookup/suppl/doi:10.1073/pnas.1616294113/-/DCSupplemental.
References
- 1.Field CB, Behrenfeld MJ, Randerson JT, Falkowski P. Primary production of the biosphere: Integrating terrestrial and oceanic components. Science. 1998;281(5374):237–240. doi: 10.1126/science.281.5374.237. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Spreitzer RJ, Salvucci ME. Rubisco: Structure, regulatory interactions, and possibilities for a better enzyme. Annu Rev Plant Biol. 2002;53:449–475. doi: 10.1146/annurev.arplant.53.100301.135233. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Badger MR, Kaplan A, Berry JA. Internal inorganic carbon pool of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii: Evidence for a carbon dioxide-concentrating mechanism. Plant Physiol. 1980;66(3):407–413. doi: 10.1104/pp.66.3.407. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Meyer M, Griffiths H. Origins and diversity of eukaryotic CO2-concentrating mechanisms: Lessons for the future. J Exp Bot. 2013;64(3):769–786. doi: 10.1093/jxb/ers390. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Giordano M, Beardall J, Raven JA. CO2-concentrating mechanisms in algae: Mechanisms, environmental modulation, and evolution. Annu Rev Plant Biol. 2005;56:99–131. doi: 10.1146/annurev.arplant.56.032604.144052. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Moroney JV, Ynalvez RA. Proposed carbon dioxide-concentrating mechanism in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Eukaryot Cell. 2007;6(8):1251–1259. doi: 10.1128/EC.00064-07. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Wang Y, Stessman DJ, Spalding MH. The CO2-concentrating mechanism and photosynthetic carbon assimilation in limiting CO2: How Chlamydomonas works against the gradient. Plant J. 2015;82(3):429–448. doi: 10.1111/tpj.12829. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Duanmu D, Miller AR, Horken KM, Weeks DP, Spalding MH. Knockdown of limiting-CO2–induced gene HLA3 decreases HCO3− transport and photosynthetic Ci affinity in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2009;106(14):5990–5995. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0812885106. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Miura K, et al. Expression profiling-based identification of CO2-responsive genes regulated by CCM1 controlling a carbon-concentrating mechanism in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Plant Physiol. 2004;135(3):1595–1607. doi: 10.1104/pp.104.041400. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Hanson DT, Franklin LA, Samuelsson G, Badger MR. The Chlamydomonas reinhardtii cia3 mutant lacking a thylakoid lumen-localized carbonic anhydrase is limited by CO2 supply to rubisco and not photosystem II function in vivo. Plant Physiol. 2003;132(4):2267–2275. doi: 10.1104/pp.103.023481. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Benlloch R, et al. Crystal structure and functional characterization of photosystem II-associated carbonic anhydrase CAH3 in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Plant Physiol. 2015;167(3):950–962. [Google Scholar]
- 12.Engel BD, et al. 2015. Native architecture of the Chlamydomonas chloroplast revealed by in situ cryo-electron tomography. eLife 4:doi: 10.7554/eLife.04889.
- 13.Meyer MT, et al. Rubisco small-subunit α-helices control pyrenoid formation in Chlamydomonas. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2012;109(47):19474–19479. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1210993109. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Mackinder LC, et al. A repeat protein links Rubisco to form the eukaryotic carbon-concentrating organelle. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2016;113(21):5958–63. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1522866113. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Yamano T, et al. Light and low-CO2–dependent LCIB-LCIC complex localization in the chloroplast supports the carbon-concentrating mechanism in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Plant Cell Physiol. 2010;51(9):1453–1468. doi: 10.1093/pcp/pcq105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Wang Y, Spalding MH. LCIB in the Chlamydomonas CO2-concentrating mechanism. Photosynth Res. 2014;121(2-3):185–192. doi: 10.1007/s11120-013-9956-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Spalding MH, Spreitzer RJ, Ogren WL. Reduced inorganic carbon transport in a CO2-requiring mutant of Chlamydomonas reinhardii. Plant Physiol. 1983;73(2):273–276. doi: 10.1104/pp.73.2.273. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Brueggeman AJ, et al. Activation of the carbon-concentrating mechanism by CO2 deprivation coincides with massive transcriptional restructuring in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Plant Cell. 2012;24(5):1860–1875. doi: 10.1105/tpc.111.093435. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Fang W, et al. Transcriptome-wide changes in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii gene expression regulated by carbon dioxide and the CO2-concentrating mechanism regulator CIA5/CCM1. Plant Cell. 2012;24(5):1876–1893. doi: 10.1105/tpc.112.097949. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Duanmu D, Wang Y, Spalding MH. Thylakoid lumen carbonic anhydrase (CAH3) mutation suppresses air-Dier phenotype of LCIB mutant in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Plant Physiol. 2009;149(2):929–937. doi: 10.1104/pp.108.132456. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Wang Y, Spalding MH. Acclimation to very low CO2: Contribution of limiting CO2-inducible proteins, LCIB and LCIA, to inorganic carbon uptake in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Plant Physiol. 2014;166(4):2040–2050. doi: 10.1104/pp.114.248294. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Mitra M, Lato SM, Ynalvez RA, Xiao Y, Moroney JV. Identification of a new chloroplast carbonic anhydrase in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Plant Physiol. 2004;135(1):173–182. doi: 10.1104/pp.103.037283. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Hopkinson BM, Dupont CL, Matsuda Y. The physiology and genetics of CO2-concentrating mechanisms in model diatoms. Curr Opin Plant Biol. 2016;31:51–57. doi: 10.1016/j.pbi.2016.03.013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Bowler C, et al. The Phaeodactylum genome reveals the evolutionary history of diatom genomes. Nature. 2008;456(7219):239–244. doi: 10.1038/nature07410. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Kikutani S, et al. Redox regulation of carbonic anhydrases via thioredoxin in chloroplast of the marine diatom Phaeodactylum tricornutum. J Biol Chem. 2012;287(24):20689–20700. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111.322743. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Wilbur KM, Anderson NG. Electrometric and colorimetric determination of carbonic anhydrase. J Biol Chem. 1948;176(1):147–154. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Kikutani S, et al. Thylakoid luminal θ-carbonic anhydrase critical for growth and photosynthesis in the marine diatom Phaeodactylum tricornutum. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2016;113(35):9828–9833. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1603112113. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Jones DT, Cozzetto D. DISOPRED3: Precise disordered region predictions with annotated protein-binding activity. Bioinformatics. 2015;31(6):857–863. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btu744. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Sheldrick GM. A short history of SHELX. Acta Crystallogr A. 2008;64(Pt 1):112–122. doi: 10.1107/S0108767307043930. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.McCoy AJ, Grosse-Kunstleve RW, Storoni LC, Read RJ. Likelihood-enhanced fast translation functions. Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr. 2005;61(Pt 4):458–464. doi: 10.1107/S0907444905001617. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Rowlett RS. Structure and catalytic mechanism of β-carbonic anhydrases. Subcell Biochem. 2014;75:53–76. doi: 10.1007/978-94-007-7359-2_4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Krissinel E, Henrick K. Inference of macromolecular assemblies from crystalline state. J Mol Biol. 2007;372(3):774–797. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2007.05.022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Holm L, Sander C. Touring protein fold space with Dali/FSSP. Nucleic Acids Res. 1998;26(1):316–319. doi: 10.1093/nar/26.1.316. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Supuran CT, Scozzafava A, Conway J. 2004. Carbonic Anhydrase: Its Inhibitors and Activators, CRC Enzyme Inhibitor Series (CRC Press, Boca Raton, FL), pp 1–23.
- 35.Lindskog S. Structure and mechanism of carbonic anhydrase. Pharmacol Ther. 1997;74(1):1–20. doi: 10.1016/s0163-7258(96)00198-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Mader P, et al. Structural basis for the interaction between carbonic anhydrase and 1,2,3,4-tetrahydroisoquinolin-2-ylsulfonamides. J Med Chem. 2011;54(7):2522–2526. doi: 10.1021/jm2000213. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Kimber MS, Pai EF. The active site architecture of Pisum sativum beta-carbonic anhydrase is a mirror image of that of alpha-carbonic anhydrases. EMBO J. 2000;19(7):1407–1418. doi: 10.1093/emboj/19.7.1407. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Xu Y, Feng L, Jeffrey PD, Shi Y, Morel FM. Structure and metal exchange in the cadmium carbonic anhydrase of marine diatoms. Nature. 2008;452(7183):56–61. doi: 10.1038/nature06636. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Zubrienė A, et al. Intrinsic thermodynamics of 4-substituted-2,3,5,6-tetrafluorobenzenesulfonamide binding to carbonic anhydrases by isothermal titration calorimetry. Biophys Chem. 2015;205:51–65. doi: 10.1016/j.bpc.2015.05.009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Rowlett RS, Tu C, Murray PS, Chamberlin JE. Examination of the role of Gln-158 in the mechanism of CO2 hydration catalyzed by beta-carbonic anhydrase from Arabidopsis thaliana. Arch Biochem Biophys. 2004;425(1):25–32. doi: 10.1016/j.abb.2004.02.033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Strop P, Smith KS, Iverson TM, Ferry JG, Rees DC. Crystal structure of the “cab”-type beta class carbonic anhydrase from the archaeon Methanobacterium thermoautotrophicum. J Biol Chem. 2001;276(13):10299–10305. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M009182200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Frost SC, McKenna R. 2014. Carbonic Anhydrase: Mechanism, Regulation, Links to Disease, and Industrial Applications, Subcellular Biochemistry (Springer, Dordrecht, The Netherlands), pp 89–103.
- 43.Gray JJ, et al. Protein–protein docking with simultaneous optimization of rigid-body displacement and side-chain conformations. J Mol Biol. 2003;331(1):281–299. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(03)00670-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Peña KL, Castel SE, de Araujo C, Espie GS, Kimber MS. Structural basis of the oxidative activation of the carboxysomal gamma-carbonic anhydrase, CcmM. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2010;107(6):2455–2460. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0910866107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Hoffmann KM, Million-Perez HR, Merkhofer R, Nicholson H, Rowlett RS. Allosteric reversion of Haemophilus influenzae β-carbonic anhydrase via a proline shift. Biochemistry. 2015;54(2):598–611. doi: 10.1021/bi501116e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Price GD, Badger MR. Expression of human carbonic anhydrase in the Cyanobacterium synechococcus PCC7942 creates a high-CO2–requiring phenotype: Evidence for a central role for carboxysomes in the CO2-concentrating mechanism. Plant Physiol. 1989;91(2):505–513. doi: 10.1104/pp.91.2.505. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.