Abstract
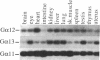
Heterotrimeric guanine nucleotide-binding regulatory proteins (G proteins) are central to the signaling processes of multicellular organisms. We have explored the diversity of the G protein subunits in mammals and found evidence for a large family of genes that encode the alpha subunits. Amino acid sequence comparisons show that the different alpha subunits fall into at least three classes. These classes have been conserved in animals separated by considerable evolutionary distances; they are present in mammals, Drosophila, and nematodes. We have now obtained cDNA clones encoding two murine alpha subunits, G alpha 12 and G alpha 13, that define a fourth class. The translation products are predicted to have molecular masses of 44 kDa and to be insensitive to ADP-ribosylation by pertussis toxin. They share 67% amino acid sequence identity with each other and less than 45% identity with other alpha subunits. Their transcripts can be detected in every tissue examined, although the relative levels of the G alpha 13 message appear somewhat variable.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bourne H. R., Sanders D. A., McCormick F. The GTPase superfamily: a conserved switch for diverse cell functions. Nature. 1990 Nov 8;348(6297):125–132. doi: 10.1038/348125a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bourne H. R., Sanders D. A., McCormick F. The GTPase superfamily: conserved structure and molecular mechanism. Nature. 1991 Jan 10;349(6305):117–127. doi: 10.1038/349117a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown A. M., Birnbaumer L. Ionic channels and their regulation by G protein subunits. Annu Rev Physiol. 1990;52:197–213. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.52.030190.001213. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buss J. E., Mumby S. M., Casey P. J., Gilman A. G., Sefton B. M. Myristoylated alpha subunits of guanine nucleotide-binding regulatory proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Nov;84(21):7493–7497. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.21.7493. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casey P. J., Fong H. K., Simon M. I., Gilman A. G. Gz, a guanine nucleotide-binding protein with unique biochemical properties. J Biol Chem. 1990 Feb 5;265(4):2383–2390. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feig L. A., Pan B. T., Roberts T. M., Cooper G. M. Isolation of ras GTP-binding mutants using an in situ colony-binding assay. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jul;83(13):4607–4611. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.13.4607. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gautam N., Baetscher M., Aebersold R., Simon M. I. A G protein gamma subunit shares homology with ras proteins. Science. 1989 May 26;244(4907):971–974. doi: 10.1126/science.2499046. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gautam N., Northup J., Tamir H., Simon M. I. G protein diversity is increased by associations with a variety of gamma subunits. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Oct;87(20):7973–7977. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.20.7973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilman A. G. G proteins: transducers of receptor-generated signals. Annu Rev Biochem. 1987;56:615–649. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.56.070187.003151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halliday K. R. Regional homology in GTP-binding proto-oncogene products and elongation factors. J Cyclic Nucleotide Protein Phosphor Res. 1983;9(6):435–448. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsu W. H., Rudolph U., Sanford J., Bertrand P., Olate J., Nelson C., Moss L. G., Boyd A. E., Codina J., Birnbaumer L. Molecular cloning of a novel splice variant of the alpha subunit of the mammalian Go protein. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jul 5;265(19):11220–11226. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones D. T., Masters S. B., Bourne H. R., Reed R. R. Biochemical characterization of three stimulatory GTP-binding proteins. The large and small forms of Gs and the olfactory-specific G-protein, Golf. J Biol Chem. 1990 Feb 15;265(5):2671–2676. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamps M. P., Buss J. E., Sefton B. M. Mutation of NH2-terminal glycine of p60src prevents both myristoylation and morphological transformation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jul;82(14):4625–4628. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.14.4625. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. The scanning model for translation: an update. J Cell Biol. 1989 Feb;108(2):229–241. doi: 10.1083/jcb.108.2.229. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee Y. J., Dobbs M. B., Verardi M. L., Hyde D. R. dgq: a drosophila gene encoding a visual system-specific G alpha molecule. Neuron. 1990 Dec;5(6):889–898. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(90)90349-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine M. A., Smallwood P. M., Moen P. T., Jr, Helman L. J., Ahn T. G. Molecular cloning of beta 3 subunit, a third form of the G protein beta-subunit polypeptide. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Mar;87(6):2329–2333. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.6.2329. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lochrie M. A., Mendel J. E., Sternberg P. W., Simon M. I. Homologous and unique G protein alpha subunits in the nematode Caenorhabditis elegans. Cell Regul. 1991 Feb;2(2):135–154. doi: 10.1091/mbc.2.2.135. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lochrie M. A., Simon M. I. G protein multiplicity in eukaryotic signal transduction systems. Biochemistry. 1988 Jul 12;27(14):4957–4965. doi: 10.1021/bi00414a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pang I. H., Sternweis P. C. Purification of unique alpha subunits of GTP-binding regulatory proteins (G proteins) by affinity chromatography with immobilized beta gamma subunits. J Biol Chem. 1990 Oct 25;265(30):18707–18712. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parks S., Wieschaus E. The Drosophila gastrulation gene concertina encodes a G alpha-like protein. Cell. 1991 Jan 25;64(2):447–458. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90652-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Provost N. M., Somers D. E., Hurley J. B. A Drosophila melanogaster G protein alpha subunit gene is expressed primarily in embryos and pupae. J Biol Chem. 1988 Aug 25;263(24):12070–12076. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quan F., Wolfgang W. J., Forte M. A. The Drosophila gene coding for the alpha subunit of a stimulatory G protein is preferentially expressed in the nervous system. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jun;86(11):4321–4325. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.11.4321. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhee S. G., Suh P. G., Ryu S. H., Lee S. Y. Studies of inositol phospholipid-specific phospholipase C. Science. 1989 May 5;244(4904):546–550. doi: 10.1126/science.2541501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robishaw J. D., Kalman V. K., Moomaw C. R., Slaughter C. A. Existence of two gamma subunits of the G proteins in brain. J Biol Chem. 1989 Sep 25;264(27):15758–15761. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt C. J., Garen-Fazio S., Chow Y. K., Neer E. J. Neuronal expression of a newly identified Drosophila melanogaster G protein alpha 0 subunit. Cell Regul. 1989 Nov;1(1):125–134. doi: 10.1091/mbc.1.1.125. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smrcka A. V., Hepler J. R., Brown K. O., Sternweis P. C. Regulation of polyphosphoinositide-specific phospholipase C activity by purified Gq. Science. 1991 Feb 15;251(4995):804–807. doi: 10.1126/science.1846707. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strathmann M., Hamilton B. A., Mayeda C. A., Simon M. I., Meyerowitz E. M., Palazzolo M. J. Transposon-facilitated DNA sequencing. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Feb 15;88(4):1247–1250. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.4.1247. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strathmann M., Simon M. I. G protein diversity: a distinct class of alpha subunits is present in vertebrates and invertebrates. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Dec;87(23):9113–9117. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.23.9113. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strathmann M., Wilkie T. M., Simon M. I. Alternative splicing produces transcripts encoding two forms of the alpha subunit of GTP-binding protein Go. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Sep;87(17):6477–6481. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.17.6477. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strathmann M., Wilkie T. M., Simon M. I. Diversity of the G-protein family: sequences from five additional alpha subunits in the mouse. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Oct;86(19):7407–7409. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.19.7407. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stryer L. Cyclic GMP cascade of vision. Annu Rev Neurosci. 1986;9:87–119. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ne.09.030186.000511. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor S. J., Smith J. A., Exton J. H. Purification from bovine liver membranes of a guanine nucleotide-dependent activator of phosphoinositide-specific phospholipase C. Immunologic identification as a novel G-protein alpha subunit. J Biol Chem. 1990 Oct 5;265(28):17150–17156. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thambi N. C., Quan F., Wolfgang W. J., Spiegel A., Forte M. Immunological and molecular characterization of Go alpha-like proteins in the Drosophila central nervous system. J Biol Chem. 1989 Nov 5;264(31):18552–18560. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yatani A., Mattera R., Codina J., Graf R., Okabe K., Padrell E., Iyengar R., Brown A. M., Birnbaumer L. The G protein-gated atrial K+ channel is stimulated by three distinct Gi alpha-subunits. Nature. 1988 Dec 15;336(6200):680–682. doi: 10.1038/336680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoon J., Shortridge R. D., Bloomquist B. T., Schneuwly S., Perdew M. H., Pak W. L. Molecular characterization of Drosophila gene encoding G0 alpha subunit homolog. J Biol Chem. 1989 Nov 5;264(31):18536–18543. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Sousa S. M., Hoveland L. L., Yarfitz S., Hurley J. B. The Drosophila Go alpha-like G protein gene produces multiple transcripts and is expressed in the nervous system and in ovaries. J Biol Chem. 1989 Nov 5;264(31):18544–18551. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]