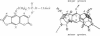Abstract
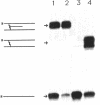
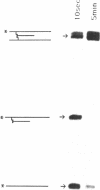
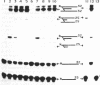
On the basis of the structure of DNA-psoralen bis adducts (formed by psoralen with two thymines on opposite strands), a psoralen-oligonucleotide conjugate was designed to photoinduce a cross-link between the two DNA strands at a specific sequence. Psoralen was attached via its C-5 position to a 5'-thiophosphate group of an 11-mer homopyrimidine oligonucleotide. The 11-mer binds to an 11-base-pair homopurine.homopyrimidine sequence of a DNA fragment, where it forms a triple helix. Upon near-UV-irradiation, the two strands of DNA are crosslinked at the TpA step present at the triplex-duplex junction. The reaction is specific for the homopurine.homopyrimidine DNA sequence and requires both oligonucleotide recognition of the DNA major groove and intercalation of psoralen at the triplex-duplex junction. The yield of the photo-induced cross-linking reaction is quite high (greater than 80%). Such psoralen-oligonucleotide conjugates are probes of sequence-specific triple-helix formation and could be used to selectively control gene expression or to induce site-directed mutations.
Full text
PDF
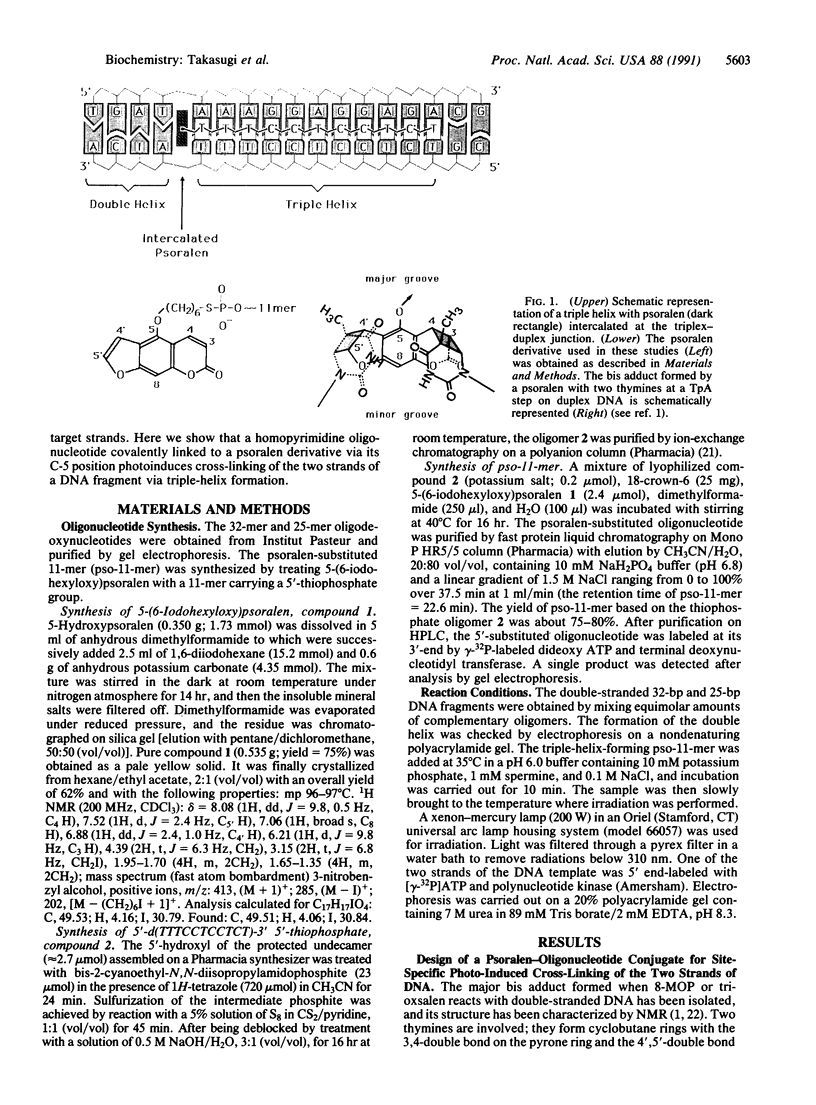

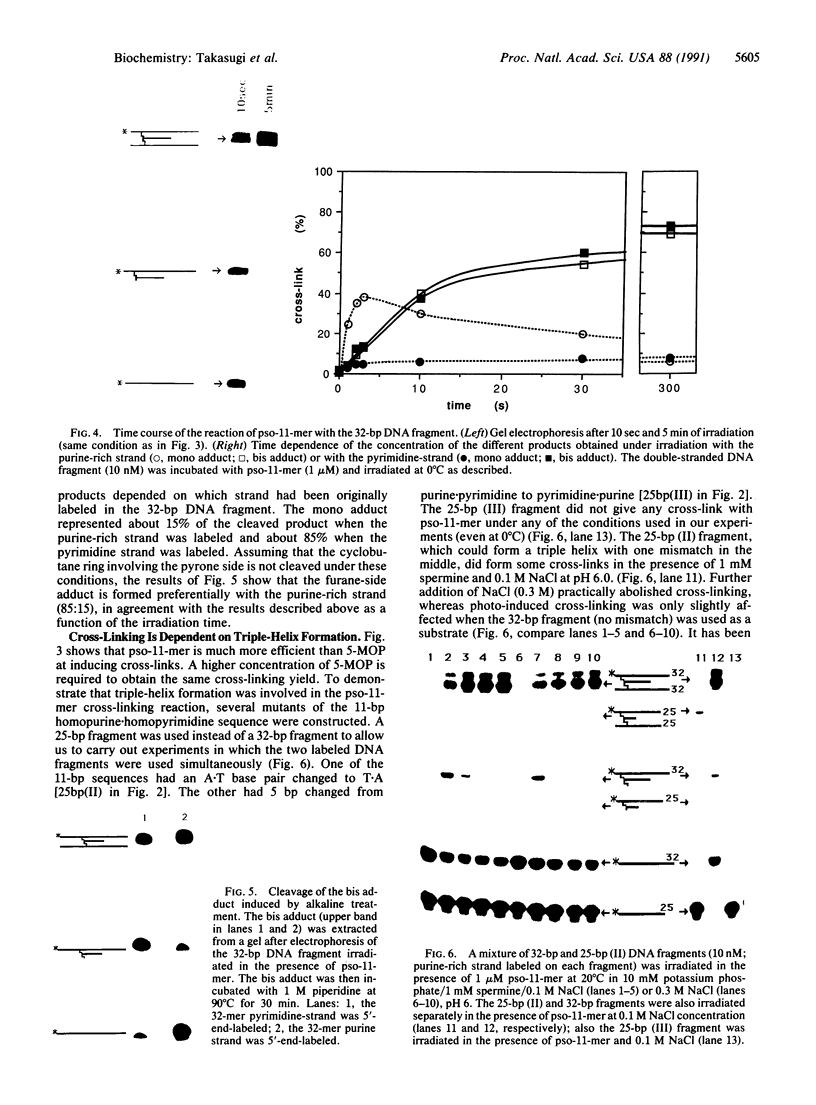

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Averbeck D. Relationship between lesions photoinduced by mono- and bi-functional furocoumarins in DNA and genotoxic effects in diploid yeast. Mutat Res. 1985 Sep;151(2):217–233. doi: 10.1016/0027-5107(85)90074-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheng S., Van Houten B., Gamper H. B., Sancar A., Hearst J. E. Use of psoralen-modified oligonucleotides to trap three-stranded RecA-DNA complexes and repair of these cross-linked complexes by ABC excinuclease. J Biol Chem. 1988 Oct 15;263(29):15110–15117. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cimino G. D., Gamper H. B., Isaacs S. T., Hearst J. E. Psoralens as photoactive probes of nucleic acid structure and function: organic chemistry, photochemistry, and biochemistry. Annu Rev Biochem. 1985;54:1151–1193. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.54.070185.005443. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- François J. C., Saison-Behmoaras T., Barbier C., Chassignol M., Thuong N. T., Hélène C. Sequence-specific recognition and cleavage of duplex DNA via triple-helix formation by oligonucleotides covalently linked to a phenanthroline-copper chelate. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Dec;86(24):9702–9706. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.24.9702. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- François J. C., Saison-Behmoaras T., Hélène C. Sequence-specific recognition of the major groove of DNA by oligodeoxynucleotides via triple helix formation. Footprinting studies. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Dec 23;16(24):11431–11440. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.24.11431. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- François J. C., Saison-Behmoaras T., Thuong N. T., Hélène C. Inhibition of restriction endonuclease cleavage via triple helix formation by homopyrimidine oligonucleotides. Biochemistry. 1989 Dec 12;28(25):9617–9619. doi: 10.1021/bi00451a011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gamper H. B., Cimino G. D., Hearst J. E. Solution hybridization of crosslinkable DNA oligonucleotides to bacteriophage M13 DNA. Effect of secondary structure on hybridization kinetics and equilibria. J Mol Biol. 1987 Sep 20;197(2):349–362. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90128-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanvey J. C., Shimizu M., Wells R. D. Site-specific inhibition of EcoRI restriction/modification enzymes by a DNA triple helix. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Jan 11;18(1):157–161. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.1.157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le Doan T., Perrouault L., Praseuth D., Habhoub N., Decout J. L., Thuong N. T., Lhomme J., Hélène C. Sequence-specific recognition, photocrosslinking and cleavage of the DNA double helix by an oligo-[alpha]-thymidylate covalently linked to an azidoproflavine derivative. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Oct 12;15(19):7749–7760. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.19.7749. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee B. L., Murakami A., Blake K. R., Lin S. B., Miller P. S. Interaction of psoralen-derivatized oligodeoxyribonucleoside methylphosphonates with single-stranded DNA. Biochemistry. 1988 May 3;27(9):3197–3203. doi: 10.1021/bi00409a011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maher L. J., 3rd, Dervan P. B., Wold B. J. Kinetic analysis of oligodeoxyribonucleotide-directed triple-helix formation on DNA. Biochemistry. 1990 Sep 18;29(37):8820–8826. doi: 10.1021/bi00489a045. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maher L. J., 3rd, Wold B., Dervan P. B. Inhibition of DNA binding proteins by oligonucleotide-directed triple helix formation. Science. 1989 Aug 18;245(4919):725–730. doi: 10.1126/science.2549631. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moser H. E., Dervan P. B. Sequence-specific cleavage of double helical DNA by triple helix formation. Science. 1987 Oct 30;238(4827):645–650. doi: 10.1126/science.3118463. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perrouault L., Asseline U., Rivalle C., Thuong N. T., Bisagni E., Giovannangeli C., Le Doan T., Hélène C. Sequence-specific artificial photo-induced endonucleases based on triple helix-forming oligonucleotides. Nature. 1990 Mar 22;344(6264):358–360. doi: 10.1038/344358a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pieles U., Englisch U. Psoralen covalently linked to oligodeoxyribonucleotides: synthesis, sequence specific recognition of DNA and photo-cross-linking to pyrimidine residues of DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Jan 11;17(1):285–299. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.1.285. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Praseuth D., Perrouault L., Le Doan T., Chassignol M., Thuong N., Hélène C. Sequence-specific binding and photocrosslinking of alpha and beta oligodeoxynucleotides to the major groove of DNA via triple-helix formation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Mar;85(5):1349–1353. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.5.1349. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shi Y. B., Spielmann H. P., Hearst J. E. Base-catalyzed reversal of a psoralen-DNA cross-link. Biochemistry. 1988 Jul 12;27(14):5174–5178. doi: 10.1021/bi00414a034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sun J. S., François J. C., Montenay-Garestier T., Saison-Behmoaras T., Roig V., Thuong N. T., Hélène C. Sequence-specific intercalating agents: intercalation at specific sequences on duplex DNA via major groove recognition by oligonucleotide-intercalator conjugates. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Dec;86(23):9198–9202. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.23.9198. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teare J., Wollenzien P. Specificity of site directed psoralen addition to RNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 May 11;17(9):3359–3372. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.9.3359. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yeung A. T., Dinehart W. J., Jones B. K. Alkali reversal of psoralen cross-link for the targeted delivery of psoralen monoadduct lesion. Biochemistry. 1988 Aug 23;27(17):6332–6338. doi: 10.1021/bi00417a020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yeung A. T., Jones B. K., Chu C. T. Photoreactivities and thermal properties of psoralen cross-links. Biochemistry. 1988 May 3;27(9):3204–3210. doi: 10.1021/bi00409a012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]