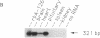Abstract
Previous molecular cloning experiments showed that multiple isoforms of the alpha 1 subunit of voltage-gated Ca channels are expressed in the mammalian brain (designated rbA, rbB, rbC, and rbD). We report here the isolation and characterization of cDNAs encoding the rat brain class A (rbA) Ca channel. The rbA-126 cDNA encodes a 2212-amino acid protein that shares 33% sequence identity with the alpha 1 subunits of cardiac and skeletal muscle dihydropyridine-sensitive Ca channels. When compared with other Ca channels, the rbA channel is notably different in both the carboxyl terminus and in a large (474-amino acid) hydrophilic segment between domains II and III. Northern blot analysis shows that rbA transcripts are expressed in all regions of the rat central nervous system, but most prominently in the cerebellum. A more widespread distribution of rbA Ca channels is indicated by PCR analysis, which demonstrates the presence of class A transcripts in the rat heart and pituitary but not in the spleen, kidney, or liver. The rbA cDNA appears to encode a Ca channel alpha 1 subunit that is distinct from the dihydropyridine-sensitive Ca channel sequences and that is expressed in a variety of excitable cells.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Auffray C., Rougeon F. Purification of mouse immunoglobulin heavy-chain messenger RNAs from total myeloma tumor RNA. Eur J Biochem. 1980 Jun;107(2):303–314. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1980.tb06030.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Auld V. J., Goldin A. L., Krafte D. S., Catterall W. A., Lester H. A., Davidson N., Dunn R. J. A neutral amino acid change in segment IIS4 dramatically alters the gating properties of the voltage-dependent sodium channel. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jan;87(1):323–327. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.1.323. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Auld V. J., Goldin A. L., Krafte D. S., Marshall J., Dunn J. M., Catterall W. A., Lester H. A., Davidson N., Dunn R. J. A rat brain Na+ channel alpha subunit with novel gating properties. Neuron. 1988 Aug;1(6):449–461. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(88)90176-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biel M., Ruth P., Bosse E., Hullin R., Stühmer W., Flockerzi V., Hofmann F. Primary structure and functional expression of a high voltage activated calcium channel from rabbit lung. FEBS Lett. 1990 Sep 3;269(2):409–412. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(90)81205-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biggin M. D., Gibson T. J., Hong G. F. Buffer gradient gels and 35S label as an aid to rapid DNA sequence determination. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jul;80(13):3963–3965. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.13.3963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell K. P., Leung A. T., Sharp A. H. The biochemistry and molecular biology of the dihydropyridine-sensitive calcium channel. Trends Neurosci. 1988 Oct;11(10):425–430. doi: 10.1016/0166-2236(88)90193-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Catterall W. A., Seagar M. J., Takahashi M. Molecular properties of dihydropyridine-sensitive calcium channels in skeletal muscle. J Biol Chem. 1988 Mar 15;263(8):3535–3538. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Catterall W. A. Structure and function of voltage-sensitive ion channels. Science. 1988 Oct 7;242(4875):50–61. doi: 10.1126/science.2459775. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cortés R., Supavilai P., Karobath M., Palacios J. M. Calcium antagonist binding sites in the rat brain: quantitative autoradiographic mapping using the 1,4-dihydropyridines [3H]PN 200-110 and [3H]PY 108-068. J Neural Transm. 1984;60(3-4):169–197. doi: 10.1007/BF01249092. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellis S. B., Williams M. E., Ways N. R., Brenner R., Sharp A. H., Leung A. T., Campbell K. P., McKenna E., Koch W. J., Hui A. Sequence and expression of mRNAs encoding the alpha 1 and alpha 2 subunits of a DHP-sensitive calcium channel. Science. 1988 Sep 23;241(4873):1661–1664. doi: 10.1126/science.2458626. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henikoff S. Unidirectional digestion with exonuclease III creates targeted breakpoints for DNA sequencing. Gene. 1984 Jun;28(3):351–359. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90153-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hess P. Calcium channels in vertebrate cells. Annu Rev Neurosci. 1990;13:337–356. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ne.13.030190.002005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerr L. M., Filloux F., Olivera B. M., Jackson H., Wamsley J. K. Autoradiographic localization of calcium channels with [125I]omega-conotoxin in rat brain. Eur J Pharmacol. 1988 Jan 27;146(1):181–183. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(88)90501-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koch W. J., Ellinor P. T., Schwartz A. cDNA cloning of a dihydropyridine-sensitive calcium channel from rat aorta. Evidence for the existence of alternatively spliced forms. J Biol Chem. 1990 Oct 15;265(29):17786–17791. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. Compilation and analysis of sequences upstream from the translational start site in eukaryotic mRNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 25;12(2):857–872. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.2.857. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kyte J., Doolittle R. F. A simple method for displaying the hydropathic character of a protein. J Mol Biol. 1982 May 5;157(1):105–132. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90515-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Llinás R., Sugimori M., Lin J. W., Cherksey B. Blocking and isolation of a calcium channel from neurons in mammals and cephalopods utilizing a toxin fraction (FTX) from funnel-web spider poison. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Mar;86(5):1689–1693. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.5.1689. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacKinnon R., Heginbotham L., Abramson T. Mapping the receptor site for charybdotoxin, a pore-blocking potassium channel inhibitor. Neuron. 1990 Dec;5(6):767–771. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(90)90335-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacKinnon R., Yellen G. Mutations affecting TEA blockade and ion permeation in voltage-activated K+ channels. Science. 1990 Oct 12;250(4978):276–279. doi: 10.1126/science.2218530. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mikami A., Imoto K., Tanabe T., Niidome T., Mori Y., Takeshima H., Narumiya S., Numa S. Primary structure and functional expression of the cardiac dihydropyridine-sensitive calcium channel. Nature. 1989 Jul 20;340(6230):230–233. doi: 10.1038/340230a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noda M., Ikeda T., Kayano T., Suzuki H., Takeshima H., Kurasaki M., Takahashi H., Numa S. Existence of distinct sodium channel messenger RNAs in rat brain. Nature. 1986 Mar 13;320(6058):188–192. doi: 10.1038/320188a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noda M., Suzuki H., Numa S., Stühmer W. A single point mutation confers tetrodotoxin and saxitoxin insensitivity on the sodium channel II. FEBS Lett. 1989 Dec 18;259(1):213–216. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(89)81531-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perez-Reyes E., Wei X. Y., Castellano A., Birnbaumer L. Molecular diversity of L-type calcium channels. Evidence for alternative splicing of the transcripts of three non-allelic genes. J Biol Chem. 1990 Nov 25;265(33):20430–20436. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plummer M. R., Logothetis D. E., Hess P. Elementary properties and pharmacological sensitivities of calcium channels in mammalian peripheral neurons. Neuron. 1989 May;2(5):1453–1463. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(89)90191-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Proudfoot N. J., Brownlee G. G. 3' non-coding region sequences in eukaryotic messenger RNA. Nature. 1976 Sep 16;263(5574):211–214. doi: 10.1038/263211a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Regan L. J., Sah D. W., Bean B. P. Ca2+ channels in rat central and peripheral neurons: high-threshold current resistant to dihydropyridine blockers and omega-conotoxin. Neuron. 1991 Feb;6(2):269–280. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(91)90362-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reuter H. Calcium channel modulation by neurotransmitters, enzymes and drugs. Nature. 1983 Feb 17;301(5901):569–574. doi: 10.1038/301569a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snutch T. P., Leonard J. P., Gilbert M. M., Lester H. A., Davidson N. Rat brain expresses a heterogeneous family of calcium channels. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 May;87(9):3391–3395. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.9.3391. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stühmer W., Conti F., Suzuki H., Wang X. D., Noda M., Yahagi N., Kubo H., Numa S. Structural parts involved in activation and inactivation of the sodium channel. Nature. 1989 Jun 22;339(6226):597–603. doi: 10.1038/339597a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanabe T., Beam K. G., Adams B. A., Niidome T., Numa S. Regions of the skeletal muscle dihydropyridine receptor critical for excitation-contraction coupling. Nature. 1990 Aug 9;346(6284):567–569. doi: 10.1038/346567a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanabe T., Beam K. G., Powell J. A., Numa S. Restoration of excitation-contraction coupling and slow calcium current in dysgenic muscle by dihydropyridine receptor complementary DNA. Nature. 1988 Nov 10;336(6195):134–139. doi: 10.1038/336134a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanabe T., Takeshima H., Mikami A., Flockerzi V., Takahashi H., Kangawa K., Kojima M., Matsuo H., Hirose T., Numa S. Primary structure of the receptor for calcium channel blockers from skeletal muscle. Nature. 1987 Jul 23;328(6128):313–318. doi: 10.1038/328313a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tempel B. L., Papazian D. M., Schwarz T. L., Jan Y. N., Jan L. Y. Sequence of a probable potassium channel component encoded at Shaker locus of Drosophila. Science. 1987 Aug 14;237(4816):770–775. doi: 10.1126/science.2441471. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas P. S. Hybridization of denatured RNA and small DNA fragments transferred to nitrocellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Sep;77(9):5201–5205. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.9.5201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsien R. W. Calcium channels in excitable cell membranes. Annu Rev Physiol. 1983;45:341–358. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.45.030183.002013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]