Abstract
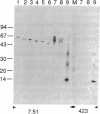
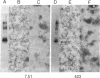
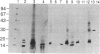
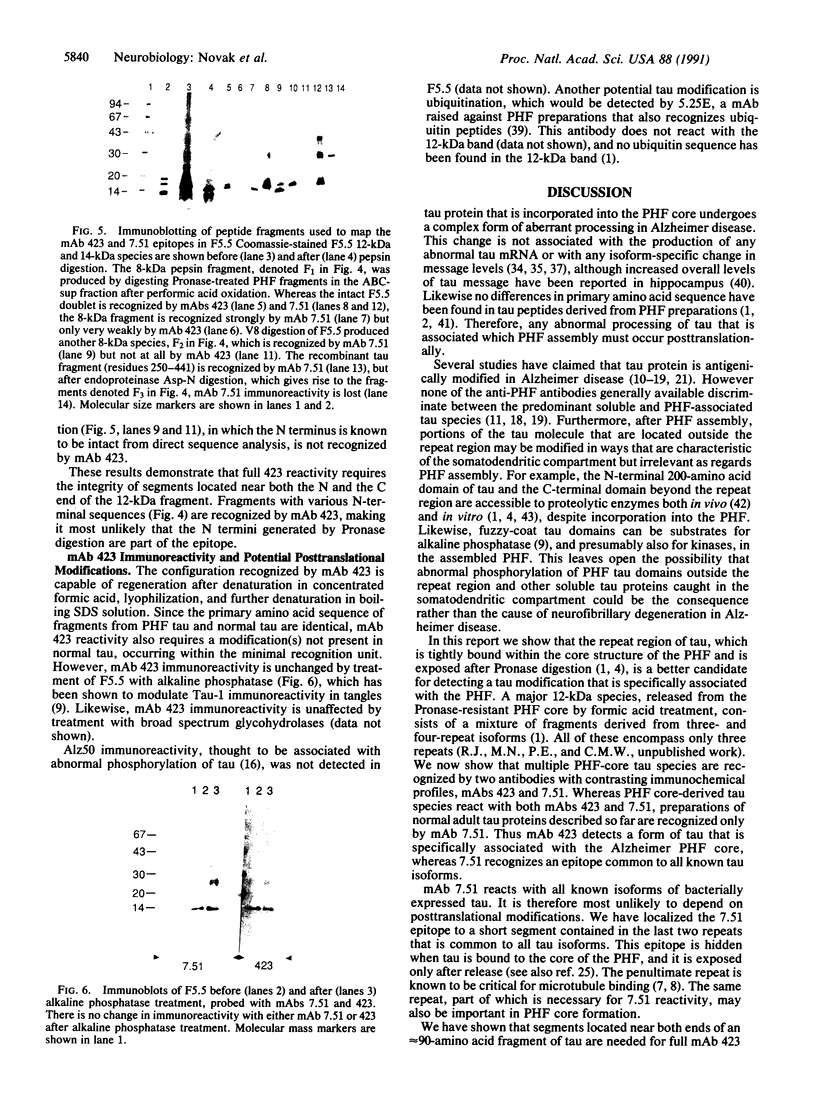
The microtubule-associated protein tau that is incorporated into paired helical filaments (PHFs) undergoes some form of aberrant posttranslational processing in Alzheimer disease. Difficulties in deciding which changes are critical for PHF formation stem in part from the lack of immunochemical markers specific for PHF tau. The only monoclonal antibody (mAb) that is known to react with PHF tau but not with the predominant normal adult tau species is mAb 423. Another mAb (7.51, described in this paper) recognizes a segment of tau that is included in the minimal recognition unit required by mAb 423. Unlike 423, which is PHF tau-specific, mAb 7.51 recognizes all PHF core-derived tau as well as native soluble tau and recombinant tau expressed in bacteria and so serves as a generic tau marker. Both epitopes are in the 12-kDa fragment released from the Pronase-resistant core of the PHF (which encompasses the tandem repeat region). The mAb 7.51 epitope requires segments located in the last two repeats, which are common to all tau isoforms. The mAb 423 epitope requires sequences located near both the N and the C terminus of the 12-kDa fragment common to three- and four-repeat tau isoforms. Fragments denatured by concentrated formic acid and SDS regain 423 reactivity when denaturing agents are removed. Since the primary amino acid sequences of PHF tau and normal tau are identical in the repeat region, we conclude that 423 reactivity also requires a modification(s) occurring within an approximately 90-residue segment that are not present in tau proteins so far described in the human brain.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aizawa H., Kawasaki H., Murofushi H., Kotani S., Suzuki K., Sakai H. A common amino acid sequence in 190-kDa microtubule-associated protein and tau for the promotion of microtubule assembly. J Biol Chem. 1989 Apr 5;264(10):5885–5890. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barton A. J., Harrison P. J., Najlerahim A., Heffernan J., McDonald B., Robinson J. R., Davies D. C., Harrison W. J., Mitra P., Hardy J. A. Increased tau messenger RNA in Alzheimer's disease hippocampus. Am J Pathol. 1990 Sep;137(3):497–502. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bondareff W., Wischik C. M., Novak M., Amos W. B., Klug A., Roth M. Molecular analysis of neurofibrillary degeneration in Alzheimer's disease. An immunohistochemical study. Am J Pathol. 1990 Sep;137(3):711–723. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crowther T., Goedert M., Wischik C. M. The repeat region of microtubule-associated protein tau forms part of the core of the paired helical filament of Alzheimer's disease. Ann Med. 1989;21(2):127–132. doi: 10.3109/07853898909149199. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drapeau G. R. Protease from Staphyloccus aureus. Methods Enzymol. 1976;45:469–475. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(76)45041-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flament S., Delacourte A. Abnormal tau species are produced during Alzheimer's disease neurodegenerating process. FEBS Lett. 1989 Apr 24;247(2):213–216. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(89)81337-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flament S., Delacourte A., Delaère P., Duyckaerts C., Hauw J. J. Correlation between microscopical changes and Tau 64 and 69 biochemical detection in senile dementia of the Alzheimer type. Tau 64 and 69 are reliable markers of the neurofibrillary degeneration. Acta Neuropathol. 1990;80(2):212–215. doi: 10.1007/BF00308927. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goedert M., Jakes R. Expression of separate isoforms of human tau protein: correlation with the tau pattern in brain and effects on tubulin polymerization. EMBO J. 1990 Dec;9(13):4225–4230. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07870.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goedert M., Spillantini M. G., Jakes R., Rutherford D., Crowther R. A. Multiple isoforms of human microtubule-associated protein tau: sequences and localization in neurofibrillary tangles of Alzheimer's disease. Neuron. 1989 Oct;3(4):519–526. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(89)90210-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goedert M., Spillantini M. G., Potier M. C., Ulrich J., Crowther R. A. Cloning and sequencing of the cDNA encoding an isoform of microtubule-associated protein tau containing four tandem repeats: differential expression of tau protein mRNAs in human brain. EMBO J. 1989 Feb;8(2):393–399. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03390.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goedert M., Wischik C. M., Crowther R. A., Walker J. E., Klug A. Cloning and sequencing of the cDNA encoding a core protein of the paired helical filament of Alzheimer disease: identification as the microtubule-associated protein tau. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jun;85(11):4051–4055. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.11.4051. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg S. G., Davies P. A preparation of Alzheimer paired helical filaments that displays distinct tau proteins by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Aug;87(15):5827–5831. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.15.5827. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grundke-Iqbal I., Iqbal K., Tung Y. C., Quinlan M., Wisniewski H. M., Binder L. I. Abnormal phosphorylation of the microtubule-associated protein tau (tau) in Alzheimer cytoskeletal pathology. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jul;83(13):4913–4917. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.13.4913. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harrington C. R., Edwards P. C., Wischik C. M. Competitive ELISA for the measurement of tau protein in Alzheimer's disease. J Immunol Methods. 1990 Dec 5;134(2):261–271. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(90)90388-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harrington C. R., Mukaetova-Ladinska E. B., Hills R., Edwards P. C., Montejo de Garcini E., Novak M., Wischik C. M. Measurement of distinct immunochemical presentations of tau protein in Alzheimer disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jul 1;88(13):5842–5846. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.13.5842. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ihara Y., Nukina N., Miura R., Ogawara M. Phosphorylated tau protein is integrated into paired helical filaments in Alzheimer's disease. J Biochem. 1986 Jun;99(6):1807–1810. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a135662. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joly J. C., Purich D. L. Peptides corresponding to the second repeated sequence in MAP-2 inhibit binding of microtubule-associated proteins to microtubules. Biochemistry. 1990 Sep 25;29(38):8916–8920. doi: 10.1021/bi00490a006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KIDD M. Paired helical filaments in electron microscopy of Alzheimer's disease. Nature. 1963 Jan 12;197:192–193. doi: 10.1038/197192b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kondo J., Honda T., Mori H., Hamada Y., Miura R., Ogawara M., Ihara Y. The carboxyl third of tau is tightly bound to paired helical filaments. Neuron. 1988 Nov;1(9):827–834. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(88)90130-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kontseková E., Novák M., Kontsek P., Borecký L., Lesso J. The effect of postfusion cell density on establishment of hybridomas. Folia Biol (Praha) 1988;34(1):18–22. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kosik K. S., Orecchio L. D., Binder L., Trojanowski J. Q., Lee V. M., Lee G. Epitopes that span the tau molecule are shared with paired helical filaments. Neuron. 1988 Nov;1(9):817–825. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(88)90129-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kratzin H. D., Wiltfang J., Karas M., Neuhoff V., Hilschmann N. Gas-phase sequencing after electroblotting on polyvinylidene difluoride membranes assigns correct molecular weights to myoglobin molecular weight markers. Anal Biochem. 1989 Nov 15;183(1):1–8. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(89)90161-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ksiezak-Reding H., Binder L. I., Yen S. H. Immunochemical and biochemical characterization of tau proteins in normal and Alzheimer's disease brains with Alz 50 and Tau-1. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jun 15;263(17):7948–7953. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ksiezak-Reding H., Chien C. H., Lee V. M., Yen S. H. Mapping of the Alz 50 epitope in microtubule-associated proteins tau. J Neurosci Res. 1990 Mar;25(3):412–419. doi: 10.1002/jnr.490250319. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee V. M., Balin B. J., Otvos L., Jr, Trojanowski J. Q. A68: a major subunit of paired helical filaments and derivatized forms of normal Tau. Science. 1991 Feb 8;251(4994):675–678. doi: 10.1126/science.1899488. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsudaira P. Sequence from picomole quantities of proteins electroblotted onto polyvinylidene difluoride membranes. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jul 25;262(21):10035–10038. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mori H., Hamada Y., Kawaguchi M., Honda T., Kondo J., Ihara Y. A distinct form of tau is selectively incorporated into Alzheimer's paired helical filaments. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1989 Mar 31;159(3):1221–1226. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(89)92240-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Novak M., Wischik C. M., Edwards P., Pannell R., Milstein C. Characterisation of the first monoclonal antibody against the pronase resistant core of the Alzheimer PHF. Prog Clin Biol Res. 1989;317:755–761. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nukina N., Kosik K. S., Selkoe D. J. The monoclonal antibody, Alz 50, recognizes tau proteins in Alzheimer's disease brain. Neurosci Lett. 1988 May 3;87(3):240–246. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(88)90455-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perry G., Mulvihill P., Fried V. A., Smith H. T., Grundke-Iqbal I., Iqbal K. Immunochemical properties of ubiquitin conjugates in the paired helical filaments of Alzheimer disease. J Neurochem. 1989 May;52(5):1523–1528. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1989.tb09203.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sallantin M., Huet J. C., Demarteau C., Pernollet J. C. Reassessment of commercially available molecular weight standards for peptide sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis using electroblotting and microsequencing. Electrophoresis. 1990 Jan;11(1):34–36. doi: 10.1002/elps.1150110108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shelanski M. L., Gaskin F., Cantor C. R. Microtubule assembly in the absence of added nucleotides. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Mar;70(3):765–768. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.3.765. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steiner B., Mandelkow E. M., Biernat J., Gustke N., Meyer H. E., Schmidt B., Mieskes G., Söling H. D., Drechsel D., Kirschner M. W. Phosphorylation of microtubule-associated protein tau: identification of the site for Ca2(+)-calmodulin dependent kinase and relationship with tau phosphorylation in Alzheimer tangles. EMBO J. 1990 Nov;9(11):3539–3544. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07563.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uéda K., Masliah E., Saitoh T., Bakalis S. L., Scoble H., Kosik K. S. Alz-50 recognizes a phosphorylated epitope of tau protein. J Neurosci. 1990 Oct;10(10):3295–3304. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.10-10-03295.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wischik C. M., Novak M., Edwards P. C., Klug A., Tichelaar W., Crowther R. A. Structural characterization of the core of the paired helical filament of Alzheimer disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jul;85(13):4884–4888. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.13.4884. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wischik C. M., Novak M., Thøgersen H. C., Edwards P. C., Runswick M. J., Jakes R., Walker J. E., Milstein C., Roth M., Klug A. Isolation of a fragment of tau derived from the core of the paired helical filament of Alzheimer disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jun;85(12):4506–4510. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.12.4506. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolozin B. L., Pruchnicki A., Dickson D. W., Davies P. A neuronal antigen in the brains of Alzheimer patients. Science. 1986 May 2;232(4750):648–650. doi: 10.1126/science.3083509. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolozin B., Davies P. Alzheimer-related neuronal protein A68: specificity and distribution. Ann Neurol. 1987 Oct;22(4):521–526. doi: 10.1002/ana.410220412. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]