Abstract
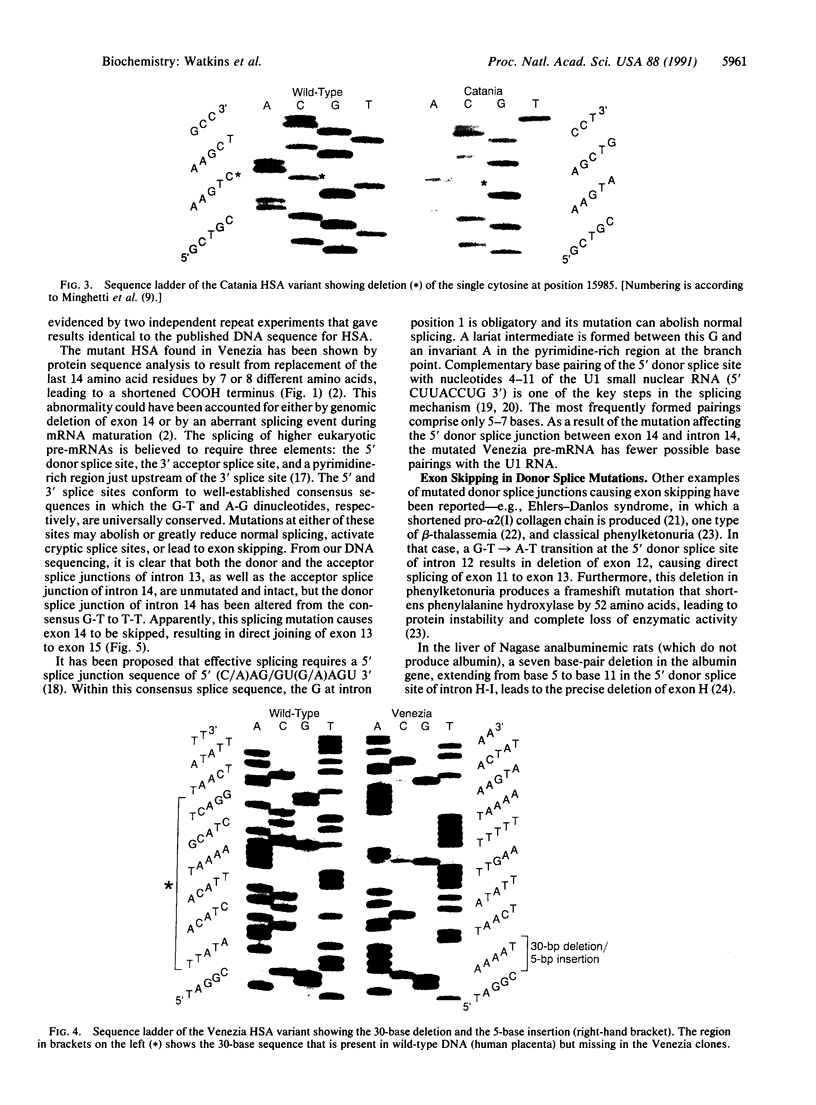
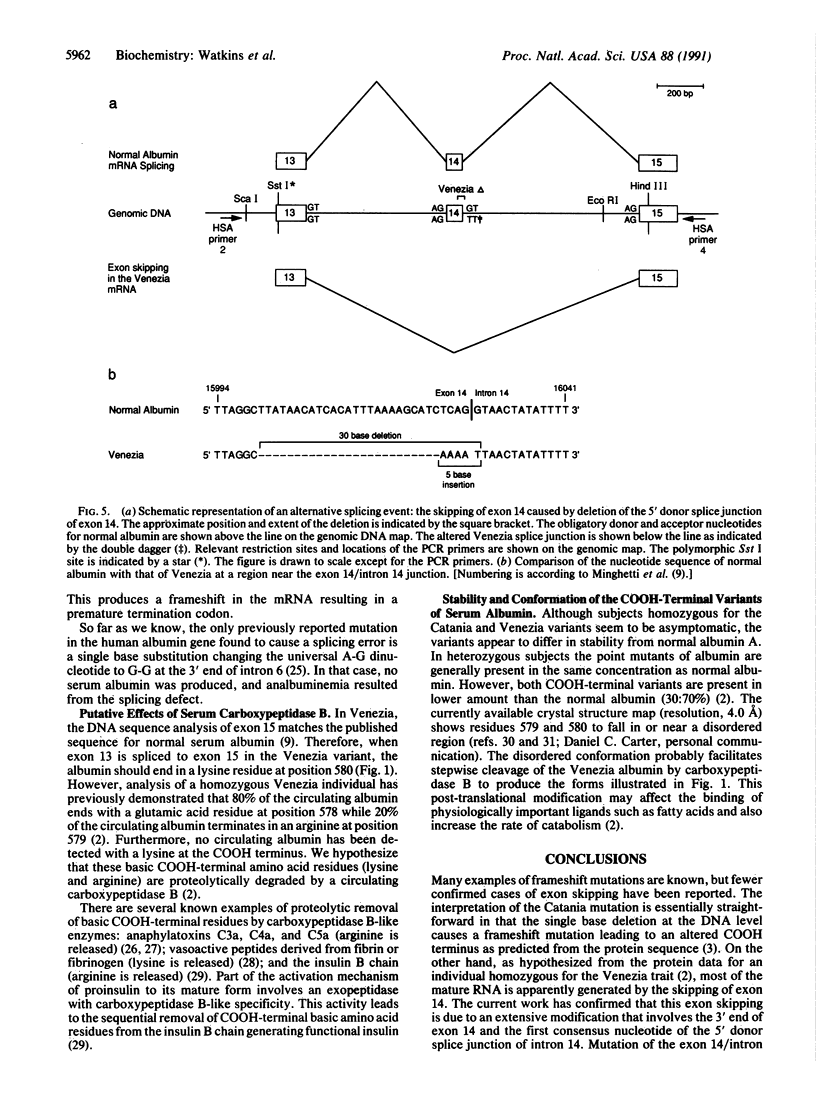
At least 35 allelic variants of human serum albumin have been sequenced at the protein level. All except two COOH-terminal variants, Catania and Venezia, are readily explainable as single-point substitutions. The two chain-termination variants are clustered in certain locations in Italy and are found in numerous unrelated individuals. In order to correlate the protein change in these variants with the corresponding DNA mutation, the two variant albumin genes have been cloned, sequenced, and compared to normal albumin genomic DNA. In the Catania variant, a single base deletion and subsequent frameshift leads to a shortened and altered COOH terminus. Albumin Venezia is caused by a mutation that alters the first consensus nucleotide of the 5' donor splice junction of intron 14 and the 3' end of exon 14, which is shortened from 68 to 43 base pairs. This change leads to an exon skipping event resulting in direct splicing of exon 13 to exon 15. The predicted Venezia albumin product has a truncated amino acid sequence (580 residues instead of 585), and the COOH-terminal sequence is altered after Glu-571. The variant COOH terminus ends with the dibasic sequence Arg-Lys that is apparently removed through stepwise cleavage by serum carboxypeptidase B to yield several forms of circulating albumin.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arai K., Madison J., Shimizu A., Putnam F. W. Point substitutions in albumin genetic variants from Asia. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jan;87(1):497–501. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.1.497. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Belew M., Gerdin B., Lindeberg G., Porath J., Saldeen T., Wallin R. Structure-activity relationships of vasoactive peptides derived from fibrin or fibrinogen degraded by plasmin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 Feb 27;621(2):169–178. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(80)90169-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bokisch V. A., Müller-Eberhard H. J. Anaphylatoxin inactivator of human plasma: its isolation and characterization as a carboxypeptidase. J Clin Invest. 1970 Dec;49(12):2427–2436. doi: 10.1172/JCI106462. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brennan S. O., Arai K., Madison J., Laurell C. B., Galliano M., Watkins S., Peach R., Myles T., George P., Putnam F. W. Hypermutability of CpG dinucleotides in the propeptide-encoding sequence of the human albumin gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 May;87(10):3909–3913. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.10.3909. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carter D. C., He X. M., Munson S. H., Twigg P. D., Gernert K. M., Broom M. B., Miller T. Y. Three-dimensional structure of human serum albumin. Science. 1989 Jun 9;244(4909):1195–1198. doi: 10.1126/science.2727704. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carter D. C., He X. M. Structure of human serum albumin. Science. 1990 Jul 20;249(4966):302–303. doi: 10.1126/science.2374930. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galliano M., Minchiotti L., Iadarola P., Zapponi M. C., Ferri G., Castellani A. A. Structural characterization of a chain termination mutant of human serum albumin. J Biol Chem. 1986 Mar 25;261(9):4283–4287. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galliano M., Minchiotti L., Porta F., Rossi A., Ferri G., Madison J., Watkins S., Putnam F. W. Mutations in genetic variants of human serum albumin found in Italy. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Nov;87(22):8721–8725. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.22.8721. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorski J. P., Hugli T. E., Müller-Eberhard H. J. C4a: the third anaphylatoxin of the human complement system. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Oct;76(10):5299–5302. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.10.5299. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gross-Bellard M., Oudet P., Chambon P. Isolation of high-molecular-weight DNA from mammalian cells. Eur J Biochem. 1973 Jul 2;36(1):32–38. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1973.tb02881.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmes D. S., Quigley M. A rapid boiling method for the preparation of bacterial plasmids. Anal Biochem. 1981 Jun;114(1):193–197. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90473-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kemmler W., Peterson J. D., Steiner D. F. Studies on the conversion of proinsulin to insulin. I. Conversion in vitro with trypsin and carboxypeptidase B. J Biol Chem. 1971 Nov 25;246(22):6786–6791. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lerner M. R., Boyle J. A., Mount S. M., Wolin S. L., Steitz J. A. Are snRNPs involved in splicing? Nature. 1980 Jan 10;283(5743):220–224. doi: 10.1038/283220a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marvit J., DiLella A. G., Brayton K., Ledley F. D., Robson K. J., Woo S. L. GT to AT transition at a splice donor site causes skipping of the preceding exon in phenylketonuria. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Jul 24;15(14):5613–5628. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.14.5613. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minchiotti L., Galliano M., Iadarola P., Meloni M. L., Ferri G., Porta F., Castellani A. A. The molecular defect in a COOH-terminal-modified and shortened mutant of human serum albumin. J Biol Chem. 1989 Feb 25;264(6):3385–3389. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minghetti P. P., Ruffner D. E., Kuang W. J., Dennison O. E., Hawkins J. W., Beattie W. G., Dugaiczyk A. Molecular structure of the human albumin gene is revealed by nucleotide sequence within q11-22 of chromosome 4. J Biol Chem. 1986 May 25;261(15):6747–6757. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mount S. M. A catalogue of splice junction sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Jan 22;10(2):459–472. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.2.459. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mullis K., Faloona F., Scharf S., Saiki R., Horn G., Erlich H. Specific enzymatic amplification of DNA in vitro: the polymerase chain reaction. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1986;51(Pt 1):263–273. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1986.051.01.032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed K. C., Mann D. A. Rapid transfer of DNA from agarose gels to nylon membranes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Oct 25;13(20):7207–7221. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.20.7207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogers J., Wall R. A mechanism for RNA splicing. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Apr;77(4):1877–1879. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.4.1877. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruffner D. E., Dugaiczyk A. Splicing mutation in human hereditary analbuminemia. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Apr;85(7):2125–2129. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.7.2125. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shalaby F., Shafritz D. A. Exon skipping during splicing of albumin mRNA precursors in Nagase analbuminemic rats. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Apr;87(7):2652–2656. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.7.2652. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi N., Takahashi Y., Blumberg B. S., Putnam F. W. Amino acid substitutions in genetic variants of human serum albumin and in sequences inferred from molecular cloning. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jul;84(13):4413–4417. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.13.4413. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi N., Takahashi Y., Isobe T., Putnam F. W., Fujita M., Satoh C., Neel J. V. Amino acid substitutions in inherited albumin variants from Amerindian and Japanese populations. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Nov;84(22):8001–8005. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.22.8001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi N., Takahashi Y., Putnam F. W. Structural changes and metal binding by proalbumins and other amino-terminal genetic variants of human serum albumin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Nov;84(21):7403–7407. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.21.7403. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Treisman R., Proudfoot N. J., Shander M., Maniatis T. A single-base change at a splice site in a beta 0-thalassemic gene causes abnormal RNA splicing. Cell. 1982 Jul;29(3):903–911. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90452-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weil D., Bernard M., Combates N., Wirtz M. K., Hollister D. W., Steinmann B., Ramirez F. Identification of a mutation that causes exon skipping during collagen pre-mRNA splicing in an Ehlers-Danlos syndrome variant. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jun 25;263(18):8561–8564. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]