Abstract
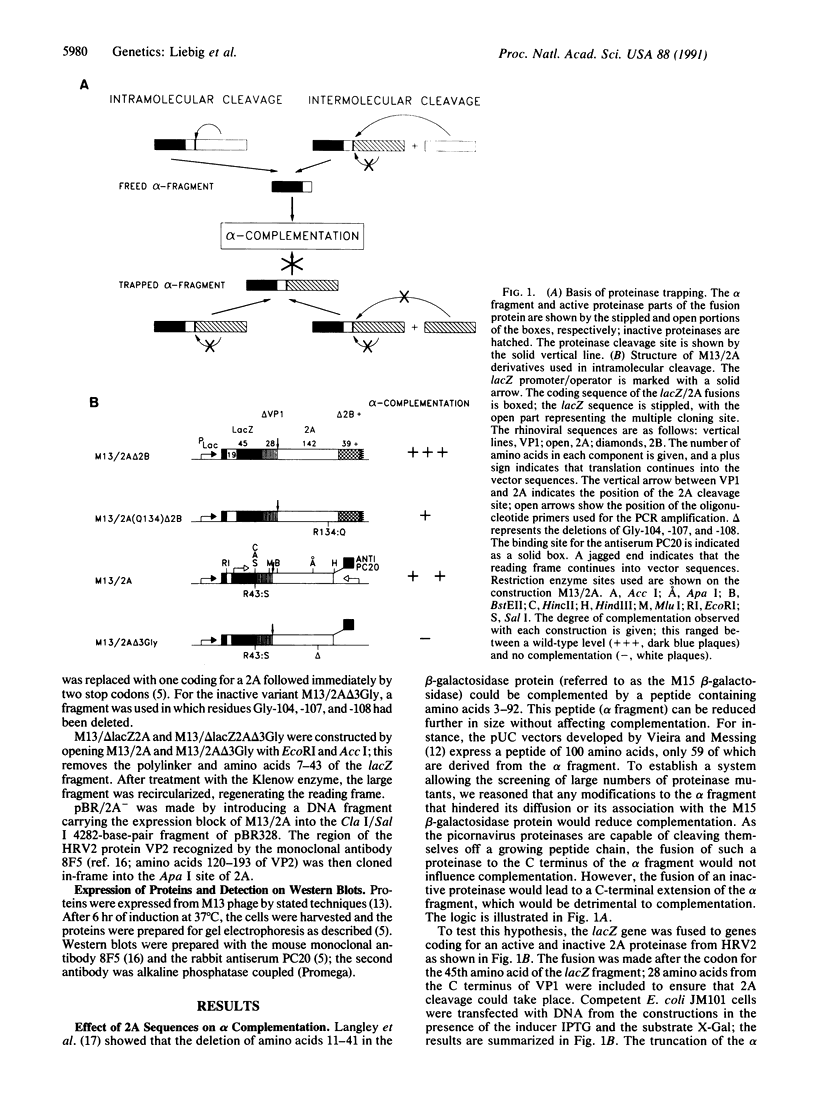
Many virally encoded proteinases cleave themselves out of a polyprotein, with cleavage occurring usually at their own N terminus. This property was used to develop an in vivo screening system using the lacZ gene fragment of M13mp18. When a fusion protein of the alpha fragment of beta-galactosidase and an active 2A proteinase of human rhinovirus 2 was expressed, alpha complementation was not affected, as the 2A proteinase cleaved itself off the alpha fragment. However, fusion of an inactive 2A prevented alpha complementation, as the 2A polypeptide remained fused to the alpha fragment. After random mutation of the 2A gene by PCR amplification, mutants were screened; M13 phage defective in alpha complementation were obtained at an efficiency of 5% and were shown to contain mutated 2A genes. Intermolecular cleavage was then examined by expressing an alpha fragment-inactive proteinase fusion protein as substrate for an active 2A proteinase expressed from an M13 vector. alpha complementation indicated intermolecular processing of the 2A cleavage site on the alpha fragment-inactive proteinase fusion protein. This versatile system thus allows the high-density screening of both active and inactive proteinase mutants, cleaving either intramolecularly or intermolecularly, and should be applicable to other proteinases of high specificity.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baum E. Z., Bebernitz G. A., Gluzman Y. beta-Galactosidase containing a human immunodeficiency virus protease cleavage site is cleaved and inactivated by human immunodeficiency virus protease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Dec;87(24):10023–10027. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.24.10023. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bazan J. F., Fletterick R. J. Viral cysteine proteases are homologous to the trypsin-like family of serine proteases: structural and functional implications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Nov;85(21):7872–7876. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.21.7872. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Etchison D., Hansen J., Ehrenfeld E., Edery I., Sonenberg N., Milburn S., Hershey J. W. Demonstration in vitro that eucaryotic initiation factor 3 is active but that a cap-binding protein complex is inactive in poliovirus-infected HeLa cells. J Virol. 1984 Sep;51(3):832–837. doi: 10.1128/jvi.51.3.832-837.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorbalenya A. E., Blinov V. M., Donchenko A. P. Poliovirus-encoded proteinase 3C: a possible evolutionary link between cellular serine and cysteine proteinase families. FEBS Lett. 1986 Jan 6;194(2):253–257. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(86)80095-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanecak R., Semler B. L., Anderson C. W., Wimmer E. Proteolytic processing of poliovirus polypeptides: antibodies to polypeptide P3-7c inhibit cleavage at glutamine-glycine pairs. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jul;79(13):3973–3977. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.13.3973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hellen C. U., Kräusslich H. G., Wimmer E. Proteolytic processing of polyproteins in the replication of RNA viruses. Biochemistry. 1989 Dec 26;28(26):9881–9890. doi: 10.1021/bi00452a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kräusslich H. G., Nicklin M. J., Toyoda H., Etchison D., Wimmer E. Poliovirus proteinase 2A induces cleavage of eucaryotic initiation factor 4F polypeptide p220. J Virol. 1987 Sep;61(9):2711–2718. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.9.2711-2718.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langley K. E., Villarejo M. R., Fowler A. V., Zamenhof P. J., Zabin I. Molecular basis of beta-galactosidase alpha-complementation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Apr;72(4):1254–1257. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.4.1254. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skern T., Neubauer C., Frasel L., Gründler P., Sommergruber W., Zorn M., Kuechler E., Blaas D. A neutralizing epitope on human rhinovirus type 2 includes amino acid residues between 153 and 164 of virus capsid protein VP2. J Gen Virol. 1987 Feb;68(Pt 2):315–323. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-68-2-315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skern T., Sommergruber W., Auer H., Volkmann P., Zorn M., Liebig H. D., Fessl F., Blaas D., Kuechler E. Substrate requirements of a human rhinoviral 2A proteinase. Virology. 1991 Mar;181(1):46–54. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(91)90468-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sommergruber W., Zorn M., Blaas D., Fessl F., Volkmann P., Maurer-Fogy I., Pallai P., Merluzzi V., Matteo M., Skern T. Polypeptide 2A of human rhinovirus type 2: identification as a protease and characterization by mutational analysis. Virology. 1989 Mar;169(1):68–77. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(89)90042-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sun X. H., Baltimore D. Human immunodeficiency virus tat-activated expression of poliovirus protein 2A inhibits mRNA translation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Apr;86(7):2143–2146. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.7.2143. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabor S., Richardson C. C. DNA sequence analysis with a modified bacteriophage T7 DNA polymerase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jul;84(14):4767–4771. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.14.4767. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor J. W., Ott J., Eckstein F. The rapid generation of oligonucleotide-directed mutations at high frequency using phosphorothioate-modified DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Dec 20;13(24):8765–8785. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.24.8765. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toyoda H., Nicklin M. J., Murray M. G., Anderson C. W., Dunn J. J., Studier F. W., Wimmer E. A second virus-encoded proteinase involved in proteolytic processing of poliovirus polyprotein. Cell. 1986 Jun 6;45(5):761–770. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90790-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ullmann A., Jacob F., Monod J. Characterization by in vitro complementation of a peptide corresponding to an operator-proximal segment of the beta-galactosidase structural gene of Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1967 Mar 14;24(2):339–343. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(67)90341-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vieira J., Messing J. The pUC plasmids, an M13mp7-derived system for insertion mutagenesis and sequencing with synthetic universal primers. Gene. 1982 Oct;19(3):259–268. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90015-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]