Abstract
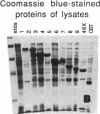
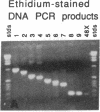
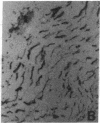
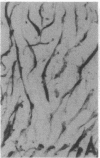
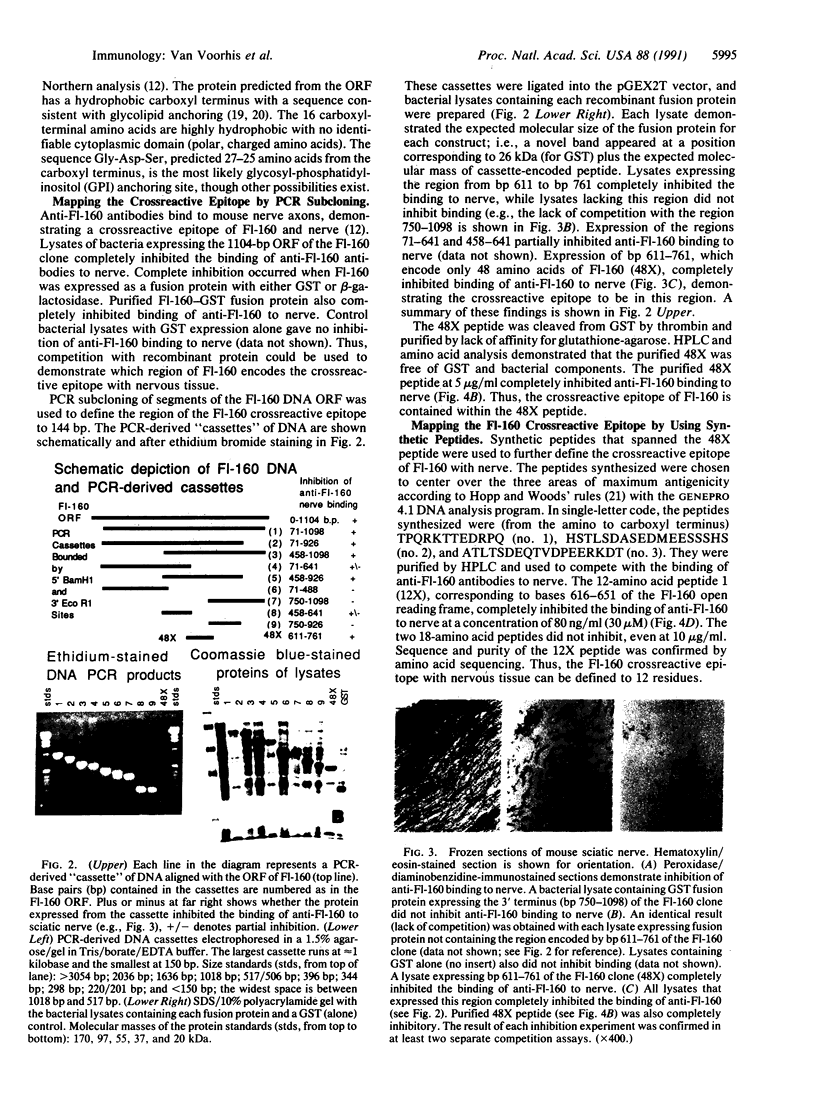
Antigenic mimicry by Trypanosoma cruzi antigens that share epitopes with mammalian tissues may drive autoreactive B- or T-cell clones to expand and cause autoimmune pathogenesis. We have been studying one of these antigens, F1-160, a 160-kDa protein on the surface of T. cruzi that antigenically mimics a 48-kDa protein found in mammalian axonal and myenteric plexus cells. The F1-160 antigen has been characterized by cloning and expression of T. cruzi DNA encoding F1-160 in Escherichia coli. Recombinant peptides from various regions of the F1-160 gene were expressed and used to compete with affinity-purified polyclonal anti-F1-160 antibodies binding to nerve. Recombinant 48-amino acid peptide (48X) derived from expression of base pairs 611-761 of the DNA sequence completely inhibited anti-F1-160 binding to nerve. Recombinant peptides expressed from DNA lacking this region did not inhibit anti-F1-160 binding to nerve. Three peptides were synthesized to encompass the 48X peptide, a 12-amino acid peptide and two 18-amino acid peptides. The 12-amino acid peptide TPQRKTTEDRPQ (12X), corresponding to bases 615-651, completely inhibited the binding of anti-F1-160 antibodies to nerve at a concentration of 80 ng/ml (30 microM). The two 18-residue peptides did not inhibit, even at 10 micrograms/ml. Thus, the epitope of F1-160 crossreactive with nervous tissue can be mapped to a 12-amino acid peptide. Some humans with T. cruzi infection make antibodies to F1-160 and to the 48X and 12X peptides. Control sera from uninfected persons did not react with these antigens. Anti-48X antibodies, immunoselected from human serum with 48X peptide, bind to human nerve axons. This demonstrates that some individuals infected with T. cruzi make antibodies to the F1-160 epitope crossreactive with nervous tissues.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andrews N. W., Robbins E. S., Ley V., Hong K. S., Nussenzweig V. Developmentally regulated, phospholipase C-mediated release of the major surface glycoprotein of amastigotes of Trypanosoma cruzi. J Exp Med. 1988 Feb 1;167(2):300–314. doi: 10.1084/jem.167.2.300. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bidlingmeyer B. A., Cohen S. A., Tarvin T. L. Rapid analysis of amino acids using pre-column derivatization. J Chromatogr. 1984 Dec 7;336(1):93–104. doi: 10.1016/s0378-4347(00)85133-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cossio P. M., Diez C., Szarfman A., Kreutzer E., Candiolo B., Arana R. M. Chagasic cardiopathy. Demonstration of a serum gamma globulin factor which reacts with endocardium and vascular structures. Circulation. 1974 Jan;49(1):13–21. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.49.1.13. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cross G. A. Glycolipid anchoring of plasma membrane proteins. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1990;6:1–39. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.06.110190.000245. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferguson M. A., Williams A. F. Cell-surface anchoring of proteins via glycosyl-phosphatidylinositol structures. Annu Rev Biochem. 1988;57:285–320. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.57.070188.001441. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hontebeyrie-Joskowicz M., Said G., Milon G., Marchal G., Eisen H. L3T4+ T cells able to mediate parasite-specific delayed-type hypersensitivity play a role in the pathology of experimental Chagas' disease. Eur J Immunol. 1987 Jul;17(7):1027–1033. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830170720. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hopp T. P., Woods K. R. Prediction of protein antigenic determinants from amino acid sequences. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jun;78(6):3824–3828. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.6.3824. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khoury E. L., Ritacco V., Cossio P. M., Laguens R. P., Szarfman A., Diez C., Arana R. M. Circulating antibodies to peripheral nerve in American trypanosomiasis (Chagas' disease). Clin Exp Immunol. 1979 Apr;36(1):8–15. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Köberle F. Chagas' disease and Chagas' syndromes: the pathology of American trypanosomiasis. Adv Parasitol. 1968;6:63–116. doi: 10.1016/s0065-308x(08)60472-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laguens R. P., Meckert P. C., Chambo G., Gelpi R. J. Chronic Chagas disease in the mouse. II. Transfer of the heart disease by means of immunocompetent cells. Medicina (B Aires) 1981;41(1):40–43. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petry K., Nudelman E., Eisen H., Hakomori S. Sulfated lipids represent common antigens on the surface of Trypanosoma cruzi and mammalian tissues. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1988 Aug;30(2):113–121. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(88)90104-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petry K., Voisin P., Baltz T. Complex lipids as common antigens to Trypanosoma cruzi, T. dionisii, T. vespertilionis and nervous tissue (astrocytes, neurons). Acta Trop. 1987 Dec;44(4):381–386. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petry K., Voisin P., Baltz T., Labouesse J. Epitopes common to trypanosomes (T. cruzi, T. dionisii and T. vespertilionis (Schizotrypanum)): astrocytes and neurons. J Neuroimmunol. 1987 Oct;16(2):237–252. doi: 10.1016/0165-5728(87)90078-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plata F., Garcia Pons F., Eisen H. Antigenic polymorphism of Trypanosoma cruzi: clonal analysis of trypomastigote surface antigens. Eur J Immunol. 1984 May;14(5):392–399. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830140503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rifkin M. R., Landsberger F. R. Trypanosome variant surface glycoprotein transfer to target membranes: a model for the pathogenesis of trypanosomiasis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jan;87(2):801–805. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.2.801. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith D. B., Johnson K. S. Single-step purification of polypeptides expressed in Escherichia coli as fusions with glutathione S-transferase. Gene. 1988 Jul 15;67(1):31–40. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90005-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snary D., Flint J. E., Wood J. N., Scott M. T., Chapman M. D., Dodd J., Jessell T. M., Miles M. A. A monoclonal antibody with specificity for Trypanosoma cruzi, central and peripheral neurones and glia. Clin Exp Immunol. 1983 Dec;54(3):617–624. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szarfman A., Terranova V. P., Rennard S. I., Foidart J. M., de Fatima Lima M., Scheinman J. I., Martin G. R. Antibodies to laminin in Chagas' disease. J Exp Med. 1982 Apr 1;155(4):1161–1171. doi: 10.1084/jem.155.4.1161. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Rosenfelder G., Wieslander J., Avila J. L., Rojas M., Szarfman A., Esser K., Nowack H., Timpl R. Circulating antibodies to mouse laminin in Chagas disease, American cutaneous leishmaniasis, and normal individuals recognize terminal galactosyl(alpha 1-3)-galactose epitopes. J Exp Med. 1987 Aug 1;166(2):419–432. doi: 10.1084/jem.166.2.419. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Voorhis W. C., Eisen H. Fl-160. A surface antigen of Trypanosoma cruzi that mimics mammalian nervous tissue. J Exp Med. 1989 Mar 1;169(3):641–652. doi: 10.1084/jem.169.3.641. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood J. N., Hudson L., Jessell T. M., Yamamoto M. A monoclonal antibody defining antigenic determinants on subpopulations of mammalian neurones and Trypanosoma cruzi parasites. Nature. 1982 Mar 4;296(5852):34–38. doi: 10.1038/296034a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]