Fig. 4.
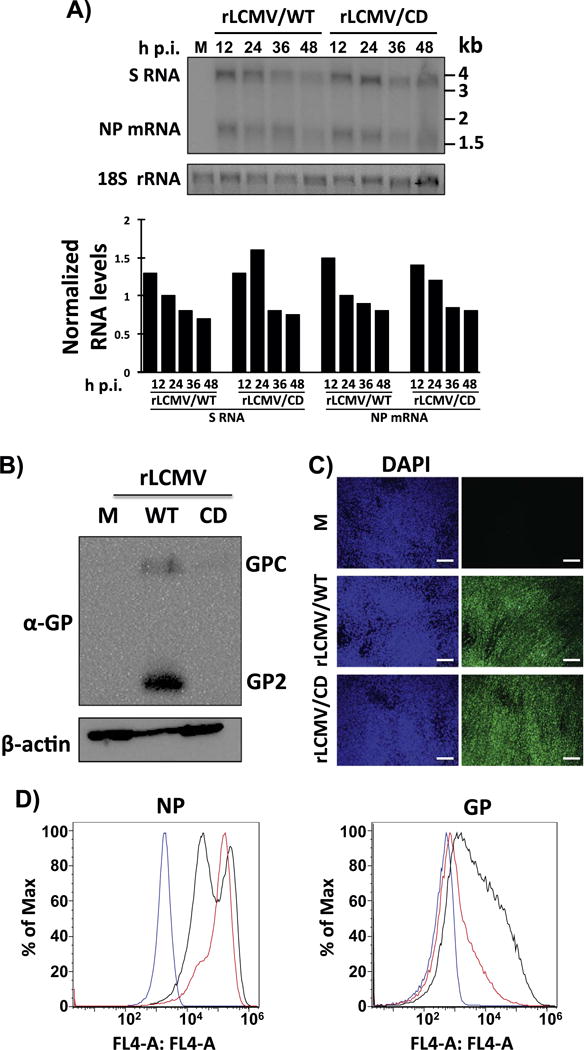
Viral RNA synthesis (A) and GP expression levels (B–D) in rLCMV/CD-infected BHK-21 cells. A) Cells were infected (moi=0.1) with rLCMV/WT or rLCMV/CD. At the indicated times, RNA was isolated and analyzed by NB hybridization using a double strand DNA NP probe that hybridized to the S genome and NP mRNA species. Signals corresponding to the S and NP mRNA species were quantified and normalized first with respect levels of 18 S rRNA used as loading and transfer control. Corrected S and NP mRNA species signals were then normalized to the signals detected at 24 h p.i. in rLCMV/WT-infected cells. B–D) Cells were mock (M) infected or infected (moi=0.01) with rLCMV/WT or rLCMV/CD. At 48 h p.i., cells lysates were prepared and evaluated for GP expression levels by WB (B) using the LCMV GP mouse monoclonal antibody 83.6. Expression levels of β-actin were used as loading controls. Infection levels at the same times post-infection were evaluated by IFA using the LCMV NP mouse monoclonal antibody 1.1.3 (C). Nuclei were stained with DAPI. Scale bar=100 μm. Cells mock-infected (blue line) or infected with rLCMV/WT (black line) or rLCMV/CD (red line) were subjected to FACS analysis with the LCMV NP monoclonal antibody 1.1.3 or the LCMV GP monoclonal antibody 36.1 (D).
