Abstract
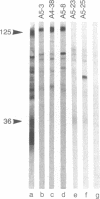
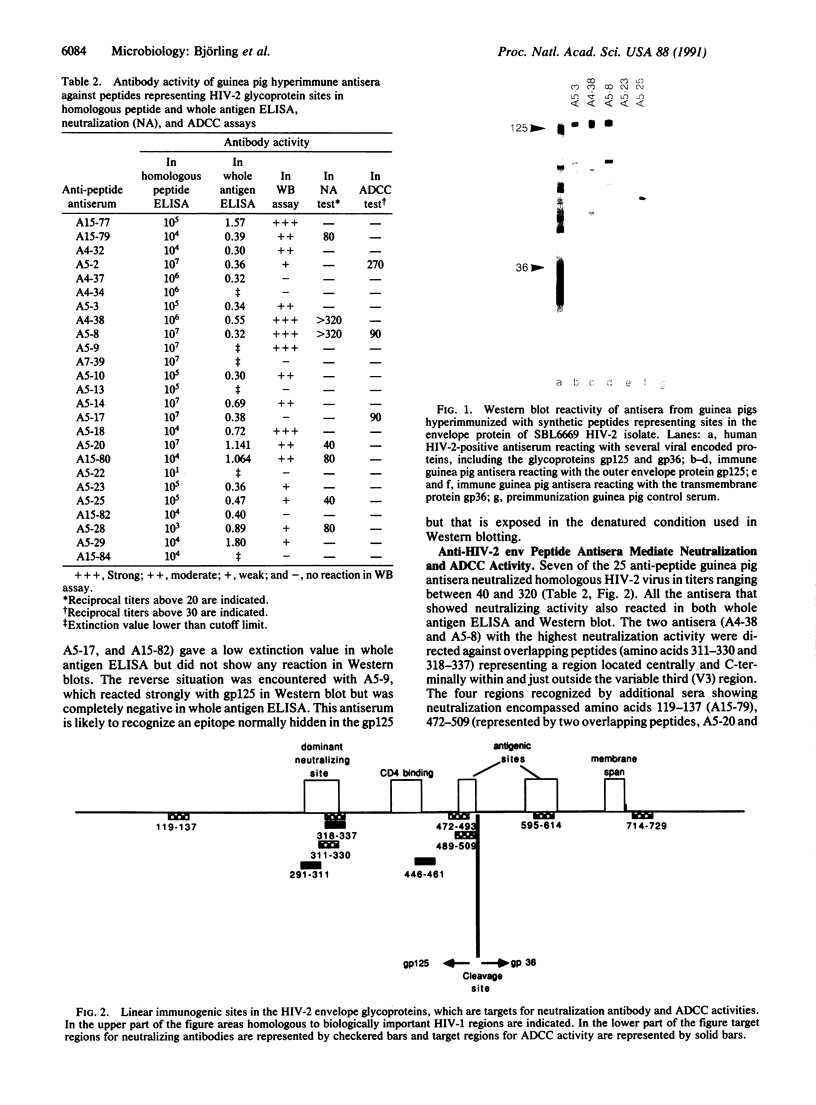
Twenty-five 13- to 35-amino-acid-long peptides representing regions of human immunodeficiency virus type 2 (HIV-2), strain SBL6669, envelope proteins were evaluated for their immunogenic activity in guinea pigs. The peptides were selected to provide homologous representation of sites in the HIV-1 envelope proteins that were previously documented to have a particular immunogenic importance. A number of the HIV-2 peptides were found to be capable of inducing strain SBL6669 neutralizing and antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity (ADCC) antibodies. Two overlapping peptides covering amino acids 311-337 representing the central and C-terminal part of the variable third (V3) region, terminology according to Modrow et al. [Modrow, S., Hahn, B., Shaw, G. M., Gallo, R. C., Wong-Staal, F. & Wolf, H. (1987) J. Virol. 61, 570-578], showed the most pronounced capacity to induce neutralizing antibodies. One of the peptides (amino acids 318-337) also induced antibodies mediating ADCC. Two additional regions in the large glycoprotein, gp125, containing linear sites reacting with neutralizing antibodies were identified (amino acids, 119-137 and 472-509). The transmembrane protein, gp36, of HIV-2 harbored two regions of importance for induction of neutralizing antibodies (amino acids 595-614 and 714-729). ADCC activity was induced by two additional gp125-specific peptides (amino acids 291-311 and 446-461). Thus, except for the single V3-specific site there was no correlation between linear immunogenic sites stimulating neutralizing antibody and ADCC activity. These findings pave the way for development of synthetic vaccines against HIV-2 and possibly also simian immunodeficiency virus infections. The capacity of such a product to induce protective immunity can be evaluated in macaque monkeys.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Albert J., Bredberg U., Chiodi F., Böttiger B., Fenyö E. M., Norrby E., Biberfeld G. A new human retrovirus isolate of West African origin (SBL-6669) and its relationship to HTLV-IV, LAV-II, and HTLV-IIIB. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 1987 Spring;3(1):3–10. doi: 10.1089/aid.1987.3.3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biberfeld G., Thorstensson R., Bergström M., Naucler A., Costa C. M. Enzyme immunoassays for the demonstration of antibodies to HIV-2SBL-6669 and HTLV-IV (SIVmac). AIDS. 1988 Jun;2(3):195–199. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolognesi D. P. HIV antibodies and vaccine design. AIDS. 1989;3 (Suppl 1):S111–S118. doi: 10.1097/00002030-198901001-00016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Broliden P. A., Ljunggren K., Hinkula J., Norrby E., Akerblom L., Wahren B. A monoclonal antibody to human immunodeficiency virus type 1 which mediates cellular cytotoxicity and neutralization. J Virol. 1990 Feb;64(2):936–940. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.2.936-940.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Böttiger B., Karlsson A., Andreasson P. A., Nauclér A., Costa C. M., Norrby E., Biberfeld G. Envelope cross-reactivity between human immunodeficiency virus types 1 and 2 detected by different serological methods: correlation between cross-neutralization and reactivity against the main neutralizing site. J Virol. 1990 Jul;64(7):3492–3499. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.7.3492-3499.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chanh T. C., Dreesman G. R., Kanda P., Linette G. P., Sparrow J. T., Ho D. D., Kennedy R. C. Induction of anti-HIV neutralizing antibodies by synthetic peptides. EMBO J. 1986 Nov;5(11):3065–3071. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04607.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiodi F., von Gegerfeldt A., Albert J., Fenyö E. M., Gaines H., von Sydow M., Biberfeld G., Parks E., Norrby E. Site-directed ELISA with synthetic peptides representing the HIV transmembrane glycoprotein. J Med Virol. 1987 Sep;23(1):1–9. doi: 10.1002/jmv.1890230102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clavel F., Guétard D., Brun-Vézinet F., Chamaret S., Rey M. A., Santos-Ferreira M. O., Laurent A. G., Dauguet C., Katlama C., Rouzioux C. Isolation of a new human retrovirus from West African patients with AIDS. Science. 1986 Jul 18;233(4761):343–346. doi: 10.1126/science.2425430. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dalgleish A. G., Chanh T. C., Kennedy R. C., Kanda P., Clapham P. R., Weiss R. A. Neutralization of diverse HIV-1 strains by monoclonal antibodies raised against a gp41 synthetic peptide. Virology. 1988 Jul;165(1):209–215. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(88)90674-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Desrosiers R. C., Ringler D. J. Use of simian immunodeficiency viruses for AIDS research. Intervirology. 1989;30(6):301–312. doi: 10.1159/000150108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franchini G., Fargnoli K. A., Giombini F., Jagodzinski L., De Rossi A., Bosch M., Biberfeld G., Fenyo E. M., Albert J., Gallo R. C. Molecular and biological characterization of a replication competent human immunodeficiency type 2 (HIV-2) proviral clone. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Apr;86(7):2433–2437. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.7.2433. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gnann J. W., Jr, Nelson J. A., Oldstone M. B. Fine mapping of an immunodominant domain in the transmembrane glycoprotein of human immunodeficiency virus. J Virol. 1987 Aug;61(8):2639–2641. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.8.2639-2641.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goudsmit J., Debouck C., Meloen R. H., Smit L., Bakker M., Asher D. M., Wolff A. V., Gibbs C. J., Jr, Gajdusek D. C. Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 neutralization epitope with conserved architecture elicits early type-specific antibodies in experimentally infected chimpanzees. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jun;85(12):4478–4482. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.12.4478. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Houghten R. A. General method for the rapid solid-phase synthesis of large numbers of peptides: specificity of antigen-antibody interaction at the level of individual amino acids. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Aug;82(15):5131–5135. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.15.5131. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kenealy W. R., Matthews T. J., Ganfield M. C., Langlois A. J., Waselefsky D. M., Petteway S. R., Jr Antibodies from human immunodeficiency virus-infected individuals bind to a short amino acid sequence that elicits neutralizing antibodies in animals. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 1989 Apr;5(2):173–182. doi: 10.1089/aid.1989.5.173. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kennedy R. C., Henkel R. D., Pauletti D., Allan J. S., Lee T. H., Essex M., Dreesman G. R. Antiserum to a synthetic peptide recognizes the HTLV-III envelope glycoprotein. Science. 1986 Mar 28;231(4745):1556–1559. doi: 10.1126/science.3006246. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kowalski M., Potz J., Basiripour L., Dorfman T., Goh W. C., Terwilliger E., Dayton A., Rosen C., Haseltine W., Sodroski J. Functional regions of the envelope glycoprotein of human immunodeficiency virus type 1. Science. 1987 Sep 11;237(4820):1351–1355. doi: 10.1126/science.3629244. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LaRosa G. J., Davide J. P., Weinhold K., Waterbury J. A., Profy A. T., Lewis J. A., Langlois A. J., Dreesman G. R., Boswell R. N., Shadduck P. Conserved sequence and structural elements in the HIV-1 principal neutralizing determinant. Science. 1990 Aug 24;249(4971):932–935. doi: 10.1126/science.2392685. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lasky L. A., Nakamura G., Smith D. H., Fennie C., Shimasaki C., Patzer E., Berman P., Gregory T., Capon D. J. Delineation of a region of the human immunodeficiency virus type 1 gp120 glycoprotein critical for interaction with the CD4 receptor. Cell. 1987 Sep 11;50(6):975–985. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90524-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu F. T., Zinnecker M., Hamaoka T., Katz D. H. New procedures for preparation and isolation of conjugates of proteins and a synthetic copolymer of D-amino acids and immunochemical characterization of such conjugates. Biochemistry. 1979 Feb 20;18(4):690–693. doi: 10.1021/bi00571a022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ljunggren K., Böttiger B., Biberfeld G., Karlson A., Fenyö E. M., Jondal M. Antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity-inducing antibodies against human immunodeficiency virus. Presence at different clinical stages. J Immunol. 1987 Oct 1;139(7):2263–2267. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsushita S., Robert-Guroff M., Rusche J., Koito A., Hattori T., Hoshino H., Javaherian K., Takatsuki K., Putney S. Characterization of a human immunodeficiency virus neutralizing monoclonal antibody and mapping of the neutralizing epitope. J Virol. 1988 Jun;62(6):2107–2114. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.6.2107-2114.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Modrow S., Hahn B. H., Shaw G. M., Gallo R. C., Wong-Staal F., Wolf H. Computer-assisted analysis of envelope protein sequences of seven human immunodeficiency virus isolates: prediction of antigenic epitopes in conserved and variable regions. J Virol. 1987 Feb;61(2):570–578. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.2.570-578.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norrby E., Biberfeld G., Chiodi F., von Gegerfeldt A., Nauclér A., Parks E., Lerner R. Discrimination between antibodies to HIV and to related retroviruses using site-directed serology. Nature. 1987 Sep 17;329(6136):248–250. doi: 10.1038/329248a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norrby E., Putkonen P., Böttiger B., Utter G., Biberfeld G. Comparison of linear antigenic sites in the envelope proteins of human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) type 2 and type 1. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 1991 Mar;7(3):279–285. doi: 10.1089/aid.1991.7.279. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palker T. J., Clark M. E., Langlois A. J., Matthews T. J., Weinhold K. J., Randall R. R., Bolognesi D. P., Haynes B. F. Type-specific neutralization of the human immunodeficiency virus with antibodies to env-encoded synthetic peptides. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Mar;85(6):1932–1936. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.6.1932. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palker T. J., Matthews T. J., Clark M. E., Cianciolo G. J., Randall R. R., Langlois A. J., White G. C., Safai B., Snyderman R., Bolognesi D. P. A conserved region at the COOH terminus of human immunodeficiency virus gp120 envelope protein contains an immunodominant epitope. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Apr;84(8):2479–2483. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.8.2479. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Putkonen P., Böttiger B., Warstedt K., Thorstensson R., Albert J., Biberfeld G. Experimental infection of cynomolgus monkeys (Macaca fascicularis) with HIV-2. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 1989;2(4):366–373. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Putkonen P., Thorstensson R., Albert J., Hild K., Norrby E., Biberfeld P., Biberfeld G. Infection of cynomolgus monkeys with HIV-2 protects against pathogenic consequences of a subsequent simian immunodeficiency virus infection. AIDS. 1990 Aug;4(8):783–789. doi: 10.1097/00002030-199008000-00010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Putkonen P., Thorstensson R., Walther L., Albert J., Akerblom L., Granquist O., Wadell G., Norrby E., Biberfeld G. Vaccine protection against HIV-2 infection in cynomolgus monkeys. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 1991 Mar;7(3):271–277. doi: 10.1089/aid.1991.7.271. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Putkonen P., Warstedt K., Thorstensson R., Benthin R., Albert J., Lundgren B., Oberg B., Norrby E., Biberfeld G. Experimental infection of cynomolgus monkeys (Macaca fascicularis) with simian immunodeficiency virus (SIVsm). J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 1989;2(4):359–365. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Putney S. D., Matthews T. J., Robey W. G., Lynn D. L., Robert-Guroff M., Mueller W. T., Langlois A. J., Ghrayeb J., Petteway S. R., Jr, Weinhold K. J. HTLV-III/LAV-neutralizing antibodies to an E. coli-produced fragment of the virus envelope. Science. 1986 Dec 12;234(4782):1392–1395. doi: 10.1126/science.2431482. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rusche J. R., Javaherian K., McDanal C., Petro J., Lynn D. L., Grimaila R., Langlois A., Gallo R. C., Arthur L. O., Fischinger P. J. Antibodies that inhibit fusion of human immunodeficiency virus-infected cells bind a 24-amino acid sequence of the viral envelope, gp120. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 May;85(9):3198–3202. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.9.3198. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rusche J. R., Lynn D. L., Robert-Guroff M., Langlois A. J., Lyerly H. K., Carson H., Krohn K., Ranki A., Gallo R. C., Bolognesi D. P. Humoral immune response to the entire human immunodeficiency virus envelope glycoprotein made in insect cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Oct;84(19):6924–6928. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.19.6924. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider J., Hunsmann G. Simian lentiviruses--the SIV group. AIDS. 1988 Feb;2(1):1–9. doi: 10.1097/00002030-198802000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sodroski J., Goh W. C., Rosen C., Campbell K., Haseltine W. A. Role of the HTLV-III/LAV envelope in syncytium formation and cytopathicity. 1986 Jul 31-Aug 6Nature. 322(6078):470–474. doi: 10.1038/322470a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Starcich B. R., Hahn B. H., Shaw G. M., McNeely P. D., Modrow S., Wolf H., Parks E. S., Parks W. P., Josephs S. F., Gallo R. C. Identification and characterization of conserved and variable regions in the envelope gene of HTLV-III/LAV, the retrovirus of AIDS. Cell. 1986 Jun 6;45(5):637–648. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90778-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stein B. S., Gowda S. D., Lifson J. D., Penhallow R. C., Bensch K. G., Engleman E. G. pH-independent HIV entry into CD4-positive T cells via virus envelope fusion to the plasma membrane. Cell. 1987 Jun 5;49(5):659–668. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90542-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thorstensson R., Walther L., Putkonen P., Albert J., Biberfeld G. A capture enzyme immunoassay for detection of HIV-2/SIV antigen. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 1991;4(4):374–379. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang J. J., Steel S., Wisniewolski R., Wang C. Y. Detection of antibodies to human T-lymphotropic virus type III by using a synthetic peptide of 21 amino acid residues corresponding to a highly antigenic segment of gp41 envelope protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Aug;83(16):6159–6163. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.16.6159. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong-Staal F., Shaw G. M., Hahn B. H., Salahuddin S. Z., Popovic M., Markham P., Redfield R., Gallo R. C. Genomic diversity of human T-lymphotropic virus type III (HTLV-III). Science. 1985 Aug 23;229(4715):759–762. doi: 10.1126/science.2992084. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]