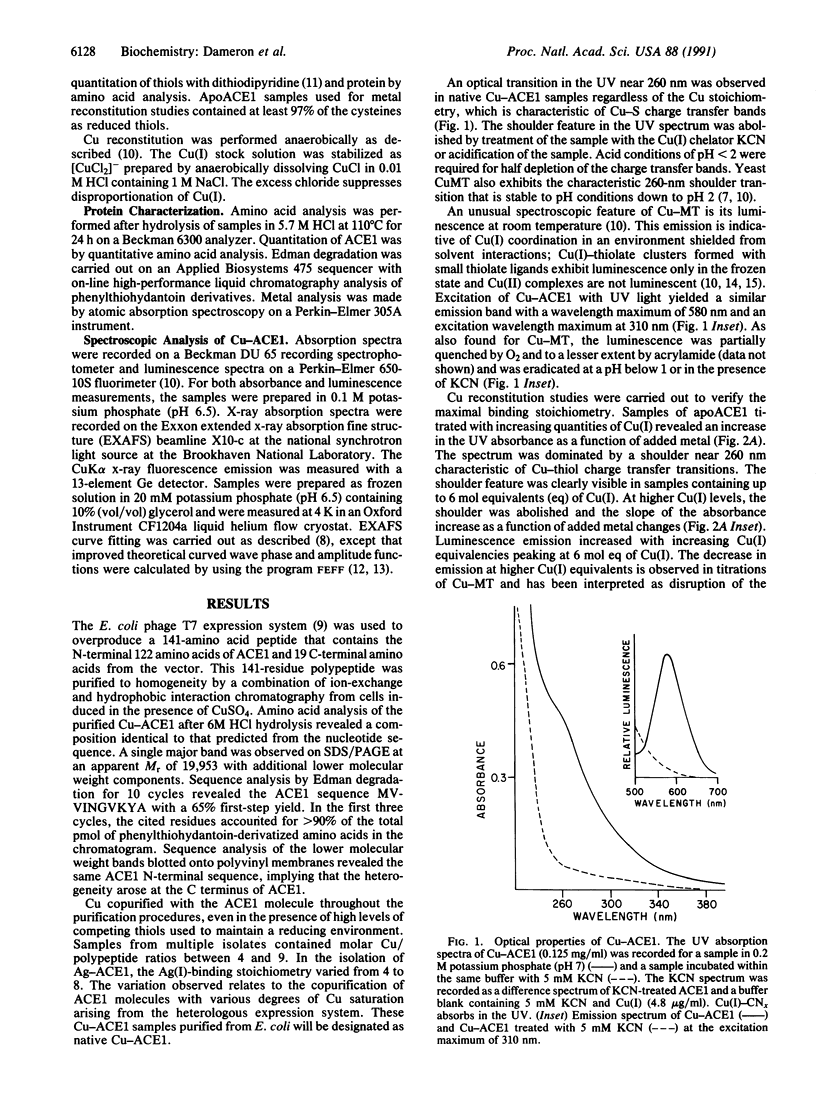
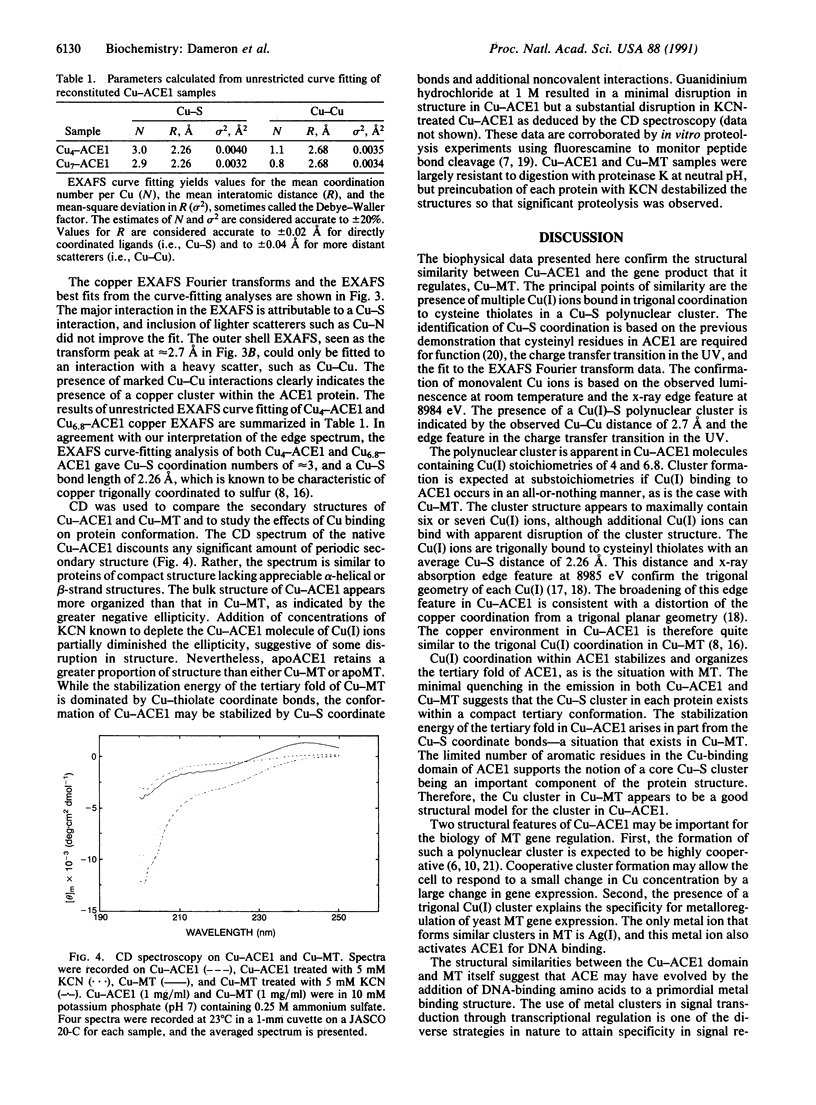
Abstract
ACE1 is the transcriptional activator of the metallothionein (CUP1 locus) gene in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Previous data had implicated the N-terminal domain of ACE1 as responsible for the Cu-dependent specific DNA binding. An expression system in Escherichia coli was constructed to enable the isolation of an ACE1 domain containing the DNA and Cu-binding regions. Here we report the purification and characterization of the Cu-ACE1 truncated molecule. Spectroscopic techniques showed that ACE1 contains an unusual type of DNA binding structure that is based on a polynuclear Cu(I)-cysteinyl thiolate cluster. The cluster consists of six or seven Cu(I) ions coordinated to cysteinyl thiolates in a trigonal geometry distorted from planarity. The Cu(I)-cysteine cluster of Cu-ACE1 exhibits structural properties analogous to the Cu(I)-thiolate polynuclear cluster in yeast Cu-metallothionein itself, suggesting an unusual mechanism for the evolution of this regulatory factor. The Cu cluster organizes and stabilizes the conformation of the N-terminal domain of ACE1 for specific DNA binding.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Buchman C., Skroch P., Welch J., Fogel S., Karin M. The CUP2 gene product, regulator of yeast metallothionein expression, is a copper-activated DNA-binding protein. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Sep;9(9):4091–4095. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.9.4091. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Byrd J., Berger R. M., McMillin D. R., Wright C. F., Hamer D., Winge D. R. Characterization of the copper-thiolate cluster in yeast metallothionein and two truncated mutants. J Biol Chem. 1988 May 15;263(14):6688–6694. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fürst P., Hamer D. Cooperative activation of a eukaryotic transcription factor: interaction between Cu(I) and yeast ACE1 protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jul;86(14):5267–5271. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.14.5267. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fürst P., Hu S., Hackett R., Hamer D. Copper activates metallothionein gene transcription by altering the conformation of a specific DNA binding protein. Cell. 1988 Nov 18;55(4):705–717. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90229-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- George G. N., Byrd J., Winge D. R. X-ray absorption studies of yeast copper metallothionein. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jun 15;263(17):8199–8203. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- George G. N., Winge D., Stout C. D., Cramer S. P. X-ray absorption studies of the copper-beta domain of rat liver metallothionein. J Inorg Biochem. 1986 Jul;27(3):213–220. doi: 10.1016/0162-0134(86)80062-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Good M., Hollenstein R., Sadler P. J., Vasák M. 113Cd NMR studies on metal-thiolate cluster formation in rabbit Cd(II)-metallothionein: evidence for a pH dependence. Biochemistry. 1988 Sep 6;27(18):7163–7166. doi: 10.1021/bi00418a074. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grassetti D. R., Murray J. F., Jr Determination of sulfhydryl groups with 2,2'- or 4,4'-dithiodipyridine. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1967 Mar;119(1):41–49. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(67)90426-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hu S., Fürst P., Hamer D. The DNA and Cu binding functions of ACE1 are interdigitated within a single domain. New Biol. 1990 Jun;2(6):544–555. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Struhl K. Helix-turn-helix, zinc-finger, and leucine-zipper motifs for eukaryotic transcriptional regulatory proteins. Trends Biochem Sci. 1989 Apr;14(4):137–140. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(89)90145-X. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Studier F. W., Rosenberg A. H., Dunn J. J., Dubendorff J. W. Use of T7 RNA polymerase to direct expression of cloned genes. Methods Enzymol. 1990;185:60–89. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(90)85008-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szczypka M. S., Thiele D. J. A cysteine-rich nuclear protein activates yeast metallothionein gene transcription. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Feb;9(2):421–429. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.2.421. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welch J., Fogel S., Buchman C., Karin M. The CUP2 gene product regulates the expression of the CUP1 gene, coding for yeast metallothionein. EMBO J. 1989 Jan;8(1):255–260. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03371.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winge D. R., Nielson K. B., Gray W. R., Hamer D. H. Yeast metallothionein. Sequence and metal-binding properties. J Biol Chem. 1985 Nov 25;260(27):14464–14470. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



