Abstract
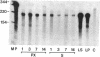
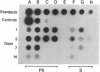
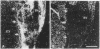
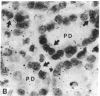
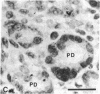
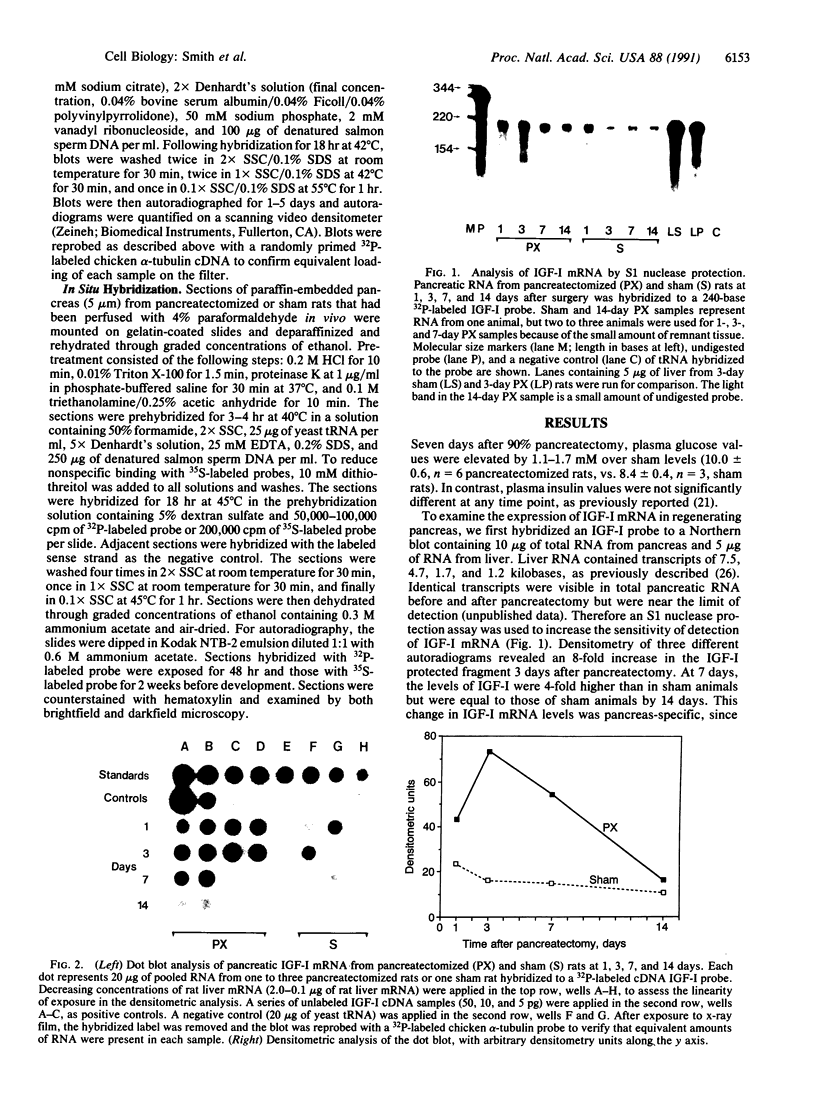
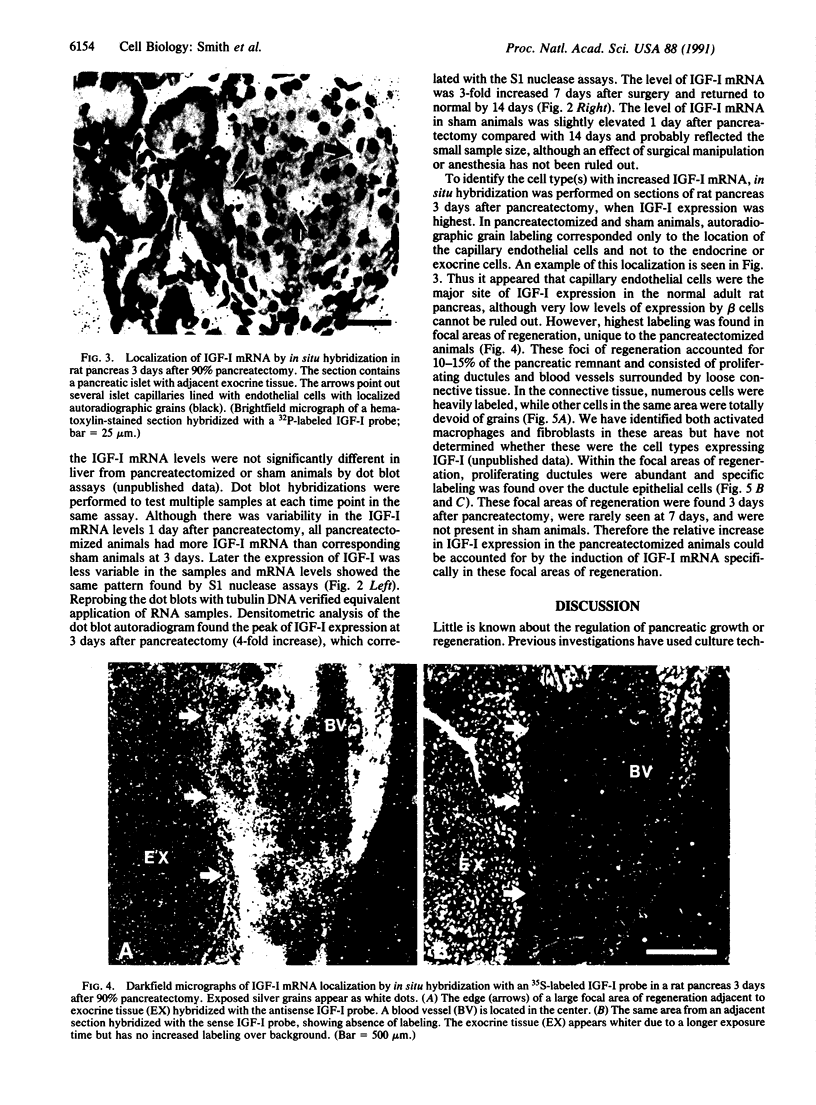
Insulin-like growth factor I (IGF-I) mRNA expression was studied after 90% partial pancreatectomy in the rat to determine whether IGF-I was associated with pancreatic regeneration. The level of IGF-I mRNA was maximally increased (4-fold above control value) 3 days after pancreatectomy, but thereafter gradually decreased, returning to control levels by 14 days after surgery. By in situ hybridization, IGF-I mRNA in both pancreatectomized and sham-operated rats was localized to capillary endothelial cells, indicating that this is the site of IGF-I expression in the normal rat pancreas. However, enhanced IGF-I mRNA expression was localized to focal areas of regeneration unique to pancreatectomized rats. In these areas, epithelial cells of proliferating ductules and individual connective tissue cells expressed IGF-I, suggesting that IGF-I may play an important role in the growth or differentiation of pancreatic tissue.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adamo M., Lowe W. L., Jr, LeRoith D., Roberts C. T., Jr Insulin-like growth factor I messenger ribonucleic acids with alternative 5'-untranslated regions are differentially expressed during development of the rat. Endocrinology. 1989 Jun;124(6):2737–2744. doi: 10.1210/endo-124-6-2737. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Albano J. D., Ekins R. P., Maritz G., Turner R. C. A sensitive, precise radioimmunoassay of serum insulin relying on charcoal separation of bound and free hormone moieties. Acta Endocrinol (Copenh) 1972 Jul;70(3):487–509. doi: 10.1530/acta.0.0700487. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bar R. S., Boes M., Dake B. L., Booth B. A., Henley S. A., Sandra A. Insulin, insulin-like growth factors, and vascular endothelium. Am J Med. 1988 Nov 28;85(5A):59–70. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(88)90398-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berk A. J., Sharp P. A. Sizing and mapping of early adenovirus mRNAs by gel electrophoresis of S1 endonuclease-digested hybrids. Cell. 1977 Nov;12(3):721–732. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90272-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonner-Weir S., Deery D., Leahy J. L., Weir G. C. Compensatory growth of pancreatic beta-cells in adult rats after short-term glucose infusion. Diabetes. 1989 Jan;38(1):49–53. doi: 10.2337/diab.38.1.49. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonner-Weir S., Trent D. F., Weir G. C. Partial pancreatectomy in the rat and subsequent defect in glucose-induced insulin release. J Clin Invest. 1983 Jun;71(6):1544–1553. doi: 10.1172/JCI110910. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brannon P. M., Hirschi K., Korc M. Effects of epidermal growth factor, insulin and insulin-like growth factor I on rat pancreatic acinar cells cultured in serum-free medium. Pancreas. 1988;3(1):41–48. doi: 10.1097/00006676-198802000-00008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brockenbrough J. S., Weir G. C., Bonner-Weir S. Discordance of exocrine and endocrine growth after 90% pancreatectomy in rats. Diabetes. 1988 Feb;37(2):232–236. doi: 10.2337/diab.37.2.232. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chick W. L. Beta cell replication in rat pancreatic monolayer cultures. Effects of glucose, tolbutamide, glucocorticoid, growth hormone and glucagon. Diabetes. 1973 Sep;22(9):687–693. doi: 10.2337/diab.22.9.687. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clemmons D. R., Van Wyk J. J. Evidence for a functional role of endogenously produced somatomedinlike peptides in the regulation of DNA synthesis in cultured human fibroblasts and porcine smooth muscle cells. J Clin Invest. 1985 Jun;75(6):1914–1918. doi: 10.1172/JCI111906. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daughaday W. H., Rotwein P. Insulin-like growth factors I and II. Peptide, messenger ribonucleic acid and gene structures, serum, and tissue concentrations. Endocr Rev. 1989 Feb;10(1):68–91. doi: 10.1210/edrv-10-1-68. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edwall D., Schalling M., Jennische E., Norstedt G. Induction of insulin-like growth factor I messenger ribonucleic acid during regeneration of rat skeletal muscle. Endocrinology. 1989 Feb;124(2):820–825. doi: 10.1210/endo-124-2-820. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fagin J. A., Melmed S. Relative increase in insulin-like growth factor I messenger ribonucleic acid levels in compensatory renal hypertrophy. Endocrinology. 1987 Feb;120(2):718–724. doi: 10.1210/endo-120-2-718. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Florini J. R., Ewton D. Z., Falen S. L., Van Wyk J. J. Biphasic concentration dependency of stimulation of myoblast differentiation by somatomedins. Am J Physiol. 1986 May;250(5 Pt 1):C771–C778. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1986.250.5.C771. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Han V. K., D'Ercole A. J., Lund P. K. Cellular localization of somatomedin (insulin-like growth factor) messenger RNA in the human fetus. Science. 1987 Apr 10;236(4798):193–197. doi: 10.1126/science.3563497. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Han V. K., Lund P. K., Lee D. C., D'Ercole A. J. Expression of somatomedin/insulin-like growth factor messenger ribonucleic acids in the human fetus: identification, characterization, and tissue distribution. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1988 Feb;66(2):422–429. doi: 10.1210/jcem-66-2-422. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansson H. A., Dahlin L. B., Danielsen N., Fryklund L., Nachemson A. K., Polleryd P., Rozell B., Skottner A., Stemme S., Lundborg G. Evidence indicating trophic importance of IGF-I in regenerating peripheral nerves. Acta Physiol Scand. 1986 Apr;126(4):609–614. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1986.tb07862.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansson H. A., Jennische E., Skottner A. Regenerating endothelial cells express insulin-like growth factor-I immunoreactivity after arterial injury. Cell Tissue Res. 1987 Dec;250(3):499–505. doi: 10.1007/BF00218940. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill D. J., Frazer A., Swenne I., Wirdnam P. K., Milner R. D. Somatomedin-C in human fetal pancreas. Cellular localization and release during organ culture. Diabetes. 1987 Apr;36(4):465–471. doi: 10.2337/diab.36.4.465. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hynes M. A., Van Wyk J. J., Brooks P. J., D'Ercole A. J., Jansen M., Lund P. K. Growth hormone dependence of somatomedin-C/insulin-like growth factor-I and insulin-like growth factor-II messenger ribonucleic acids. Mol Endocrinol. 1987 Mar;1(3):233–242. doi: 10.1210/mend-1-3-233. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jennische E., Skottner A., Hansson H. A. Satellite cells express the trophic factor IGF-I in regenerating skeletal muscle. Acta Physiol Scand. 1987 Jan;129(1):9–15. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1987.tb08034.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kern P. A., Svoboda M. E., Eckel R. H., Van Wyk J. J. Insulinlike growth factor action and production in adipocytes and endothelial cells from human adipose tissue. Diabetes. 1989 Jun;38(6):710–717. doi: 10.2337/diab.38.6.710. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Logsdon C. D. Stimulation of pancreatic acinar cell growth by CCK, epidermal growth factor, and insulin in vitro. Am J Physiol. 1986 Oct;251(4 Pt 1):G487–G494. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1986.251.4.G487. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lund P. K., Moats-Staats B. M., Hynes M. A., Simmons J. G., Jansen M., D'Ercole A. J., Van Wyk J. J. Somatomedin-C/insulin-like growth factor-I and insulin-like growth factor-II mRNAs in rat fetal and adult tissues. J Biol Chem. 1986 Nov 5;261(31):14539–14544. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nielsen J. H. Growth and function of the pancreatic beta cell in vitro: effects of glucose, hormones and serum factors on mouse, rat and human pancreatic islets in organ culture. Acta Endocrinol Suppl (Copenh) 1985;266:1–39. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pictet R. L., Clark W. R., Williams R. H., Rutter W. J. An ultrastructural analysis of the developing embryonic pancreas. Dev Biol. 1972 Dec;29(4):436–467. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(72)90083-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rabinovitch A., Quigley C., Russell T., Patel Y., Mintz D. H. Insulin and multiplication stimulating activity (an insulin-like growth factor) stimulate islet (beta-cell replication in neonatal rat pancreatic monolayer cultures. Diabetes. 1982 Feb;31(2):160–164. doi: 10.2337/diab.31.2.160. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rappolee D. A., Mark D., Banda M. J., Werb Z. Wound macrophages express TGF-alpha and other growth factors in vivo: analysis by mRNA phenotyping. Science. 1988 Aug 5;241(4866):708–712. doi: 10.1126/science.3041594. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Romanus J. A., Rabinovitch A., Rechler M. M. Neonatal rat islet cell cultures synthesize insulin-like growth factor I. Diabetes. 1985 Jul;34(7):696–702. doi: 10.2337/diab.34.7.696. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosen K. M., Lamperti E. D., Villa-Komaroff L. Optimizing the northern blot procedure. Biotechniques. 1990 Apr;8(4):398–403. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rotwein P., Pollock K. M., Watson M., Milbrandt J. D. Insulin-like growth factor gene expression during rat embryonic development. Endocrinology. 1987 Dec;121(6):2141–2144. doi: 10.1210/endo-121-6-2141. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sara V. R., Hall K. Insulin-like growth factors and their binding proteins. Physiol Rev. 1990 Jul;70(3):591–614. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1990.70.3.591. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scharfmann R., Corvol M., Czernichow P. Characterization of insulinlike growth factor I produced by fetal rat pancreatic islets. Diabetes. 1989 Jun;38(6):686–690. doi: 10.2337/diab.38.6.686. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmid C., Steiner T., Froesch E. R. Insulin-like growth factor I supports differentiation of cultured osteoblast-like cells. FEBS Lett. 1984 Jul 23;173(1):48–52. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(84)81015-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith P. J., Wise L. S., Berkowitz R., Wan C., Rubin C. S. Insulin-like growth factor-I is an essential regulator of the differentiation of 3T3-L1 adipocytes. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jul 5;263(19):9402–9408. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swenne I., Hill D. J., Strain A. J., Milner R. D. Growth hormone regulation of somatomedin C/insulin-like growth factor I production and DNA replication in fetal rat islets in tissue culture. Diabetes. 1987 Mar;36(3):288–294. doi: 10.2337/diab.36.3.288. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swenne I. The role of glucose in the in vitro regulation of cell cycle kinetics and proliferation of fetal pancreatic B-cells. Diabetes. 1982 Sep;31(9):754–760. doi: 10.2337/diab.31.9.754. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Schravendijk C. F., Foriers A., Van den Brande J. L., Pipeleers D. G. Evidence for the presence of type I insulin-like growth factor receptors on rat pancreatic A and B cells. Endocrinology. 1987 Nov;121(5):1784–1788. doi: 10.1210/endo-121-5-1784. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]