Abstract
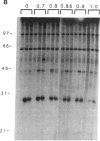
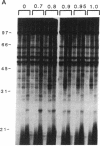
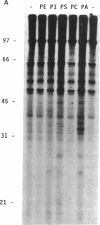
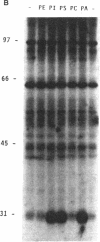
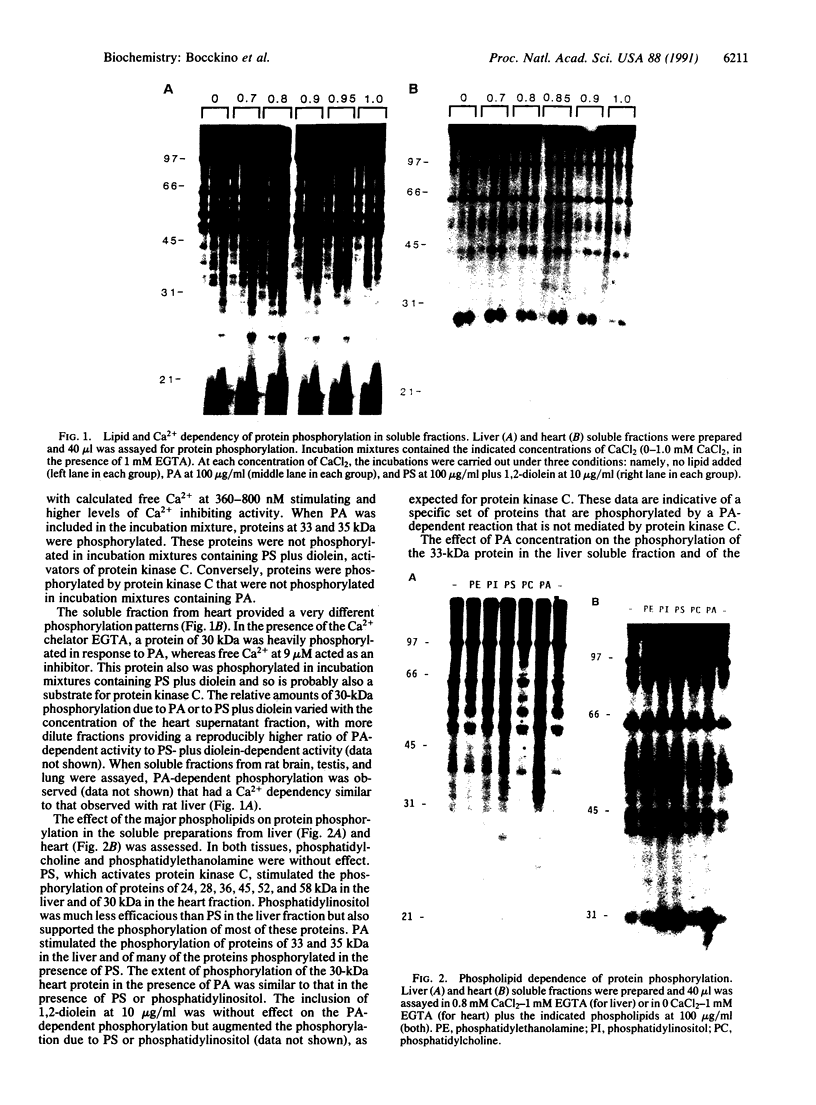
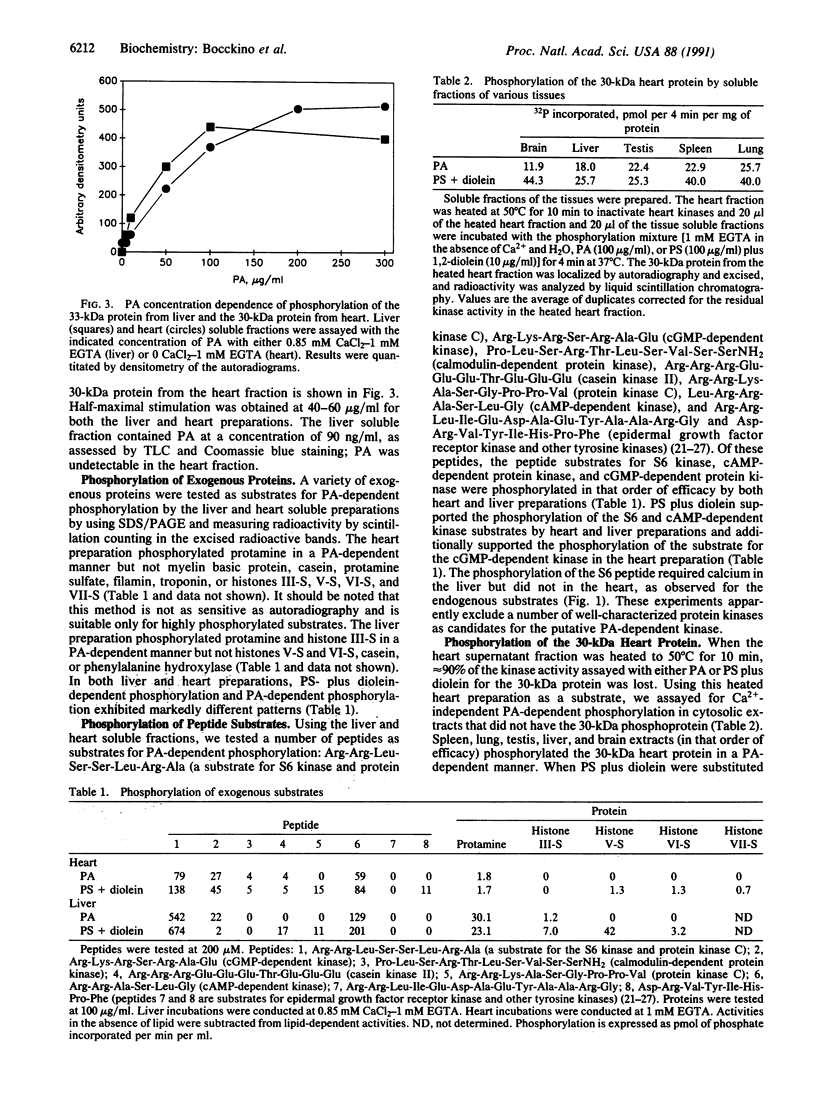
Phosphatidate-dependent protein phosphorylation was observed in soluble extracts from rat liver, brain, lung, and testis. The phosphorylation was stimulated by free Ca2+ in the range of 360-800 nM. Incubation mixtures containing phosphatidate provided markedly different profiles of protein phosphorylation from those with phosphatidylserine plus 1,2-diolein. Phosphatidate-dependent phosphorylation of a 30-kDa protein in the soluble fraction from heart was also observed. This phosphorylation did not require Ca2+. Soluble fractions from liver, testis, brain, and lung phosphorylated the 30-kDa heart protein in a phosphatidate-dependent Ca(2+)-independent manner. We propose that part of the action of phosphatidate in cells may be mediated by a protein kinase(s).
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Balsinde J., Diez E., Mollinedo F. Phosphatidylinositol-specific phospholipase D: a pathway for generation of a second messenger. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 Jul 29;154(2):502–508. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(88)90168-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bocckino S. B., Blackmore P. F., Wilson P. B., Exton J. H. Phosphatidate accumulation in hormone-treated hepatocytes via a phospholipase D mechanism. J Biol Chem. 1987 Nov 5;262(31):15309–15315. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bocckino S. B., Wilson P., Exton J. H. An enzymatic assay for picomole levels of phosphatidate. Anal Biochem. 1989 Jul;180(1):24–27. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(89)90083-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bollag W. B., Barrett P. Q., Isales C. M., Liscovitch M., Rasmussen H. A potential role for phospholipase-D in the angiotensin-II-induced stimulation of aldosterone secretion from bovine adrenal glomerulosa cells. Endocrinology. 1990 Sep;127(3):1436–1443. doi: 10.1210/endo-127-3-1436. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burns D. J., Bloomenthal J., Lee M. H., Bell R. M. Expression of the alpha, beta II, and gamma protein kinase C isozymes in the baculovirus-insect cell expression system. Purification and characterization of the individual isoforms. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jul 15;265(20):12044–12051. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casnellie J. E., Harrison M. L., Pike L. J., Hellström K. E., Krebs E. G. Phosphorylation of synthetic peptides by a tyrosine protein kinase from the particulate fraction of a lymphoma cell line. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jan;79(2):282–286. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.2.282. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cockcroft S. Ca2+-dependent conversion of phosphatidylinositol to phosphatidate in neutrophils stimulated with fMet-Leu-Phe or ionophore A23187. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1984 Aug 15;795(1):37–46. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(84)90102-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Exton J. H. Signaling through phosphatidylcholine breakdown. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jan 5;265(1):1–4. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glass D. B., Krebs E. G. Phosphorylation by guanosine 3':5'-monophosphate-dependent protein kinase of synthetic peptide analogs of a site phosphorylated in histone H2B. J Biol Chem. 1982 Feb 10;257(3):1196–1200. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hokin-Neaverson M. Acetylcholine causes a net decrease in phosphatidylinositol and a net increase in phosphatidic acid in mouse pancreas. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1974 Jun 4;58(3):763–768. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(74)80483-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaibuchi K., Takai Y., Nishizuka Y. Cooperative roles of various membrane phospholipids in the activation of calcium-activated, phospholipid-dependent protein kinase. J Biol Chem. 1981 Jul 25;256(14):7146–7149. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kemp B. E., Graves D. J., Benjamini E., Krebs E. G. Role of multiple basic residues in determining the substrate specificity of cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase. J Biol Chem. 1977 Jul 25;252(14):4888–4894. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knauss T. C., Jaffer F. E., Abboud H. E. Phosphatidic acid modulates DNA synthesis, phospholipase C, and platelet-derived growth factor mRNAs in cultured mesangial cells. Role of protein kinase C. J Biol Chem. 1990 Aug 25;265(24):14457–14463. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kroll M. H., Zavoico G. B., Schafer A. I. Second messenger function of phosphatidic acid in platelet activation. J Cell Physiol. 1989 Jun;139(3):558–564. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041390315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuenzel E. A., Krebs E. G. A synthetic peptide substrate specific for casein kinase II. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Feb;82(3):737–741. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.3.737. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liscovitch M., Amsterdam A. Gonadotropin-releasing hormone activates phospholipase D in ovarian granulosa cells. Possible role in signal transduction. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jul 15;264(20):11762–11767. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGhee J. G., Shoback D. M. Effects of phosphatidic acid on parathyroid hormone release, intracellular free Ca2+, and inositol phosphates in dispersed bovine parathyroid cells. Endocrinology. 1990 Feb;126(2):899–907. doi: 10.1210/endo-126-2-899. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Metz S. A., Dunlop M. Stimulation of insulin release by phospholipase D. A potential role for endogenous phosphatidic acid in pancreatic islet function. Biochem J. 1990 Sep 1;270(2):427–435. doi: 10.1042/bj2700427. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moolenaar W. H., Kruijer W., Tilly B. C., Verlaan I., Bierman A. J., de Laat S. W. Growth factor-like action of phosphatidic acid. Nature. 1986 Sep 11;323(6084):171–173. doi: 10.1038/323171a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murayama T., Ui M. Phosphatidic acid may stimulate membrane receptors mediating adenylate cyclase inhibition and phospholipid breakdown in 3T3 fibroblasts. J Biol Chem. 1987 Apr 25;262(12):5522–5529. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Negami A. I., Sasaki H., Yamamura H. Activation of phosphorylase kinase through autophosphorylation by membrane component phospholipids. Eur J Biochem. 1986 Jun 16;157(3):597–603. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1986.tb09707.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Negami A. I., Sasaki H., Yamamura H. Stimulating effect of phosphatidic acid on autophosphorylation of phosphorylase kinase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1985 Sep 16;131(2):712–719. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(85)91296-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Brian C. A., Lawrence D. S., Kaiser E. T., Weinstein I. B. Protein kinase C phosphorylates the synthetic peptide Arg-Arg-Lys-Ala-Ser-Gly-Pro-Pro-Val in the presence of phospholipid plus either Ca2+ or a phorbol ester tumor promoter. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1984 Oct 15;124(1):296–302. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(84)90951-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearson R. B., Woodgett J. R., Cohen P., Kemp B. E. Substrate specificity of a multifunctional calmodulin-dependent protein kinase. J Biol Chem. 1985 Nov 25;260(27):14471–14476. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelech S. L., Olwin B. B., Krebs E. G. Fibroblast growth factor treatment of Swiss 3T3 cells activates a subunit S6 kinase that phosphorylates a synthetic peptide substrate. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Aug;83(16):5968–5972. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.16.5968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Putney J. W., Jr, Weiss S. J., Van De Walle C. M., Haddas R. A. Is phosphatidic acid a calcium ionophore under neurohumoral control? Nature. 1980 Mar 27;284(5754):345–347. doi: 10.1038/284345a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reinhold S. L., Prescott S. M., Zimmerman G. A., McIntyre T. M. Activation of human neutrophil phospholipase D by three separable mechanisms. FASEB J. 1990 Feb 1;4(2):208–214. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.4.2.2105252. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roskoski R., Jr Assays of protein kinase. Methods Enzymol. 1983;99:3–6. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)99034-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salmon D. M., Honeyman T. W. Proposed mechanism of cholinergic action in smooth muscle. Nature. 1980 Mar 27;284(5754):344–345. doi: 10.1038/284344a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schimmel R. J., Honeyman T. W., McMahon K. K., Serio R., Clark R. B. Inhibition of cyclic AMP accumulation in hamster adipocytes with phosphatidic acid: differences and similarities with alpha adrenergic effects. J Cyclic Nucleotide Res. 1980;6(6):437–449. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sekiguchi K., Tsukuda M., Ase K., Kikkawa U., Nishizuka Y. Mode of activation and kinetic properties of three distinct forms of protein kinase C from rat brain. J Biochem. 1988 May;103(5):759–765. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a122343. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siegmann D. W. Stimulation of quiescent 3T3 cells by phosphatidic acid-containing liposomes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1987 May 29;145(1):228–233. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(87)91310-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu C. L., Tsai M. H., Stacey D. W. Cellular ras activity and phospholipid metabolism. Cell. 1988 Jan 15;52(1):63–71. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90531-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]