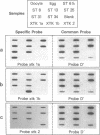
Abstract
Insulin and insulin-like growth factor I (IGF-I) initiate their metabolic, growth, and differentiation effects through binding to the insulin receptor and the IGF-I receptor, two members of the tyrosine kinase family of receptors. To study the role of these peptides and receptors in early development, we used the polymerase chain reaction and embryo-derived RNA to generate partial cDNA sequences of the insulin receptor and IGF-I receptor from the amphibian Xenopus laevis. Three unique tyrosine kinase-related sequences were obtained. Two of the nucleotide sequences, XTK 1a and XTK 1b, corresponded to peptide that share 92% amino acid identity, and each is 89% identical to the human insulin receptor. The third sequence, XTK 2, corresponds to a peptide that has 92% amino acid identity with the human IGF-I receptor but only 80% identity with XTK 1a and XTK 1b. On the basis of these similarities, the pattern of conserved amino acids, and the tetraploid nature of the Xenopus genome, we suggest that XTK 1a and XTK 1b most likely represent the product of two different nonallelic insulin receptor genes, while XTK 2 may be one of the probable two Xenopus IGF-I receptor genes. By reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction and gene-specific hybridization, expression of the three XTK sequences was detected in the oocyte, unfertilized egg, and embryos through gastrulation, neurulation, and tailbud stages. Competition binding assays with Xenopus membrane preparations demonstrated insulin receptors and IGF-I receptors in older tadpoles. IGF-I receptors were also present in oocytes, eggs, and gastrula embryos. By contrast, insulin binding was present but atypical in oocytes and was barely detected in eggs and gastrula embryos. The expression of receptors for insulin and IGF-I in early Xenopus embryos and their apparent distinct developmental regulation suggest that these molecules and their ligands may be important in early Xenopus development.
Full text
PDF

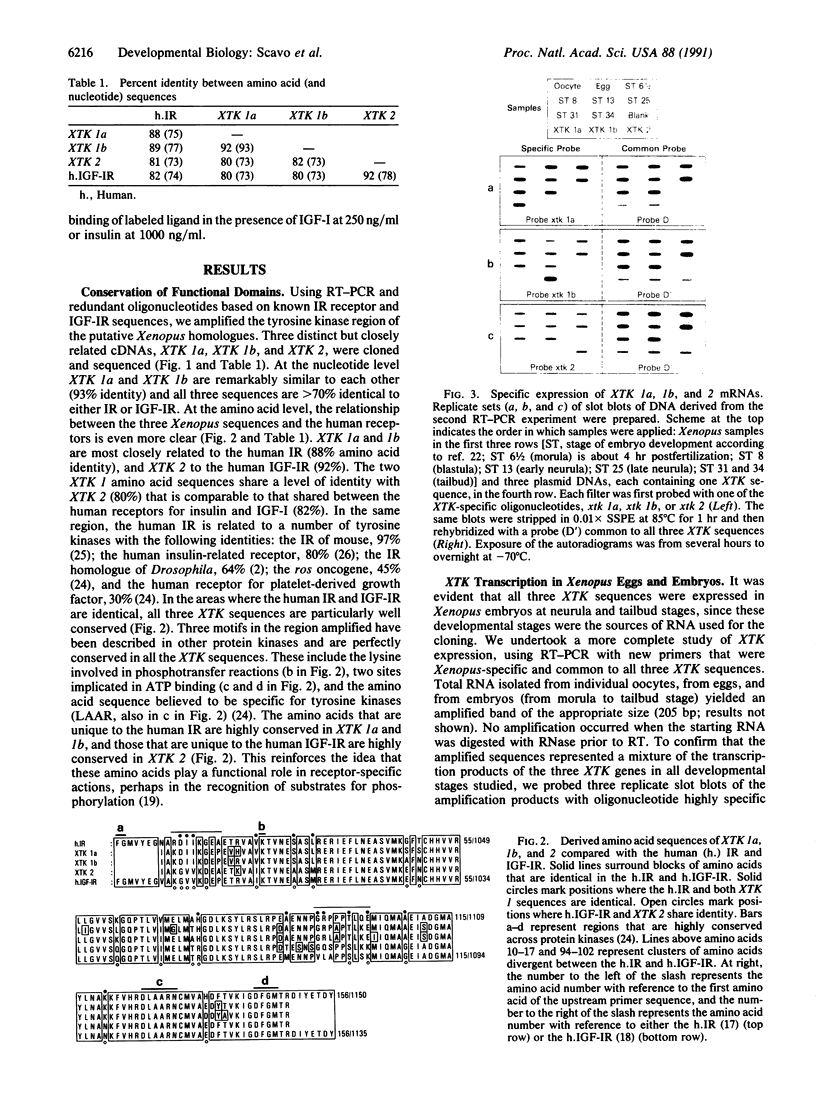
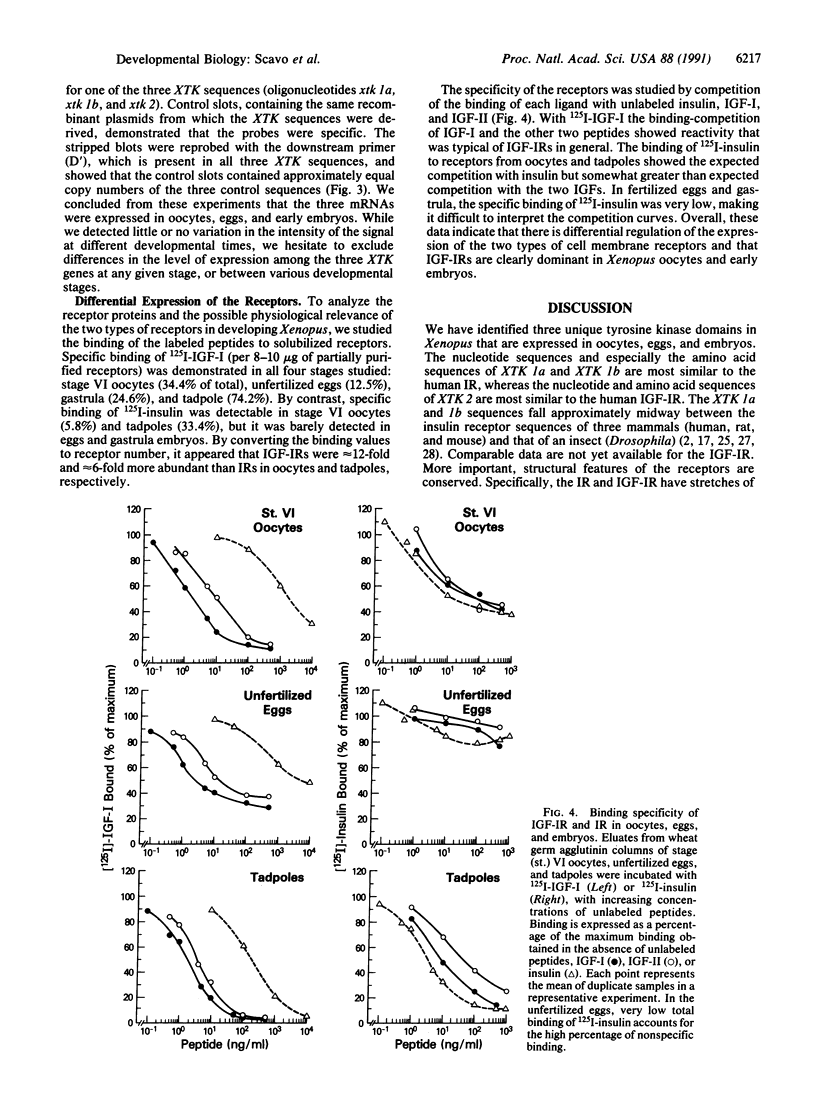

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alemany J., Zelenka P., Serrano J., de Pablo F. Insulin-like growth factor I and insulin regulate delta-crystallin gene expression in developing lens. J Biol Chem. 1989 Oct 15;264(29):17559–17563. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Czech M. P. Signal transmission by the insulin-like growth factors. Cell. 1989 Oct 20;59(2):235–238. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90281-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ebina Y., Ellis L., Jarnagin K., Edery M., Graf L., Clauser E., Ou J. H., Masiarz F., Kan Y. W., Goldfine I. D. The human insulin receptor cDNA: the structural basis for hormone-activated transmembrane signalling. Cell. 1985 Apr;40(4):747–758. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90334-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flores-Riveros J. R., Sibley E., Kastelic T., Lane M. D. Substrate phosphorylation catalyzed by the insulin receptor tyrosine kinase. Kinetic correlation to autophosphorylation of specific sites in the beta subunit. J Biol Chem. 1989 Dec 25;264(36):21557–21572. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garofalo R. S., Rosen O. M. Tissue localization of Drosophila melanogaster insulin receptor transcripts during development. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Apr;8(4):1638–1647. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.4.1638. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Girbau M., Bassas L., Alemany J., de Pablo F. In situ autoradiography and ligand-dependent tyrosine kinase activity reveal insulin receptors and insulin-like growth factor I receptors in prepancreatic chicken embryos. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Aug;86(15):5868–5872. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.15.5868. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Girbau M., Gomez J. A., Lesniak M. A., de Pablo F. Insulin and insulin-like growth factor I both stimulate metabolism, growth, and differentiation in the postneurula chick embryo. Endocrinology. 1987 Oct;121(4):1477–1482. doi: 10.1210/endo-121-4-1477. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein B. J., Dudley A. L. The rat insulin receptor: primary structure and conservation of tissue-specific alternative messenger RNA splicing. Mol Endocrinol. 1990 Feb;4(2):235–244. doi: 10.1210/mend-4-2-235. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hainaut P., Kowalski A., Giorgetti S., Baron V., Van Obberghen E. Insulin and insulin-like-growth-factor-I (IGF-I) receptors in Xenopus laevis oocytes. Comparison with insulin receptors from liver and muscle. Biochem J. 1991 Feb 1;273(Pt 3):673–678. doi: 10.1042/bj2730673. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanks S. K., Quinn A. M., Hunter T. The protein kinase family: conserved features and deduced phylogeny of the catalytic domains. Science. 1988 Jul 1;241(4861):42–52. doi: 10.1126/science.3291115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heyner S., Smith R. M., Schultz G. A. Temporally regulated expression of insulin and insulin-like growth factors and their receptors in early mammalian development. Bioessays. 1989 Dec;11(6):171–176. doi: 10.1002/bies.950110604. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janicot M., Lane M. D. Activation of glucose uptake by insulin and insulin-like growth factor I in Xenopus oocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Apr;86(8):2642–2646. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.8.2642. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kajimoto Y., Rotwein P. Evolution of insulin-like growth factor I (IGF-I): structure and expression of an IGF-I precursor from Xenopus laevis. Mol Endocrinol. 1990 Feb;4(2):217–226. doi: 10.1210/mend-4-2-217. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kintner C. R., Melton D. A. Expression of Xenopus N-CAM RNA in ectoderm is an early response to neural induction. Development. 1987 Mar;99(3):311–325. doi: 10.1242/dev.99.3.311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lammers R., Gray A., Schlessinger J., Ullrich A. Differential signalling potential of insulin- and IGF-1-receptor cytoplasmic domains. EMBO J. 1989 May;8(5):1369–1375. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03517.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ludwig S., Muller-Wieland D., Goldstein B. J., Kahn C. R. The insulin receptor gene and its expression in insulin-resistant mice. Endocrinology. 1988 Jul;123(1):594–600. doi: 10.1210/endo-123-1-594. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maller J. L., Pike L. J., Freidenberg G. R., Cordera R., Stith B. J., Olefsky J. M., Krebs E. G. Increased phosphorylation of ribosomal protein S6 following microinjection of insulin receptor-kinase into Xenopus oocytes. Nature. 1986 Apr 3;320(6061):459–461. doi: 10.1038/320459a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller D. S. Stimulation of RNA and protein synthesis by intracellular insulin. Science. 1988 Apr 22;240(4851):506–509. doi: 10.1126/science.2451860. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller D. S. Stimulation of protein synthesis in stage IV Xenopus oocytes by microinjected insulin. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jun 25;264(18):10438–10446. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moxham C. P., Duronio V., Jacobs S. Insulin-like growth factor I receptor beta-subunit heterogeneity. Evidence for hybrid tetramers composed of insulin-like growth factor I and insulin receptor heterodimers. J Biol Chem. 1989 Aug 5;264(22):13238–13244. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petruzzelli L., Herrera R., Arenas-Garcia R., Fernandez R., Birnbaum M. J., Rosen O. M. Isolation of a Drosophila genomic sequence homologous to the kinase domain of the human insulin receptor and detection of the phosphorylated Drosophila receptor with an anti-peptide antibody. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jul;83(13):4710–4714. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.13.4710. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sadler S. E., Maller J. L. In vivo regulation of cyclic AMP phosphodiesterase in Xenopus oocytes. Stimulation by insulin and insulin-like growth factor 1. J Biol Chem. 1987 Aug 5;262(22):10644–10650. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakanoue Y., Hashimoto E., Nakamura S., Yamamura H. Insulin-stimulated serine kinase in Xenopus oocyte plasma membrane. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 Feb 15;150(3):1176–1184. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(88)90753-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scavo L. M., Serrano J., Roth J., de Pablo F. Genes for the insulin receptor and the insulin-like growth factor I receptor are expressed in the chicken embryo blastoderm and throughout organogenesis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1991 May 15;176(3):1393–1401. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(91)90441-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shier P., Watt V. M. Primary structure of a putative receptor for a ligand of the insulin family. J Biol Chem. 1989 Sep 5;264(25):14605–14608. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shuldiner A. R., Nirula A., Scott L. A., Roth J. Evidence that Xenopus laevis contains two different nonallelic insulin-like growth factor-I genes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1990 Jan 15;166(1):223–230. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(90)91934-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shuldiner A. R., Phillips S., Roberts C. T., Jr, LeRoith D., Roth J. Xenopus laevis contains two nonallelic preproinsulin genes. cDNA cloning and evolutionary perspective. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jun 5;264(16):9428–9432. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Treadway J. L., Morrison B. D., Goldfine I. D., Pessin J. E. Assembly of insulin/insulin-like growth factor-1 hybrid receptors in vitro. J Biol Chem. 1989 Dec 25;264(36):21450–21453. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ullrich A., Gray A., Tam A. W., Yang-Feng T., Tsubokawa M., Collins C., Henzel W., Le Bon T., Kathuria S., Chen E. Insulin-like growth factor I receptor primary structure: comparison with insulin receptor suggests structural determinants that define functional specificity. EMBO J. 1986 Oct;5(10):2503–2512. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04528.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Pablo F., Girbau M., Gomez J. A., Hernandez E., Roth J. Insulin antibodies retard and insulin accelerates growth and differentiation in early embryos. Diabetes. 1985 Oct;34(10):1063–1067. doi: 10.2337/diab.34.10.1063. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Pablo F., Scott L. A., Roth J. Insulin and insulin-like growth factor I in early development: peptides, receptors and biological events. Endocr Rev. 1990 Nov;11(4):558–577. doi: 10.1210/edrv-11-4-558. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]