Abstract
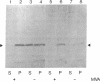
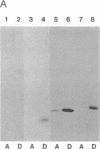
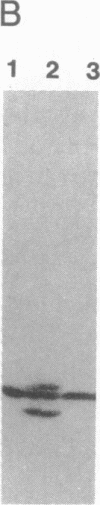
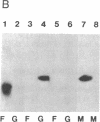
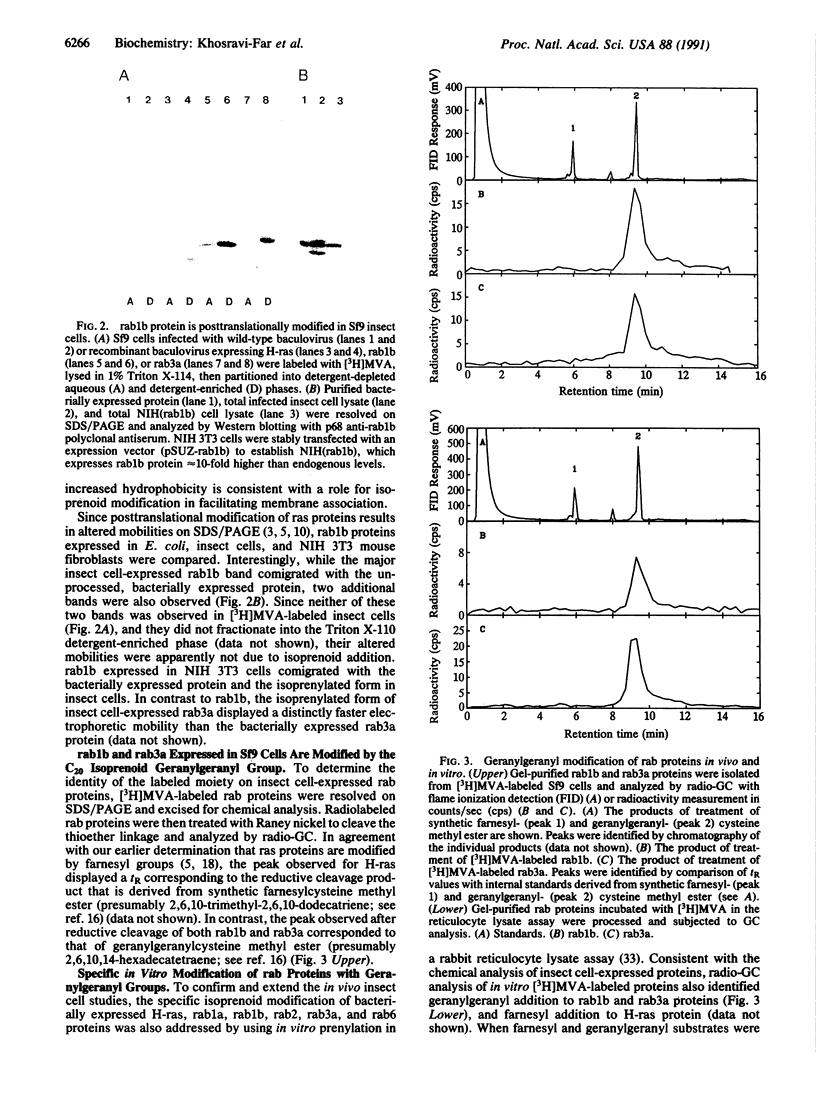
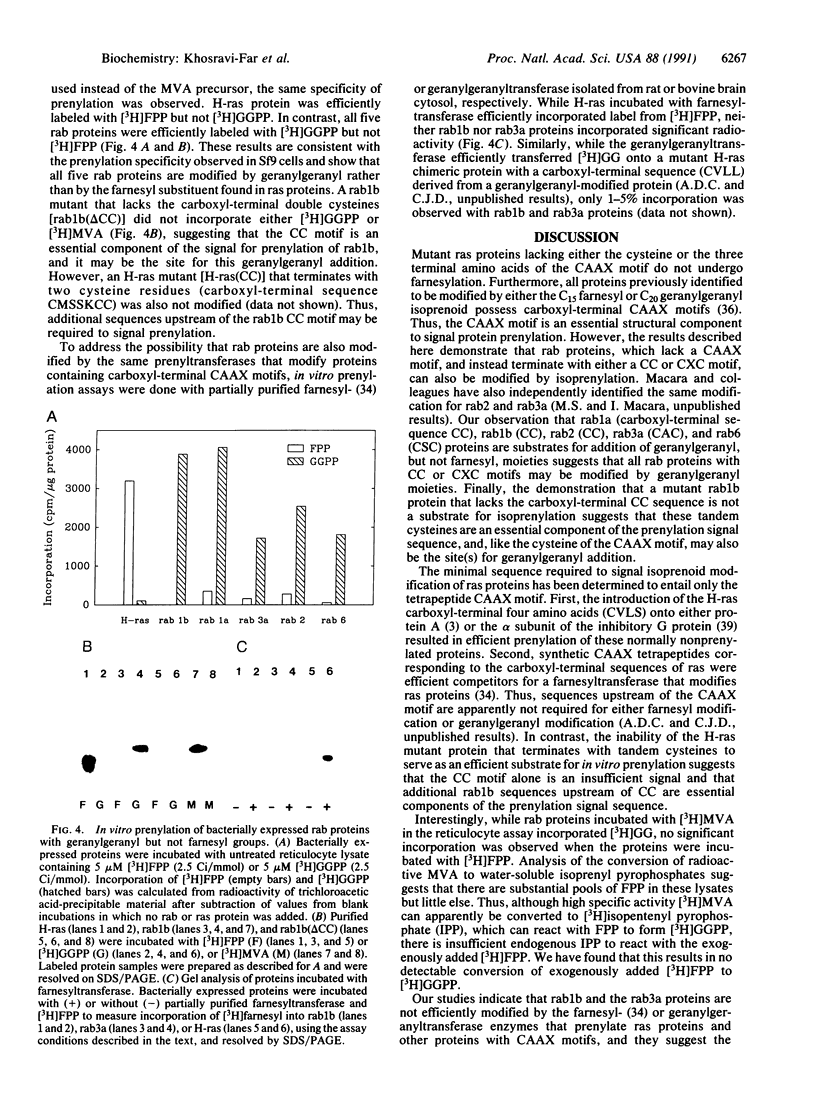
Mevalonate starvation of hamster fibroblasts resulted in a shift of rab1b from the membrane to the cytosolic fraction, suggesting that rab1b depends upon an isoprenoid modification for its membrane localization. rab1b and rab3a proteins expressed in insect cells incorporated a product of [3H]mevalonate, and gas chromatography analysis of material released by Raney nickel cleavage demonstrated that rab1b and rab3a are modified by geranylgeranyl groups. Additionally, in vitro prenylation analysis demonstrated farnesyl modification of H-ras but geranylgeranyl modification of five rab proteins (1a, 1b, 2, 3a, and 6). Together, these results suggest that the carboxyl-terminal CC/CXC motifs (X = any amino acid) specifically signal for addition of geranylgeranyl, but not farnesyl, groups. A rab1b mutant protein lacking the two carboxyl-terminal cysteine residues was not prenylated in vitro. However, since a mutant H-ras protein that terminates with tandem cysteine residues was also not modified, the CC motif may be essential, but not sufficient, to signal prenylation of rab1b. Finally, rab1b and rab3a proteins were not efficient substrates for either farnesyl- or geranylgeranyltransferase activities that modify CAAX-containing proteins (A = any aliphatic amino acid). Therefore, rab proteins may be modified by a prenyltransferase(s) distinct from the prenyltransferases that modify carboxyl-terminal CAAX proteins.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Balch W. E. Small GTP-binding proteins in vesicular transport. Trends Biochem Sci. 1990 Dec;15(12):473–477. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(90)90301-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bordier C. Phase separation of integral membrane proteins in Triton X-114 solution. J Biol Chem. 1981 Feb 25;256(4):1604–1607. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bourne H. R. Do GTPases direct membrane traffic in secretion? Cell. 1988 Jun 3;53(5):669–671. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90081-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buss J. E., Quilliam L. A., Kato K., Casey P. J., Solski P. A., Wong G., Clark R., McCormick F., Bokoch G. M., Der C. J. The COOH-terminal domain of the Rap1A (Krev-1) protein is isoprenylated and supports transformation by an H-Ras:Rap1A chimeric protein. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Mar;11(3):1523–1530. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.3.1523. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casey P. J., Solski P. A., Der C. J., Buss J. E. p21ras is modified by a farnesyl isoprenoid. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Nov;86(21):8323–8327. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.21.8323. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chavrier P., Parton R. G., Hauri H. P., Simons K., Zerial M. Localization of low molecular weight GTP binding proteins to exocytic and endocytic compartments. Cell. 1990 Jul 27;62(2):317–329. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90369-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clarke S., Vogel J. P., Deschenes R. J., Stock J. Posttranslational modification of the Ha-ras oncogene protein: evidence for a third class of protein carboxyl methyltransferases. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jul;85(13):4643–4647. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.13.4643. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davisson V. J., Woodside A. B., Poulter C. D. Synthesis of allylic and homoallylic isoprenoid pyrophosphates. Methods Enzymol. 1985;110:130–144. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(85)10068-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deschenes R. J., Stimmel J. B., Clarke S., Stock J., Broach J. R. RAS2 protein of Saccharomyces cerevisiae is methyl-esterified at its carboxyl terminus. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jul 15;264(20):11865–11873. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Downward J. The ras superfamily of small GTP-binding proteins. Trends Biochem Sci. 1990 Dec;15(12):469–472. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(90)90300-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farnsworth C. C., Gelb M. H., Glomset J. A. Identification of geranylgeranyl-modified proteins in HeLa cells. Science. 1990 Jan 19;247(4940):320–322. doi: 10.1126/science.2296721. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischer von Mollard G., Mignery G. A., Baumert M., Perin M. S., Hanson T. J., Burger P. M., Jahn R., Südhof T. C. rab3 is a small GTP-binding protein exclusively localized to synaptic vesicles. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Mar;87(5):1988–1992. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.5.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujiyama A., Tamanoi F. RAS2 protein of Saccharomyces cerevisiae undergoes removal of methionine at N terminus and removal of three amino acids at C terminus. J Biol Chem. 1990 Feb 25;265(6):3362–3368. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glomset J. A., Gelb M. H., Farnsworth C. C. Prenyl proteins in eukaryotic cells: a new type of membrane anchor. Trends Biochem Sci. 1990 Apr;15(4):139–142. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(90)90213-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goud B., Zahraoui A., Tavitian A., Saraste J. Small GTP-binding protein associated with Golgi cisternae. Nature. 1990 Jun 7;345(6275):553–556. doi: 10.1038/345553a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gutierrez L., Magee A. I., Marshall C. J., Hancock J. F. Post-translational processing of p21ras is two-step and involves carboxyl-methylation and carboxy-terminal proteolysis. EMBO J. 1989 Apr;8(4):1093–1098. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03478.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall A. The cellular functions of small GTP-binding proteins. Science. 1990 Aug 10;249(4969):635–640. doi: 10.1126/science.2116664. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hancock J. F., Magee A. I., Childs J. E., Marshall C. J. All ras proteins are polyisoprenylated but only some are palmitoylated. Cell. 1989 Jun 30;57(7):1167–1177. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90054-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson J. H., Cochrane C. G., Bourne J. R., Solski P. A., Buss J. E., Der C. J. Farnesol modification of Kirsten-ras exon 4B protein is essential for transformation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Apr;87(8):3042–3046. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.8.3042. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones T. L., Spiegel A. M. Isoprenylation of an inhibitory G protein alpha subunit occurs only upon mutagenesis of the carboxyl terminus. J Biol Chem. 1990 Nov 15;265(32):19389–19392. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawata M., Farnsworth C. C., Yoshida Y., Gelb M. H., Glomset J. A., Takai Y. Posttranslationally processed structure of the human platelet protein smg p21B: evidence for geranylgeranylation and carboxyl methylation of the C-terminal cysteine. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Nov;87(22):8960–8964. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.22.8960. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowe P. N., Sydenham M., Page M. J. The Ha-ras protein, p21, is modified by a derivative of mevalonate and methyl-esterified when expressed in the insect/baculovirus system. Oncogene. 1990 Jul;5(7):1045–1048. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maltese W. A., Robishaw J. D. Isoprenylation of C-terminal cysteine in a G-protein gamma subunit. J Biol Chem. 1990 Oct 25;265(30):18071–18074. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mumby S. M., Casey P. J., Gilman A. G., Gutowski S., Sternweis P. C. G protein gamma subunits contain a 20-carbon isoprenoid. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Aug;87(15):5873–5877. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.15.5873. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quilliam L. A., Der C. J., Clark R., O'Rourke E. C., Zhang K., McCormick F., Bokoch G. M. Biochemical characterization of baculovirus-expressed rap1A/Krev-1 and its regulation by GTPase-activating proteins. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Jun;10(6):2901–2908. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.6.2901. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reiss Y., Goldstein J. L., Seabra M. C., Casey P. J., Brown M. S. Inhibition of purified p21ras farnesyl:protein transferase by Cys-AAX tetrapeptides. Cell. 1990 Jul 13;62(1):81–88. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90242-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rilling H. C., Breunger E., Epstein W. W., Crain P. F. Prenylated proteins: the structure of the isoprenoid group. Science. 1990 Jan 19;247(4940):318–320. doi: 10.1126/science.2296720. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schafer W. R., Kim R., Sterne R., Thorner J., Kim S. H., Rine J. Genetic and pharmacological suppression of oncogenic mutations in ras genes of yeast and humans. Science. 1989 Jul 28;245(4916):379–385. doi: 10.1126/science.2569235. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sinensky M., Beck L. A., Leonard S., Evans R. Differential inhibitory effects of lovastatin on protein isoprenylation and sterol synthesis. J Biol Chem. 1990 Nov 15;265(32):19937–19941. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sinensky M., Logel J. Defective macromolecule biosynthesis and cell-cycle progression in a mammalian cell starved for mevalonate. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 May;82(10):3257–3261. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.10.3257. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Studier F. W., Moffatt B. A. Use of bacteriophage T7 RNA polymerase to direct selective high-level expression of cloned genes. J Mol Biol. 1986 May 5;189(1):113–130. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90385-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Touchot N., Zahraoui A., Vielh E., Tavitian A. Biochemical properties of the YPT-related rab1B protein. Comparison with rab1A. FEBS Lett. 1989 Oct 9;256(1-2):79–84. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(89)81722-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tucker J., Sczakiel G., Feuerstein J., John J., Goody R. S., Wittinghofer A. Expression of p21 proteins in Escherichia coli and stereochemistry of the nucleotide-binding site. EMBO J. 1986 Jun;5(6):1351–1358. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04366.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vorburger K., Kitten G. T., Nigg E. A. Modification of nuclear lamin proteins by a mevalonic acid derivative occurs in reticulocyte lysates and requires the cysteine residue of the C-terminal CXXM motif. EMBO J. 1989 Dec 20;8(13):4007–4013. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08583.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willumsen B. M., Christensen A., Hubbert N. L., Papageorge A. G., Lowy D. R. The p21 ras C-terminus is required for transformation and membrane association. Nature. 1984 Aug 16;310(5978):583–586. doi: 10.1038/310583a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willumsen B. M., Norris K., Papageorge A. G., Hubbert N. L., Lowy D. R. Harvey murine sarcoma virus p21 ras protein: biological and biochemical significance of the cysteine nearest the carboxy terminus. EMBO J. 1984 Nov;3(11):2581–2585. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02177.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamane H. K., Farnsworth C. C., Xie H. Y., Evans T., Howald W. N., Gelb M. H., Glomset J. A., Clarke S., Fung B. K. Membrane-binding domain of the small G protein G25K contains an S-(all-trans-geranylgeranyl)cysteine methyl ester at its carboxyl terminus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jan 1;88(1):286–290. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.1.286. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamane H. K., Farnsworth C. C., Xie H. Y., Howald W., Fung B. K., Clarke S., Gelb M. H., Glomset J. A. Brain G protein gamma subunits contain an all-trans-geranylgeranylcysteine methyl ester at their carboxyl termini. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Aug;87(15):5868–5872. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.15.5868. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zahraoui A., Touchot N., Chardin P., Tavitian A. The human Rab genes encode a family of GTP-binding proteins related to yeast YPT1 and SEC4 products involved in secretion. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jul 25;264(21):12394–12401. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]