Abstract
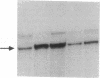
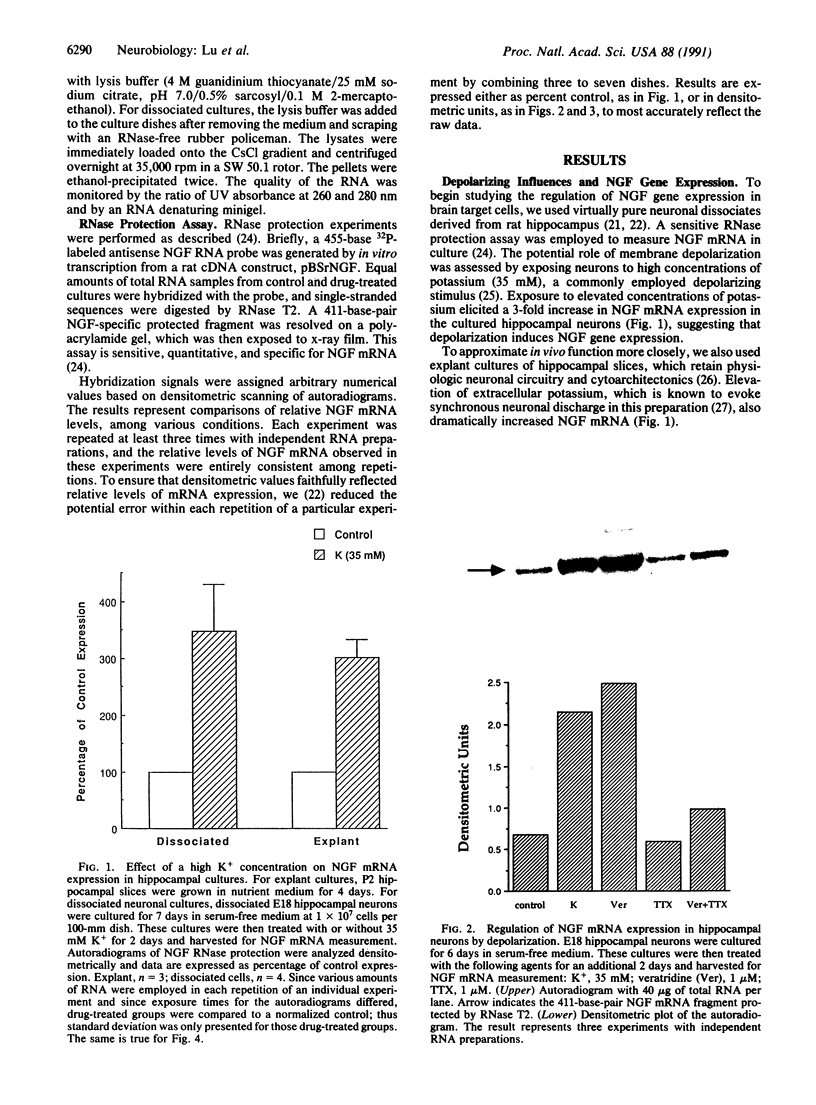
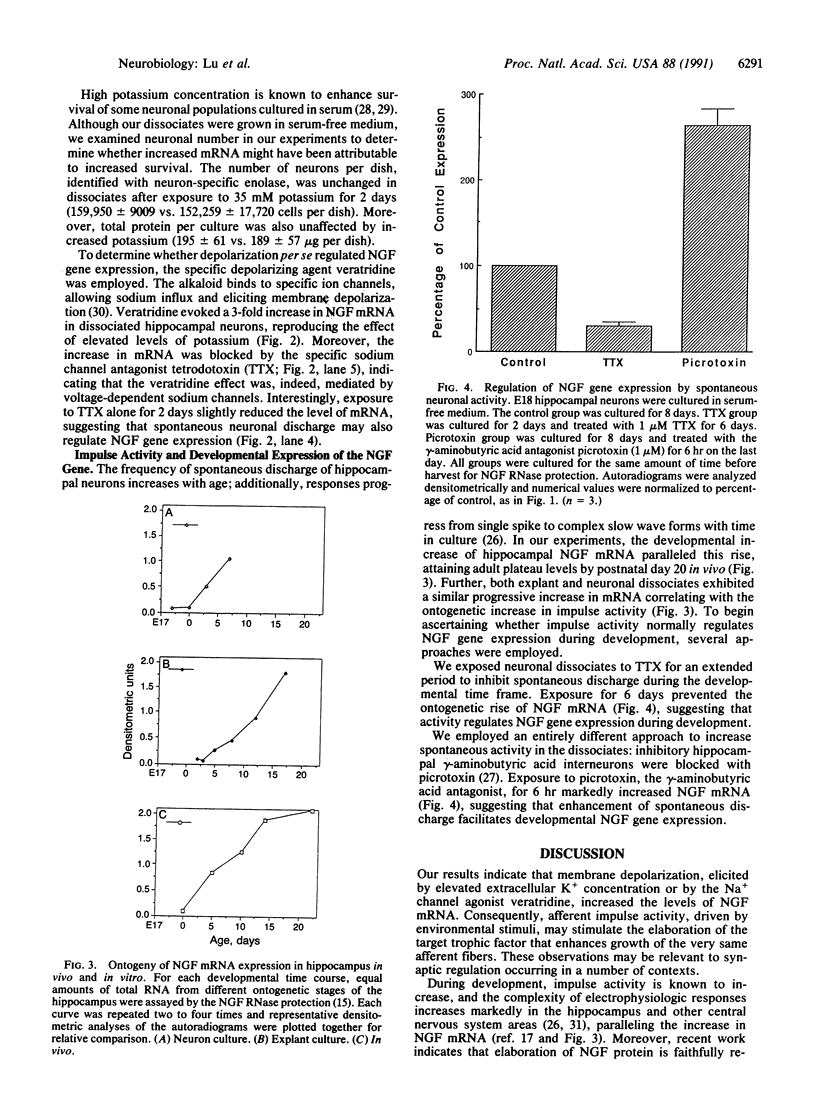
Although trophic factors and neuronal activity have been implicated in regulating functional synaptic circuits, the relationship of trophic interaction to impulse activity in synaptogenesis remains unclear. Using cultured hippocampus as a model system, we provide direct evidence that depolarization and impulse activity specifically increase nerve growth factor gene expression in neurons. Depolarizing stimuli, such as a high K+ concentration or the Na+ channel agonist veratridine, elicited a 3-fold increase of nerve growth factor mRNA levels in both explant and dissociated cultures. Blockade of depolarization by tetrodotoxin prevented the increase of neuronal nerve growth factor mRNA. Further, nerve growth factor gene expression was stimulated by picrotoxin, a gamma-aminobutyric acid antagonist frequently used to enhance hippocampal neuronal activity. Impulse regulation of trophic gene function may be relevant to developmental synaptogenesis and synaptic strengthening in learning and memory.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ayer-LeLievre C., Olson L., Ebendal T., Seiger A., Persson H. Expression of the beta-nerve growth factor gene in hippocampal neurons. Science. 1988 Jun 3;240(4857):1339–1341. doi: 10.1126/science.2897715. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barde Y. A. What, if anything, is a neurotrophic factor? Trends Neurosci. 1988 Aug;11(8):343–346. doi: 10.1016/0166-2236(88)90055-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Black I. B. Trophic molecules and evolution of the nervous system. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Nov;83(21):8249–8252. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.21.8249. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown T. H., Chapman P. F., Kairiss E. W., Keenan C. L. Long-term synaptic potentiation. Science. 1988 Nov 4;242(4879):724–728. doi: 10.1126/science.2903551. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dichter M. A., Ayala G. F. Cellular mechanisms of epilepsy: a status report. Science. 1987 Jul 10;237(4811):157–164. doi: 10.1126/science.3037700. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dreyfus C. F. Effects of nerve growth factor on cholinergic brain neurons. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1989 Apr;10(4):145–149. doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(89)90166-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dreyfus C. F., Friedman W. J., Markey K. A., Black I. B. Depolarizing stimuli increase tyrosine hydroxylase in the mouse locus coeruleus in culture. Brain Res. 1986 Aug 6;379(2):216–222. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(86)90774-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edwards R. H., Selby M. J., Mobley W. C., Weinrich S. L., Hruby D. E., Rutter W. J. Processing and secretion of nerve growth factor: expression in mammalian cells with a vaccinia virus vector. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Jun;8(6):2456–2464. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.6.2456. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evers J., Laser M., Sun Y. A., Xie Z. P., Poo M. M. Studies of nerve-muscle interactions in Xenopus cell culture: analysis of early synaptic currents. J Neurosci. 1989 May;9(5):1523–1539. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.09-05-01523.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gall C. M., Isackson P. J. Limbic seizures increase neuronal production of messenger RNA for nerve growth factor. Science. 1989 Aug 18;245(4919):758–761. doi: 10.1126/science.2549634. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallo V., Kingsbury A., Balázs R., Jørgensen O. S. The role of depolarization in the survival and differentiation of cerebellar granule cells in culture. J Neurosci. 1987 Jul;7(7):2203–2213. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.07-07-02203.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hubel D. H., Wiesel T. N., LeVay S. Plasticity of ocular dominance columns in monkey striate cortex. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1977 Apr 26;278(961):377–409. doi: 10.1098/rstb.1977.0050. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kessler J. A., Bell W. O., Black I. B. Interactions between the sympathetic and sensory innervation of the iris. J Neurosci. 1983 Jun;3(6):1301–1307. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.03-06-01301.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Large T. H., Bodary S. C., Clegg D. O., Weskamp G., Otten U., Reichardt L. F. Nerve growth factor gene expression in the developing rat brain. Science. 1986 Oct 17;234(4774):352–355. doi: 10.1126/science.3764415. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lu B., Buck C. R., Dreyfus C. F., Black I. B. Expression of NGF and NGF receptor mRNAs in the developing brain: evidence for local delivery and action of NGF. Exp Neurol. 1989 Jun;104(3):191–199. doi: 10.1016/0014-4886(89)90029-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lu B., Yokoyama M., Dreyfus C. F., Black I. B. NGF gene expression in actively growing brain glia. J Neurosci. 1991 Feb;11(2):318–326. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.11-02-00318.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson P. G., Yu C., Fields R. D., Neale E. A. Synaptic connections in vitro: modulation of number and efficacy by electrical activity. Science. 1989 May 5;244(4904):585–587. doi: 10.1126/science.2717942. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishi R., Berg D. K. Effects of high K+ concentrations on the growth and development of ciliary ganglion neurons in cell culture. Dev Biol. 1981 Oct 30;87(2):301–307. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(81)90153-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Purves D. Neuronal competition. Nature. 1980 Oct 16;287(5783):585–586. doi: 10.1038/287585a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwab M. E., Otten U., Agid Y., Thoenen H. Nerve growth factor (NGF) in the rat CNS: absence of specific retrograde axonal transport and tyrosine hydroxylase induction in locus coeruleus and substantia nigra. Brain Res. 1979 Jun 8;168(3):473–483. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(79)90303-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schäfer T., Schwab M. E., Thoenen H. Increased formation of preganglionic synapses and axons due to a retrograde trans-synaptic action of nerve growth factor in the rat sympathetic nervous system. J Neurosci. 1983 Jul;3(7):1501–1510. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.03-07-01501.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shatz C. J., Stryker M. P. Prenatal tetrodotoxin infusion blocks segregation of retinogeniculate afferents. Science. 1988 Oct 7;242(4875):87–89. doi: 10.1126/science.3175636. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevens C. F. Strengthening the synapses. Nature. 1989 Apr 6;338(6215):460–461. doi: 10.1038/338460a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thoenen H., Barde Y. A. Physiology of nerve growth factor. Physiol Rev. 1980 Oct;60(4):1284–1335. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1980.60.4.1284. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whittemore S. R., Lärkfors L., Ebendal T., Holets V. R., Ericsson A., Persson H. Increased beta-nerve growth factor messenger RNA and protein levels in neonatal rat hippocampus following specific cholinergic lesions. J Neurosci. 1987 Jan;7(1):244–251. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.07-01-00244.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zafra F., Hengerer B., Leibrock J., Thoenen H., Lindholm D. Activity dependent regulation of BDNF and NGF mRNAs in the rat hippocampus is mediated by non-NMDA glutamate receptors. EMBO J. 1990 Nov;9(11):3545–3550. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07564.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]