Abstract
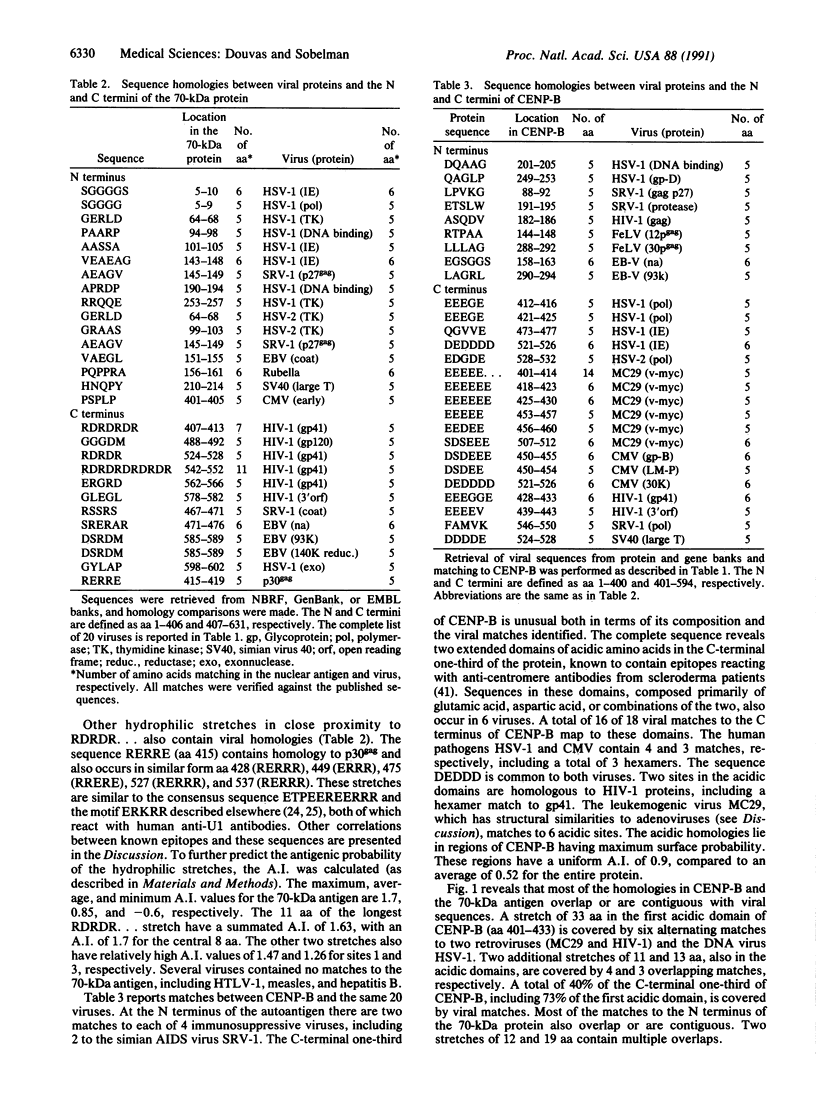
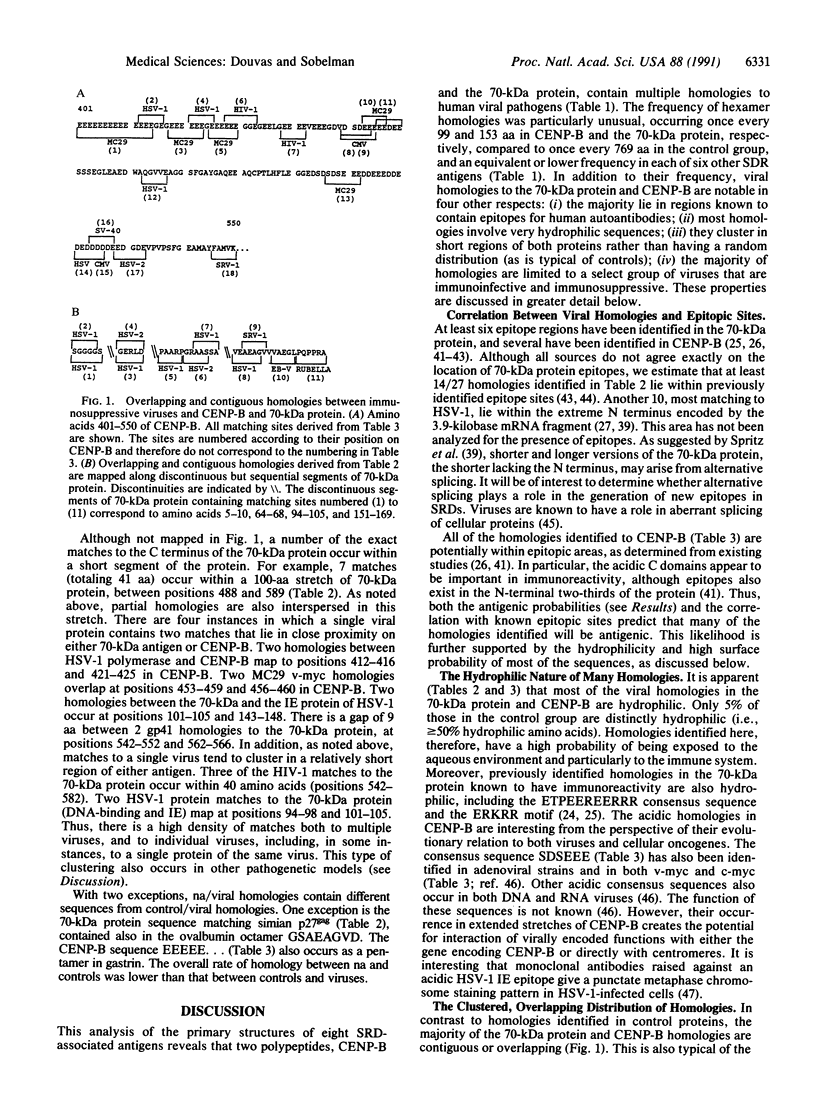
Amino acid (aa) sequence homologies between viruses and autoimmune nuclear antigens are suggestive of viral involvement in disorders such as systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) and scleroderma. We analyzed the frequency of exact homologies of greater than or equal to 5 aa between 61 viral proteins (19,827 aa), 8 nuclear antigens (3813 aa), and 41 control proteins (11,743 aa). Both pentamer and hexamer homologies between control proteins and viruses are unexpectedly abundant, with hexamer matches occurring in 1 of 3 control proteins (or once every 769 aa). However, 2 nuclear antigens, the SLE-associated 70-kDa antigen and the scleroderma-associated CENP-B protein, are highly unusual in containing multiple homologies to a group of synergizing immunosuppressive viruses. Two viruses, herpes simplex virus 1 (HSV-1) and human immunodeficiency virus 1 (HIV-1), contain sequences exactly duplicated at 15 sites in the 70-kDa antigen and at 10 sites in CENP-B protein. The immediate-early (IE) protein of HSV-1, which activates HIV-1 regulatory functions, contains three homologies to the 70-kDa antigen (two hexamers and a pentamer) and two to CENP-B (a hexamer and pentamer). There are four homologies (including a hexamer) common to the 70-kDa antigen and Epstein-Barr virus, and three homologies (including two hexamers) common to CENP-B and cytomegalovirus. The majority of homologies in both nuclear antigens are clustered in highly charged C-terminal domains containing epitopes for human autoantibodies. Furthermore, most homologies have a contiguous or overlapping distribution, thereby creating a high density of potential epitopes. In addition to the exact homologies tabulated, motifs of matching sequences are repeated frequently in these domains. Our analysis suggests that coexpression of heterologous viruses having common immunosuppressive functions may generate autoantibodies cross-reacting with certain nuclear proteins.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Albrecht M. A., DeLuca N. A., Byrn R. A., Schaffer P. A., Hammer S. M. The herpes simplex virus immediate-early protein, ICP4, is required to potentiate replication of human immunodeficiency virus in CD4+ lymphocytes. J Virol. 1989 May;63(5):1861–1868. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.5.1861-1868.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ben-Chetrit E., Gandy B. J., Tan E. M., Sullivan K. F. Isolation and characterization of a cDNA clone encoding the 60-kD component of the human SS-A/Ro ribonucleoprotein autoantigen. J Clin Invest. 1989 Apr;83(4):1284–1292. doi: 10.1172/JCI114013. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bjorkman P. J., Saper M. A., Samraoui B., Bennett W. S., Strominger J. L., Wiley D. C. The foreign antigen binding site and T cell recognition regions of class I histocompatibility antigens. Nature. 1987 Oct 8;329(6139):512–518. doi: 10.1038/329512a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bringmann P., Lührmann R. Purification of the individual snRNPs U1, U2, U5 and U4/U6 from HeLa cells and characterization of their protein constituents. EMBO J. 1986 Dec 20;5(13):3509–3516. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04676.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calin A., Marder A., Becks E., Burns T. Genetic differences between B27 positive patients with ankylosing spondylitis and B27 positive healthy controls. Arthritis Rheum. 1983 Dec;26(12):1460–1464. doi: 10.1002/art.1780261207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chambers J. C., Kenan D., Martin B. J., Keene J. D. Genomic structure and amino acid sequence domains of the human La autoantigen. J Biol Chem. 1988 Dec 5;263(34):18043–18051. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chou P. Y., Fasman G. D. Prediction of the secondary structure of proteins from their amino acid sequence. Adv Enzymol Relat Areas Mol Biol. 1978;47:45–148. doi: 10.1002/9780470122921.ch2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cram D. S., Fisicaro N., Coppel R. L., Whittingham S., Harrison L. C. Mapping of multiple B cell epitopes on the 70-kilodalton autoantigen of the U1 ribonucleoprotein complex. J Immunol. 1990 Jul 15;145(2):630–635. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- D'Arpa P., Machlin P. S., Ratrie H., 3rd, Rothfield N. F., Cleveland D. W., Earnshaw W. C. cDNA cloning of human DNA topoisomerase I: catalytic activity of a 67.7-kDa carboxyl-terminal fragment. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Apr;85(8):2543–2547. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.8.2543. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Desai S. M., Kalyanaraman V. S., Casey J. M., Srinivasan A., Andersen P. R., Devare S. G. Molecular cloning and primary nucleotide sequence analysis of a distinct human immunodeficiency virus isolate reveal significant divergence in its genomic sequences. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Nov;83(21):8380–8384. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.21.8380. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Earnshaw W. C., Machlin P. S., Bordwell B. J., Rothfield N. F., Cleveland D. W. Analysis of anticentromere autoantibodies using cloned autoantigen CENP-B. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jul;84(14):4979–4983. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.14.4979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Earnshaw W. C., Sullivan K. F., Machlin P. S., Cooke C. A., Kaiser D. A., Pollard T. D., Rothfield N. F., Cleveland D. W. Molecular cloning of cDNA for CENP-B, the major human centromere autoantigen. J Cell Biol. 1987 Apr;104(4):817–829. doi: 10.1083/jcb.104.4.817. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ewing C., Ebringer R., Tribbick G., Geysen H. M. Antibody activity in ankylosing spondylitis sera to two sites on HLA B27.1 at the MHC groove region (within sequence 65-85), and to a Klebsiella pneumoniae nitrogenase reductase peptide (within sequence 181-199). J Exp Med. 1990 May 1;171(5):1635–1647. doi: 10.1084/jem.171.5.1635. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox R. I., Chilton T., Scott S., Benton L., Howell F. V., Vaughan J. H. Potential role of Epstein-Barr virus in Sjögren's syndrome. Rheum Dis Clin North Am. 1987 Aug;13(2):275–292. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox R. Epstein-Barr virus and human autoimmune diseases: possibilities and pitfalls. J Virol Methods. 1988 Sep;21(1-4):19–27. doi: 10.1016/0166-0934(88)90049-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox R. Epstein-Barr virus and human autoimmune diseases: possibilities and pitfalls. J Virol Methods. 1988 Sep;21(1-4):19–27. doi: 10.1016/0166-0934(88)90049-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Francoeur A. M. Anti-SM and anti-U1-RNP lupus antibody fine specificities. J Clin Immunol. 1989 May;9(3):256–263. doi: 10.1007/BF00916822. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garnier J., Osguthorpe D. J., Robson B. Analysis of the accuracy and implications of simple methods for predicting the secondary structure of globular proteins. J Mol Biol. 1978 Mar 25;120(1):97–120. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90297-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gimble J. M., Duh E., Ostrove J. M., Gendelman H. E., Max E. E., Rabson A. B. Activation of the human immunodeficiency virus long terminal repeat by herpes simplex virus type 1 is associated with induction of a nuclear factor that binds to the NF-kappa B/core enhancer sequence. J Virol. 1988 Nov;62(11):4104–4112. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.11.4104-4112.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guldner H. H., Netter H. J., Szostecki C., Jaeger E., Will H. Human anti-p68 autoantibodies recognize a common epitope of U1 RNA containing small nuclear ribonucleoprotein and influenza B virus. J Exp Med. 1990 Mar 1;171(3):819–829. doi: 10.1084/jem.171.3.819. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guldner H. H., Netter H. J., Szostecki C., Lakomek H. J., Will H. Epitope mapping with a recombinant human 68-kDa (U1) ribonucleoprotein antigen reveals heterogeneous autoantibody profiles in human autoimmune sera. J Immunol. 1988 Jul 15;141(2):469–475. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guldner H. H., Netter H. J., Szostecki C., Lakomek H. J., Will H. Epitope mapping with a recombinant human 68-kDa (U1) ribonucleoprotein antigen reveals heterogeneous autoantibody profiles in human autoimmune sera. J Immunol. 1988 Jul 15;141(2):469–475. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Habets W. J., Sillekens P. T., Hoet M. H., Schalken J. A., Roebroek A. J., Leunissen J. A., van de Ven W. J., van Venrooij W. J. Analysis of a cDNA clone expressing a human autoimmune antigen: full-length sequence of the U2 small nuclear RNA-associated B" antigen. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Apr;84(8):2421–2425. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.8.2421. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kenney S., Kamine J., Markovitz D., Fenrick R., Pagano J. An Epstein-Barr virus immediate-early gene product trans-activates gene expression from the human immunodeficiency virus long terminal repeat. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Mar;85(5):1652–1656. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.5.1652. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krieg A. M., Khan A. S., Steinberg A. D. Expression of an endogenous retroviral transcript is associated with murine lupus. Arthritis Rheum. 1989 Mar;32(3):322–329. doi: 10.1002/anr.1780320314. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurata A., Katamine S., Fukuda T., Mine M., Ikari N., Kanazawa H., Matsunaga M., Eguchi K., Nagataki S. Production of a monoclonal antibody to a membrane antigen of human T-cell leukaemia virus (HTLV1/ATLV)-infected cell lines from a systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) patient: serological analyses for HTLV1 infections in SLE patients. Clin Exp Immunol. 1985 Oct;62(1):65–74. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kyte J., Doolittle R. F. A simple method for displaying the hydropathic character of a protein. J Mol Biol. 1982 May 5;157(1):105–132. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90515-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lane H. C., Fauci A. S. Immunologic abnormalities in the acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. Annu Rev Immunol. 1985;3:477–500. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.03.040185.002401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lerner M. R., Steitz J. A. Antibodies to small nuclear RNAs complexed with proteins are produced by patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Nov;76(11):5495–5499. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.11.5495. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maul G. G., Jimenez S. A., Riggs E., Ziemnicka-Kotula D. Determination of an epitope of the diffuse systemic sclerosis marker antigen DNA topoisomerase I: sequence similarity with retroviral p30gag protein suggests a possible cause for autoimmunity in systemic sclerosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Nov;86(21):8492–8496. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.21.8492. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakabayashi K., Saito M., Nagasawa T., Takada M. Antibodies to rheumatoid arthritis nuclear antigen (RANA) in Japanese patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatol Int. 1985;5(2):61–67. doi: 10.1007/BF00270298. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okamoto T., Tamura T., Takano T. Evidence in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus of the presence of antibodies against RNA-dependent DNA polymerase of baboon endogenous virus. Clin Exp Immunol. 1983 Dec;54(3):747–755. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pruijn G. J., Kusters H. G., Gmelig Meyling F. H., van der Vliet P. C. Inhibition of adenovirus DNA replication in vitro by autoimmune sera. Eur J Biochem. 1986 Jan 15;154(2):363–370. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1986.tb09406.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Query C. C., Bentley R. C., Keene J. D. A common RNA recognition motif identified within a defined U1 RNA binding domain of the 70K U1 snRNP protein. Cell. 1989 Apr 7;57(1):89–101. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90175-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Query C. C., Keene J. D. A human autoimmune protein associated with U1 RNA contains a region of homology that is cross-reactive with retroviral p30gag antigen. Cell. 1987 Oct 23;51(2):211–220. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90148-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ralston R., Bishop J. M. The protein products of the myc and myb oncogenes and adenovirus E1a are structurally related. Nature. 1983 Dec 22;306(5945):803–806. doi: 10.1038/306803a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenthal C. J., Franklin E. C. Depression of cellular-mediated immunity in systemic lupus erythematosus. relation to disease activity. Arthritis Rheum. 1975 May-Jun;18(3):207–217. doi: 10.1002/art.1780180303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosson D., Dugan D., Reddy E. P. Aberrant splicing events that are induced by proviral integration: implications for myb oncogene activation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 May;84(10):3171–3175. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.10.3171. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rucheton M., Graafland H., Fanton H., Ursule L., Ferrier P., Larsen C. J. Presence of circulating antibodies against gag-gene MuLV proteins in patients with autoimmune connective tissue disorders. Virology. 1985 Jul 30;144(2):468–480. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(85)90287-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakane T., Steinberg A. D., Arnett F. C., Reinertsen J. L., Green I. Studies of immune functions of patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 1979 Jul;22(7):770–776. doi: 10.1002/art.1780220713. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sany J. Quel est le rôle du virus d'Epstein-Barr dans la pathogénie des connectivités? Presse Med. 1987 Apr 25;16(15):725–728. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwimmbeck P. L., Yu D. T., Oldstone M. B. Autoantibodies to HLA B27 in the sera of HLA B27 patients with ankylosing spondylitis and Reiter's syndrome. Molecular mimicry with Klebsiella pneumoniae as potential mechanism of autoimmune disease. J Exp Med. 1987 Jul 1;166(1):173–181. doi: 10.1084/jem.166.1.173. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sillekens P. T., Beijer R. P., Habets W. J., van Venrooij W. J. Human U1 snRNP-specific C protein: complete cDNA and protein sequence and identification of a multigene family in mammals. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Sep 12;16(17):8307–8321. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.17.8307. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skolnik P. R., Kosloff B. R., Hirsch M. S. Bidirectional interactions between human immunodeficiency virus type 1 and cytomegalovirus. J Infect Dis. 1988 Mar;157(3):508–514. doi: 10.1093/infdis/157.3.508. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spritz R. A., Strunk K., Surowy C. S., Hoch S. O., Barton D. E., Francke U. The human U1-70K snRNP protein: cDNA cloning, chromosomal localization, expression, alternative splicing and RNA-binding. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Dec 23;15(24):10373–10391. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.24.10373. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinberg A. D., Klassen L. W., Budman D. R., Williams G. W. Immunofluorescence studies of anti-T cell antibodies and T cells in systemic lupus erythematosus. Selective loss of brightly staining T cells in active disease. Arthritis Rheum. 1979 Feb;22(2):114–122. doi: 10.1002/art.1780220203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Theissen H., Etzerodt M., Reuter R., Schneider C., Lottspeich F., Argos P., Lührmann R., Philipson L. Cloning of the human cDNA for the U1 RNA-associated 70K protein. EMBO J. 1986 Dec 1;5(12):3209–3217. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04631.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolf H., Modrow S., Motz M., Jameson B. A., Hermann G., Förtsch B. An integrated family of amino acid sequence analysis programs. Comput Appl Biosci. 1988 Mar;4(1):187–191. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/4.1.187. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



