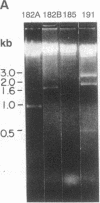
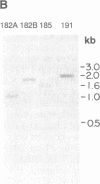
Abstract
The Kell blood group is a major antigenic system in human erythrocytes. Kell antigens reside on a 93-kDa membrane glycoprotein that is surface-exposed and associated with the underlying cytoskeleton. We isolated tryptic peptides and, based on the amino acid sequence of one of the peptides and by using the PCR, prepared a specific oligonucleotide to screen a lambda gt10 human bone-marrow cDNA library. Four clones were isolated, one containing cDNA with an open reading frame for an 83-kDa protein. All known Kell amino acid sequences were present in the deduced sequence; moreover, rabbit antibody to a 30-amino acid peptide, prepared from this sequence, reacted on an immunoblot with authentic Kell protein. The Kell cDNA sequence predicts a 732-amino acid protein. Hydropathy analysis indicates a single membrane-spanning region, suggesting that Kell protein is oriented with 47 of its N-terminal amino acids in the cell cytoplasm, and a 665-amino acid segment, which contains six possible N-glycosylation sites, is located extracellularly. Computer-based search showed that Kell has structural and sequence homology to a family of zinc metalloglycoproteins with neutral endopeptidase activity.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Advani H., Zamor J., Judd W. J., Johnson C. L., Marsh W. L. Inactivation of Kell blood group antigens by 2-aminoethylisothiouronium bromide. Br J Haematol. 1982 May;51(1):107–115. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1982.tb07295.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benchetrit T., Bissery V., Mornon J. P., Devault A., Crine P., Roques B. P. Primary structure homologies between two zinc metallopeptidases, the neutral endopeptidase 24.11 ("enkephalinase") and thermolysin, through clustering analysis. Biochemistry. 1988 Jan 26;27(2):592–596. doi: 10.1021/bi00402a014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bertelson C. J., Pogo A. O., Chaudhuri A., Marsh W. L., Redman C. M., Banerjee D., Symmans W. A., Simon T., Frey D., Kunkel L. M. Localization of the McLeod locus (XK) within Xp21 by deletion analysis. Am J Hum Genet. 1988 May;42(5):703–711. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Branch D. R., Muensch H. A., Sy Siok Hian A. L., Petz L. D. Disulfide bonds are a requirement for Kell and Cartwright (Yta) blood group antigen integrity. Br J Haematol. 1983 Aug;54(4):573–578. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1983.tb02136.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Branch D. R., Petz L. D. A new reagent (ZZAP) having multiple applications in immunohematology. Am J Clin Pathol. 1982 Aug;78(2):161–167. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/78.2.161. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomczynski P., Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987 Apr;162(1):156–159. doi: 10.1006/abio.1987.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- D'Adamio L., Shipp M. A., Masteller E. L., Reinherz E. L. Organization of the gene encoding common acute lymphoblastic leukemia antigen (neutral endopeptidase 24.11): multiple miniexons and separate 5' untranslated regions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Sep;86(18):7103–7107. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.18.7103. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devault A., Lazure C., Nault C., Le Moual H., Seidah N. G., Chrétien M., Kahn P., Powell J., Mallet J., Beaumont A. Amino acid sequence of rabbit kidney neutral endopeptidase 24.11 (enkephalinase) deduced from a complementary DNA. EMBO J. 1987 May;6(5):1317–1322. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02370.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freedman L. P., Luisi B. F., Korszun Z. R., Basavappa R., Sigler P. B., Yamamoto K. R. The function and structure of the metal coordination sites within the glucocorticoid receptor DNA binding domain. Nature. 1988 Aug 11;334(6182):543–546. doi: 10.1038/334543a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartmann E., Rapoport T. A., Lodish H. F. Predicting the orientation of eukaryotic membrane-spanning proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Aug;86(15):5786–5790. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.15.5786. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henikoff S. Unidirectional digestion with exonuclease III creates targeted breakpoints for DNA sequencing. Gene. 1984 Jun;28(3):351–359. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90153-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holland E. C., Leung J. O., Drickamer K. Rat liver asialoglycoprotein receptor lacks a cleavable NH2-terminal signal sequence. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Dec;81(23):7338–7342. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.23.7338. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaber A., Blanchard D., Goossens D., Bloy C., Lambin P., Rouger P., Salmon C., Cartron J. P. Characterization of the blood group Kell (K1) antigen with a human monoclonal antibody. Blood. 1989 May 1;73(6):1597–1602. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson P. F., McKnight S. L. Eukaryotic transcriptional regulatory proteins. Annu Rev Biochem. 1989;58:799–839. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.58.070189.004055. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnston M. Genetic evidence that zinc is an essential co-factor in the DNA binding domain of GAL4 protein. Nature. 1987 Jul 23;328(6128):353–355. doi: 10.1038/328353a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Judson P. A., Anstee D. J. Comparative effect of trypsin and chymotrypsin on blood group antigens. Med Lab Sci. 1977 Jan;34(1):1–6. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kyte J., Doolittle R. F. A simple method for displaying the hydropathic character of a protein. J Mol Biol. 1982 May 5;157(1):105–132. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90515-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Letarte M., Vera S., Tran R., Addis J. B., Onizuka R. J., Quackenbush E. J., Jongeneel C. V., McInnes R. R. Common acute lymphocytic leukemia antigen is identical to neutral endopeptidase. J Exp Med. 1988 Oct 1;168(4):1247–1253. doi: 10.1084/jem.168.4.1247. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malfroy B., Schofield P. R., Kuang W. J., Seeburg P. H., Mason A. J., Henzel W. J. Molecular cloning and amino acid sequence of rat enkephalinase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1987 Apr 14;144(1):59–66. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(87)80475-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marsh W. L., Redman C. M. Recent developments in the Kell blood group system. Transfus Med Rev. 1987 Apr;1(1):4–20. doi: 10.1016/s0887-7963(87)70002-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marsh W. L., Redman C. M. The Kell blood group system: a review. Transfusion. 1990 Feb;30(2):158–167. doi: 10.1046/j.1537-2995.1990.30290162904.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKerrow J. H. Human fibroblast collagenase contains an amino acid sequence homologous to the zinc-binding site of Serratia protease. J Biol Chem. 1987 May 5;262(13):5943–5943. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearson W. R., Lipman D. J. Improved tools for biological sequence comparison. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Apr;85(8):2444–2448. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.8.2444. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prober J. M., Trainor G. L., Dam R. J., Hobbs F. W., Robertson C. W., Zagursky R. J., Cocuzza A. J., Jensen M. A., Baumeister K. A system for rapid DNA sequencing with fluorescent chain-terminating dideoxynucleotides. Science. 1987 Oct 16;238(4825):336–341. doi: 10.1126/science.2443975. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Redman C. M., Avellino G., Pfeffer S. R., Mukherjee T. K., Nichols M., Rubinstein P., Marsh W. L. Kell blood group antigens are part of a 93,000-dalton red cell membrane protein. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jul 15;261(20):9521–9525. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Redman C. M., Lee S., ten Huinink D., Rabin B. I., Johnson C. L., Oyen R., Marsh W. L. Comparison of human and chimpanzee Kell blood group systems. Transfusion. 1989 Jul-Aug;29(6):486–490. doi: 10.1046/j.1537-2995.1989.29689318444.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Redman C. M., Marsh W. L., Mueller K. A., Avellino G. P., Johnson C. L. Isolation of Kell-active protein from the red cell membrane. Transfusion. 1984 Mar-Apr;24(2):176–178. doi: 10.1046/j.1537-2995.1984.24284173356.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Redman C. M., Marsh W. L., Scarborough A., Johnson C. L., Rabin B. I., Overbeeke M. Biochemical studies on McLeod phenotype red cells and isolation of Kx antigen. Br J Haematol. 1988 Jan;68(1):131–136. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1988.tb04191.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shipp M. A., Vijayaraghavan J., Schmidt E. V., Masteller E. L., D'Adamio L., Hersh L. B., Reinherz E. L. Common acute lymphoblastic leukemia antigen (CALLA) is active neutral endopeptidase 24.11 ("enkephalinase"): direct evidence by cDNA transfection analysis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jan;86(1):297–301. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.1.297. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]