Abstract
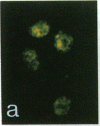
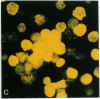
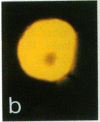
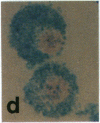
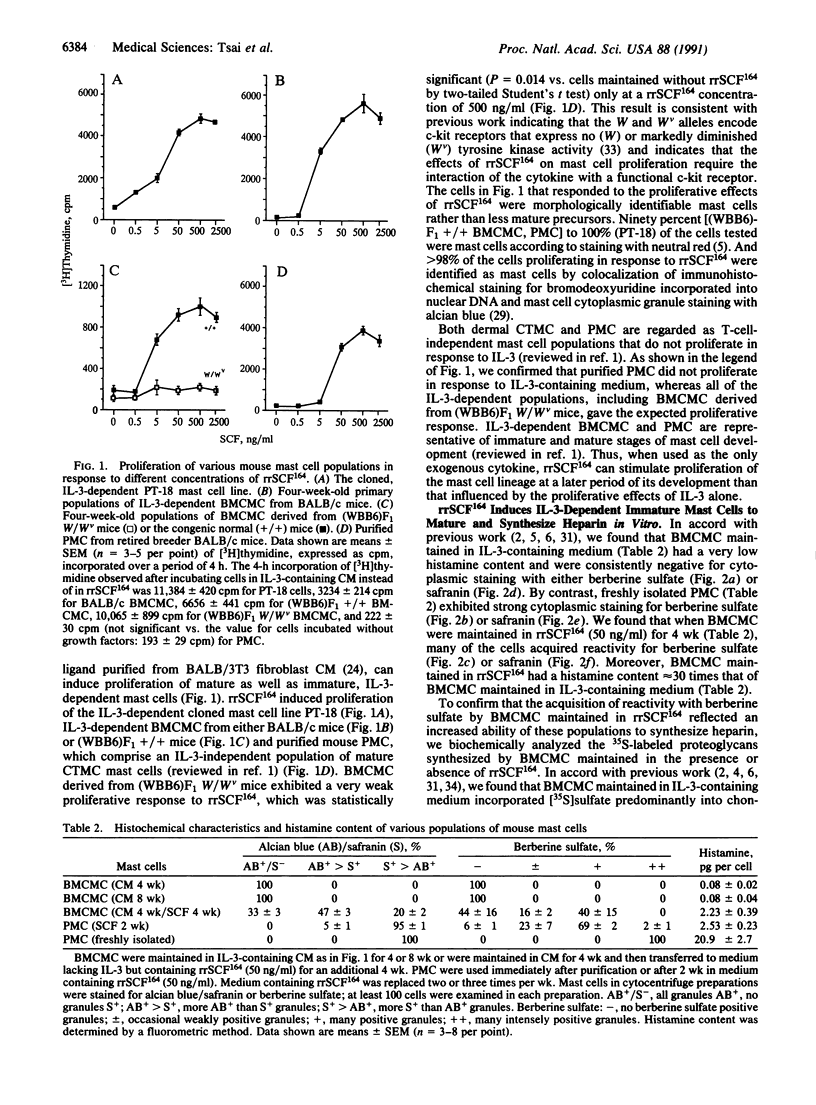
We investigated the effects of a newly recognized multifunctional growth factor, the c-kit ligand stem cell factor (SCF), on mouse mast cell proliferation and phenotype. Recombinant rat SCF164 (rrSCF164) induced the development of large numbers of dermal mast cells in normal mice in vivo. Many of these mast cells had features of "connective tissue-type mast cells" (CTMC), in that they were reactive both with the heparin-binding fluorescent dye berberine sulfate and with safranin. In vitro, rrSCF164 induced the proliferation of cloned interleukin 3 (IL-3)-dependent mouse mast cells and primary populations of IL-3-dependent, bone marrow-derived cultured mast cells (BMCMC), which represent immature mast cells, and purified peritoneal mast cells, which represent a type of mature CTMC. BMCMC maintained in rrSCF164 not only proliferated but also matured. Prior to exposure to rrSCF164, the BMCMC were alcian blue positive, safranin negative, and berberine sulfate negative; had a histamine content of 0.08 +/- 0.02 pg per cell; and incorporated [35S]sulfate into chondroitin sulfates. After 4 wk in rrSCF164, the BMCMC were predominantly safranin positive and berberine sulfate positive, had a histamine content of 2.23 +/- 0.39 pg per cell, and synthesized 35S-labeled proteoglycans that included substantial amounts (41-70%) of [35S]heparin. These findings identify SCF as a single cytokine that can induce immature, IL-3-dependent mast cells to mature and to acquire multiple characteristics of CTMC. These findings also directly demonstrate that SCF can regulate the development of a cellular lineage expressing c-kit through effects on both proliferation and maturation.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson D. M., Lyman S. D., Baird A., Wignall J. M., Eisenman J., Rauch C., March C. J., Boswell H. S., Gimpel S. D., Cosman D. Molecular cloning of mast cell growth factor, a hematopoietin that is active in both membrane bound and soluble forms. Cell. 1990 Oct 5;63(1):235–243. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90304-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bland C. E., Ginsburg H., Silbert J. E., Metcalfe D. D. Mouse heparin proteoglycan. Synthesis by mast cell-fibroblast monolayers during lymphocyte-dependent mast cell proliferation. J Biol Chem. 1982 Aug 10;257(15):8661–8666. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burd P. R., Rogers H. W., Gordon J. R., Martin C. A., Jayaraman S., Wilson S. D., Dvorak A. M., Galli S. J., Dorf M. E. Interleukin 3-dependent and -independent mast cells stimulated with IgE and antigen express multiple cytokines. J Exp Med. 1989 Jul 1;170(1):245–257. doi: 10.1084/jem.170.1.245. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chabot B., Stephenson D. A., Chapman V. M., Besmer P., Bernstein A. The proto-oncogene c-kit encoding a transmembrane tyrosine kinase receptor maps to the mouse W locus. Nature. 1988 Sep 1;335(6185):88–89. doi: 10.1038/335088a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Copeland N. G., Gilbert D. J., Cho B. C., Donovan P. J., Jenkins N. A., Cosman D., Anderson D., Lyman S. D., Williams D. E. Mast cell growth factor maps near the steel locus on mouse chromosome 10 and is deleted in a number of steel alleles. Cell. 1990 Oct 5;63(1):175–183. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90298-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Enerbäck L. Berberine sulphate binding to mast cell polyanions: a cytofluorometric method for the quantitation of heparin. Histochemistry. 1974;42(4):301–313. doi: 10.1007/BF00492678. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flanagan J. G., Leder P. The kit ligand: a cell surface molecule altered in steel mutant fibroblasts. Cell. 1990 Oct 5;63(1):185–194. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90299-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujita J., Onoue H., Ebi Y., Nakayama H., Kanakura Y. In vitro duplication and in vivo cure of mast-cell deficiency of Sl/Sld mutant mice by cloned 3T3 fibroblasts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Apr;86(8):2888–2891. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.8.2888. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galli S. J., Arizono N., Murakami T., Dvorak A. M., Fox J. G. Development of large numbers of mast cells at sites of idiopathic chronic dermatitis in genetically mast cell-deficient WBB6F1-W/Wv mice. Blood. 1987 Jun;69(6):1661–1666. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galli S. J., Dvorak A. M., Marcum J. A., Ishizaka T., Nabel G., Der Simonian H., Pyne K., Goldin J. M., Rosenberg R. D., Cantor H. Mast cell clones: a model for the analysis of cellular maturation. J Cell Biol. 1982 Nov;95(2 Pt 1):435–444. doi: 10.1083/jcb.95.2.435. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galli S. J. New insights into "the riddle of the mast cells": microenvironmental regulation of mast cell development and phenotypic heterogeneity. Lab Invest. 1990 Jan;62(1):5–33. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galli S. J., Wershil B. K., Gordon J. R., Martin T. R. Mast cells: immunologically specific effectors and potential sources of multiple cytokines during IgE-dependent responses. Ciba Found Symp. 1989;147:53–73. doi: 10.1002/9780470513866.ch5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geissler E. N., Ryan M. A., Housman D. E. The dominant-white spotting (W) locus of the mouse encodes the c-kit proto-oncogene. Cell. 1988 Oct 7;55(1):185–192. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90020-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon J. R., Burd P. R., Galli S. J. Mast cells as a source of multifunctional cytokines. Immunol Today. 1990 Dec;11(12):458–464. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(90)90176-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon J. R., Galli S. J. Mast cells as a source of both preformed and immunologically inducible TNF-alpha/cachectin. Nature. 1990 Jul 19;346(6281):274–276. doi: 10.1038/346274a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon J. R., Galli S. J. Phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate-induced development of functionally active mast cells in W/Wv but not Sl/Sld genetically mast cell-deficient mice. Blood. 1990 Apr 15;75(8):1637–1645. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamaguchi Y., Kanakura Y., Fujita J., Takeda S., Nakano T., Tarui S., Honjo T., Kitamura Y. Interleukin 4 as an essential factor for in vitro clonal growth of murine connective tissue-type mast cells. J Exp Med. 1987 Jan 1;165(1):268–273. doi: 10.1084/jem.165.1.268. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang E., Nocka K., Beier D. R., Chu T. Y., Buck J., Lahm H. W., Wellner D., Leder P., Besmer P. The hematopoietic growth factor KL is encoded by the Sl locus and is the ligand of the c-kit receptor, the gene product of the W locus. Cell. 1990 Oct 5;63(1):225–233. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90303-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanakura Y., Thompson H., Nakano T., Yamamura T., Asai H., Kitamura Y., Metcalfe D. D., Galli S. J. Multiple bidirectional alterations of phenotype and changes in proliferative potential during the in vitro and in vivo passage of clonal mast cell populations derived from mouse peritoneal mast cells. Blood. 1988 Sep;72(3):877–885. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levi-Schaffer F., Austen K. F., Gravallese P. M., Stevens R. L. Coculture of interleukin 3-dependent mouse mast cells with fibroblasts results in a phenotypic change of the mast cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Sep;83(17):6485–6488. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.17.6485. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin F. H., Suggs S. V., Langley K. E., Lu H. S., Ting J., Okino K. H., Morris C. F., McNiece I. K., Jacobsen F. W., Mendiaz E. A. Primary structure and functional expression of rat and human stem cell factor DNAs. Cell. 1990 Oct 5;63(1):203–211. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90301-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsui Y., Zsebo K. M., Hogan B. L. Embryonic expression of a haematopoietic growth factor encoded by the Sl locus and the ligand for c-kit. Nature. 1990 Oct 18;347(6294):667–669. doi: 10.1038/347667a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakahata T., Kobayashi T., Ishiguro A., Tsuji K., Naganuma K., Ando O., Yagi Y., Tadokoro K., Akabane T. Extensive proliferation of mature connective-tissue type mast cells in vitro. Nature. 1986 Nov 6;324(6092):65–67. doi: 10.1038/324065a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakano T., Sonoda T., Hayashi C., Yamatodani A., Kanayama Y., Yamamura T., Asai H., Yonezawa T., Kitamura Y., Galli S. J. Fate of bone marrow-derived cultured mast cells after intracutaneous, intraperitoneal, and intravenous transfer into genetically mast cell-deficient W/Wv mice. Evidence that cultured mast cells can give rise to both connective tissue type and mucosal mast cells. J Exp Med. 1985 Sep 1;162(3):1025–1043. doi: 10.1084/jem.162.3.1025. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nocka K., Buck J., Levi E., Besmer P. Candidate ligand for the c-kit transmembrane kinase receptor: KL, a fibroblast derived growth factor stimulates mast cells and erythroid progenitors. EMBO J. 1990 Oct;9(10):3287–3294. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07528.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nocka K., Tan J. C., Chiu E., Chu T. Y., Ray P., Traktman P., Besmer P. Molecular bases of dominant negative and loss of function mutations at the murine c-kit/white spotting locus: W37, Wv, W41 and W. EMBO J. 1990 Jun;9(6):1805–1813. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08305.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plaut M., Pierce J. H., Watson C. J., Hanley-Hyde J., Nordan R. P., Paul W. E. Mast cell lines produce lymphokines in response to cross-linkage of Fc epsilon RI or to calcium ionophores. Nature. 1989 May 4;339(6219):64–67. doi: 10.1038/339064a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Razin E., Stevens R. L., Akiyama F., Schmid K., Austen K. F. Culture from mouse bone marrow of a subclass of mast cells possessing a distinct chondroitin sulfate proteoglycan with glycosaminoglycans rich in N-acetylgalactosamine-4,6-disulfate. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jun 25;257(12):7229–7236. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell E. S. Hereditary anemias of the mouse: a review for geneticists. Adv Genet. 1979;20:357–459. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sredni B., Friedman M. M., Bland C. E., Metcalfe D. D. Ultrastructural, biochemical, and functional characteristics of histamine-containing cells cloned from mouse bone marrow: tentative identification as mucosal mast cells. J Immunol. 1983 Aug;131(2):915–922. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson H. L., Schulman E. S., Metcalfe D. D. Identification of chondroitin sulfate E in human lung mast cells. J Immunol. 1988 Apr 15;140(8):2708–2713. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams D. E., Eisenman J., Baird A., Rauch C., Van Ness K., March C. J., Park L. S., Martin U., Mochizuki D. Y., Boswell H. S. Identification of a ligand for the c-kit proto-oncogene. Cell. 1990 Oct 5;63(1):167–174. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90297-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wodnar-Filipowicz A., Heusser C. H., Moroni C. Production of the haemopoietic growth factors GM-CSF and interleukin-3 by mast cells in response to IgE receptor-mediated activation. Nature. 1989 May 11;339(6220):150–152. doi: 10.1038/339150a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zsebo K. M., Williams D. A., Geissler E. N., Broudy V. C., Martin F. H., Atkins H. L., Hsu R. Y., Birkett N. C., Okino K. H., Murdock D. C. Stem cell factor is encoded at the Sl locus of the mouse and is the ligand for the c-kit tyrosine kinase receptor. Cell. 1990 Oct 5;63(1):213–224. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90302-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zsebo K. M., Wypych J., McNiece I. K., Lu H. S., Smith K. A., Karkare S. B., Sachdev R. K., Yuschenkoff V. N., Birkett N. C., Williams L. R. Identification, purification, and biological characterization of hematopoietic stem cell factor from buffalo rat liver--conditioned medium. Cell. 1990 Oct 5;63(1):195–201. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90300-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]