Abstract
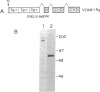
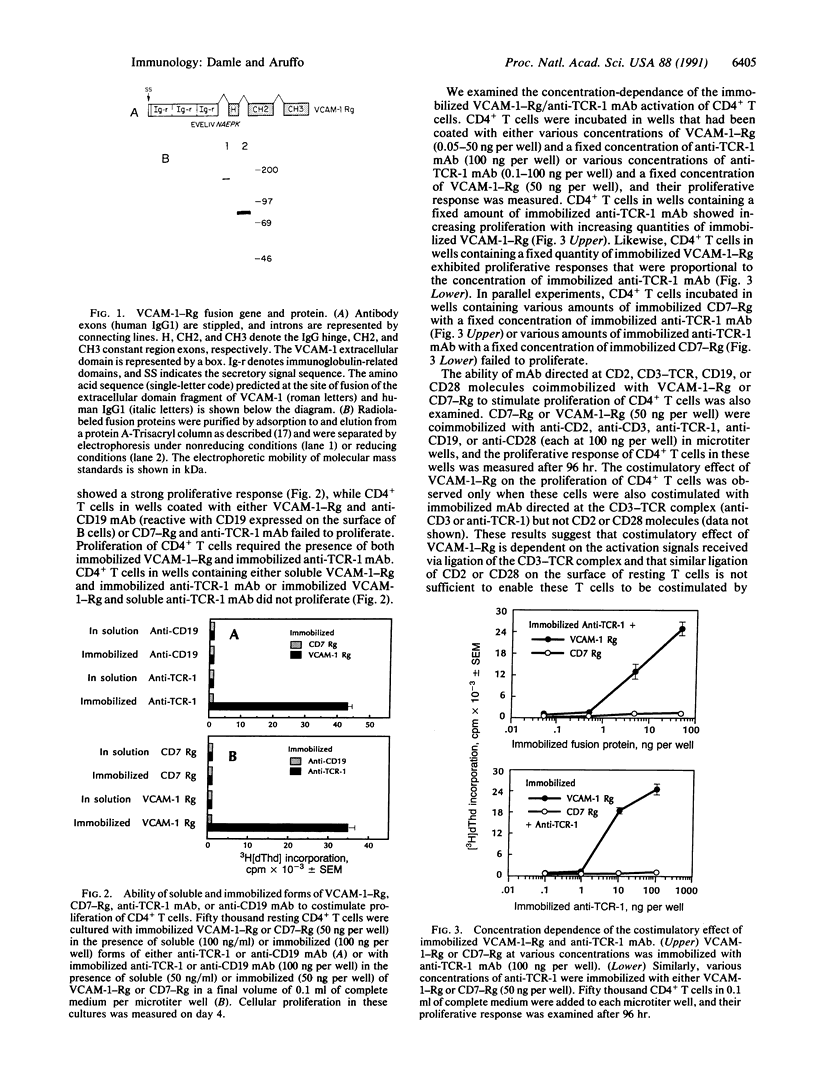
Effective stimulation of CD4+ T cells in an immune response depends on activation signals transduced via not only the CD3-T-cell receptor (TCR) complex but also those generated by accessory cell-surface proteins, including some that mediate adhesion between T cells and antigen-presenting cells (APC). Three members of the Ig superfamily, CD54 [intercellular cell adhesion molecule 1 (ICAM-1)], CD58 [lymphocyte function-associated antigen 3 (LFA-3)], and B7, expressed on the surface of APC, have been shown to mediate both adhesion and signaling during T cell-APC interactions. Recently another member of the Ig superfamily, [vascular cell adhesion molecule 1 (VCAM-1; INCAM110)], has been identified. VCAM-1 mediates adhesion between endothelial cells and activated lymphocytes and certain tumor cells. Here, using a soluble VCAM-1 fusion protein with receptor globulin (Rg), we examined the role of VCAM-1 in T-cell activation. We observed that CD4+ T cells, which are inefficiently stimulated by immobilized anti-TCR-1 or anti-CD3 monoclonal antibody (mAb) alone, can be induced to proliferate when exposed to immobilized VCAM-1-Rg in conjunction with either immobilized anti-TCR-1 or immobilized anti-CD3 mAb. The costimulatory effects of VCAM-1-Rg on CD4+T cells is inhibited by mAb to either the CD29 (integrin beta 1)-CD49d [very late activation antigen 4 alpha (VLA-4 alpha)] complex on the surface of CD4+ T cells or to VCAM-1. Stimulation of CD4+ T cells with immobilized VCAM-1-Rg and anti-TCR or -CD3 mAb results in the synthesis of both interleukin 2 (IL-2) receptors and IL-2. In addition, anti-CD25 (anti-IL-2 receptor a) mAb significantly inhibited the VCAM-1-Rg/anti-TCR or -CD3 mAb-driven activation of CD4+ T cells, indicating that endogenously produced IL-2 is in part responsible for the observed T-cell proliferation. Collectively, these results suggest that VCAM-1 can play an important costimulatory role during the activation of CD4+ T cells.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aruffo A., Stamenkovic I., Melnick M., Underhill C. B., Seed B. CD44 is the principal cell surface receptor for hyaluronate. Cell. 1990 Jun 29;61(7):1303–1313. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90694-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Damle N. K., Doyle L. V. Stimulation via the CD3 and CD28 molecules induces responsiveness to IL-4 in CD4+CD29+CD45R- memory T lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1989 Sep 15;143(6):1761–1767. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis L. S., Oppenheimer-Marks N., Bednarczyk J. L., McIntyre B. W., Lipsky P. E. Fibronectin promotes proliferation of naive and memory T cells by signaling through both the VLA-4 and VLA-5 integrin molecules. J Immunol. 1990 Aug 1;145(3):785–793. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elices M. J., Osborn L., Takada Y., Crouse C., Luhowskyj S., Hemler M. E., Lobb R. R. VCAM-1 on activated endothelium interacts with the leukocyte integrin VLA-4 at a site distinct from the VLA-4/fibronectin binding site. Cell. 1990 Feb 23;60(4):577–584. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90661-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freedman A. S., Munro J. M., Rice G. E., Bevilacqua M. P., Morimoto C., McIntyre B. W., Rhynhart K., Pober J. S., Nadler L. M. Adhesion of human B cells to germinal centers in vitro involves VLA-4 and INCAM-110. Science. 1990 Aug 31;249(4972):1030–1033. doi: 10.1126/science.1697696. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillis S., Ferm M. M., Ou W., Smith K. A. T cell growth factor: parameters of production and a quantitative microassay for activity. J Immunol. 1978 Jun;120(6):2027–2032. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graber N., Gopal T. V., Wilson D., Beall L. D., Polte T., Newman W. T cells bind to cytokine-activated endothelial cells via a novel, inducible sialoglycoprotein and endothelial leukocyte adhesion molecule-1. J Immunol. 1990 Aug 1;145(3):819–830. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hemler M. E. VLA proteins in the integrin family: structures, functions, and their role on leukocytes. Annu Rev Immunol. 1990;8:365–400. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.08.040190.002053. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hynes R. O. Integrins: a family of cell surface receptors. Cell. 1987 Feb 27;48(4):549–554. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90233-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- June C. H., Ledbetter J. A., Linsley P. S., Thompson C. B. Role of the CD28 receptor in T-cell activation. Immunol Today. 1990 Jun;11(6):211–216. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(90)90085-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kishimoto T. K., Larson R. S., Corbi A. L., Dustin M. L., Staunton D. E., Springer T. A. The leukocyte integrins. Adv Immunol. 1989;46:149–182. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60653-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linsley P. S., Brady W., Grosmaire L., Aruffo A., Damle N. K., Ledbetter J. A. Binding of the B cell activation antigen B7 to CD28 costimulates T cell proliferation and interleukin 2 mRNA accumulation. J Exp Med. 1991 Mar 1;173(3):721–730. doi: 10.1084/jem.173.3.721. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuyama T., Yamada A., Kay J., Yamada K. M., Akiyama S. K., Schlossman S. F., Morimoto C. Activation of CD4 cells by fibronectin and anti-CD3 antibody. A synergistic effect mediated by the VLA-5 fibronectin receptor complex. J Exp Med. 1989 Oct 1;170(4):1133–1148. doi: 10.1084/jem.170.4.1133. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nojima Y., Humphries M. J., Mould A. P., Komoriya A., Yamada K. M., Schlossman S. F., Morimoto C. VLA-4 mediates CD3-dependent CD4+ T cell activation via the CS1 alternatively spliced domain of fibronectin. J Exp Med. 1990 Oct 1;172(4):1185–1192. doi: 10.1084/jem.172.4.1185. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osborn L., Hession C., Tizard R., Vassallo C., Luhowskyj S., Chi-Rosso G., Lobb R. Direct expression cloning of vascular cell adhesion molecule 1, a cytokine-induced endothelial protein that binds to lymphocytes. Cell. 1989 Dec 22;59(6):1203–1211. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90775-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pober J. S., Doukas J., Hughes C. C., Savage C. O., Munro J. M., Cotran R. S. The potential roles of vascular endothelium in immune reactions. Hum Immunol. 1990 Jun;28(2):258–262. doi: 10.1016/0198-8859(90)90027-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rice G. E., Munro J. M., Bevilacqua M. P. Inducible cell adhesion molecule 110 (INCAM-110) is an endothelial receptor for lymphocytes. A CD11/CD18-independent adhesion mechanism. J Exp Med. 1990 Apr 1;171(4):1369–1374. doi: 10.1084/jem.171.4.1369. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimizu Y., Van Seventer G. A., Horgan K. J., Shaw S. Regulated expression and binding of three VLA (beta 1) integrin receptors on T cells. Nature. 1990 May 17;345(6272):250–253. doi: 10.1038/345250a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimizu Y., van Seventer G. A., Horgan K. J., Shaw S. Costimulation of proliferative responses of resting CD4+ T cells by the interaction of VLA-4 and VLA-5 with fibronectin or VLA-6 with laminin. J Immunol. 1990 Jul 1;145(1):59–67. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Springer T. A. Adhesion receptors of the immune system. Nature. 1990 Aug 2;346(6283):425–434. doi: 10.1038/346425a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Springer T. A., Dustin M. L., Kishimoto T. K., Marlin S. D. The lymphocyte function-associated LFA-1, CD2, and LFA-3 molecules: cell adhesion receptors of the immune system. Annu Rev Immunol. 1987;5:223–252. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.05.040187.001255. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wayner E. A., Garcia-Pardo A., Humphries M. J., McDonald J. A., Carter W. G. Identification and characterization of the T lymphocyte adhesion receptor for an alternative cell attachment domain (CS-1) in plasma fibronectin. J Cell Biol. 1989 Sep;109(3):1321–1330. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.3.1321. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss A. Structure and function of the T cell antigen receptor. J Clin Invest. 1990 Oct;86(4):1015–1022. doi: 10.1172/JCI114803. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]