Abstract
Background
The safety and effectiveness of the fully repositionable LOTUS valve system as compared with the balloon‐expandable Edwards SAPIEN 3 prosthesis for the treatment of aortic stenosis has not been evaluated to date.
Methods and Results
All patients undergoing transcatheter aortic valve implantation with the Edwards SAPIEN 3 or the LOTUS valve system were included into the Swiss Transcatheter Aortic Valve Implantation Registry. An adjusted analysis was performed to compare the early clinical safety outcome according to the Valve Academic Research Consortium‐2 definition. Between February 2014 and September 2015, 140 and 815 patients were treated with the LOTUS and the Edwards SAPIEN 3 valve, respectively. There was no difference in crude and adjusted analyses of the early safety outcome between patients treated with LOTUS (14.3%) and those treated with Edwards SAPIEN 3 (14.6%) (crude hazard ratio, 0.97; 95% CI, 0.61–1.56 [P=0.915]; adjusted hazard ratio, 1.03; 95% CI, 0.64–1.67 [P=0.909]). More than mild aortic regurgitation was <2% for both devices. A total of 34.3% of patients treated with LOTUS and 14.1% of patients treated with Edwards SAPIEN 3 required a permanent pacemaker (HR, 2.76; 95% CI, 1.97–3.87 [P<0.001]).
Conclusions
The repositionable LOTUS valve system and the balloon‐expandable Edwards SAPIEN 3 prosthesis appeared comparable in regard to the Valve Academic Research Consortium‐2 early safety outcome, and the rates of more than mild aortic regurgitation were exceedingly low for both devices. The need for new permanent pacemaker implantation was more frequent among patients treated with the LOTUS valve.
Keywords: aortic valve regurgitation, newer‐generation devices, permanent pacemaker, transcatheter aortic valve replacement
Subject Categories: Aortic Valve Replacement/Transcather Aortic Valve Implantation
Introduction
Transcatheter aortic valve implantation (TAVI) has gained wide acceptance for the treatment of severe aortic stenosis among patients deemed to be at increased risk for surgical aortic valve replacement. Expansion of TAVI to lower risk patients is critically dependent on the refinement of early‐generation devices to further reduce the risk of paravalvular regurgitation, device malposition, atrioventricular (AV) conductance disturbances, access‐site complications, and peri‐interventional bleeding. Newer‐generation devices feature external cuffs or internal skirts to seal the prosthesis to the aortic annulus and reduce the risk of paravalvular regurgitation. Atraumatic, precurved, and steerable delivery catheter systems aim for a reduction of plaque embolization, and smaller catheter diameters mitigate the risk of access site complications and bleeding.1
The LOTUS valve system (Boston Scientific, Natwick, MA) is a novel, fully repositionable TAVI prosthesis that permits evaluation of the final configuration of the deployed valve, the degree of aortic regurgitation, as well as reduced coronary flow before detachment. Single‐arm registries of the LOTUS valve showed high rates of procedural success and suggested substantially lower rates of paravalvular regurgitation compared with early‐generation devices2, 3, 4; conversely, rates of AV conduction disturbances were relatively high, resulting in permanent pacemaker implantation in 1 in every fourth patient up to one in every third patient.2, 3
The safety and effectiveness of the fully repositionable LOTUS valve system as compared with other newer‐generation TAVI devices have not been evaluated to date. We therefore performed an adjusted comparison of the LOTUS valve system with the balloon‐expandable Edwards SAPIEN 3 prosthesis in patients with aortic stenosis undergoing TAVI within the nationwide Swiss Transcatheter Aortic Valve Implantation Registry (NCT01368250).
Methods
Study Population
All patients undergoing TAVI procedures performed in Switzerland are consecutively captured in a nationwide, prospective cohort study (ClinicalTrials.gov NCT01368250).5 For the purpose of the present analysis, we investigated all patients with severe aortic stenosis treated with the Edwards SAPIEN 3 prosthesis or the LOTUS valve system. Selection of TAVI candidates, device allocation, and periprocedural management was left to the discretion of the operators. All data were recorded in a Web‐based database held at the Clinical Trials Unit of the University of Bern, Switzerland. The Swiss TAVI registry has been approved by the local cantonal ethics committee and the institutional review boards of all participating sites. All patients provided written informed consent for study participation and prospective follow‐up assessment.
Devices
The LOTUS valve system consists of a single nitinol wire that is braided into a stent frame upon foreshortening and mechanical expansion. Positioning is facilitated by a radiopaque marker. The prosthesis is attached to the delivery system with 3 coupling fingers; buckles at the distal end connect to posts located at the commissures of the 3 leaflets upon shortening, and lock the valve in its final configuration. The stent frame accommodates a bovine pericardial valve and comes in 3 prosthesis sizes (23 mm, 25 mm, and 27 mm) fitting an annulus diameter ranging from 20 mm to 26 mm. An adaptive seal in the distal portion of the prosthesis and an outer sleeve have been designed to reduce paravalvular regurgitation. The LOTUS prosthesis is fully repositionable and allows for an assessment of the final result before detachment of the valve from the coupling fingers of the delivery system. The precurved delivery catheter has a diameter of 18 F to 20 F and is not steerable. The valve can be implanted without rapid ventricular stimulation and predilatation is not necessary in all cases. The LOTUS valve system received CE mark approval on October 28, 2013, and on July 14, 2014, for its 23/27 mm and 25 mm prosthesis, respectively, and since then has become available for commercial use and implantation in Switzerland.
The Edwards SAPIEN 3 valve (Edwards Lifesciences, Irvine, CA) is the fourth iteration of the first balloon‐expandable transcatheter aortic valve prosthesis. The stent frame houses a valve made of 3 modified pericardial tissue leaflets, and accommodates annulus sizes from 18 mm to 28 mm using 3 device sizes (23 mm, 26 mm, 29 mm). An outer sealing skirt in the distal portion of the prosthesis complements the inner PET skirt and aims at a reduction of paravalvular aortic regurgitation. The prosthesis is loaded on the delivery balloon in the abdominal aorta rendering the delivery catheter compatible with 14 F to 16 F. The Commander delivery catheter is steerable and has a wheel to fine‐adjust valve positioning.6 The Edwards SAPIEN 3 valve was introduced in Switzerland for implantation on January 27, 2014, and completely replaced the previously available Edwards SAPIEN XT prosthesis.
Definitions
Patients underwent transthoracic echocardiography before hospital discharge, and were contacted for clinical follow‐up at 30 days. Standardized interviews, documentation from referring physicians, and hospital discharge summaries were used for the collection of clinical end points. All end points were defined according to the updated version of the Valve Academic Research Consortium (VARC2) definitions.7 An independent clinical event committee adjudicated all events. The prespecified end point was the VARC2 early safety outcome, a composite of all‐cause mortality, stroke, life‐threatening bleeding, acute kidney injury stage 2 or 3, coronary obstruction requiring intervention, major vascular complication, and valve‐related dysfunction requiring repeat procedure.
Statistical Analysis
Continuous data are reported as mean±SD, and categorical variables are reported as number (percentage) of patients. Events are reported as counts of first occurrence per (sub‐)type of event within 30 days of follow‐up (% of all patients). Event rates at 30 days were compared for patients treated with the LOTUS versus the Edwards SAPIEN 3 bioprosthesis using Cox regressions, censoring patients at death or lost to follow‐up. Reported are crude hazard ratios (HRs; with 95% CIs) with P values from Wald chi‐square tests, or continuity correct risk ratios with P values from Fisher exact tests in case of zero events. Multiple imputation of missing data was performed using chained equations (n=20 data sets generated) before the adjusted analyses. Details on the missing data are summarized in Table S1. Reported are adjusted HRs (95% CIs), with the two valves compared, adjusting for age, dyslipidemia, peripheral vascular disease, aortic regurgitation moderate or severe, aortic valve area, New York Heart Association class III or IV, and Society of Thoracic Surgeons (STS) predicted risk of mortality score. No adjusted analyses were performed if there were fewer than 5 events overall. The estimates of adjusted HRs from 20 data sets after multiple imputation of missing values were combined using Rubin's rule and presented with adjusted P values. Two‐sided P values <0.05 were considered statistically significant. Stratified analyses of the following subgroups were performed: age (≥83 years versus <83 years—median), sex (female versus male), left ventricular ejection fraction (≤40% versus >40%), peripheral vascular disease (yes versus no), STS risk score (>4 versus ≤4), and P value for the interaction between subgroups and valve type. All analyses were performed with Stata version 14 (StataCorp, College Station, TX).
Results
Patient Population
Between February 4, 2014, and September 29, 2015, 140 patients were treated with the LOTUS valve system and 815 patients with the Edwards SAPIEN 3 prosthesis in 12 centers across Switzerland. Baseline characteristics are summarized in Table 1. Age, sex, medical history, and cardiovascular risk factors were well balanced between the two treatment arms. Compared with patients treated with the LOTUS valve system, patients treated with the Edward SAPIEN 3 prosthesis more commonly had peripheral vascular disease (15.5% versus 7.9%, P=0.01) and higher estimated surgical risk as assessed by the logistic EuroScore (18.9±14.8% versus 15.0±8.6%, P=0.018) and STS score (5.0±3.8% versus 4.1±2.4%, P=0.005).
Table 1.
Baseline Characteristics
| LOTUS | Edwards S3 | Difference (95% CI) | P Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| N=140 | N=815 | |||
| Age, y | 82.97±5.40 | 81.92±6.37 | 1.05 (−0.07 to 2.17) | 0.065 |
| Female sex, No. (%) | 65 (46.4) | 352 (43.2) | 3.2% (−5.7% to 12.1%) | 0.519 |
| Body mass index, kg/m2 | 26.64±4.77 | 26.95±5.27 | −0.31 (−1.25 to 0.63) | 0.516 |
| Cardiac risk factors | ||||
| Diabetes mellitus, No. (%) | 33 (23.6) | 200 (24.5) | 1.0% (−6.8% to 8.7%) | 0.915 |
| Dyslipidemia, No. (%) | 80 (57.1) | 392 (48.1) | −9.0% (−18.0% to −0.1%) | 0.055 |
| Hypertension, No. (%) | 114 (81.4) | 625 (76.8) | −4.6% (−12.2%; 2.9%) | 0.273 |
| Medical history | ||||
| Previous pacemaker implantation, No. (%) | 15 (10.7) | 80 (9.8) | −0.9% (−6.3% to 4.5%) | 0.760 |
| Previous myocardial infarction, No. (%) | 21 (15.0) | 122 (15.0) | −0.0% (−6.4% to 6.4%) | 1.000 |
| Previous cardiac surgery, No. (%) | 14 (10.0) | 114 (14.0) | 4.0% (−2.1% to 10.1%) | 0.228 |
| Previous cerebrovascular accident, No. (%) | 14 (10.0) | 91 (11.2) | 1.2% (−4.5% to 6.8%) | 0.771 |
| Clinical features | ||||
| Peripheral vascular disease, No. (%) | 11 (7.9) | 126 (15.5) | 7.6% (1.3%–13.9%) | 0.018 |
| Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, No. (%) | 11 (7.9) | 91 (11.2) | 3.3% (−2.2% to 8.9%) | 0.300 |
| Coronary artery disease, No. (%) | 85 (60.7) | 477 (58.5) | −2.2% (−11.0% to 6.7%) | 0.643 |
| Left ventricular ejection fraction, % | 56.13±12.13 | 55.14±14.44 | 0.98 (−1.79 to 3.76) | 0.487 |
| Aortic valve area, cm2 | 0.66±0.22 | 0.71±0.23 | −0.05 (−0.10 to −0.00) | 0.046 |
| Mean transvalvular aortic gradient, mm Hg | 49.36±19.54 | 46.14±21.50 | 3.22 (−0.89 to 7.32) | 0.125 |
| Symptoms on admission | ||||
| NYHA class | 0.061 | |||
| NYHA I or II, No. (%) | 58 (41.4) | 255 (33.2) | 8.2% (−0.4% to 16.7%) | 0.066 |
| NYHA III or IV, No. (%) | 82 (58.6) | 512 (66.8) | −8.2% (−16.7% to 0.4%) | 0.066 |
| CCS angina class | n=140 | n=811 | 0.508 | |
| No angina, No. (%) | 113 (80.7) | 626 (77.2) | 3.5% (−4.0% to 11.0%) | 0.381 |
| CCS I or II, No. (%) | 21 (15.0) | 131 (16.2) | −1.2% (−7.7% to 5.4%) | 0.803 |
| CCS III or IV, n (%) | 6 (4.3) | 54 (6.7) | −2.4% (−6.7% to 2.0%) | 0.349 |
| Risk assessment | ||||
| Log EuroScore, % | 14.95±8.62 | 18.85±14.78 | −3.90 (−7.14 to −0.67) | 0.018 |
| STS score, % | 4.10±2.42 | 5.04±3.76 | −0.93 (−1.58 to −0.28) | 0.005 |
Values are expressed as means with SDs (P value from t tests) or counts (% of all patients; P value from Fisher or chi‐square tests). CCS indicates Canadian Cardiovascular Society; NYHA, New York Heart Association; STS, Society of Thoracic Surgeons.
Procedural Characteristics
Procedural characteristics are shown in Table 2. Although procedure time was comparable, the amount of contrast media was greater with the LOTUS valve system compared with the Edwards SAPIEN 3 prosthesis (177±77 mL versus 153±93 mL, P=0.004). Patients treated with Edwards SAPIEN 3 more commonly underwent femoral surgical access (12.6% versus 5.7%, P=0.018) and predilatation with balloon valvuloplasty (81.8% versus 31.4%, P<0.001). Device success was 77.1% among patients treated with the LOTUS valve and 75.7% among patients treated with the Edwards SAPIEN 3 prosthesis (P=0.713). There were no significant differences between the two devices with regards to transprosthetic gradient, patient prosthesis mismatch, or postprocedural aortic valve area, respectively (Table 3). Patients treated with the LOTUS valve more commonly had no aortic regurgitation after intervention (71.4% versus 53.2%, difference 18.3%; 95% CI, 9.4–27.1) (Table 2). Whereas 7 patients (0.9%) treated with the Edwards SAPIEN 3 prosthesis underwent valve in series implantation due to malpositioning, no case of valve malpositioning was reported in the LOTUS cohort (P=0.271).
Table 2.
Procedural Characteristics
| LOTUS | Edwards S3 | Difference (95% CI) | P Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| N=140 | N=815 | |||
| Procedure time, min | 69.81±26.09 | 70.25±33.47 | −0.44 (−6.40 to 5.52) | 0.885 |
| Amount of contrast, mL | 177.10±77.06 | 152.59±93.34 | 24.51 (7.78–41.24) | 0.004 |
| General anesthesia, No. (%) | 35 (25.0) | 314 (38.5) | −13.5% (−22.1% to −4.9%) | 0.002 |
| Type of transfemoral access | 0.018 | |||
| Percutaneous, No. (%) | 132 (94.3) | 712 (87.4) | 6.9% (1.2%–12.7%) | |
| Surgical, No. (%) | 8 (5.7) | 103 (12.6) | −6.9% (−12.7% to −1.2%) | |
| Concomitant procedure | ||||
| Percutaneous coronary intervention, No. (%) | 12 (8.6) | 50 (6.1) | −2.4% (−6.9% to 2.0%) | 0.268 |
| Device features | ||||
| Valve size | ||||
| 23 mm | 44 (31.4%) | 216 (26.5%) | ||
| 25 mm | 51 (36.4%) | |||
| 26 mm | 351 (43.1%) | |||
| 27 mm | 45 (32.1%) | |||
| 29 mm | 248 (30.4%) | |||
| Prior balloon aortic valvuloplasty, No. (%) | 44 (31.4) | 667 (81.8) | 50.4% (43.3%; 57.6%) | <0.001 |
| Device success, No. (%) | 108 (77.1%) | 617 (75.7%) | 1.4% (−6.2% to 9.1%) | 0.713 |
| Valve in series, No. (%) | 0 (0.0%) | 7 (0.9%) | −0.9% (−2.4% to 0.7%) | 0.271 |
| Repeat unplanned intervention within 30 days | 1 (0.7%) | 11 (1.3%) | −0.6% (−2.6% to 1.4%) | 0.533 |
| Patient prosthesis mismatch, No. (%) | 0.928 | |||
| Insignificant | 114 (81.4%) | 661 (81.1%) | 0.3% (−6.7% to 7.4%) | |
| Moderate/severe | 26 (18.6%) | 154 (18.9%) | −0.3% (−7.4% to 6.7%) | |
| Aortic regurgitation post‐TAVI | <0.001 | |||
| Grade 0, No. (%) | 100 (71.4) | 430 (53.2) | 18.3% (9.4%–27.1%) | |
| Grade 1, No. (%) | 39 (27.9) | 369 (45.6) | −17.8% (−26.6% to −8.9%) | |
| Grade 2, No. (%) | 1 (0.7) | 10 (1.2) | −0.5% (−2.4% to 1.4%) | |
| Grade 3, No. (%) | 0 | 0 | na | |
| Postprocedure | ||||
| Mean transprosthetic gradient, mm Hg | 10.29±6.10 | 9.51±5.10 | 0.79 (−0.17 to 1.74) | 0.106 |
| Aortic valve area, mm | 1.78±0.61 | 1.75±0.53 | 0.03 (−0.10 to 0.16) | 0.675 |
| In‐hospital course | ||||
| Any PRBC, No. (%) | 11 (7.9) | 111 (13.6) | 5.8% (−0.2% to 11.8%) | 0.074 |
| Number of PRBC, median (interquartile range) | 2.0 (1.0–4.0) | 2.0 (2.0–3.3) | 1.85 (0.03–3.68) | 0.839 |
| Overall in‐hospital stay after TAVI, days | 9.34±4.40 | 9.47±5.55 | −0.13 (−1.10 to 0.84) | 0.790 |
Values are expressed as means with standard deviations (P values from t tests) or counts (% of all patients; P values from Fisher tests or chi‐square tests). PRBC indicates packed red blood cell; TAVI, transcatheter aortic valve implantation.
Table 3.
Clinical Outcomes at 30 Days
| LOTUS | Edwards S3 | HR (95% CI) | P Value | Adjusted HR (95% CI) | Adjusted P Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N=140 | N=815 | |||||
| Early safety primary end point VARC2 | 20 (14.3) | 119 (14.6) | 0.97 (0.61–1.56) | 0.915 | 1.03 (0.64–1.67) | 0.909 |
| Mortality, No. (%) | 3 (2.2) | 23 (2.8) | 0.75 (0.22–2.49) | 0.636 | 0.75 (0.22–2.51) | 0.636 |
| Cardiovascular Mortality, No. (%) | 2 (1.5) | 21 (2.6) | 0.55 (0.13–2.33) | 0.414 | 0.51 (0.12–2.21) | 0.371 |
| Cerebrovascular accident, No. (%) | 6 (4.3) | 25 (3.1) | 1.40 (0.57–3.41) | 0.461 | 1.42 (0.57–3.50) | 0.448 |
| Disabling stroke, No. (%) | 3 (2.1) | 9 (1.1) | 1.93 (0.52–7.15) | 0.322 | 2.01 (0.53–7.61) | 0.304 |
| Nondisabling stroke, No. (%) | 3 (2.1) | 11 (1.4) | 1.58 (0.44–5.68) | 0.480 | 1.59 (0.43–5.79) | 0.485 |
| TIA, No. (%) | 0 (0.0) | 5 (0.6) | 0.53 (0.03–9.53) | 1.000 | ||
| MI, No. (%) | 0 (0.0) | 9 (1.1) | 0.31 (0.02–5.30) | 0.371 | ||
| Periprocedural MI, No. (%) | 0 (0.0) | 7 (0.9) | 0.39 (0.02–6.79) | 0.602 | ||
| Spontaneous MI, n (%) | 0 (0.0) | 2 (0.3) | 1.16 (0.06–24.03) | 1.000 | ||
| Acute kidney injury, No. (%) | 2 (1.4) | 26 (3.2) | 0.44 (0.10–1.86) | 0.265 | 0.62 (0.14–2.67) | 0.522 |
| Stage 1, No. (%) | 1 (0.7) | 5 (0.6) | 1.16 (0.14–9.94) | 0.891 | 1.06 (0.12–9.55) | 0.960 |
| Stage 2, No. (%) | 0 (0.0) | 6 (0.7) | 0.45 (0.03–7.94) | 0.600 | ||
| Stage 3, No. (%) | 1 (0.7) | 15 (1.9) | 0.38 (0.05–2.90) | 0.353 | 0.61 (0.08–4.79) | 0.642 |
| Bleeding, No. (%) | 17 (12.2) | 131 (16.2) | 0.74 (0.45–1.23) | 0.246 | 0.79 (0.47–1.32) | 0.368 |
| Life‐threatening bleeding, No. (%) | 6 (4.3) | 45 (5.5) | 0.77 (0.33–1.81) | 0.550 | 0.79 (0.33–1.87) | 0.586 |
| Major bleeding, No. (%) | 8 (5.7) | 59 (7.3) | 0.78 (0.37–1.63) | 0.512 | 0.81 (0.38–1.71) | 0.572 |
| Minor bleeding, No. (%) | 3 (2.1) | 28 (3.5) | 0.62 (0.19–2.03) | 0.425 | 0.75 (0.22–2.49) | 0.633 |
| Vascular access site and access‐related complications, No. (%) | 19 (13.6) | 112 (13.8) | 0.98 (0.60–1.60) | 0.946 | 0.96 (0.59–1.58) | 0.880 |
| Major vascular complications, No. (%) | 10 (7.2) | 76 (9.3) | 0.76 (0.39–1.47) | 0.416 | 0.72 (0.37–1.41) | 0.342 |
| Minor vascular complications, No. (%) | 8 (5.7) | 32 (3.9) | 1.45 (0.67–3.16) | 0.344 | 1.45 (0.66–3.19) | 0.357 |
| Structural valve deterioration, No. (%) | 0 (0.0) | 1 (0.1) | 1.93 (0.08–47.14) | 1.000 | ||
| Repeat unplanned intervention, No. (%) | 1 (0.7) | 11 (1.4) | 0.52 (0.07–4.04) | 0.534 | 0.38 (0.05–3.04) | 0.363 |
| Valve‐related dysfunction requiring intervention | 0 (0.0) | 3 (0.4) | 0.83 (0.04–15.98) | 1.000 | ||
| Valve in valve treatment, No. (%) | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | ||||
| Surgical revision, No. (%) | 0 (0.0) | 3 (0.4) | 0.83 (0.04–15.98) | 1.000 | ||
| Other, No. (%) | 1 (0.7) | 8 (1.0) | 0.72 (0.09–5.73) | 0.754 | 0.53 (0.06–4.32) | 0.550 |
| Permanent pacemaker implantation, No. (%) | 48 (34.3) | 113 (14.1) | 2.76 (1.97–3.87) | <0.001 | 2.63 (1.86–3.73) | <0.001 |
Depicted are the number of first events within 30 days with percentage of all patients. All clinical outcomes were adjudicated, except for pacemaker implantations. Cox regressions reporting hazard ratios (HRs; with 95% CIs) or continuity corrected risk ratios (95% CIs) in case of zero events with Fisher exact P values. Adjusted HR from Cox regressions, adjusting for age, dyslipidemia, peripheral vascular disease, aortic regurgitation moderate or severe, aortic valve area, New York Heart Association class III or IV, and Society of Thoracic Surgery risk score (combining the estimates of 20 data sets using Rubin's rule because of missing data). Multiple imputation of missing data was performed using chained equations (n=20 data sets generated). There was no adjusted analyses if there were fewer than 5 events overall. MI indicates myocardial infarction; TIA, transient ischemic attack; VARC2, Valve Academic Research Consortium.
Clinical Outcomes
The early VARC2 safety end point occurred in 14.3% of patients treated with the LOTUS and 14.6% of patients treated with the Edwards SAPIEN 3 prosthesis with no difference in crude (HR, 0.97; 95% CI, 0.61–1.56 [P=0.915]) and adjusted (HR, 1.03; 95% CI, 0.64–1.67 [P=0.909]) analyses (Figure 1). Individual components of the primary composite end point are summarized in Table 3. All‐cause mortality at 30 days was 2.2% among patients treated with the LOTUS valve system, and 2.8% among patients treated with the Edwards SAPIEN 3 valve (adjusted HR, 0.75; 95% CI, 0.22–2.51 [P=0.636]). Estimated and observed mortality are illustrated in Figure 2. There were no significant differences between the two devices with regard to mortality, cerebrovascular accidents, myocardial infarction, vascular access site, and bleeding complications. While none of the patients in the LOTUS group experienced periprocedural myocardial infarction, 7 patients treated with the Edwards SAPIEN 3 prosthesis did (0.9%) (HR, 0.39; 95% CI, 0.02–6.79 [P=0.602]).
Figure 1.
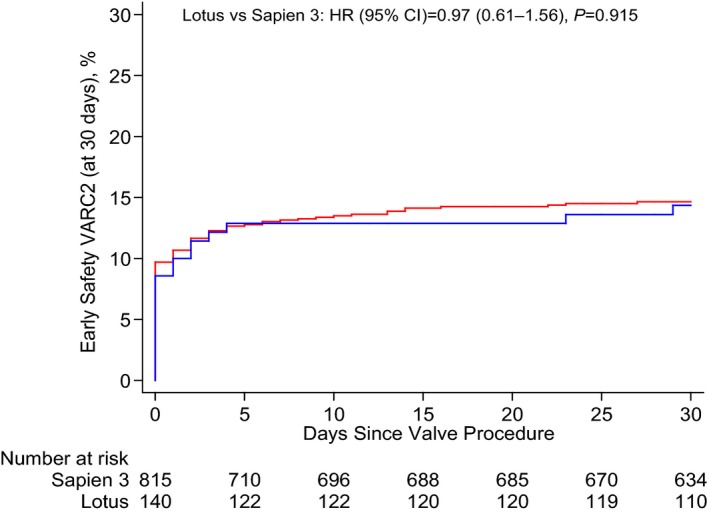
Kaplan–Meier estimates of the Valve Academic Research Consortium 2 (VARC2) early safety composite outcome at 30 days. The blue line relates to the LOTUS valve system; the red line relates to the Edwards SAPIEN 3 valve. HR indicates hazard ratio.
Figure 2.
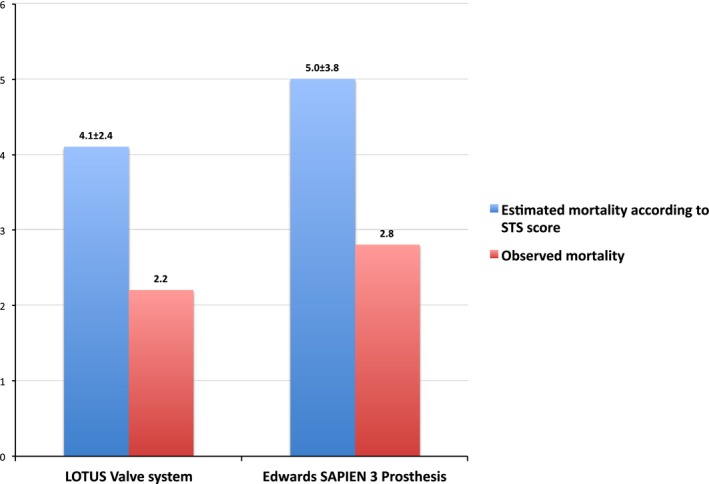
Bar graph of estimated and observed mortality at 30 days. Society of Thoracic Surgeons (STS) risk scores were used to estimate mortality at 30 days.
Despite a higher amount of contrast used in patients treated with the LOTUS valve, there were no differences with respect to acute kidney injury. The number of permanent pacemaker implantations was higher in patients treated with the LOTUS (34.3%) as compared with the Edwards SAPIEN 3 prosthesis (14.1%) (HR, 2.76; 95% CI, 1.97–3.87 [P<0.001]) (Figure 3). In a stratified analysis for the VARC2 early safety outcome, there were no significant interactions across major subgroups, with the exception of a positive effect for treatment with the LOTUS valve among patients 83 years and older (P for interaction=0.030) (Figure 4).
Figure 3.
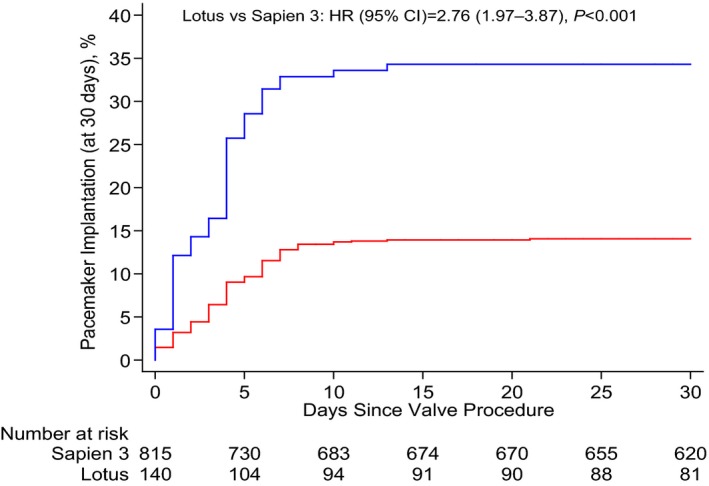
Kaplan–Meier estimates for permanent pacemaker implantation within 30 days. The blue line relates to the LOTUS valve system; the red line relates to the Edwards SAPIEN 3 valve. HR indicates hazard ratio.
Figure 4.
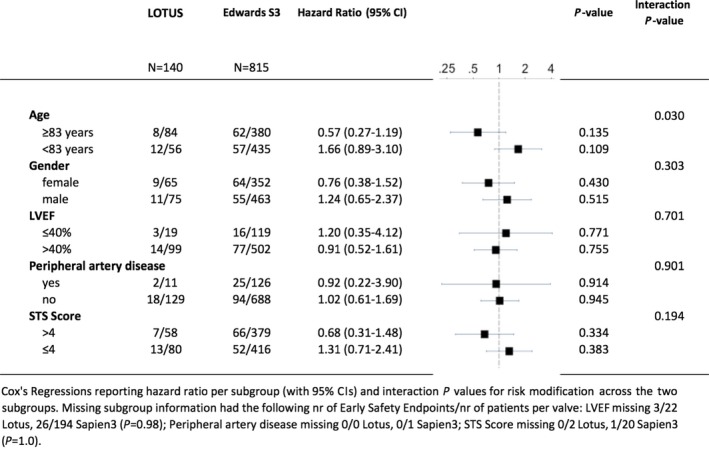
Stratified analysis for the Valve Academic Research Consortium 2 Early Composite Safety Outcome (based on crude hazard ratios). LVEF indicates left ventricular ejection fraction; STS, Society of Thoracic Surgeons.
Discussion
The key findings of our analysis can be summarized as follows.
In a nationwide prospective registry of patients undergoing TAVI, we found no differences for the primary end point, the early composite safety end point within 30 days between patients treated with the fully repositionable LOTUS valve system versus the balloon‐expandable Edwards SAPIEN 3 prosthesis.
Rates of device success were comparable for both devices.
More than mild residual aortic regurgitation was exceedingly low with both devices.
Patients treated with the LOTUS valve system had a 2‐ to 3‐fold increased risk of permanent pacemaker implantation compared with patients treated with the Edwards SAPIEN 3 prosthesis.
Newer‐generation TAVI devices are characterized by improved device success as compared with early‐generation devices primarily by a reduction of moderate or severe prosthetic valve regurgitation, which has consistently been associated with increased late mortality.8, 9 Documentation of moderate to severe aortic regurgitation has been reported in up to 14% of patients treated with early‐generation devices,8, 9, 10 and motivated the development of internal skirts and external cuffs to seal the prosthesis to the aortic annulus and reduce paravalvular regurgitation. Complimentary to technical refinements of the devices, dedicated imaging tools have been introduced allowing for precise device positioning within the annular landing zone. In the Swiss TAVI registry, moderate or severe aortic regurgitation was documented in 0.7% and 1.2% of patients treated with LOTUS and Edwards SAPIEN 3, respectively. Our findings are consistent with the Repositionable Percutaneous Replacement of Stenotic Aortic Valve Through Implantation of Lotus Valve System: Evaluation of Safety and Performance (REPRISE) II study and the UK LOTUS registry, reporting moderate or severe aortic regurgitation in 1% and 0.8% of patients, respectively.2, 3 Reduction of paravalvular aortic regurgitation results from a combination of both, the full repositionability of the LOTUS valve allowing for an assessment of the result prior to deployment, and the prosthesis design with an adaptive seal in the distal portion and an outer sleeve.6 A similarly low incidence of moderate to severe aortic regurgitation was documented with the Edwards SAPIEN 3 valve that has been refined by an external sealing cuff that mimics a parachute. The incidence of more than mild paravalvular regurgitation decreased from 5.3% to 1.3% (P=0.04) as compared with its predecessor in a previous analysis from the Swiss TAVI registry including almost 600 patients.11
Rates of permanent pacemaker implantation amounted to 34% among patients treated with the LOTUS valve, and were 2‐ to 3‐fold higher compared with patients treated with the Edwards SAPIEN 3 prosthesis. Comparable rates of AV conductance disturbances and permanent pacemaker implantation have been consistently reported in the REPRISE II study (28.6%) and the UK LOTUS registry (31.8%).2, 3 The effect of permanent pacemaker implantation after TAVI on long‐term outcomes remains a matter of debate.12, 13 No difference in 1‐year mortality was documented in patients with a previous permanent pacemaker, a new permanent pacemaker, or no pacemaker in a prospective registry of 353 patients from 2 institutions.12 In contrast, permanent pacemaker implantation after TAVI was reported to be an independent predictor of 1‐year mortality in an analysis of the Placement of Aortic Transcatheter Valves (PARTNER I) trial.13 Moreover, permanent pacemaker implantation was associated with a longer duration of hospitalization and higher rates of repeat hospitalization at 1 year.14 The degree of pacemaker dependency accompanied by ventricular dyssynchrony may reconcile the differential in clinical findings between studies. AV conductance disturbances along with pacemaker dependency after TAVI may be temporary rather than permanent in nature. In a small study of 36 patients with new pacemaker following implantation of a self‐expandable prosthesis, more than half of the patients were pacemaker independent at a median follow‐up of 12 months.15
The rates of the early composite safety end point were comparable between the two devices at 30 days. In line, there were no differences with respect to cardiovascular mortality, myocardial infarction, bleeding, or vascular access site complications. The observed mortality rate (LOTUS 2.2% versus SAPIEN 3 2.8%) was substantially lower as compared with the STS estimates. The overall incidence of stroke was 4.3% and 3.1% of patients treated with the LOTUS valve system and the Edwards SAPIEN 3 prosthesis, respectively. The incidence of stroke at 30 days was 5.9% in the REPRISE II study and 3.9% in the UK LOTUS registry,2, 3 while large nationwide TAVI registries reported stroke rates in the range of 1.5% to 4%.9, 11, 16, 17, 18, 19 Although the signal has to be interpreted with caution, several reasons may account for a potential difference in cerebrovascular events between the two devices. A significantly lower rate of prior balloon valvuloplasty among patients treated with the LOTUS valve as compared with the Edwards SAPIEN valve may affect the rates of stroke. In a small study of 87 patients, the volume of new cerebral ischemic lesions as assessed by diffusion‐weighted magnetic resonance imaging was significantly higher among patients without as compared with patients with prior balloon aortic valvuloplasty.20 In contrast, a recent meta‐analysis of 18 studies with 2443 patients demonstrated a trend towards a reduced risk of clinically relevant stroke with direct TAVI. However, the findings should be interpreted with caution given the limitations of the nonrandomized studies included in the meta‐analysis and the unadjusted nature of the summary measures used.21 The effect of predilatation on clinical outcome is currently being investigated in the Transcatheter Aortic Valve Implantation Without Predilatation (SIMPLIFy TAVI) study (NCT 01539746) and the Balloon Expandable Transcatheter Aortic Valve Implantation Without Predilatation of Aortic Valve (EASE‐IT) study (NCT02127580). Moreover, differences in the delivery catheter diameter, flexibility, and steerability may affect the risk of plaque abrasion in the aortic arch. Finally, full repositionability of the LOTUS valve may increase the inclination of repeated prosthesis placement, which, in turn, has been associated with an increased risk of stroke.22
Study Limitations
The present analysis has several limitations. First, there was no random allocation to treatment with the LOTUS valve or the Edwards SAPIEN 3 prosthesis, respectively. Although baseline characteristics between the two treatment arms were comparable, we cannot exclude selection of treatment according to concealed confounders. We used an adjusted analysis to correct for differences in baseline characteristics. Second, the number of patients included in the analysis was limited, and the duration of follow‐up did not extend beyond 30 days. However, it constitutes the largest series reported to date and data are consistent with previously reported single‐arm registries. Third, differences in balloon valvuloplasty prior to device implantation may have confounded the clinical results. However, our analysis reflects routine clinical practice with the 2 devices by experienced operators. Finally, implantation depth and oversizing have both been associated with an increased rate of conductance disturbances, respectively. Neither of which were prospectively documented in our registry.
Conclusions
In a nationwide registry, no statistical difference was found between the repositionable LOTUS valve system and the balloon‐expandable Edwards SAPIEN 3 prosthesis with respect to the VARC2 early safety outcome for the treatment. Rates of moderate or severe aortic regurgitation are exceedingly low for both devices. The need for new permanent pacemaker implantation was more frequent among patients treated with the LOTUS valve.
Sources of Funding
The Swiss TAVI registry is supported by a study grant from the Swiss Heart Foundation and the Swiss Working Group of Interventional Cardiology, and is sponsored by unrestricted funds from Boston Scientific, Edwards Lifesciences, Medtronic, St. Jude Medical, and Symetis. The study sponsors had no role in the study design, data collection, data analysis, data interpretation, or writing of the report.
Disclosures
Dr Pilgrim serves as a consultant to St. Jude Medical, and received research contracts to the institution from Edwards Lifesciences and Symetis. Dr Nietlispach serves as consultant to Edwards Lifesciences and St. Jude Medical. Dr Tueller received speakers' fees from Edwards Lifesciences and travel expenses from Medtronic. Dr Toggweiler is a proctor for Symetis and received speakers' fees from Edwards Lifesciences and Medtronic. Dr Jeger serves as a consultant to St. Jude Medical and has received reimbursement for travel expenses from Medtronic, Boston Scientific, and Edwards Lifesciences. Dr Ferrari is a proctor for Edwards Lifesciences. Dr Noble serves as consultant for Medtronic. Dr Roffi received institutional research grants from Abbott Vascular, Boston Scientific, Biotronik, Biosensor, and Medtronic. Dr Huber is a proctor for Edwards Lifesciences and Consultant for Medtronic. Dr Windecker has received research contracts to the institution from Abbott, Boston Scientific, Biosensors, Cordis, Medtronic, and St. Jude. Dr Wenaweser serves as proctor for Medtronic, Edwards Lifesciences, and Boston Scientific and has received an unrestricted grant from Medtronic to the institution (University of Bern). All of the other authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Supporting information
Table S1. Missing Baseline Characteristics, Multiple Imputation, and Adjusted Analyses
Appendix S1. Collaborators and Swiss Transcatheter Aortic Valve Implantation Registry Investigators.
(J Am Heart Assoc. 2016;5:e004088 doi: 10.1161/JAHA.116.004088)
A complete list of the Collaborators and Swiss Transcatheter Aortic Valve Implantation Registry Investigators can be found in the Supplemental Material.
References
- 1. Pilgrim T, Windecker S. Newer‐generation devices for transcatheter aortic valve replacement. JACC Cardiovasc Interv. 2016;9:373–375. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2. Meredith Am IT, Walters DL, Dumonteil N, Worthley SG, Tchétché D, Manoharan G, Blackman DJ, Rioufol G, Hildick‐Smith D, Whitbourn RJ, Lefèvre T, Lange R, Müller R, Redwood S, Allocco DJ, Dawkins KD. Transcatheter aortic valve replacement for severe symptomatic aortic stenosis using a repositionable valve system: 30‐day primary endpoint results from the REPRISE II study. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2014;64:1339–1348. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3. Rampat R, Khawaja MZ, Byrne J, MacCarthy P, Blackman DJ, Krishnamurthy A, Gunarathne A, Kovac J, Banning A, Kharbanda R, Firoozi S, Brecker S, Redwood S, Bapat V, Mullen M, Aggarwal S, Manoharan G, Spence MS, Khogali S, Dooley M, Cockburn J, de Belder A, Trivedi U, Hildick‐Smith D. Transcatheter aortic valve replacement using the repositionable LOTUS valve. JACC Cardiovasc Interv. 2016;9:367–372. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4. Meredith IT, Walters DL, Dumonteil N, Worthley SG, Tchétché D, Manoharan G, Blackman DJ, Rioufol G, Hildick‐Smith D, Whitbourn RJ, Lefèvre T, Lange R, Müller R, Redwood S, Feldman TE, Allocco DJ, Dawkins KD. 1‐year outcomes with the fully repositionable and retrievable Lotus Transcatheter Aortic Replacement Valve in 120 high‐risk surgical patients with severe aortic stenosis. JACC Cardiovasc Interv. 2016;9:376–384. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5. Wenaweser P, Stortecky S, Heg D, Tueller D, Nietlispach F, Falk V, Pedrazzini G, Jeger R, Reuthebuch O, Carrel T, Räber L, Amann FW, Ferrari E, Toggweiler S, Noble S, Roffi M, Gruenenfelder J, Jüni P, Windecker S, Huber C. Short‐term clinical outcomes among patients undergoing transcatheter aortic valve implantation in Switzerland: the Swiss TAVI registry. EuroIntervention. 2014;10:982–989. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6. Tchetche D, Van Mieghem NM. New‐generation TAVI devices: description and specifications. EuroIntervention. 2014;10(suppl U):U90–U100. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7. Kappetein AP, Head SJ, Généreux P, Piazza N, van Mieghem NM, Blackstone EH, Brott TG, Cohen DJ, Cutlip DE, van Es G‐A, Hahn RT, Kirtane AJ, Krucoff MW, Kodali S, Mack MJ, Mehran R, Rodés‐Cabau J, Vranckx P, Webb JG, Windecker S, Serruys PW, Leon MB. Updated standardized endpoint definitions for transcatheter aortic valve implantation: the Valve Academic Research Consortium‐2 consensus document. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2012;60:1438–1454. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8. Kodali SK, Williams MR, Smith CR, Svensson LG, Webb JG, Makkar RR, Fontana GP, Dewey TM, Thourani VH, Pichard AD, Fischbein M, Szeto WY, Lim S, Greason KL, Teirstein PS, Malaisrie SC, Douglas PS, Hahn RT, Whisenant B, Zajarias A, Wang D, Akin JJ, Anderson WN, Leon MB; PARTNER Trial Investigators . Two‐year outcomes after transcatheter or surgical aortic‐valve replacement. N Engl J Med. 2012;366:1686–1695. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9. Ludman PF, Moat N, de Belder MA, Blackman DJ, Duncan A, Banya W, MacCarthy PA, Cunningham D, Wendler O, Marlee D, Hildick‐Smith D, Young CP, Kovac J, Uren NG, Spyt T, Trivedi U, Howell J, Gray H; UK TAVI Steering Committee and the National Institute for Cardiovascular Outcomes Research . Transcatheter aortic valve implantation in the United Kingdom: temporal trends, predictors of outcome, and 6‐year follow‐up: a report from the UK Transcatheter Aortic Valve Implantation (TAVI) Registry, 2007 to 2012. Circulation. 2015;131:1181–1190. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10. Abdel‐Wahab M, Comberg T, Büttner HJ, El‐Mawardy M, Chatani K, Gick M, Geist V, Richardt G, Neumann F‐J; Segeberg‐Krozingen TAVI Registry . Aortic regurgitation after transcatheter aortic valve implantation with balloon‐ and self‐expandable prostheses: a pooled analysis from a 2‐center experience. JACC Cardiovasc Interv. 2014;7:284–292. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11. Binder RK, Stortecky S, Heg D, Tueller D, Jeger R, Toggweiler S, Pedrazzini G, Amann FW, Ferrari E, Noble S, Nietlispach F, Maisano F, Räber L, Roffi M, Grünenfelder J, Jüni P, Huber C, Windecker S, Wenaweser P. Procedural results and clinical outcomes of transcatheter aortic valve implantation in Switzerland: an observational cohort study of Sapien 3 versus Sapien XT transcatheter heart valves. Circ Cardiovasc Interv. 2015;8:e002653. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12. Buellesfeld L, Stortecky S, Heg D, Hausen S, Mueller R, Wenaweser P, Pilgrim T, Gloekler S, Khattab AA, Huber C, Carrel T, Eberle B, Meier B, Boekstegers P, Jüni P, Gerckens U, Grube E, Windecker S. Impact of permanent pacemaker implantation on clinical outcome among patients undergoing transcatheter aortic valve implantation. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2012;60:493–501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13. Dizon JM, Nazif TM, Hess PL, Biviano A, Garan H, Douglas PS, Kapadia S, Babaliaros V, Herrmann HC, Szeto WY, Jilaihawi H, Fearon WF, Tuzcu EM, Pichard AD, Makkar R, Williams M, Hahn RT, Xu K, Smith CR, Leon MB, Kodali SK; PARTNER Publications Office . Chronic pacing and adverse outcomes after transcatheter aortic valve implantation. Heart. 2015;101:1665–1671. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14. Nazif TM, Dizon JM, Hahn RT, Xu K, Babaliaros V, Douglas PS, El‐Chami MF, Herrmann HC, Mack M, Makkar RR, Miller DC, Pichard A, Tuzcu EM, Szeto WY, Webb JG, Moses JW, Smith CR, Williams MR, Leon MB, Kodali SK. Predictors and clinical outcomes of permanent pacemaker implantation after transcatheter aortic valve replacement. JACC Cardiovasc Interv. 2015;8:60–69. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15. Van der Boon RMA, Van Mieghem NM, Theuns DA, Nuis R‐J, Nauta ST, Serruys PW, Jordaens L, van Domburg RT, de Jaegere PPT. Pacemaker dependency after transcatheter aortic valve implantation with the self‐expanding Medtronic CoreValve System. Int J Cardiol. 2013;168:1269–1273. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16. Walther T, Hamm CW, Schuler G, Berkowitsch A, Kötting J, Mangner N, Mudra H, Beckmann A, Cremer J, Welz A, Lange R, Kuck K‐H, Mohr FW, Möllmann H; GARY Executive Board . Perioperative results and complications in 15,964 transcatheter aortic valve replacements: prospective data from the GARY registry. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2015;65:2173–2180. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17. Mack MJ, Brennan JM, Brindis R, Carroll J, Edwards F, Grover F, Shahian D, Tuzcu EM, Peterson ED, Rumsfeld JS, Hewitt K, Shewan C, Michaels J, Christensen B, Christian A, O'Brien S, Holmes D; STS/ACC TVT Registry . Outcomes following transcatheter aortic valve replacement in the United States. JAMA. 2013;310:2069–2077. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18. Holmes DR, Brennan JM, Rumsfeld JS, Dai D, O'Brien SM, Vemulapalli S, Edwards FH, Carroll J, Shahian D, Grover F, Tuzcu EM, Peterson ED, Brindis RG, Mack MJ. Clinical outcomes at 1 year following transcatheter aortic valve replacement. JAMA. 2015;313:1019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19. Thourani VH, Kodali S, Makkar RR, Herrmann HC, Williams M, Babaliaros V, Smalling R, Lim S, Malaisrie SC, Kapadia S, Szeto WY, Greason KL, Kereiakes D, Ailawadi G, Whisenant BK, Devireddy C, Leipsic J, Hahn RT, Pibarot P, Weissman NJ, Jaber WA, Cohen DJ, Suri R, Tuzcu EM, Svensson LG, Webb JG, Moses JW, Mack MJ, Miller DC, Smith CR, Alu MC, Parvataneni R, D'Agostino RB, Leon MB. Transcatheter aortic valve replacement versus surgical valve replacement in intermediate‐risk patients: a propensity score analysis. Lancet. 2016. Available at: http://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S0140673616300733. Accessed April 23, 2016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20. Bijuklic K, Haselbach T, Witt J, Krause K, Hansen L, Gehrckens R, Rieß F‐C, Schofer J. Increased risk of cerebral embolization after implantation of a balloon‐expandable aortic valve without prior balloon valvuloplasty. JACC Cardiovasc Interv. 2015;8:1608–1613. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21. Liao Y, Meng Y, Zhao Z, Zuo Z, Li Y, Xiong T, Cao J, Xu Y, Feng Y, Chen M. Meta‐analysis of the effectiveness and safety of transcatheter aortic valve implantation without balloon predilation. Am J Cardiol. 2016. Available at: http://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S000291491630296X. Accessed April 23, 2016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22. Stortecky S, Windecker S, Pilgrim T, Heg D, Buellesfeld L, Khattab AA, Huber C, Gloekler S, Nietlispach F, Mattle H, Jüni P, Wenaweser P. Cerebrovascular accidents complicating transcatheter aortic valve implantation: frequency, timing and impact on outcomes. EuroIntervention. 2012;8:62–70. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Table S1. Missing Baseline Characteristics, Multiple Imputation, and Adjusted Analyses
Appendix S1. Collaborators and Swiss Transcatheter Aortic Valve Implantation Registry Investigators.


