Abstract
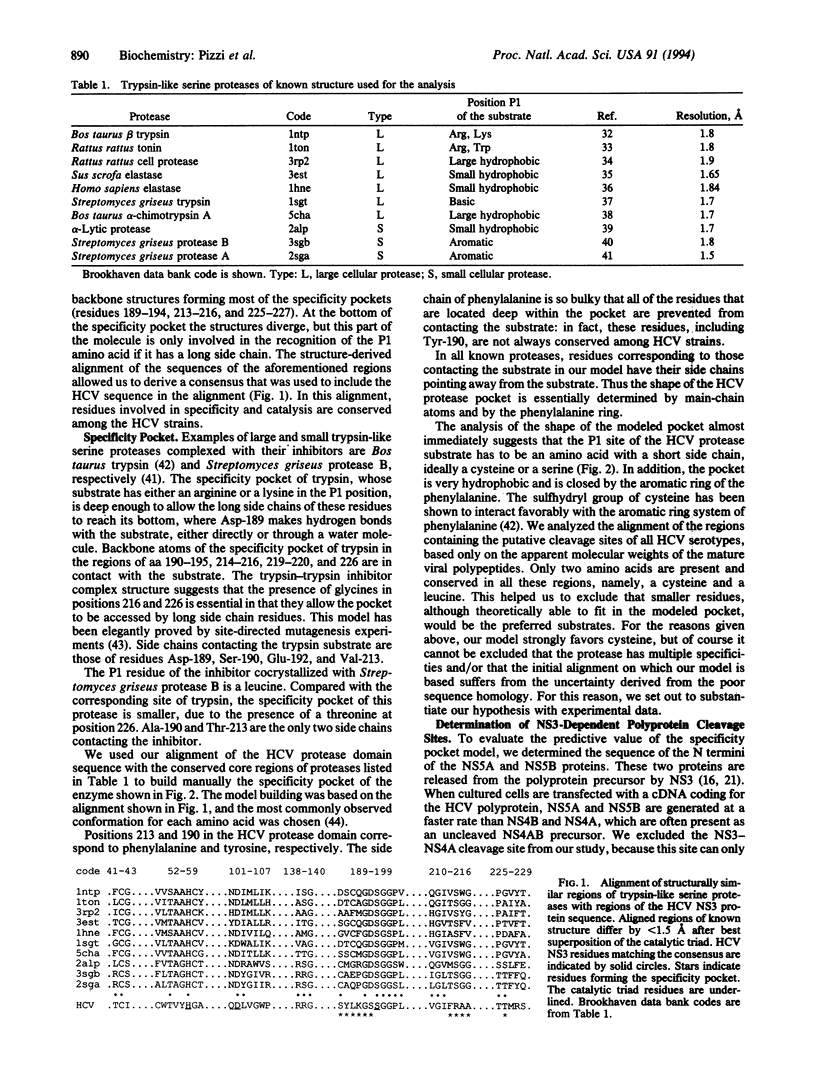
We have built a model of the specificity pocket of the protease of hepatitis C virus on the basis of the known structures of trypsin-like serine proteases and of the conservation pattern of the protease sequences among various hepatitis C strains. The model allowed us to predict that the substrate of this protease should have a cysteine residue in position P1. This hypothesis was subsequently proved by N-terminal sequencing of two products of the protease. The success of this "blind" test increases our confidence in the overall correctness of our proposed alignment of the enzyme sequence with those of other proteases of known structure and constitutes a first step in the construction of a complete model of the viral protease domain.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bazan J. F., Fletterick R. J. Detection of a trypsin-like serine protease domain in flaviviruses and pestiviruses. Virology. 1989 Aug;171(2):637–639. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(89)90639-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernstein F. C., Koetzle T. F., Williams G. J., Meyer E. F., Jr, Brice M. D., Rodgers J. R., Kennard O., Shimanouchi T., Tasumi M. The Protein Data Bank: a computer-based archival file for macromolecular structures. J Mol Biol. 1977 May 25;112(3):535–542. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(77)80200-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blevins R. A., Tulinsky A. The refinement and the structure of the dimer of alpha-chymotrypsin at 1.67-A resolution. J Biol Chem. 1985 Apr 10;260(7):4264–4275. doi: 10.2210/pdb5cha/pdb. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bode W., Walter J., Huber R., Wenzel H. R., Tschesche H. The refined 2.2-A (0.22-nm) X-ray crystal structure of the ternary complex formed by bovine trypsinogen, valine-valine and the Arg15 analogue of bovine pancreatic trypsin inhibitor. Eur J Biochem. 1984 Oct 1;144(1):185–190. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1984.tb08447.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen P. J., Lin M. H., Tai K. F., Liu P. C., Lin C. J., Chen D. S. The Taiwanese hepatitis C virus genome: sequence determination and mapping the 5' termini of viral genomic and antigenomic RNA. Virology. 1992 May;188(1):102–113. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(92)90739-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Choo Q. L., Kuo G., Weiner A. J., Overby L. R., Bradley D. W., Houghton M. Isolation of a cDNA clone derived from a blood-borne non-A, non-B viral hepatitis genome. Science. 1989 Apr 21;244(4902):359–362. doi: 10.1126/science.2523562. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Choo Q. L., Richman K. H., Han J. H., Berger K., Lee C., Dong C., Gallegos C., Coit D., Medina-Selby R., Barr P. J. Genetic organization and diversity of the hepatitis C virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Mar 15;88(6):2451–2455. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.6.2451. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craik C. S., Largman C., Fletcher T., Roczniak S., Barr P. J., Fletterick R., Rutter W. J. Redesigning trypsin: alteration of substrate specificity. Science. 1985 Apr 19;228(4697):291–297. doi: 10.1126/science.3838593. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devereux J., Haeberli P., Smithies O. A comprehensive set of sequence analysis programs for the VAX. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 11;12(1 Pt 1):387–395. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.1part1.387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuerst T. R., Niles E. G., Studier F. W., Moss B. Eukaryotic transient-expression system based on recombinant vaccinia virus that synthesizes bacteriophage T7 RNA polymerase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Nov;83(21):8122–8126. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.21.8122. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujinaga M., Delbaere L. T., Brayer G. D., James M. N. Refined structure of alpha-lytic protease at 1.7 A resolution. Analysis of hydrogen bonding and solvent structure. J Mol Biol. 1985 Aug 5;184(3):479–502. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90296-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujinaga M., James M. N. Rat submaxillary gland serine protease, tonin. Structure solution and refinement at 1.8 A resolution. J Mol Biol. 1987 May 20;195(2):373–396. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90658-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grakoui A., McCourt D. W., Wychowski C., Feinstone S. M., Rice C. M. Characterization of the hepatitis C virus-encoded serine proteinase: determination of proteinase-dependent polyprotein cleavage sites. J Virol. 1993 May;67(5):2832–2843. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.5.2832-2843.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grakoui A., Wychowski C., Lin C., Feinstone S. M., Rice C. M. Expression and identification of hepatitis C virus polyprotein cleavage products. J Virol. 1993 Mar;67(3):1385–1395. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.3.1385-1395.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hijikata M., Kato N., Ootsuyama Y., Nakagawa M., Shimotohno K. Gene mapping of the putative structural region of the hepatitis C virus genome by in vitro processing analysis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jul 1;88(13):5547–5551. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.13.5547. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Houghton M., Weiner A., Han J., Kuo G., Choo Q. L. Molecular biology of the hepatitis C viruses: implications for diagnosis, development and control of viral disease. Hepatology. 1991 Aug;14(2):381–388. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inchauspe G., Zebedee S., Lee D. H., Sugitani M., Nasoff M., Prince A. M. Genomic structure of the human prototype strain H of hepatitis C virus: comparison with American and Japanese isolates. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Nov 15;88(22):10292–10296. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.22.10292. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kato N., Hijikata M., Ootsuyama Y., Nakagawa M., Ohkoshi S., Sugimura T., Shimotohno K. Molecular cloning of the human hepatitis C virus genome from Japanese patients with non-A, non-B hepatitis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Dec;87(24):9524–9528. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.24.9524. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kossiakoff A. A. Use of the neutron diffraction--H/D exchange technique to determine the conformational dynamics of trypsin. Basic Life Sci. 1984;27:281–304. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4899-0375-4_17. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuo G., Choo Q. L., Alter H. J., Gitnick G. L., Redeker A. G., Purcell R. H., Miyamura T., Dienstag J. L., Alter M. J., Stevens C. E. An assay for circulating antibodies to a major etiologic virus of human non-A, non-B hepatitis. Science. 1989 Apr 21;244(4902):362–364. doi: 10.1126/science.2496467. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer E., Cole G., Radhakrishnan R., Epp O. Structure of native porcine pancreatic elastase at 1.65 A resolutions. Acta Crystallogr B. 1988 Feb 1;44(Pt 1):26–38. doi: 10.1107/s0108768187007559. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller R. H., Purcell R. H. Hepatitis C virus shares amino acid sequence similarity with pestiviruses and flaviviruses as well as members of two plant virus supergroups. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Mar;87(6):2057–2061. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.6.2057. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moult J., Sussman F., James M. N. Electron density calculations as an extension of protein structure refinement. Streptomyces griseus protease A at 1.5 A resolution. J Mol Biol. 1985 Apr 20;182(4):555–566. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90241-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Navia M. A., McKeever B. M., Springer J. P., Lin T. Y., Williams H. R., Fluder E. M., Dorn C. P., Hoogsteen K. Structure of human neutrophil elastase in complex with a peptide chloromethyl ketone inhibitor at 1.84-A resolution. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jan;86(1):7–11. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.1.7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neurath H. Evolution of proteolytic enzymes. Science. 1984 Apr 27;224(4647):350–357. doi: 10.1126/science.6369538. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okamoto H., Kurai K., Okada S., Yamamoto K., Lizuka H., Tanaka T., Fukuda S., Tsuda F., Mishiro S. Full-length sequence of a hepatitis C virus genome having poor homology to reported isolates: comparative study of four distinct genotypes. Virology. 1992 May;188(1):331–341. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(92)90762-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okamoto H., Okada S., Sugiyama Y., Kurai K., Iizuka H., Machida A., Miyakawa Y., Mayumi M. Nucleotide sequence of the genomic RNA of hepatitis C virus isolated from a human carrier: comparison with reported isolates for conserved and divergent regions. J Gen Virol. 1991 Nov;72(Pt 11):2697–2704. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-72-11-2697. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ponder J. W., Richards F. M. Tertiary templates for proteins. Use of packing criteria in the enumeration of allowed sequences for different structural classes. J Mol Biol. 1987 Feb 20;193(4):775–791. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90358-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Read R. J., Fujinaga M., Sielecki A. R., James M. N. Structure of the complex of Streptomyces griseus protease B and the third domain of the turkey ovomucoid inhibitor at 1.8-A resolution. Biochemistry. 1983 Sep 13;22(19):4420–4433. doi: 10.1021/bi00288a012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Read R. J., James M. N. Refined crystal structure of Streptomyces griseus trypsin at 1.7 A resolution. J Mol Biol. 1988 Apr 5;200(3):523–551. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90541-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Remington S. J., Woodbury R. G., Reynolds R. A., Matthews B. W., Neurath H. The structure of rat mast cell protease II at 1.9-A resolution. Biochemistry. 1988 Oct 18;27(21):8097–8105. doi: 10.1021/bi00421a019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saito I., Miyamura T., Ohbayashi A., Harada H., Katayama T., Kikuchi S., Watanabe Y., Koi S., Onji M., Ohta Y. Hepatitis C virus infection is associated with the development of hepatocellular carcinoma. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Sep;87(17):6547–6549. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.17.6547. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takamizawa A., Mori C., Fuke I., Manabe S., Murakami S., Fujita J., Onishi E., Andoh T., Yoshida I., Okayama H. Structure and organization of the hepatitis C virus genome isolated from human carriers. J Virol. 1991 Mar;65(3):1105–1113. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.3.1105-1113.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka T., Kato N., Nakagawa M., Ootsuyama Y., Cho M. J., Nakazawa T., Hijikata M., Ishimura Y., Shimotohno K. Molecular cloning of hepatitis C virus genome from a single Japanese carrier: sequence variation within the same individual and among infected individuals. Virus Res. 1992 Apr;23(1-2):39–53. doi: 10.1016/0168-1702(92)90066-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomei L., Failla C., Santolini E., De Francesco R., La Monica N. NS3 is a serine protease required for processing of hepatitis C virus polyprotein. J Virol. 1993 Jul;67(7):4017–4026. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.7.4017-4026.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]