Abstract
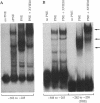
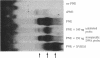
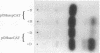
The calcidiol (25-hydroxyvitamin D3) 24-hydroxylase is one of the key enzymes in the metabolism of vitamin D. This enzyme acts on both calcidiol and calcitriol (1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3) to initiate degradation of these potent vitamin D metabolites and is tightly regulated. Calcitriol itself induces this enzyme and acts at the transcriptional level. Transcriptional regulation of genes by calcitriol has been shown to occur via the vitamin D-receptor binding to a vitamin D-response element located upstream of the transcription start site. We now report a vitamin D-response element located between nt -262 and nt -238 of the rat calcidiol 24-hydroxylase gene. This sequence binds the calcitriol receptor and confers vitamin D-dependent transactivation of transcription to its own, as well as heterologous, promoter.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen K. S., Prahl J. M., DeLuca H. F. Isolation and expression of human 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 24-hydroxylase cDNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 May 15;90(10):4543–4547. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.10.4543. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dame M. C., Pierce E. A., Prahl J. M., Hayes C. E., DeLuca H. F. Monoclonal antibodies to the porcine intestinal receptor for 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3: interaction with distinct receptor domains. Biochemistry. 1986 Aug 12;25(16):4523–4534. doi: 10.1021/bi00364a011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darwish H. M., DeLuca H. F. Identification of a 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3-response element in the 5'-flanking region of the rat calbindin D-9k gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jan 15;89(2):603–607. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.2.603. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darwish H., DeLuca H. F. Vitamin D-regulated gene expression. Crit Rev Eukaryot Gene Expr. 1993;3(2):89–116. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeLuca H. F. The vitamin D story: a collaborative effort of basic science and clinical medicine. FASEB J. 1988 Mar 1;2(3):224–236. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Demay M. B., Gerardi J. M., DeLuca H. F., Kronenberg H. M. DNA sequences in the rat osteocalcin gene that bind the 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 receptor and confer responsiveness to 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jan;87(1):369–373. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.1.369. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Demay M. B., Kiernan M. S., DeLuca H. F., Kronenberg H. M. Sequences in the human parathyroid hormone gene that bind the 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 receptor and mediate transcriptional repression in response to 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Sep 1;89(17):8097–8101. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.17.8097. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gill R. K., Christakos S. Identification of sequence elements in mouse calbindin-D28k gene that confer 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3- and butyrate-inducible responses. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Apr 1;90(7):2984–2988. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.7.2984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman C. M., Moffat L. F., Howard B. H. Recombinant genomes which express chloramphenicol acetyltransferase in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Sep;2(9):1044–1051. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.9.1044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerner S. A., Scott R. A., Pike J. W. Sequence elements in the human osteocalcin gene confer basal activation and inducible response to hormonal vitamin D3. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jun;86(12):4455–4459. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.12.4455. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luckow B., Schütz G. CAT constructions with multiple unique restriction sites for the functional analysis of eukaryotic promoters and regulatory elements. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Jul 10;15(13):5490–5490. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.13.5490. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noda M., Vogel R. L., Craig A. M., Prahl J., DeLuca H. F., Denhardt D. T. Identification of a DNA sequence responsible for binding of the 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 receptor and 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 enhancement of mouse secreted phosphoprotein 1 (SPP-1 or osteopontin) gene expression. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Dec;87(24):9995–9999. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.24.9995. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohyama Y., Noshiro M., Eggertsen G., Gotoh O., Kato Y., Björkhem I., Okuda K. Structural characterization of the gene encoding rat 25-hydroxyvitamin D3 24-hydroxylase. Biochemistry. 1993 Jan 12;32(1):76–82. doi: 10.1021/bi00052a011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohyama Y., Noshiro M., Okuda K. Cloning and expression of cDNA encoding 25-hydroxyvitamin D3 24-hydroxylase. FEBS Lett. 1991 Jan 28;278(2):195–198. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(91)80115-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohyama Y., Okuda K. Isolation and characterization of a cytochrome P-450 from rat kidney mitochondria that catalyzes the 24-hydroxylation of 25-hydroxyvitamin D3. J Biol Chem. 1991 May 15;266(14):8690–8695. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reddy G. S., Tserng K. Y. Calcitroic acid, end product of renal metabolism of 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 through C-24 oxidation pathway. Biochemistry. 1989 Feb 21;28(4):1763–1769. doi: 10.1021/bi00430a051. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shinki T., Jin C. H., Nishimura A., Nagai Y., Ohyama Y., Noshiro M., Okuda K., Suda T. Parathyroid hormone inhibits 25-hydroxyvitamin D3-24-hydroxylase mRNA expression stimulated by 1 alpha,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 in rat kidney but not in intestine. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jul 5;267(19):13757–13762. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]