Abstract
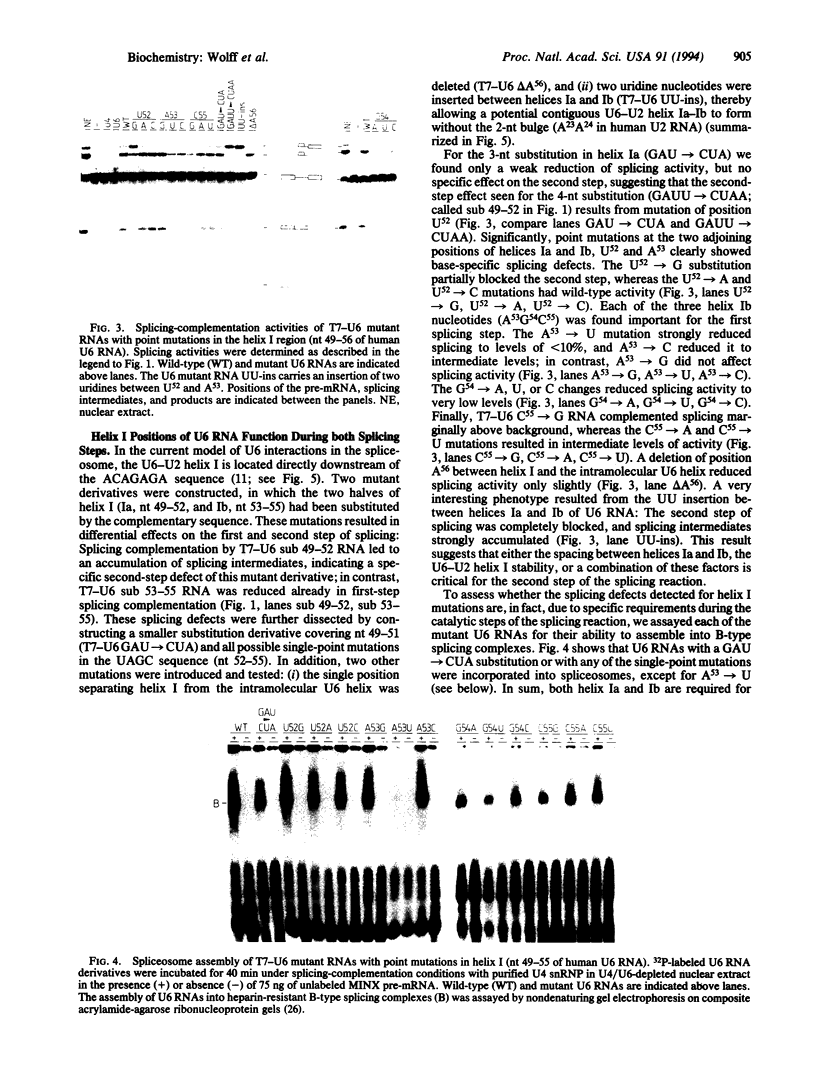
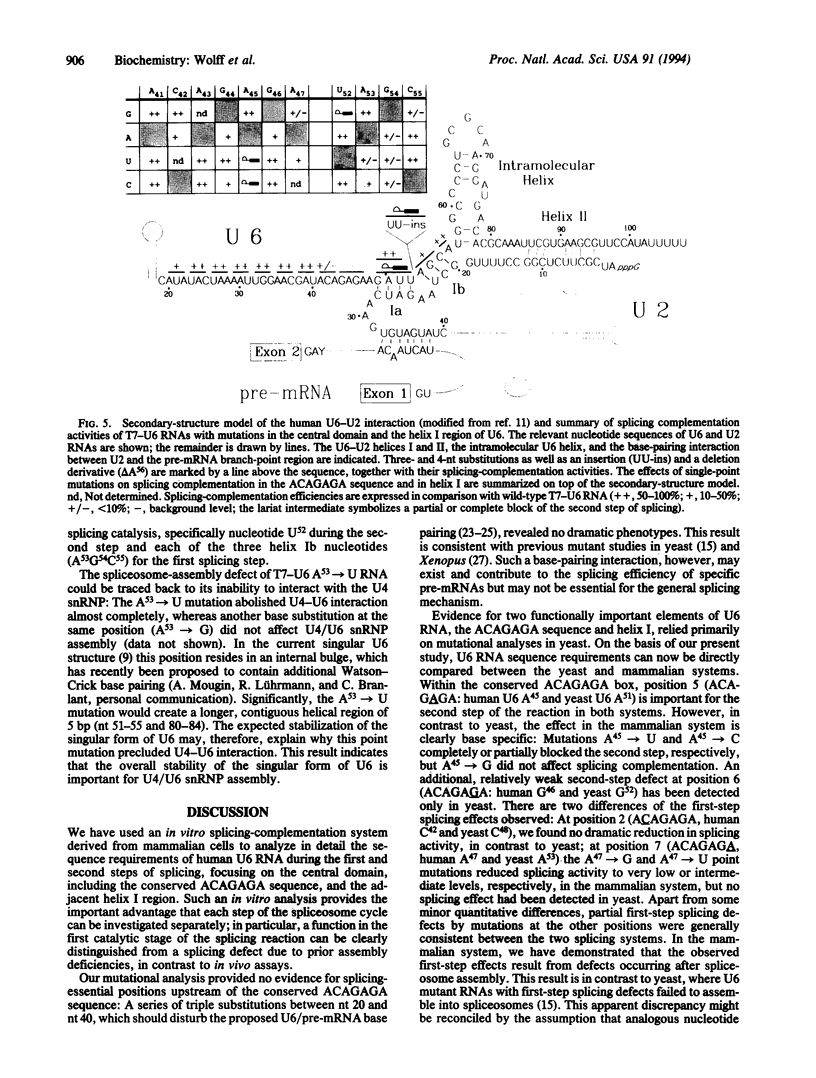
On the basis of mutational analyses in yeast, the highly conserved ACAGAGA sequence of U6 small nuclear RNA (snRNA) and the adjacent U6-U2 helix I have been proposed to be part of the active center of the spliceosome. We report here a detailed analysis of the human U6 snRNA sequence requirements during the first and second step of splicing, using a mammalian in vitro splicing-complementation system and a mutational approach. Positions A53G54C55 (helix Ib) were identified as important specifically for the first step, but not for spliceosome assembly. A45 of the ACAGAGA sequence and U52 of helix Ia function during the second step; in addition, the bulge separating helices Ia and Ib appears critical for the second step. In contrast, no splicing-essential sequences could be identified in the central domain upstream of the ACAGAGA sequence. In sum, our data demonstrate for the mammalian splicing system that discrete positions within the ACAGAGA sequence and helix I of U6 snRNA function during the first and second step of splicing, suggesting that these two sequence elements are closely associated with the catalytic center of the spliceosome. Comparison with previous results in yeast indicates a fundamental conservation of the U6 snRNA function in the pre-mRNA splicing mechanism.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bindereif A., Green M. R. An ordered pathway of snRNP binding during mammalian pre-mRNA splicing complex assembly. EMBO J. 1987 Aug;6(8):2415–2424. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02520.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brow D. A., Guthrie C. Spliceosomal RNA U6 is remarkably conserved from yeast to mammals. Nature. 1988 Jul 21;334(6179):213–218. doi: 10.1038/334213a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cech T. R. The generality of self-splicing RNA: relationship to nuclear mRNA splicing. Cell. 1986 Jan 31;44(2):207–210. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90751-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Datta B., Weiner A. M. Genetic evidence for base pairing between U2 and U6 snRNA in mammalian mRNA splicing. Nature. 1991 Aug 29;352(6338):821–824. doi: 10.1038/352821a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Datta B., Weiner A. M. The phylogenetically invariant ACAGAGA and AGC sequences of U6 small nuclear RNA are more tolerant of mutation in human cells than in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Sep;13(9):5377–5382. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.9.5377. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- England T. E., Bruce A. G., Uhlenbeck O. C. Specific labeling of 3' termini of RNA with T4 RNA ligase. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):65–74. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65011-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fabrizio P., Abelson J. Two domains of yeast U6 small nuclear RNA required for both steps of nuclear precursor messenger RNA splicing. Science. 1990 Oct 19;250(4979):404–409. doi: 10.1126/science.2145630. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green M. R. Biochemical mechanisms of constitutive and regulated pre-mRNA splicing. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1991;7:559–599. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.07.110191.003015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guthrie C. Messenger RNA splicing in yeast: clues to why the spliceosome is a ribonucleoprotein. Science. 1991 Jul 12;253(5016):157–163. doi: 10.1126/science.1853200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guthrie C., Patterson B. Spliceosomal snRNAs. Annu Rev Genet. 1988;22:387–419. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.22.120188.002131. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madhani H. D., Bordonné R., Guthrie C. Multiple roles for U6 snRNA in the splicing pathway. Genes Dev. 1990 Dec;4(12B):2264–2277. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.12b.2264. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madhani H. D., Guthrie C. A novel base-pairing interaction between U2 and U6 snRNAs suggests a mechanism for the catalytic activation of the spliceosome. Cell. 1992 Nov 27;71(5):803–817. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90556-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McPheeters D. S., Abelson J. Mutational analysis of the yeast U2 snRNA suggests a structural similarity to the catalytic core of group I introns. Cell. 1992 Nov 27;71(5):819–831. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90557-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson K. K., Green M. R. Splice site selection and ribonucleoprotein complex assembly during in vitro pre-mRNA splicing. Genes Dev. 1988 Mar;2(3):319–329. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.3.319. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rinke J., Appel B., Digweed M., Lührmann R. Localization of a base-paired interaction between small nuclear RNAs U4 and U6 in intact U4/U6 ribonucleoprotein particles by psoralen cross-linking. J Mol Biol. 1985 Oct 20;185(4):721–731. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90057-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawa H., Abelson J. Evidence for a base-pairing interaction between U6 small nuclear RNA and 5' splice site during the splicing reaction in yeast. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Dec 1;89(23):11269–11273. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.23.11269. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawa H., Shimura Y. Association of U6 snRNA with the 5'-splice site region of pre-mRNA in the spliceosome. Genes Dev. 1992 Feb;6(2):244–254. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.2.244. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharp P. A. On the origin of RNA splicing and introns. Cell. 1985 Sep;42(2):397–400. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90092-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tani T., Ohshima Y. mRNA-type introns in U6 small nuclear RNA genes: implications for the catalysis in pre-mRNA splicing. Genes Dev. 1991 Jun;5(6):1022–1031. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.6.1022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vankan P., McGuigan C., Mattaj I. W. Domains of U4 and U6 snRNAs required for snRNP assembly and splicing complementation in Xenopus oocytes. EMBO J. 1990 Oct;9(10):3397–3404. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07541.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vankan P., McGuigan C., Mattaj I. W. Roles of U4 and U6 snRNAs in the assembly of splicing complexes. EMBO J. 1992 Jan;11(1):335–343. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05056.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wassarman D. A., Steitz J. A. Interactions of small nuclear RNA's with precursor messenger RNA during in vitro splicing. Science. 1992 Sep 25;257(5078):1918–1925. doi: 10.1126/science.1411506. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiner A. M. mRNA splicing and autocatalytic introns: distant cousins or the products of chemical determinism? Cell. 1993 Jan 29;72(2):161–164. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90654-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolff T., Bindereif A. Conformational changes of U6 RNA during the spliceosome cycle: an intramolecular helix is essential both for initiating the U4-U6 interaction and for the first step of slicing. Genes Dev. 1993 Jul;7(7B):1377–1389. doi: 10.1101/gad.7.7b.1377. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolff T., Bindereif A. Reconstituted mammalian U4/U6 snRNP complements splicing: a mutational analysis. EMBO J. 1992 Jan;11(1):345–359. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05057.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu J. A., Manley J. L. Base pairing between U2 and U6 snRNAs is necessary for splicing of a mammalian pre-mRNA. Nature. 1991 Aug 29;352(6338):818–821. doi: 10.1038/352818a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zillmann M., Zapp M. L., Berget S. M. Gel electrophoretic isolation of splicing complexes containing U1 small nuclear ribonucleoprotein particles. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Feb;8(2):814–821. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.2.814. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]







