Abstract
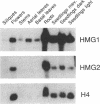
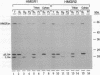
The enzyme 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-CoA reductase (HMGR; EC 1.1.1.34) catalyzes the first rate-limiting step in plant isoprenoid biosynthesis. Arabidopsis thaliana contains two genes, HMG1 and HMG2, that encode HMGR. We have cloned these two genes and analyzed their structure and expression. HMG1 and HMG2 consist of four exons and three small introns that interrupt the coding sequence at equivalent positions. The two genes share sequence similarity in the coding regions but not in the 5'- or 3'-flanking regions. HMG1 mRNA is detected in all tissues, whereas the presence of HMG2 mRNA is restricted to young seedlings, roots, and inflorescences. The similarity between the two encoded proteins (HMGR1 and HMGR2) is restricted to the regions corresponding to the membrane and the catalytic domains. Arabidopsis HMGR2 represents a divergent form of the enzyme that has no counterpart among plant HMGRs characterized so far. By using a coupled in vitro transcription-translation assay, we show that both HMGR1 and HMGR2 are cotranslationally inserted into endoplasmic reticulum-derived microsomal membranes. Our results suggest that the endoplasmic reticulum is the only cell compartment for the targeting of HMGR in Arabidopsis and support the hypothesis that in higher plants the formation of mevalonate occurs solely in the cytosol.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bach T. J., Boronat A., Caelles C., Ferrer A., Weber T., Wettstein A. Aspects related to mevalonate biosynthesis in plants. Lipids. 1991 Aug;26(8):637–648. doi: 10.1007/BF02536429. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bach T. J., Rogers D. H., Rudney H. Detergent-solubilization, purification, and characterization of membrane-bound 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-coenzyme A reductase from radish seedlings. Eur J Biochem. 1986 Jan 2;154(1):103–111. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1986.tb09364.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blobel G., Dobberstein B. Transfer of proteins across membranes. I. Presence of proteolytically processed and unprocessed nascent immunoglobulin light chains on membrane-bound ribosomes of murine myeloma. J Cell Biol. 1975 Dec;67(3):835–851. doi: 10.1083/jcb.67.3.835. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brooker J. D., Russell D. W. Subcellular localization of 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A reductase in Pisum sativum seedlings. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1975 Apr;167(2):730–737. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(75)90518-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bujard H., Gentz R., Lanzer M., Stueber D., Mueller M., Ibrahimi I., Haeuptle M. T., Dobberstein B. A T5 promoter-based transcription-translation system for the analysis of proteins in vitro and in vivo. Methods Enzymol. 1987;155:416–433. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)55028-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caelles C., Ferrer A., Balcells L., Hegardt F. G., Boronat A. Isolation and structural characterization of a cDNA encoding Arabidopsis thaliana 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A reductase. Plant Mol Biol. 1989 Dec;13(6):627–638. doi: 10.1007/BF00016018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campos N., Palau J., Torrent M., Ludevid D. Signal recognition-like particles are present in maize. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jul 15;263(20):9646–9650. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chaubet N., Clément B., Philipps G., Gigot C. Organ-specific expression of different histone H3 and H4 gene subfamilies in developing and adult maize. Plant Mol Biol. 1991 Oct;17(4):935–940. doi: 10.1007/BF00037077. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Choi D., Ward B. L., Bostock R. M. Differential induction and suppression of potato 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A reductase genes in response to Phytophthora infestans and to its elicitor arachidonic acid. Plant Cell. 1992 Oct;4(10):1333–1344. doi: 10.1105/tpc.4.10.1333. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chye M. L., Kush A., Tan C. T., Chua N. H. Characterization of cDNA and genomic clones encoding 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-coenzyme A reductase from Hevea brasiliensis. Plant Mol Biol. 1991 Apr;16(4):567–577. doi: 10.1007/BF00023422. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chye M. L., Tan C. T., Chua N. H. Three genes encode 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-coenzyme A reductase in Hevea brasiliensis: hmg1 and hmg3 are differentially expressed. Plant Mol Biol. 1992 Jun;19(3):473–484. doi: 10.1007/BF00023395. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dean C., Elzen P., Tamaki S., Dunsmuir P., Bedbrook J. Differential expression of the eight genes of the petunia ribulose bisphosphate carboxylase small subunit multi-gene family. EMBO J. 1985 Dec 1;4(12):3055–3061. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb04045.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferrer A., Aparicio C., Nogués N., Wettstein A., Bach T. J., Boronat A. Expression of catalytically active radish 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A reductase in Escherichia coli. FEBS Lett. 1990 Jun 18;266(1-2):67–71. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(90)81508-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujiki Y., Hubbard A. L., Fowler S., Lazarow P. B. Isolation of intracellular membranes by means of sodium carbonate treatment: application to endoplasmic reticulum. J Cell Biol. 1982 Apr;93(1):97–102. doi: 10.1083/jcb.93.1.97. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Genschik P., Criqui M. C., Parmentier Y., Marbach J., Durr A., Fleck J., Jamet E. Isolation and characterization of a cDNA encoding a 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A reductase from Nicotiana sylvestris. Plant Mol Biol. 1992 Oct;20(2):337–341. doi: 10.1007/BF00014504. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gil G., Faust J. R., Chin D. J., Goldstein J. L., Brown M. S. Membrane-bound domain of HMG CoA reductase is required for sterol-enhanced degradation of the enzyme. Cell. 1985 May;41(1):249–258. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90078-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glick B., Schatz G. Import of proteins into mitochondria. Annu Rev Genet. 1991;25:21–44. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.25.120191.000321. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henikoff S. Unidirectional digestion with exonuclease III in DNA sequence analysis. Methods Enzymol. 1987;155:156–165. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)55014-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joshi C. P. An inspection of the domain between putative TATA box and translation start site in 79 plant genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Aug 25;15(16):6643–6653. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.16.6643. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keegstra K. Transport and routing of proteins into chloroplasts. Cell. 1989 Jan 27;56(2):247–253. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90898-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kreuz K., Kleinig H. Synthesis of prenyl lipids in cells of spinach leaf. Compartmentation of enzymes for formation of isopentenyl diphosphate. Eur J Biochem. 1984 Jun 15;141(3):531–535. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1984.tb08225.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Learned R. M., Fink G. R. 3-Hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-coenzyme A reductase from Arabidopsis thaliana is structurally distinct from the yeast and animal enzymes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Apr;86(8):2779–2783. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.8.2779. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maldonado-Mendoza I. E., Burnett R. J., Nessler C. L. Nucleotide Sequence of a cDNA Encoding 3-Hydroxy-3-Methylglutaryl Coenzyme A Reductase from Catharanthus roseus. Plant Physiol. 1992 Nov;100(3):1613–1614. doi: 10.1104/pp.100.3.1613. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Narita J. O., Gruissem W. Tomato hydroxymethylglutaryl-CoA reductase is required early in fruit development but not during ripening. Plant Cell. 1989 Feb;1(2):181–190. doi: 10.1105/tpc.1.2.181. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Park H., Denbow C. J., Cramer C. L. Structure and nucleotide sequence of tomato HMG2 encoding 3-hydroxy-3-methyl-glutaryl coenzyme A reductase. Plant Mol Biol. 1992 Oct;20(2):327–331. doi: 10.1007/BF00014502. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts B. E., Paterson B. M. Efficient translation of tobacco mosaic virus RNA and rabbit globin 9S RNA in a cell-free system from commercial wheat germ. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Aug;70(8):2330–2334. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.8.2330. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogers S., Wells R., Rechsteiner M. Amino acid sequences common to rapidly degraded proteins: the PEST hypothesis. Science. 1986 Oct 17;234(4774):364–368. doi: 10.1126/science.2876518. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skalnik D. G., Narita H., Kent C., Simoni R. D. The membrane domain of 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-coenzyme A reductase confers endoplasmic reticulum localization and sterol-regulated degradation onto beta-galactosidase. J Biol Chem. 1988 May 15;263(14):6836–6841. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skinner M. K., Griswold M. D. Fluorographic detection of radioactivity in polyacrylamide gels with 2,5-diphenyloxazole in acetic acid and its comparison with existing procedures. Biochem J. 1983 Jan 1;209(1):281–284. doi: 10.1042/bj2090281. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walter P., Blobel G. Preparation of microsomal membranes for cotranslational protein translocation. Methods Enzymol. 1983;96:84–93. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(83)96010-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walter P., Gilmore R., Blobel G. Protein translocation across the endoplasmic reticulum. Cell. 1984 Aug;38(1):5–8. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90520-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang Z., Park H., Lacy G. H., Cramer C. L. Differential activation of potato 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A reductase genes by wounding and pathogen challenge. Plant Cell. 1991 Apr;3(4):397–405. doi: 10.1105/tpc.3.4.397. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]