Abstract
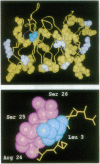
Two murine monoclonal antibodies, N901 (anti-CD56) and anti-B4 (anti-CD19), were humanized by a process we call "resurfacing." A systematic analysis of known antibody structures has been used to determine the relative solvent accessibility distributions of amino acid residues in murine and human antibody variable (Fv) regions and has shown that the sequence alignment positions of surface amino acids for human and murine variable region heavy (VH) and light (VL) chains are conserved with 98% fidelity across species. While the amino acid usage at these surface positions creates surface residue patterns that are conserved within species, there are no identical patterns across species. However, surprisingly few amino acid changes need to be made to convert a murine Fv surface pattern to that characteristic of a human surface. Resurfacing was used to change the patterns of surface accessible residues in the Fv regions of the N901 and anti-B4 antibodies to resemble those found on the Fv regions of human antibody sequences. Two different procedures for selecting a human sequence were compared. For anti-B4, a data base of clonally derived human VL-VH sequence pairs was used, while for N901, sequences for VL and VH were independently selected from the Kabat et al. data base [Kabat, E. A., Wu, T. T., Reid-Miller, M., Perry, H. M. & Gottesman, K. S. (1991) Sequences of Proteins of Immunological Interest (DHHS, Washington, DC), 5th Ed.]. Resurfaced N901 and anti-B4 antibodies had apparent affinities for their cell surface ligands that were identical to those of their respective parent murine antibodies. These data provide evidence that, despite the differences in the surfaces of mouse and human Fv regions, it is possible to substitute one for the other while retaining full antigen binding affinity.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Awdeh Z. L., Williamson A. R., Askonas B. A. One cell-one immunoglobulin. Origin of limited heterogeneity of myeloma proteins. Biochem J. 1970 Jan;116(2):241–248. doi: 10.1042/bj1160241. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernstein F. C., Koetzle T. F., Williams G. J., Meyer E. F., Jr, Brice M. D., Rodgers J. R., Kennard O., Shimanouchi T., Tasumi M. The Protein Data Bank: a computer-based archival file for macromolecular structures. J Mol Biol. 1977 May 25;112(3):535–542. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(77)80200-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bird J., Galili N., Link M., Stites D., Sklar J. Continuing rearrangement but absence of somatic hypermutation in immunoglobulin genes of human B cell precursor leukemia. J Exp Med. 1988 Jul 1;168(1):229–245. doi: 10.1084/jem.168.1.229. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bleasby A. J., Wootton J. C. Construction of validated, non-redundant composite protein sequence databases. Protein Eng. 1990 Jan;3(3):153–159. doi: 10.1093/protein/3.3.153. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bruccoleri R. E., Karplus M. Prediction of the folding of short polypeptide segments by uniform conformational sampling. Biopolymers. 1987 Jan;26(1):137–168. doi: 10.1002/bip.360260114. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chothia C., Lesk A. M., Tramontano A., Levitt M., Smith-Gill S. J., Air G., Sheriff S., Padlan E. A., Davies D., Tulip W. R. Conformations of immunoglobulin hypervariable regions. Nature. 1989 Dec 21;342(6252):877–883. doi: 10.1038/342877a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daugherty B. L., DeMartino J. A., Law M. F., Kawka D. W., Singer I. I., Mark G. E. Polymerase chain reaction facilitates the cloning, CDR-grafting, and rapid expression of a murine monoclonal antibody directed against the CD18 component of leukocyte integrins. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 May 11;19(9):2471–2476. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.9.2471. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fasullo F. J., Jr, Fritsche H. A., Jr, Liu F. J., Hamilton R. G. IgG heavy-chain subclass typing of myeloma paraproteins by isoelectric focusing immunoblot analysis. Clin Chem. 1989 Mar;35(3):364–368. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foote J., Winter G. Antibody framework residues affecting the conformation of the hypervariable loops. J Mol Biol. 1992 Mar 20;224(2):487–499. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(92)91010-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldmacher V. S., Lambert J. M., Young A. Y., Anderson J., Tinnel N. L., Kornacki M., Ritz J., Blättler W. A. Expression of the common acute lymphoblastic leukemia antigen (CALLA) on the surface of individual cells of human lymphoblastoid lines. J Immunol. 1986 Jan;136(1):320–325. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffin J. D., Hercend T., Beveridge R., Schlossman S. F. Characterization of an antigen expressed by human natural killer cells. J Immunol. 1983 Jun;130(6):2947–2951. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herron J. N., He X. M., Mason M. L., Voss E. W., Jr, Edmundson A. B. Three-dimensional structure of a fluorescein-Fab complex crystallized in 2-methyl-2,4-pentanediol. Proteins. 1989;5(4):271–280. doi: 10.1002/prot.340050404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones P. T., Dear P. H., Foote J., Neuberger M. S., Winter G. Replacing the complementarity-determining regions in a human antibody with those from a mouse. 1986 May 29-Jun 4Nature. 321(6069):522–525. doi: 10.1038/321522a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kabsch W., Sander C. Dictionary of protein secondary structure: pattern recognition of hydrogen-bonded and geometrical features. Biopolymers. 1983 Dec;22(12):2577–2637. doi: 10.1002/bip.360221211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kettleborough C. A., Saldanha J., Heath V. J., Morrison C. J., Bendig M. M. Humanization of a mouse monoclonal antibody by CDR-grafting: the importance of framework residues on loop conformation. Protein Eng. 1991 Oct;4(7):773–783. doi: 10.1093/protein/4.7.773. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klobeck H. G., Bornkamm G. W., Combriato G., Mocikat R., Pohlenz H. D., Zachau H. G. Subgroup IV of human immunoglobulin K light chains is encoded by a single germline gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Sep 25;13(18):6515–6529. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.18.6515. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. The scanning model for translation: an update. J Cell Biol. 1989 Feb;108(2):229–241. doi: 10.1083/jcb.108.2.229. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Köhler G., Milstein C. Continuous cultures of fused cells secreting antibody of predefined specificity. Nature. 1975 Aug 7;256(5517):495–497. doi: 10.1038/256495a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lambert J. M., Goldmacher V. S., Collinson A. R., Nadler L. M., Blättler W. A. An immunotoxin prepared with blocked ricin: a natural plant toxin adapted for therapeutic use. Cancer Res. 1991 Dec 1;51(23 Pt 1):6236–6242. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LoBuglio A. F., Wheeler R. H., Trang J., Haynes A., Rogers K., Harvey E. B., Sun L., Ghrayeb J., Khazaeli M. B. Mouse/human chimeric monoclonal antibody in man: kinetics and immune response. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jun;86(11):4220–4224. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.11.4220. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maeda H., Matsushita S., Eda Y., Kimachi K., Tokiyoshi S., Bendig M. M. Construction of reshaped human antibodies with HIV-neutralizing activity. Hum Antibodies Hybridomas. 1991 Jul;2(3):124–134. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marquart M., Deisenhofer J., Huber R., Palm W. Crystallographic refinement and atomic models of the intact immunoglobulin molecule Kol and its antigen-binding fragment at 3.0 A and 1.0 A resolution. J Mol Biol. 1980 Aug 25;141(4):369–391. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(80)90252-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin A. C., Cheetham J. C., Rees A. R. Modeling antibody hypervariable loops: a combined algorithm. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Dec;86(23):9268–9272. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.23.9268. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin A. C., Cheetham J. C., Rees A. R. Molecular modeling of antibody combining sites. Methods Enzymol. 1991;203:121–153. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(91)03008-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison S. L., Johnson M. J., Herzenberg L. A., Oi V. T. Chimeric human antibody molecules: mouse antigen-binding domains with human constant region domains. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Nov;81(21):6851–6855. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.21.6851. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nadler L. M., Anderson K. C., Marti G., Bates M., Park E., Daley J. F., Schlossman S. F. B4, a human B lymphocyte-associated antigen expressed on normal, mitogen-activated, and malignant B lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1983 Jul;131(1):244–250. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nitta T., Yagita H., Sato K., Okumura K. Involvement of CD56 (NKH-1/Leu-19 antigen) as an adhesion molecule in natural killer-target cell interaction. J Exp Med. 1989 Nov 1;170(5):1757–1761. doi: 10.1084/jem.170.5.1757. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Novotný J., Handschumacher M., Haber E., Bruccoleri R. E., Carlson W. B., Fanning D. W., Smith J. A., Rose G. D. Antigenic determinants in proteins coincide with surface regions accessible to large probes (antibody domains). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jan;83(2):226–230. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.2.226. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orlandi R., Güssow D. H., Jones P. T., Winter G. Cloning immunoglobulin variable domains for expression by the polymerase chain reaction. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 May;86(10):3833–3837. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.10.3833. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Padlan E. A. A possible procedure for reducing the immunogenicity of antibody variable domains while preserving their ligand-binding properties. Mol Immunol. 1991 Apr-May;28(4-5):489–498. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(91)90163-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pedersen J. T., Henry A. H., Searle S. J., Guild B. C., Roguska M., Rees A. R. Comparison of surface accessible residues in human and murine immunoglobulin Fv domains. Implication for humanization of murine antibodies. J Mol Biol. 1994 Jan 21;235(3):959–973. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1994.1050. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riechmann L., Clark M., Waldmann H., Winter G. Reshaping human antibodies for therapy. Nature. 1988 Mar 24;332(6162):323–327. doi: 10.1038/332323a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheriff S., Silverton E. W., Padlan E. A., Cohen G. H., Smith-Gill S. J., Finzel B. C., Davies D. R. Three-dimensional structure of an antibody-antigen complex. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Nov;84(22):8075–8079. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.22.8075. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silberstein L. E., Litwin S., Carmack C. E. Relationship of variable region genes expressed by a human B cell lymphoma secreting pathologic anti-Pr2 erythrocyte autoantibodies. J Exp Med. 1989 May 1;169(5):1631–1643. doi: 10.1084/jem.169.5.1631. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tainer J. A., Getzoff E. D., Alexander H., Houghten R. A., Olson A. J., Lerner R. A., Hendrickson W. A. The reactivity of anti-peptide antibodies is a function of the atomic mobility of sites in a protein. Nature. 1984 Nov 8;312(5990):127–134. doi: 10.1038/312127a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thornton J. M., Edwards M. S., Taylor W. R., Barlow D. J. Location of 'continuous' antigenic determinants in the protruding regions of proteins. EMBO J. 1986 Feb;5(2):409–413. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04226.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tracy R. P., Currie R. M., Kyle R. A., Young D. S. Two-dimensional gel electrophoresis of serum specimens from patients with monoclonal gammopathies. Clin Chem. 1982 Apr;28(4 Pt 2):900–907. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westhof E., Altschuh D., Moras D., Bloomer A. C., Mondragon A., Klug A., Van Regenmortel M. H. Correlation between segmental mobility and the location of antigenic determinants in proteins. Nature. 1984 Sep 13;311(5982):123–126. doi: 10.1038/311123a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]