Abstract
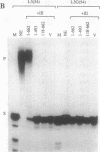
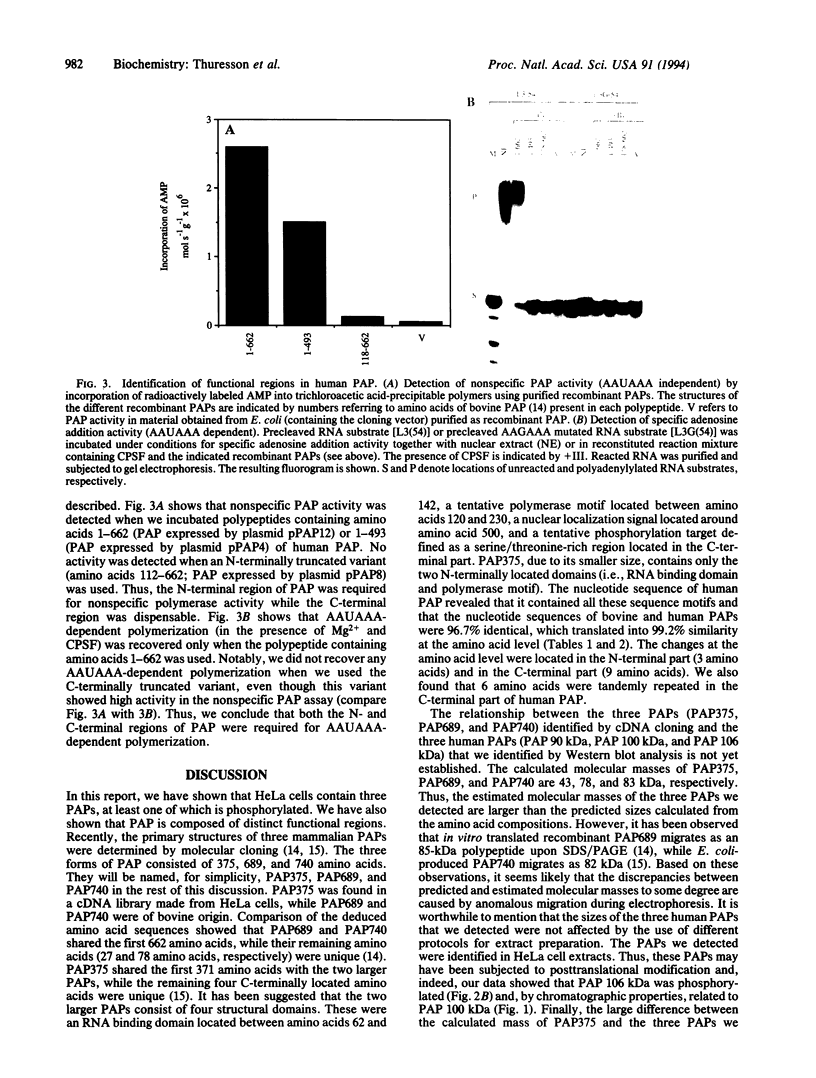
We have cloned human poly(A) polymerase (PAP) mRNA as cDNA in Escherichia coli. The primary structure of the mRNA was determined and compared to the bovine PAP mRNA sequence. The two sequences were 97% identical at the nucleotide level, which translated into 99% similarity at the amino acid level. Polypeptides representing recombinant PAP were expressed in E. coli, purified, and used as antigens to generate monoclonal antibodies. Western blot analysis using these monoclonal antibodies as probes revealed three PAPs, having estimated molecular masses of 90, 100, and 106 kDa in HeLa cell extracts. Fractionation of HeLa cells showed that the 90-kDa polypeptide was nuclear while the 100- and 106-kDa species were present in both nuclear and cytoplasmic fractions. The 106-kDa PAP was most likely a phosphorylated derivative of the 100-kDa species. PAP activity was recovered in vitro by using purified recombinant human PAP. Subsequent mutational analysis revealed that both the N- and C-terminal regions of PAP were important for activity and suggested that cleavage and polyadenylylation specificity factor (CPSF) interacted with the C-terminal region of PAP. Interestingly, tentative phosphorylation sites have been identified in this region, suggesting that phosphorylation/dephosphorylation may regulate the interaction between the two polyadenylylation factors PAP and CPSF.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aström A., Aström J., Virtanen A. A simple procedure for isolation of eukaryotic mRNA polyadenylation factors. Eur J Biochem. 1991 Dec 18;202(3):765–773. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1991.tb16431.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bardwell V. J., Wickens M. Polyadenylation-specific complexes undergo a transition early in the polymerization of a poly(A) tail. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Jan;10(1):295–302. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.1.295. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brawerman G., Mendecki J., Lee S. Y. A procedure for the isolation of mammalian messenger ribonucleic acid. Biochemistry. 1972 Feb 15;11(4):637–641. doi: 10.1021/bi00754a027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christofori G., Keller W. Poly(A) polymerase purified from HeLa cell nuclear extract is required for both cleavage and polyadenylation of pre-mRNA in vitro. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Jan;9(1):193–203. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.1.193. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dignam J. D., Lebovitz R. M., Roeder R. G. Accurate transcription initiation by RNA polymerase II in a soluble extract from isolated mammalian nuclei. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Mar 11;11(5):1475–1489. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.5.1475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerton G. L., Wardrip N. J., Hedrick J. L. A gel eluter for recovery of proteins separated by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Anal Biochem. 1982 Oct;126(1):116–121. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(82)90116-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilmartin G. M., Nevins J. R. An ordered pathway of assembly of components required for polyadenylation site recognition and processing. Genes Dev. 1989 Dec;3(12B):2180–2190. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.12b.2180. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jareborg N., Burnett S. Immunofluorescent detection of bovine papillomavirus E4 antigen in the cytoplasm of cells permissive in vitro for viral DNA amplification. J Gen Virol. 1991 Sep;72(Pt 9):2269–2274. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-72-9-2269. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keller W., Bienroth S., Lang K. M., Christofori G. Cleavage and polyadenylation factor CPF specifically interacts with the pre-mRNA 3' processing signal AAUAAA. EMBO J. 1991 Dec;10(13):4241–4249. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb05002.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manley J. L. Polyadenylation of mRNA precursors. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1988 May 6;950(1):1–12. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(88)90067-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore C. L., Sharp P. A. Accurate cleavage and polyadenylation of exogenous RNA substrate. Cell. 1985 Jul;41(3):845–855. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80065-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore C. L., Sharp P. A. Site-specific polyadenylation in a cell-free reaction. Cell. 1984 Mar;36(3):581–591. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90337-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murthy K. G., Manley J. L. Characterization of the multisubunit cleavage-polyadenylation specificity factor from calf thymus. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jul 25;267(21):14804–14811. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Proudfoot N. Poly(A) signals. Cell. 1991 Feb 22;64(4):671–674. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90495-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raabe T., Bollum F. J., Manley J. L. Primary structure and expression of bovine poly(A) polymerase. Nature. 1991 Sep 19;353(6341):229–234. doi: 10.1038/353229a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rose K. M., Jacob S. T. Nuclear poly(A) polymerase from rat liver and a hepatoma. Comparison of properties, molecular weights and amino acid compositions. Eur J Biochem. 1976 Aug 1;67(1):11–21. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1976.tb10626.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rose K. M., Jacob S. T. Phosphorylation of nuclear poly(A) polymerase. Comparison of liver and hepatoma enzymes. J Biol Chem. 1979 Oct 25;254(20):10256–10261. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryner L. C., Takagaki Y., Manley J. L. Multiple forms of poly(A) polymerases purified from HeLa cells function in specific mRNA 3'-end formation. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Oct;9(10):4229–4238. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.10.4229. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saiki R. K., Gelfand D. H., Stoffel S., Scharf S. J., Higuchi R., Horn G. T., Mullis K. B., Erlich H. A. Primer-directed enzymatic amplification of DNA with a thermostable DNA polymerase. Science. 1988 Jan 29;239(4839):487–491. doi: 10.1126/science.2448875. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheets M. D., Wickens M. Two phases in the addition of a poly(A) tail. Genes Dev. 1989 Sep;3(9):1401–1412. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.9.1401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skolnik-David H., Moore C. L., Sharp P. A. Electrophoretic separation of polyadenylation-specific complexes. Genes Dev. 1987 Sep;1(7):672–682. doi: 10.1101/gad.1.7.672. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stetler D. A., Jacob S. T. Comparison of cytosolic and nuclear poly(A) polymerases from rat liver and a hepatoma: structural and immunological properties and response to NI-type protein kinases. Biochemistry. 1985 Sep 10;24(19):5163–5169. doi: 10.1021/bi00340a031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stetler D. A., Jacob S. T. Structurally and immunologically distinct poly(A) polymerases in rat liver. Occurrence of a tumor-type enzyme in normal liver. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jun 10;259(11):7239–7244. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Studier F. W., Rosenberg A. H., Dunn J. J., Dubendorff J. W. Use of T7 RNA polymerase to direct expression of cloned genes. Methods Enzymol. 1990;185:60–89. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(90)85008-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terns M. P., Jacob S. T. Role of poly(A) polymerase in the cleavage and polyadenylation of mRNA precursor. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Apr;9(4):1435–1444. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.4.1435. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsiapalis C. M., Dorson J. W., Bollum F. J. Purification of terminal riboadenylate transferase from calf thymus gland. J Biol Chem. 1975 Jun 25;250(12):4486–4496. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahle E., Keller W. The biochemistry of 3'-end cleavage and polyadenylation of messenger RNA precursors. Annu Rev Biochem. 1992;61:419–440. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.61.070192.002223. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahle E., Martin G., Schiltz E., Keller W. Isolation and expression of cDNA clones encoding mammalian poly(A) polymerase. EMBO J. 1991 Dec;10(13):4251–4257. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb05003.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahle E. Purification and characterization of a mammalian polyadenylate polymerase involved in the 3' end processing of messenger RNA precursors. J Biol Chem. 1991 Feb 15;266(5):3131–3139. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winters M. A., Edmonds M. A poly(A) polymerase from calf thymus. Purification and properities of the enzyme. J Biol Chem. 1973 Jul 10;248(13):4756–4762. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]