Abstract
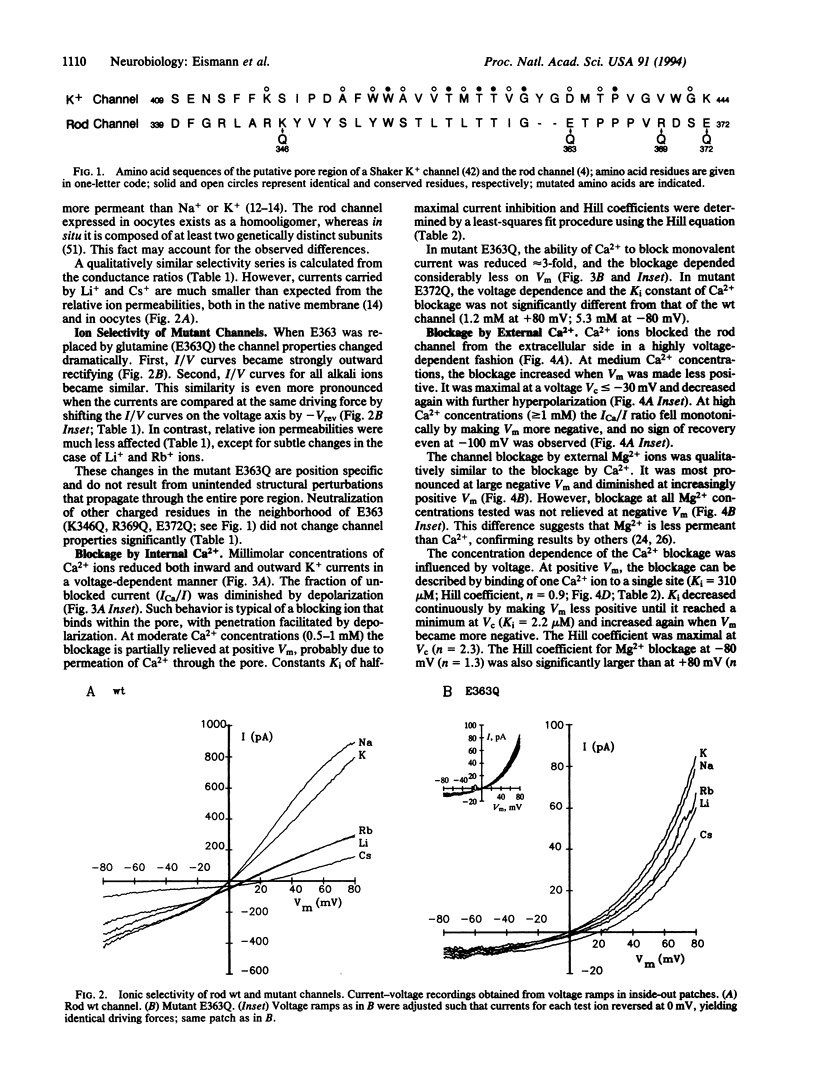
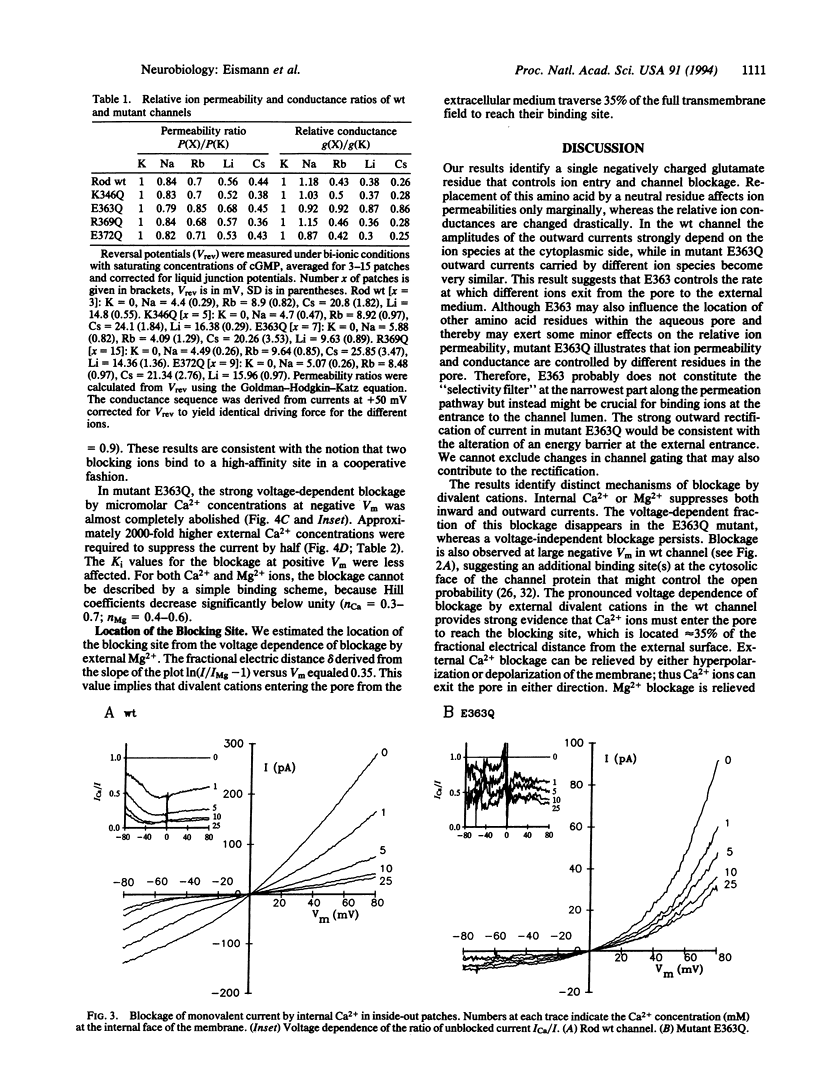
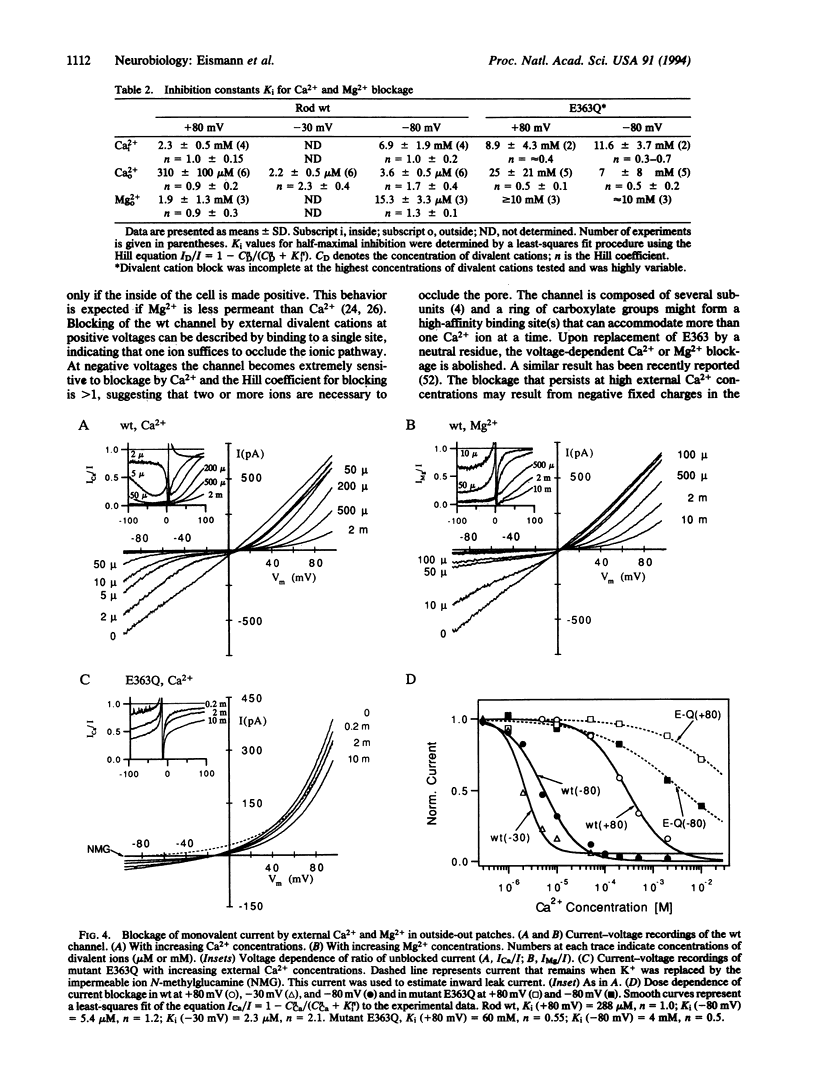
Ca2+ ions control the cGMP-gated channel of rod photoreceptor cells from the external and internal face. We studied ion selectivity and blockage by Ca2+ of wild-type and mutant channels in a heterologous expression system. External Ca2+ blocks the inward current at micromolar concentrations in a highly voltage-dependent manner. The blockage at negative membrane voltages shows a steep concentration dependence with a Hill coefficient of approximately 2. The blockage from the internal face requires approximately 1000-fold higher Ca2+ concentrations. Neutralization of a glutamate residue (E363) in the putative pore region between transmembrane segments H4 and H5 induces outward rectification and changes relative ion conductances but leaves relative ion permeabilities nearly unaffected. The current blockage at -80 mV requires approximately 2000-fold higher external Ca2+ concentrations and the voltage dependence is almost abolished. These results demonstrate that E363 represents a binding site for monovalent and divalent cations and resides in the pore lumen.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Altenhofen W., Ludwig J., Eismann E., Kraus W., Bönigk W., Kaupp U. B. Control of ligand specificity in cyclic nucleotide-gated channels from rod photoreceptors and olfactory epithelium. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Nov 1;88(21):9868–9872. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.21.9868. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bodoia R. D., Detwiler P. B. Patch-clamp recordings of the light-sensitive dark noise in retinal rods from the lizard and frog. J Physiol. 1985 Oct;367:183–216. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1985.sp015820. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bönigk W., Altenhofen W., Müller F., Dose A., Illing M., Molday R. S., Kaupp U. B. Rod and cone photoreceptor cells express distinct genes for cGMP-gated channels. Neuron. 1993 May;10(5):865–877. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(93)90202-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen T. Y., Peng Y. W., Dhallan R. S., Ahamed B., Reed R. R., Yau K. W. A new subunit of the cyclic nucleotide-gated cation channel in retinal rods. Nature. 1993 Apr 22;362(6422):764–767. doi: 10.1038/362764a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colamartino G., Menini A., Torre V. Blockage and permeation of divalent cations through the cyclic GMP-activated channel from tiger salamander retinal rods. J Physiol. 1991;440:189–206. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1991.sp018703. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dhallan R. S., Yau K. W., Schrader K. A., Reed R. R. Primary structure and functional expression of a cyclic nucleotide-activated channel from olfactory neurons. Nature. 1990 Sep 13;347(6289):184–187. doi: 10.1038/347184a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fesenko E. E., Kolesnikov S. S., Lyubarsky A. L. Induction by cyclic GMP of cationic conductance in plasma membrane of retinal rod outer segment. Nature. 1985 Jan 24;313(6000):310–313. doi: 10.1038/313310a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furman R. E., Tanaka J. C. Monovalent selectivity of the cyclic guanosine monophosphate-activated ion channel. J Gen Physiol. 1990 Jul;96(1):57–82. doi: 10.1085/jgp.96.1.57. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goulding E. H., Ngai J., Kramer R. H., Colicos S., Axel R., Siegelbaum S. A., Chess A. Molecular cloning and single-channel properties of the cyclic nucleotide-gated channel from catfish olfactory neurons. Neuron. 1992 Jan;8(1):45–58. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(92)90107-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goulding E. H., Tibbs G. R., Liu D., Siegelbaum S. A. Role of H5 domain in determining pore diameter and ion permeation through cyclic nucleotide-gated channels. Nature. 1993 Jul 1;364(6432):61–64. doi: 10.1038/364061a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray P., Attwell D. Kinetics of light-sensitive channels in vertebrate photoreceptors. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1985 Jan 22;223(1232):379–388. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1985.0007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guy H. R., Durell S. R., Warmke J., Drysdale R., Ganetzky B. Similarities in amino acid sequences of Drosophila eag and cyclic nucleotide-gated channels. Science. 1991 Nov 1;254(5032):730–730. doi: 10.1126/science.1658932. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamill O. P., Marty A., Neher E., Sakmann B., Sigworth F. J. Improved patch-clamp techniques for high-resolution current recording from cells and cell-free membrane patches. Pflugers Arch. 1981 Aug;391(2):85–100. doi: 10.1007/BF00656997. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haynes L. W., Kay A. R., Yau K. W. Single cyclic GMP-activated channel activity in excised patches of rod outer segment membrane. Nature. 1986 May 1;321(6065):66–70. doi: 10.1038/321066a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haynes L., Yau K. W. Cyclic GMP-sensitive conductance in outer segment membrane of catfish cones. Nature. 1985 Sep 5;317(6032):61–64. doi: 10.1038/317061a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heginbotham L., Abramson T., MacKinnon R. A functional connection between the pores of distantly related ion channels as revealed by mutant K+ channels. Science. 1992 Nov 13;258(5085):1152–1155. doi: 10.1126/science.1279807. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heinemann S. H., Terlau H., Stühmer W., Imoto K., Numa S. Calcium channel characteristics conferred on the sodium channel by single mutations. Nature. 1992 Apr 2;356(6368):441–443. doi: 10.1038/356441a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herlitze S., Koenen M. A general and rapid mutagenesis method using polymerase chain reaction. Gene. 1990 Jul 2;91(1):143–147. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(90)90177-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hodgkin A. L., McNaughton P. A., Nunn B. J. The ionic selectivity and calcium dependence of the light-sensitive pathway in toad rods. J Physiol. 1985 Jan;358:447–468. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1985.sp015561. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hodgkin A. L., McNaughton P. A., Nunn B. J., Yau K. W. Effect of ions on retinal rods from Bufo marinus. J Physiol. 1984 May;350:649–680. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1984.sp015223. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ildefonse M., Bennett N. Single-channel study of the cGMP-dependent conductance of retinal rods from incorporation of native vesicles into planar lipid bilayers. J Membr Biol. 1991 Aug;123(2):133–147. doi: 10.1007/BF01998084. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jan L. Y., Jan Y. N. Structural elements involved in specific K+ channel functions. Annu Rev Physiol. 1992;54:537–555. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.54.030192.002541. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karpen J. W., Brown R. L., Stryer L., Baylor D. A. Interactions between divalent cations and the gating machinery of cyclic GMP-activated channels in salamander retinal rods. J Gen Physiol. 1993 Jan;101(1):1–25. doi: 10.1085/jgp.101.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaupp U. B., Koch K. W. Role of cGMP and Ca2+ in vertebrate photoreceptor excitation and adaptation. Annu Rev Physiol. 1992;54:153–175. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.54.030192.001101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaupp U. B., Niidome T., Tanabe T., Terada S., Bönigk W., Stühmer W., Cook N. J., Kangawa K., Matsuo H., Hirose T. Primary structure and functional expression from complementary DNA of the rod photoreceptor cyclic GMP-gated channel. Nature. 1989 Dec 14;342(6251):762–766. doi: 10.1038/342762a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaupp U. B. The cyclic nucleotide-gated channels of vertebrate photoreceptors and olfactory epithelium. Trends Neurosci. 1991 Apr;14(4):150–157. doi: 10.1016/0166-2236(91)90087-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamb T. D., Matthews H. R. External and internal actions in the response of salamander retinal rods to altered external calcium concentration. J Physiol. 1988 Sep;403:473–494. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1988.sp017259. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ludwig J., Margalit T., Eismann E., Lancet D., Kaupp U. B. Primary structure of cAMP-gated channel from bovine olfactory epithelium. FEBS Lett. 1990 Sep 17;270(1-2):24–29. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(90)81226-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melton D. A., Krieg P. A., Rebagliati M. R., Maniatis T., Zinn K., Green M. R. Efficient in vitro synthesis of biologically active RNA and RNA hybridization probes from plasmids containing a bacteriophage SP6 promoter. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Sep 25;12(18):7035–7056. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.18.7035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Menini A. Currents carried by monovalent cations through cyclic GMP-activated channels in excised patches from salamander rods. J Physiol. 1990 May;424:167–185. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1990.sp018061. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Menini A., Rispoli G., Torre V. The ionic selectivity of the light-sensitive current in isolated rods of the tiger salamander. J Physiol. 1988 Aug;402:279–300. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1988.sp017204. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Methfessel C., Witzemann V., Takahashi T., Mishina M., Numa S., Sakmann B. Patch clamp measurements on Xenopus laevis oocytes: currents through endogenous channels and implanted acetylcholine receptor and sodium channels. Pflugers Arch. 1986 Dec;407(6):577–588. doi: 10.1007/BF00582635. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller C., Hughes H. Hunting for the pore of voltage-gated channels. Curr Biol. 1992 Nov;2(11):573–575. doi: 10.1016/0960-9822(92)90146-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura T., Gold G. H. A cyclic nucleotide-gated conductance in olfactory receptor cilia. 1987 Jan 29-Feb 4Nature. 325(6103):442–444. doi: 10.1038/325442a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakatani K., Yau K. W. Calcium and magnesium fluxes across the plasma membrane of the toad rod outer segment. J Physiol. 1988 Jan;395:695–729. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1988.sp016942. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pongs O., Kecskemethy N., Müller R., Krah-Jentgens I., Baumann A., Kiltz H. H., Canal I., Llamazares S., Ferrus A. Shaker encodes a family of putative potassium channel proteins in the nervous system of Drosophila. EMBO J. 1988 Apr;7(4):1087–1096. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02917.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pongs O. Structural basis of voltage-gated K+ channel pharmacology. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1992 Sep;13(9):359–365. doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(92)90109-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pugh E. N., Jr, Lamb T. D. Cyclic GMP and calcium: the internal messengers of excitation and adaptation in vertebrate photoreceptors. Vision Res. 1990;30(12):1923–1948. doi: 10.1016/0042-6989(90)90013-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Root M. J., MacKinnon R. Identification of an external divalent cation-binding site in the pore of a cGMP-activated channel. Neuron. 1993 Sep;11(3):459–466. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(93)90150-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stern J. H., Kaupp U. B., MacLeish P. R. Control of the light-regulated current in rod photoreceptors by cyclic GMP, calcium, and l-cis-diltiazem. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Feb;83(4):1163–1167. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.4.1163. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stern J. H., Knutsson H., MacLeish P. R. Divalent cations directly affect the conductance of excised patches of rod photoreceptor membrane. Science. 1987 Jun 26;236(4809):1674–1678. doi: 10.1126/science.3037695. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stühmer W., Methfessel C., Sakmann B., Noda M., Numa S. Patch clamp characterization of sodium channels expressed from rat brain cDNA. Eur Biophys J. 1987;14(3):131–138. doi: 10.1007/BF00253837. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stühmer W. Structure-function studies of voltage-gated ion channels. Annu Rev Biophys Biophys Chem. 1991;20:65–78. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.20.060191.000433. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka J. C., Furman R. E. Divalent effects on cGMP-activated currents in excised patches from amphibian photoreceptors. J Membr Biol. 1993 Feb;131(3):245–256. doi: 10.1007/BF02260113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsien R. W., Hess P., McCleskey E. W., Rosenberg R. L. Calcium channels: mechanisms of selectivity, permeation, and block. Annu Rev Biophys Biophys Chem. 1987;16:265–290. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.16.060187.001405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang J., Ellinor P. T., Sather W. A., Zhang J. F., Tsien R. W. Molecular determinants of Ca2+ selectivity and ion permeation in L-type Ca2+ channels. Nature. 1993 Nov 11;366(6451):158–161. doi: 10.1038/366158a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yau K. W., Baylor D. A. Cyclic GMP-activated conductance of retinal photoreceptor cells. Annu Rev Neurosci. 1989;12:289–327. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ne.12.030189.001445. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yau K. W., Nakatani K. Cation selectivity of light-sensitive conductance in retinal rods. Nature. 1984 May 24;309(5966):352–354. doi: 10.1038/309352a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimmerman A. L., Baylor D. A. Cation interactions within the cyclic GMP-activated channel of retinal rods from the tiger salamander. J Physiol. 1992 Apr;449:759–783. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1992.sp019112. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimmerman A. L., Baylor D. A. Cyclic GMP-sensitive conductance of retinal rods consists of aqueous pores. Nature. 1986 May 1;321(6065):70–72. doi: 10.1038/321070a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


