Abstract
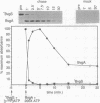
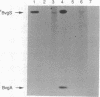
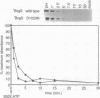
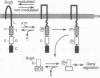
Expression of adhesins, toxins, and other virulence factors of Bordetella pertussis is under control of the BvgA and BvgS proteins, members of a bacterial two-component signal transduction family. BvgA bears sequence similarity to regulator components, whereas BvgS shows similarity to both sensor and regulator components. BvgA and the cytoplasmic portion of BvgS ('BvgS) were overexpressed and purified. 'BvgS autophosphorylated with the gamma-phosphate from [gamma-32P]ATP and phosphorylated BvgA. Kinetic analysis indicated that BvgA receives its phosphate from 'BvgS. Mutations in the transmitter, receiver, and C-terminal domains of BvgS were tested for activation of a BvgAS-dependent fhaB::lacZ reporter fusion in vivo and for autophosphorylation and phosphotransfer to BvgA in vitro. All mutations abolished activation of the fhaB::lacZ fusion. A point mutation in the transmitter (H729Q) prevented autophosphorylation of 'BvgS. In contrast to other characterized sensor proteins, autophosphorylation also required sequences in the 'BvgS receiver and C-terminal domains. A 'BvgS receiver point mutation (D1023N) had the novel phenotype of being able to autophosphorylate but unable to transfer the phosphate to BvgA. Autophosphorylation activity of the D1023N mutant protein was kinetically and chemically indistinguishable from wild-type 'BvgS despite an uncoupling of phosphotransfer from autophosphorylation. 'BvgS was shown to contain primarily amidyl phosphate and BvgA an acyl phosphate linkage. We present a model for a phosphorelay controlling virulence gene expression in B. pertussis.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akerley B. J., Miller J. F. Flagellin gene transcription in Bordetella bronchiseptica is regulated by the BvgAS virulence control system. J Bacteriol. 1993 Jun;175(11):3468–3479. doi: 10.1128/jb.175.11.3468-3479.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Akerley B. J., Monack D. M., Falkow S., Miller J. F. The bvgAS locus negatively controls motility and synthesis of flagella in Bordetella bronchiseptica. J Bacteriol. 1992 Feb;174(3):980–990. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.3.980-990.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aricó B., Miller J. F., Roy C., Stibitz S., Monack D., Falkow S., Gross R., Rappuoli R. Sequences required for expression of Bordetella pertussis virulence factors share homology with prokaryotic signal transduction proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Sep;86(17):6671–6675. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.17.6671. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang C. H., Winans S. C. Functional roles assigned to the periplasmic, linker, and receiver domains of the Agrobacterium tumefaciens VirA protein. J Bacteriol. 1992 Nov;174(21):7033–7039. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.21.7033-7039.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hess J. F., Bourret R. B., Simon M. I. Histidine phosphorylation and phosphoryl group transfer in bacterial chemotaxis. Nature. 1988 Nov 10;336(6195):139–143. doi: 10.1038/336139a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iuchi S., Lin E. C. Purification and phosphorylation of the Arc regulatory components of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1992 Sep;174(17):5617–5623. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.17.5617-5623.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jin S. G., Prusti R. K., Roitsch T., Ankenbauer R. G., Nester E. W. Phosphorylation of the VirG protein of Agrobacterium tumefaciens by the autophosphorylated VirA protein: essential role in biological activity of VirG. J Bacteriol. 1990 Sep;172(9):4945–4950. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.9.4945-4950.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jin S., Roitsch T., Ankenbauer R. G., Gordon M. P., Nester E. W. The VirA protein of Agrobacterium tumefaciens is autophosphorylated and is essential for vir gene regulation. J Bacteriol. 1990 Feb;172(2):525–530. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.2.525-530.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knapp S., Mekalanos J. J. Two trans-acting regulatory genes (vir and mod) control antigenic modulation in Bordetella pertussis. J Bacteriol. 1988 Nov;170(11):5059–5066. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.11.5059-5066.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LACEY B. W. Antigenic modulation of Bordetella pertussis. J Hyg (Lond) 1960 Mar;58:57–93. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400038134. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCleary W. R., Zusman D. R. Purification and characterization of the Myxococcus xanthus FrzE protein shows that it has autophosphorylation activity. J Bacteriol. 1990 Dec;172(12):6661–6668. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.12.6661-6668.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller J. F., Johnson S. A., Black W. J., Beattie D. T., Mekalanos J. J., Falkow S. Constitutive sensory transduction mutations in the Bordetella pertussis bvgS gene. J Bacteriol. 1992 Feb;174(3):970–979. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.3.970-979.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller J. F., Mekalanos J. J., Falkow S. Coordinate regulation and sensory transduction in the control of bacterial virulence. Science. 1989 Feb 17;243(4893):916–922. doi: 10.1126/science.2537530. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller J. F., Roy C. R., Falkow S. Analysis of Bordetella pertussis virulence gene regulation by use of transcriptional fusions in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1989 Nov;171(11):6345–6348. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.11.6345-6348.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parkinson J. S., Kofoid E. C. Communication modules in bacterial signaling proteins. Annu Rev Genet. 1992;26:71–112. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.26.120192.000443. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pazour G. J., Ta C. N., Das A. Mutants of Agrobacterium tumefaciens with elevated vir gene expression. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Aug 15;88(16):6941–6945. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.16.6941. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roy C. R., Falkow S. Identification of Bordetella pertussis regulatory sequences required for transcriptional activation of the fhaB gene and autoregulation of the bvgAS operon. J Bacteriol. 1991 Apr;173(7):2385–2392. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.7.2385-2392.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roy C. R., Miller J. F., Falkow S. Autogenous regulation of the Bordetella pertussis bvgABC operon. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 May;87(10):3763–3767. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.10.3763. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roy C. R., Miller J. F., Falkow S. The bvgA gene of Bordetella pertussis encodes a transcriptional activator required for coordinate regulation of several virulence genes. J Bacteriol. 1989 Nov;171(11):6338–6344. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.11.6338-6344.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanders D. A., Gillece-Castro B. L., Stock A. M., Burlingame A. L., Koshland D. E., Jr Identification of the site of phosphorylation of the chemotaxis response regulator protein, CheY. J Biol Chem. 1989 Dec 25;264(36):21770–21778. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stibitz S., Yang M. S. Subcellular localization and immunological detection of proteins encoded by the vir locus of Bordetella pertussis. J Bacteriol. 1991 Jul;173(14):4288–4296. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.14.4288-4296.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stock J. B., Ninfa A. J., Stock A. M. Protein phosphorylation and regulation of adaptive responses in bacteria. Microbiol Rev. 1989 Dec;53(4):450–490. doi: 10.1128/mr.53.4.450-490.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swanson R. V., Bourret R. B., Simon M. I. Intermolecular complementation of the kinase activity of CheA. Mol Microbiol. 1993 May;8(3):435–441. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1993.tb01588.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss A. A., Hewlett E. L. Virulence factors of Bordetella pertussis. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1986;40:661–686. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.40.100186.003305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wootton J. C., Drummond M. H. The Q-linker: a class of interdomain sequences found in bacterial multidomain regulatory proteins. Protein Eng. 1989 May;2(7):535–543. doi: 10.1093/protein/2.7.535. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang Y., Inouye M. Intermolecular complementation between two defective mutant signal-transducing receptors of Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Dec 15;88(24):11057–11061. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.24.11057. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]