Abstract
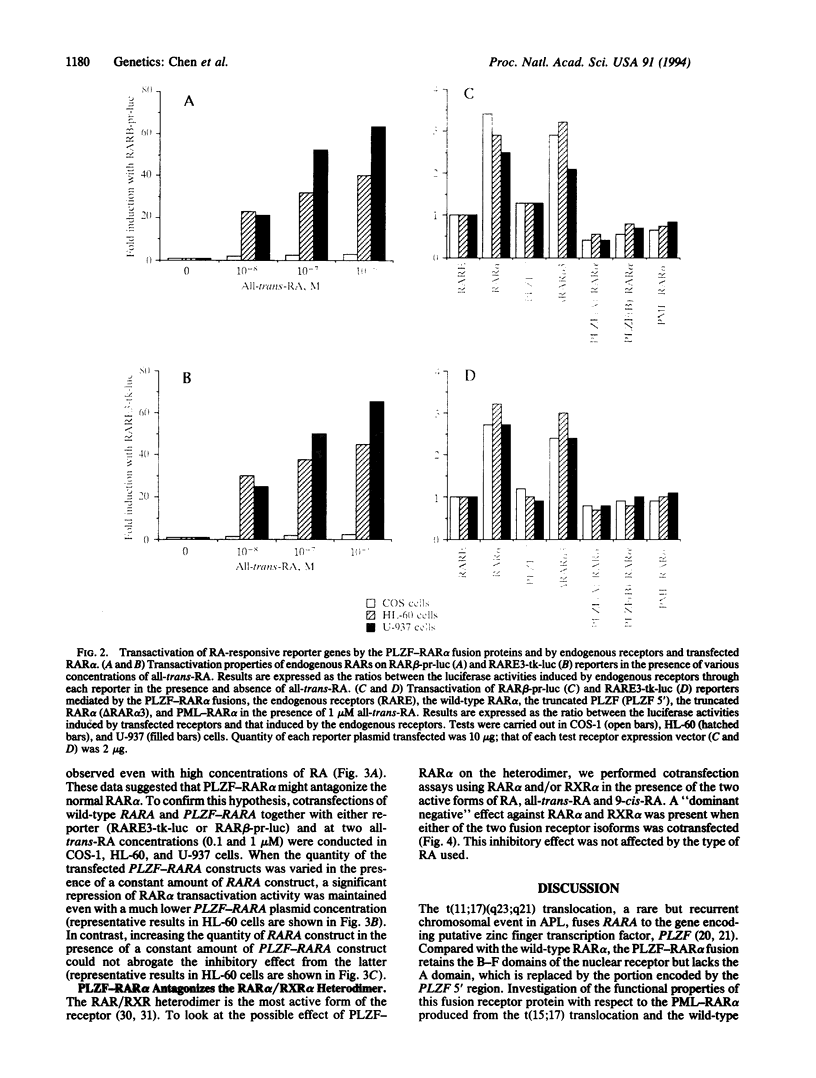
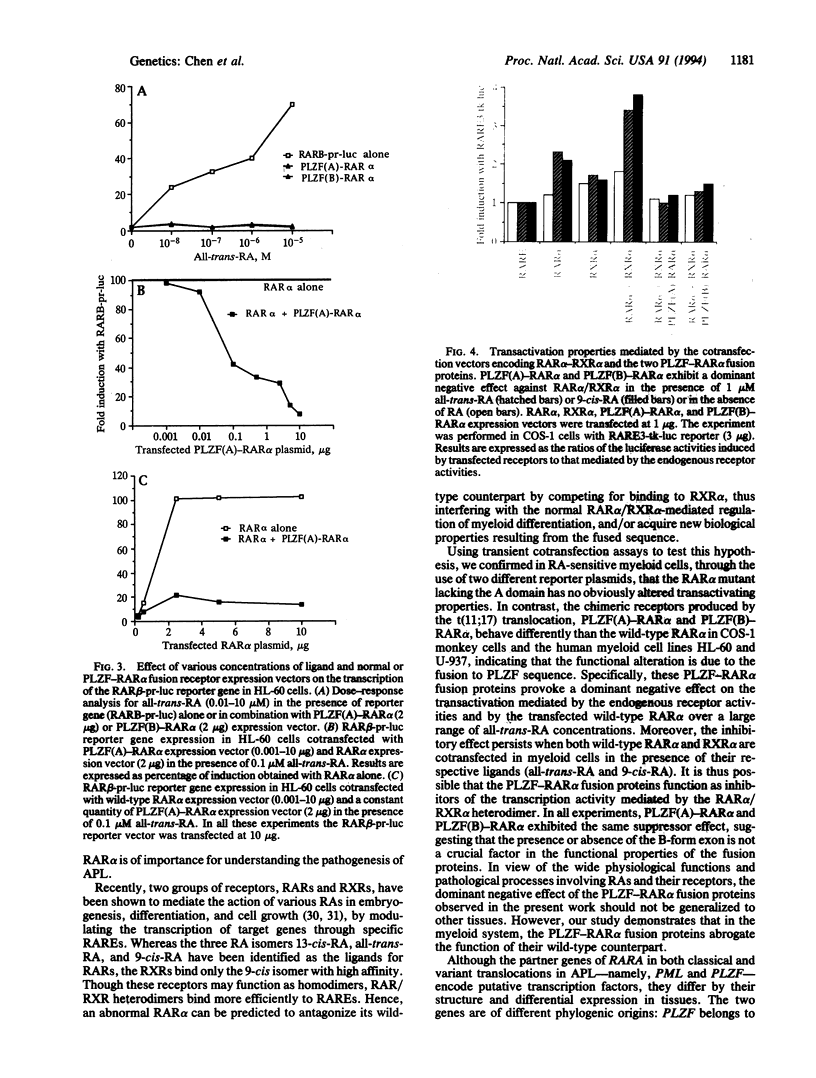
Recently, we described a recurrent variant translocation, t(11;17)(q23;q21), in acute promyelocytic leukemia (APL) which juxtaposes PLZF, a gene encoding a zinc finger protein, to RARA, encoding retinoic acid receptor alpha (RAR alpha). We have now cloned cDNAs encoding PLZF-RAR alpha chimeric proteins and studied their transactivating activities. In transient-expression assays, both the PLZF(A)-RAR alpha and PLZF(B)-RAR alpha fusion proteins like the PML-RAR alpha protein resulting from the well-known t(15;17) translocation in APL, antagonized endogenous and transfected wild-type RAR alpha in the presence of retinoic acid. Cotransfection assays showed that a significant repression of RAR alpha transactivation activity was obtained even with a very low PLZF-RAR alpha-expressing plasmid concentration. A "dominant negative" effect was observed when PLZF-RAR alpha fusion proteins were cotransfected with vectors expressing RAR alpha and retinoid X receptor alpha (RXR alpha). These abnormal transactivation properties observed in retinoic acid-sensitive myeloid cells strongly implicate the PLZF-RAR alpha fusion proteins in the molecular pathogenesis of APL.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Banker G., Goslin K. Developments in neuronal cell culture. Nature. 1988 Nov 10;336(6195):185–186. doi: 10.1038/336185a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borrow J., Goddard A. D., Sheer D., Solomon E. Molecular analysis of acute promyelocytic leukemia breakpoint cluster region on chromosome 17. Science. 1990 Sep 28;249(4976):1577–1580. doi: 10.1126/science.2218500. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breitman T. R., Collins S. J., Keene B. R. Terminal differentiation of human promyelocytic leukemic cells in primary culture in response to retinoic acid. Blood. 1981 Jun;57(6):1000–1004. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castaigne S., Chomienne C., Daniel M. T., Ballerini P., Berger R., Fenaux P., Degos L. All-trans retinoic acid as a differentiation therapy for acute promyelocytic leukemia. I. Clinical results. Blood. 1990 Nov 1;76(9):1704–1709. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang K. S., Stass S. A., Chu D. T., Deaven L. L., Trujillo J. M., Freireich E. J. Characterization of a fusion cDNA (RARA/myl) transcribed from the t(15;17) translocation breakpoint in acute promyelocytic leukemia. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Feb;12(2):800–810. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.2.800. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen S. J., Chen Z., Chen A., Tong J. H., Dong S., Wang Z. Y., Waxman S., Zelent A. Occurrence of distinct PML-RAR-alpha fusion gene isoforms in patients with acute promyelocytic leukemia detected by reverse transcriptase/polymerase chain reaction. Oncogene. 1992 Jun;7(6):1223–1232. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen S. J., Zelent A., Tong J. H., Yu H. Q., Wang Z. Y., Derré J., Berger R., Waxman S., Chen Z. Rearrangements of the retinoic acid receptor alpha and promyelocytic leukemia zinc finger genes resulting from t(11;17)(q23;q21) in a patient with acute promyelocytic leukemia. J Clin Invest. 1993 May;91(5):2260–2267. doi: 10.1172/JCI116453. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen S. J., Zhu Y. J., Tong J. H., Dong S., Huang W., Chen Y., Xiang W. M., Zhang L., Li X. S., Qian G. Q. Rearrangements in the second intron of the RARA gene are present in a large majority of patients with acute promyelocytic leukemia and are used as molecular marker for retinoic acid-induced leukemic cell differentiation. Blood. 1991 Nov 15;78(10):2696–2701. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen Z., Brand N. J., Chen A., Chen S. J., Tong J. H., Wang Z. Y., Waxman S., Zelent A. Fusion between a novel Krüppel-like zinc finger gene and the retinoic acid receptor-alpha locus due to a variant t(11;17) translocation associated with acute promyelocytic leukaemia. EMBO J. 1993 Mar;12(3):1161–1167. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05757.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomczynski P., Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987 Apr;162(1):156–159. doi: 10.1006/abio.1987.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomienne C., Ballerini P., Balitrand N., Huang M. E., Krawice I., Castaigne S., Fenaux P., Tiollais P., Dejean A., Degos L. The retinoic acid receptor alpha gene is rearranged in retinoic acid-sensitive promyelocytic leukemias. Leukemia. 1990 Dec;4(12):802–807. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giguere V., Ong E. S., Segui P., Evans R. M. Identification of a receptor for the morphogen retinoic acid. Nature. 1987 Dec 17;330(6149):624–629. doi: 10.1038/330624a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goddard A. D., Borrow J., Freemont P. S., Solomon E. Characterization of a zinc finger gene disrupted by the t(15;17) in acute promyelocytic leukemia. Science. 1991 Nov 29;254(5036):1371–1374. doi: 10.1126/science.1720570. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang M. E., Ye Y. C., Chen S. R., Chai J. R., Lu J. X., Zhoa L., Gu L. J., Wang Z. Y. Use of all-trans retinoic acid in the treatment of acute promyelocytic leukemia. Blood. 1988 Aug;72(2):567–572. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kakizuka A., Miller W. H., Jr, Umesono K., Warrell R. P., Jr, Frankel S. R., Murty V. V., Dmitrovsky E., Evans R. M. Chromosomal translocation t(15;17) in human acute promyelocytic leukemia fuses RAR alpha with a novel putative transcription factor, PML. Cell. 1991 Aug 23;66(4):663–674. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90112-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kastner P., Perez A., Lutz Y., Rochette-Egly C., Gaub M. P., Durand B., Lanotte M., Berger R., Chambon P. Structure, localization and transcriptional properties of two classes of retinoic acid receptor alpha fusion proteins in acute promyelocytic leukemia (APL): structural similarities with a new family of oncoproteins. EMBO J. 1992 Feb;11(2):629–642. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05095.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larson R. A., Kondo K., Vardiman J. W., Butler A. E., Golomb H. M., Rowley J. D. Evidence for a 15;17 translocation in every patient with acute promyelocytic leukemia. Am J Med. 1984 May;76(5):827–841. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(84)90994-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leid M., Kastner P., Chambon P. Multiplicity generates diversity in the retinoic acid signalling pathways. Trends Biochem Sci. 1992 Oct;17(10):427–433. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(92)90014-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Longo L., Pandolfi P. P., Biondi A., Rambaldi A., Mencarelli A., Lo Coco F., Diverio D., Pegoraro L., Avanzi G., Tabilio A. Rearrangements and aberrant expression of the retinoic acid receptor alpha gene in acute promyelocytic leukemias. J Exp Med. 1990 Dec 1;172(6):1571–1575. doi: 10.1084/jem.172.6.1571. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pandolfi P. P., Alcalay M., Fagioli M., Zangrilli D., Mencarelli A., Diverio D., Biondi A., Lo Coco F., Rambaldi A., Grignani F. Genomic variability and alternative splicing generate multiple PML/RAR alpha transcripts that encode aberrant PML proteins and PML/RAR alpha isoforms in acute promyelocytic leukaemia. EMBO J. 1992 Apr;11(4):1397–1407. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05185.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pandolfi P. P., Grignani F., Alcalay M., Mencarelli A., Biondi A., LoCoco F., Grignani F., Pelicci P. G. Structure and origin of the acute promyelocytic leukemia myl/RAR alpha cDNA and characterization of its retinoid-binding and transactivation properties. Oncogene. 1991 Jul;6(7):1285–1292. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petkovich M., Brand N. J., Krust A., Chambon P. A human retinoic acid receptor which belongs to the family of nuclear receptors. Nature. 1987 Dec 3;330(6147):444–450. doi: 10.1038/330444a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawyers C. L., Denny C. T., Witte O. N. Leukemia and the disruption of normal hematopoiesis. Cell. 1991 Jan 25;64(2):337–350. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90643-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Solomon E., Borrow J., Goddard A. D. Chromosome aberrations and cancer. Science. 1991 Nov 22;254(5035):1153–1160. doi: 10.1126/science.1957167. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warrell R. P., Jr, Frankel S. R., Miller W. H., Jr, Scheinberg D. A., Itri L. M., Hittelman W. N., Vyas R., Andreeff M., Tafuri A., Jakubowski A. Differentiation therapy of acute promyelocytic leukemia with tretinoin (all-trans-retinoic acid). N Engl J Med. 1991 May 16;324(20):1385–1393. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199105163242002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Thé H., Chomienne C., Lanotte M., Degos L., Dejean A. The t(15;17) translocation of acute promyelocytic leukaemia fuses the retinoic acid receptor alpha gene to a novel transcribed locus. Nature. 1990 Oct 11;347(6293):558–561. doi: 10.1038/347558a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Thé H., Lavau C., Marchio A., Chomienne C., Degos L., Dejean A. The PML-RAR alpha fusion mRNA generated by the t(15;17) translocation in acute promyelocytic leukemia encodes a functionally altered RAR. Cell. 1991 Aug 23;66(4):675–684. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90113-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Thé H., Vivanco-Ruiz M. M., Tiollais P., Stunnenberg H., Dejean A. Identification of a retinoic acid responsive element in the retinoic acid receptor beta gene. Nature. 1990 Jan 11;343(6254):177–180. doi: 10.1038/343177a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Wet J. R., Wood K. V., DeLuca M., Helinski D. R., Subramani S. Firefly luciferase gene: structure and expression in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Feb;7(2):725–737. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.2.725. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]